【Codeforces717F】Heroes of Making Magic III 线段树 + 找规律
F. Heroes of Making Magic III
time limit per test:3 seconds
memory limit per test:256 megabytes
input:standard input
output:standard output
I’m strolling on sunshine, yeah-ah! And doesn’t it feel good! Well, it certainly feels good for our Heroes of Making Magic, who are casually walking on a one-directional road, fighting imps. Imps are weak and feeble creatures and they are not good at much. However, Heroes enjoy fighting them. For fun, if nothing else.
Our Hero, Ignatius, simply adores imps. He is observing a line of imps, represented as a zero-indexed array of integers a of length n, where ai denotes the number of imps at the i-th position. Sometimes, imps can appear out of nowhere. When heroes fight imps, they select a segment of the line, start at one end of the segment, and finish on the other end, without ever exiting the segment. They can move exactly one cell left or right from their current position and when they do so, they defeat one imp on the cell that they moved to, so, the number of imps on that cell decreases by one. This also applies when heroes appear at one end of the segment, at the beginning of their walk.
Their goal is to defeat all imps on the segment, without ever moving to an empty cell in it (without imps), since they would get bored. Since Ignatius loves imps, he doesn’t really want to fight them, so no imps are harmed during the events of this task. However, he would like you to tell him whether it would be possible for him to clear a certain segment of imps in the above mentioned way if he wanted to.
You are given q queries, which have two types:
- 1 a b k — denotes that k imps appear at each cell from the interval [a, b]
- 2 a b - asks whether Ignatius could defeat all imps on the interval [a, b] in the way described above
Input
The first line contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 200 000), the length of the array a. The following line contains n integersa1, a2, ..., an (0 ≤ ai ≤ 5 000), the initial number of imps in each cell. The third line contains a single integer q (1 ≤ q ≤ 300 000), the number of queries. The remaining q lines contain one query each. Each query is provided by integers a, b and, possibly, k(0 ≤ a ≤ b < n, 0 ≤ k ≤ 5 000).
Output
For each second type of query output 1 if it is possible to clear the segment, and 0 if it is not.
Example
3
2 2 2
3
2 0 2
1 1 1 1
2 0 2
0
1
Note
For the first query, one can easily check that it is indeed impossible to get from the first to the last cell while clearing everything. After we add 1 to the second position, we can clear the segment, for example by moving in the following way: 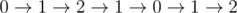 .
.
Solution
题目大意:
给定区间[0,N-1],支持两种操作:
1.区间[l,r]权值+K
2.区间是否可以删光(这里移动时不允许移动到区间之外)
这里可以删光的含义是:从一个格,可以向左/右移动一格,每移动一步,必须使左/右权值-1,当一个地方权值为0时,无法向其移动,删光即能否按照这种移动方式将这个区间中的所有权值删光。
区间上的问题显然可以考虑用线段树来实现。
问题在于这种移动方式,我们不妨考虑其性质。
对于询问一个区间是否能删光,不同的移动方法都有可能能完成,但为了方便我们只考虑其中一种方法。
对于区间$[l,r]$我们从$l$开始移动,我们就先在$l$和$l+1$之间来回,直到$l$清空,我们再在$l+1$和$l+2$之间来回,直到$l+1$清空,如此直到$r-1$和$r$
那么这样能够清空所有位置的权值的条件是:
$$a_{l}>=1$$
$$a_{l+1}-a_{l}>=0$$
$$a_{l+2}-(a_{l+1}-a_{l}+1)>=0$$
$$......$$
那么我们化简一下所有的式子可以得到:
$$a_{l}>=1$$
$$a_{l+1}-a_{l}>=0$$
