5. Fragment详解
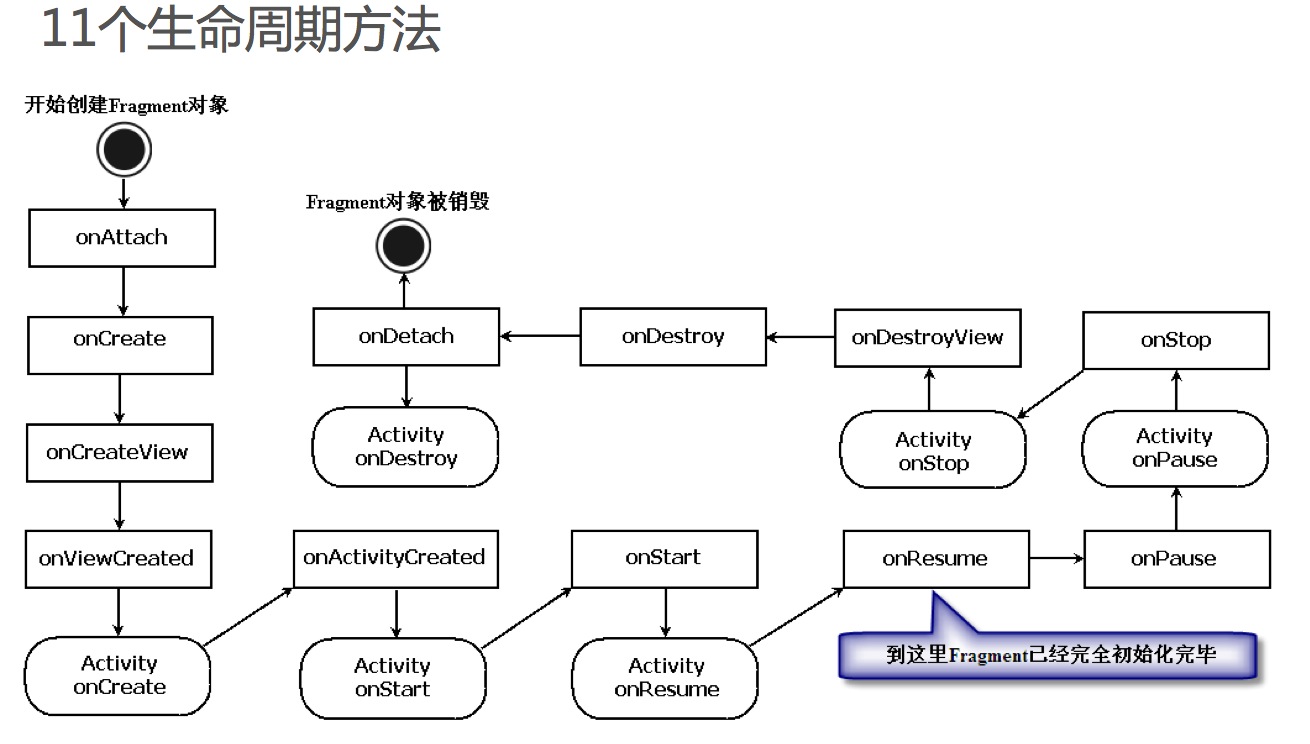
onCreateView是Fragment生命周期方法中最重要的一个。因为在该 方法中会创建在Fragment中显示的View。
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,Bundle savedInstanceState){
// 装载布局文件
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.my_fragment, null); TextView textview =
(TextView)view.findViewById(R.id.textview);
testview.setText("Fragment Test");
return view;
}
Fragment与Activity之间可以通过Fragment.setArguments方法向 Fragment传递参数值,并且可以通过Fragment.getArguments方法获取 这些传递的参数值。
范例1:第一个Fragment程序。
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle; public class FirstFragmentActivity extends Activity {
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_first_fragment);
}
}
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" > <fragment
android:id="@+id/titles"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" class="cn.eoe.first.fragment.LeftFragment" />
</LinearLayout>
package cn.eoe.first.fragment; import java.io.InputStream; import android.app.Fragment;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemClickListener;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.TextView; public class LeftFragment extends Fragment implements OnItemClickListener { private String[] data = new String[] { "灵魂战车2", "变形金刚3:月黑之时", "敢死队2" };
private ListView listView; @Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.left_fragment, null);
listView = (ListView) view.findViewById(R.id.listview_movie_list);
listView.setOnItemClickListener(this);
ArrayAdapter<String> arrayAdapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(
getActivity(), android.R.layout.simple_list_item_activated_1,
data);
listView.setAdapter(arrayAdapter);
listView.setChoiceMode(ListView.CHOICE_MODE_SINGLE); return view;
} @Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position,
long id) {
try { TextView textView = (TextView) getActivity().findViewById(
R.id.textview_detail);
InputStream is = getActivity().getResources().getAssets()
.open("m" + position);
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int count = is.read(buffer);
String detail = new String(buffer, 0, count, "utf-8");
if (textView == null) {
Intent intent = new Intent(getActivity(), DetailActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("detail", detail);
startActivity(intent);
} else {
textView.setText(detail);
}
is.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
} } }
public class DetailActivity extends Activity {
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_detail);
TextView detail = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textview_detail);
detail.setText(getIntent().getExtras().getString("detail"));
}
}
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" > <fragment
android:id="@+id/details"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
class="cn.eoe.first.fragment.RightFragment" /> </RelativeLayout>
public class RightFragment extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.right_fragment, null);
return view;
}
}
范例2:向Fragment传递数据,并获取传递数据的值
activity_fragment_argument.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" > <Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="10dp"
android:onClick="onClick_SendData"
android:text="向Fragment传递数据" /> <FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/fragment_container1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> </LinearLayout>
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.FragmentManager;
import android.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast; public class FragmentArgumentActivity extends Activity { @Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_fragment_argument);
} // 向Fragment传递数据
public void onClick_SendData(View view) {
// 获取传递的数据(页面)
MyFragment fragment = new MyFragment(); Bundle bundle = new Bundle(); bundle.putString("name", "Hello Fragment1");
fragment.setArguments(bundle);
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction fragmentTransaction = fragmentManager
.beginTransaction();
fragmentTransaction.add(R.id.fragment_container1, fragment, "fragment"); fragmentTransaction.commit(); Toast.makeText(this, "数据已成功传递.", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); } // 获取传递的数据
public void onClick_ShowArgument(View view) {
EditText editText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.edittext); String name = getFragmentManager().findFragmentByTag("fragment")
.getArguments().getString("name");
editText.setText(name);
}
}
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup; public class MyFragment extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.my_fragment, container, false);
return view;
} @Override
public void onDestroyView() {
Log.d("name", getArguments().getString("name"));
super.onDestroyView();
} }
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" > <EditText
android:id="@+id/edittext"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:onClick="onClick_ShowArgument"
android:text="获取传递的数据" /> </LinearLayout>
5. Fragment详解的更多相关文章
- Fragment详解之三——管理Fragment(1)
相关文章: 1.<Fragment详解之一--概述>2.<Fragment详解之二--基本使用方法>3.<Fragment详解之三--管理Fragment(1)>4 ...
- android——fragment详解
在android开发过程中,如果使用到了导航栏.那么不可避免的就需要使用fragment来处理界面.闲着没事,就详解一下Framgent的使用方法吧. 难得写一次.本人 shoneworn shone ...
- Android面试收集录4 Fragment详解
1.什么是Fragment? 你可以简单的理解为,Fragment是显示在Activity中的Activity. 它可以显示在Activity中,然后它也可以显示出一些内容. 因为它拥有自己的生命周期 ...
- Android 开发 之 Fragment 详解
本文转载于 : http://blog.csdn.net/shulianghan/article/details/38064191 本博客代码地址 : -- 单一 Fragment 示例 : http ...
- Android Fragment详解
一.什么是Fragment Android在3.0中引入了fragments的概念,主要目的是用在大屏幕设备上--例如平板电脑上,支持更加动态和灵活的UI设计.平板电脑的屏幕要比手机的大得多,有更多的 ...
- Fragment详解
1 Fragment简介 1.1 Fragment的设计初衷 Android3.0引入Fragment的初衷是为大屏幕的设备提供更加灵活的动态UI设计,由于大屏设备可以容纳更多的UI组件,且这些UI组 ...
- Android Fragment 详解(一)
Android从3.0开始引入fragment,主要是为了支持更动态更灵活的界面设计,比如在平板上的应用.平板机上拥有比手机更大的屏幕空间来组合和交互界面组件们.Fragment使你在做那样的设计时, ...
- Android Fragment详解(二):Fragment创建及其生命周期
Fragments的生命周期 每一个fragments 都有自己的一套生命周期回调方法和处理自己的用户输入事件. 对应生命周期可参考下图: 创建片元(Creating a Fragment) To c ...
- Android Fragment详解(一):概述
Fragment是activity的界面中的一部分或一种行为.你可以把多个Fragment们组合到一个activity中来创建一个多面界面并且你可以在多个activity中重用一个Fragment.你 ...
随机推荐
- ubuntu下搭建cocos2dx编程环境-下
前两篇介绍了cocos2d-x 下linux开发环境配置和android 环境配置问题.在这其中遇到很多问题,所以最后一篇分享一下在处理这些问题时,我是如何解决的,是怎么想的.同时总结一些解 ...
- OneThink实现多图片批量上传功能
OneThink原生系统中的图片上传功能是uploadify.swf插件进行上传的,默认是只能上传一张图片的,但是uploadify.swf是支持多图片批量上传的,那么我们稍加改动就可实现OneThi ...
- 【重走Android之路】【路线篇(二)】知识点归纳
[重走Android之路][路线篇(二)]知识点归纳 参考:http://blog.csdn.net/xujing81/article/details/7313507 第一阶段:Java面向对 ...
- JMS基本概念
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/jiuqiyuliang/article/details/46701559 The Java Message Service (JMS) API is ...
- 285. Inorder Successor in BST
题目: Given a binary search tree and a node in it, find the in-order successor of that node in the BST ...
- SQL Server ->> Msg 7411, Level 16, State 1, Line 1 -- Server 'XXXX' is not configured for RPC.
关于问题,有两个相关的服务器选项. exec sp_serveroption @server='CIA-SH-SVR-SIS', @optname='rpc', @optvalue='true' ex ...
- highCharts图表入门实例
本文通过讲解Highcharts生成一个简单的3D柱状图实例来学习Highcharts的使用. JSP 页面 1.需要引入的js文件 <script src="<%=basePa ...
- linux怎么运行.SH文件
执行sh xx.sh命令就可以执行.sh文件了.如果直接执行xx.sh文件,就报权限错误 解决办法:执行chmod u+x xx.sh 来添加执行权限
- 操刀 requirejs,自己动手写一个
前沿 写在文章的最前面 这篇文章讲的是,我怎么去写一个 requirejs . 去 github 上fork一下,顺便star~ requirejs,众所周知,是一个非常出名的js模块化工具,可以让你 ...
- 由阿里巴巴笔试题看java加载顺序
一.阿里巴巴笔试题: public class T implements Cloneable { public static int k = 0; public static T t1 = new T ...