$$a_{l+2}-a_{l+1}+a_{l}>=1$$
$$......$$
观察一下不等式右边,发现和项数的奇偶有关。
那么我们就可以得到一个通式:
$$a_{r}-a{r-1}+a{r-2}-a_{r-3}+...a_{l}>=[(r-l+1)mod1==0] $$
然后我们很直观的想法就是用线段树去维护这个东西,并且能分奇偶维护更加方便。
问题在于如何维护这个东西,我们做差,另$d_{i}=a_{1}-a{2}+a{3}...$
我们就可以利用这个东西,计算一个区间的值。 所以我们用线段树去维护这个东西。
对于一个区间$[l,r]$这个区间的值$D[l,r]$可以通过$d$来计算
然后我们按照奇偶分别维护,就可以了。
Code
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
inline int read()
{
int x=,f=; char ch=getchar();
while (ch<'' || ch>'') {if (ch=='-') f=-; ch=getchar();}
while (ch>='' && ch<='') {x=x*+ch-''; ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
#define MAXN 300010
#define INF 0x7fffffff
int N,Q,a[MAXN],d[MAXN];
namespace SegmentTree
{
struct SegmentTreeNode{int l,r,size; LL sum,tag[],D[]; bool f;}tree[MAXN<<];
#define ls now<<1
#define rs now<<1|1
inline void Update(int now,bool o)
{
tree[now].D[]=min(tree[ls].D[],tree[rs].D[o]);
tree[now].D[]=min(tree[ls].D[],tree[rs].D[o^]);
}
inline void PushDown(int now,bool o)
{
if (tree[now].l==tree[now].r) return;
if (tree[now].tag[])
tree[ls].D[]+=tree[now].tag[],tree[ls].tag[]+=tree[now].tag[],
tree[rs].D[o]+=tree[now].tag[],tree[rs].tag[o]+=tree[now].tag[],
tree[now].tag[]=;
if (tree[now].tag[])
tree[ls].D[]+=tree[now].tag[],tree[ls].tag[]+=tree[now].tag[],
tree[rs].D[o^]+=tree[now].tag[],tree[rs].tag[o^]+=tree[now].tag[],
tree[now].tag[]=;
}
inline void BuildTree(int now,int l,int r)
{
tree[now].l=l; tree[now].r=r; tree[now].size=r-l+;
if (l==r) {tree[now].D[]=d[l]; tree[now].D[]=INF; return;}
int mid=(l+r)>>;
BuildTree(ls,l,mid); BuildTree(rs,mid+,r);
Update(now,tree[ls].size&);
}
inline void Modify(int now,int L,int R,LL x,bool o)
{
if (L>R) return;
int l=tree[now].l,r=tree[now].r;
PushDown(now,tree[ls].size&);
if (L<=l && R>=r) {tree[now].tag[o]+=x; tree[now].D[o]+=x; return;}
int mid=(l+r)>>;
if (L<=mid) Modify(ls,L,R,x,o);
if (R>mid) Modify(rs,L,R,x,o^(tree[ls].size&));
Update(now,tree[ls].size&);
}
inline LL Query(int now,int L,int R,bool o)
{
if (L>R) return INF;
int l=tree[now].l,r=tree[now].r;
PushDown(now,tree[ls].size&);
if (L<=l && R>=r) return tree[now].D[o];
int mid=(l+r)>>; LL re=INF;
if (L<=mid) re=min(re,Query(ls,L,R,o));
if (R>mid) re=min(re,Query(rs,L,R,o^(tree[ls].size&)));
return re;
}
}
using namespace SegmentTree;
int main()
{
N=read();
for (int i=; i<=N-; i++) a[i]=read();
d[]=a[]; for (int i=; i<=N-; i++) d[i]=a[i]-a[i-],a[i]-=a[i-];
SegmentTree::BuildTree(,,N-);
Q=read();
while (Q--)
{
int opt=read(),L=read(),R=read(),K;
if (opt==)
{
K=read(); SegmentTree::Modify(,L,R,K,L&);
if ((R-L+)&) SegmentTree::Modify(,R+,N-,-K,(R+)&),SegmentTree::Modify(,R+,N-,K,(R+)&);
}
if (opt==)
{
LL x=L>? SegmentTree::Query(,L-,L-,(L-)&):,y=SegmentTree::Query(,R,R,R&);
if ((R-L+)&) y+=x; else y-=x;
if (y!=((R-L+)&) || SegmentTree::Query(,L,R,L&)+x< || SegmentTree::Query(,L,R,(L&)^)-x<) puts("");
else puts("");
}
// puts("=========================");
// for (int i=0; i<=N-1; i++) printf("%I64d %I64d\n",Query(1,i,i,i&1),Query(1,i,i,(i&1)^1));
// puts("=========================");
}
return ;
}
【Codeforces717F】Heroes of Making Magic III 线段树 + 找规律的更多相关文章
- W - Doom HDU - 5239 线段树 找取模的规律+求一个很大的数的平方对一个数取模的写法 特别的模数==2^63-2^31
这个题目一开始感觉还是有点难的,这个模数这么大,根本就不知道怎么写,然后去搜了题解,知道了怎么去求当x很大的时候x的平方对一个数取模怎么样不会爆掉. 然后还顺便发现了一个规律就是当一个数更新一定次数之 ...
- Codeforces 717.F Heroes of Making Magic III
F. Heroes of Making Magic III time limit per test 3 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes inpu ...
- HDU 5125 magic balls(线段树+DP)
magic balls Time Limit: 6000/3000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total ...
- HDU 5266 pog loves szh III (线段树+在线LCA转RMQ)
题目地址:HDU 5266 这题用转RMQ求LCA的方法来做的很easy,仅仅须要找到l-r区间内的dfs序最大的和最小的就能够.那么用线段树或者RMQ维护一下区间最值就能够了.然后就是找dfs序最大 ...
- SPOJ GSS3 Can you answer these queries III ——线段树
[题目分析] GSS1的基础上增加修改操作. 同理线段树即可,多写一个函数就好了. [代码] #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #inc ...
- HDU 5266 pog loves szh III 线段树,lca
Pog and Szh are playing games. Firstly Pog draw a tree on the paper. Here we define 1 as the root of ...
- ZOJ 3622 Magic Number 打表找规律
A - Magic Number Time Limit:2000MS Memory Limit:32768KB 64bit IO Format:%lld & %llu Subm ...
- SPOJ GSS3 Can you answer these queries III[线段树]
SPOJ - GSS3 Can you answer these queries III Description You are given a sequence A of N (N <= 50 ...
- spoj 1557 GSS3 - Can you answer these queries III 线段树
题目链接 给出n个数, 2种操作, 一种是将第x个数改为y, 第二种是询问区间[x,y]内的最大连续子区间. 开4个数组, 一个是区间和, 一个是区间最大值, 一个是后缀的最大值, 一个是前缀的最大值 ...
随机推荐
- Windows 双网卡指定网络出口
主要命令: ipconfig route ping tracert 指定外网路由通过本地以太网连接出去 route add -p 0.0.0.0 mask 0.0.0.0 192.168.10 ...
- Mysql数据库的基本概念和架构
数据库 1.键:主键是表中的标志列.一个键可能由几列组成.可以使用键作为表格之间的引用. CustomerID是Customers表的主键,当它出现在其他表,例如Orders表中的时候就称它为外键. ...
- Autorelease返回值的快速释放机制
+ (instancetype)createSark { return [self new];}// callerSark *sark = [Sark createSark]; 编译器改写成了形如下面 ...
- shell脚本执行时报"bad interpreter: Text file busy"的解决方法
在执行一个shell脚本时,遇到了“-bash: ./killSession.sh: /bin/bash: bad interpreter: Text file busy”错误提示,如下所示: [or ...
- 实战:rsync+inotify实现数据实时同步
Linux 内核从 2.6.13 版本开始提供了 inotify 通知接口,用来监控文件系统的各种变化情况,如文件存取.删除.移动等.利用这一机制,可以非常方便地实现文件异动告警.增量备份,并针对目录 ...
- JS导出PDF插件(支持中文、图片使用路径)
在WEB上想做一个导出PDF的功能,发现jsPDF比较多人推荐,遗憾的是不支持中文,最后找到pdfmake,很好地解决了此问题.它的效果可以先到http://pdfmake.org/playgroun ...
- WPF 无边框透明窗体
WindowStyle="None"--无边框,如果需要其它按钮,如缩小.放大.收缩.关闭按钮,可以自定义 AllowsTransparency="True"- ...
- php 三种数组
在 PHP 中,有三种数组类型: 索引数组 - 带有数字索引的数组 关联数组 - 带有指定键的数组 多维数组 - 包含一个或多个数组的数组 获得数组的长度 - count() 函数
- Linux 负载监控脚本
#!/bin/bash Date=`echo $(date +%Y\-%m\-%d\ %H:%M:%S)`HostName=`hostname`IP=`ifconfig eth0 | grep &qu ...
- 在 KVM 上安装 Win7 虚拟机
之前都是在用Linux 虚机,现在有需要用到Win7 虚机,才发现在 KVM 上安装 Win7 的过程远比想象中的复杂.本文就把其过程做个简单总结. 1. 在 Virtual Machine Mana ...
