黑马-Spring(IOC&DI) AOP
IOC(控制翻转)
概念
把对象的创建、初始化、销毁等工作交给spring容器来做
案例
环境

步骤
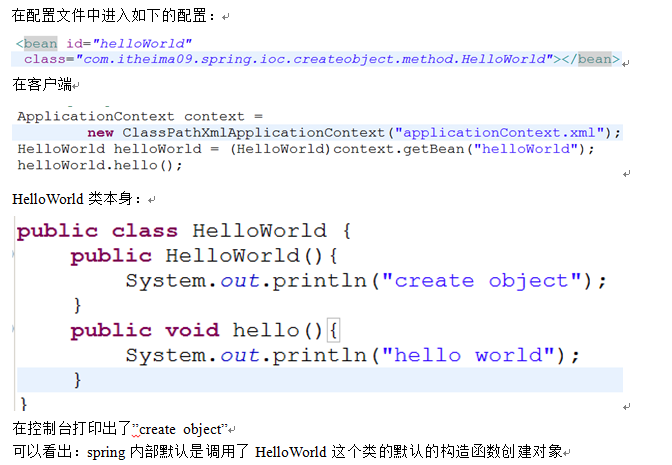
1、 写一个HelloWorld类
2、 写一个配置文件 把hello类放到spring容器中
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd">
<!--
beans
一个bean代表一个类
所以beans就是很多个类
-->
<!--
一个类
id 标示符
class 类的全名
-->
<bean id="helloWorld" class="com.itheima09.spring.ioc.helloworld.HelloWorld">
</bean>
</beans>
applicationContext.xml
3、 客户端
package com.itheima09.spring.ioc.helloworld.test; import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.itheima09.spring.ioc.helloworld.HelloWorld; public class HelloWorldTest {
@Test
public void testHello(){
HelloWorld helloWorld = new HelloWorld();
helloWorld.hello();
} @Test
public void testHello_Spring(){
/**
* 1、启动spring容器
* 2、从spring容器中把对象提取出来
* 3、对象调用方法
*/
//启动了spring容器了
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//从spring容器中把helloWorld对象提取出来了
HelloWorld helloWorld = (HelloWorld)context.getBean("helloWorld");
helloWorld.hello();
}
}
4、 说明:
Spring容器的作用就是为HelloWorld这个类创建对象
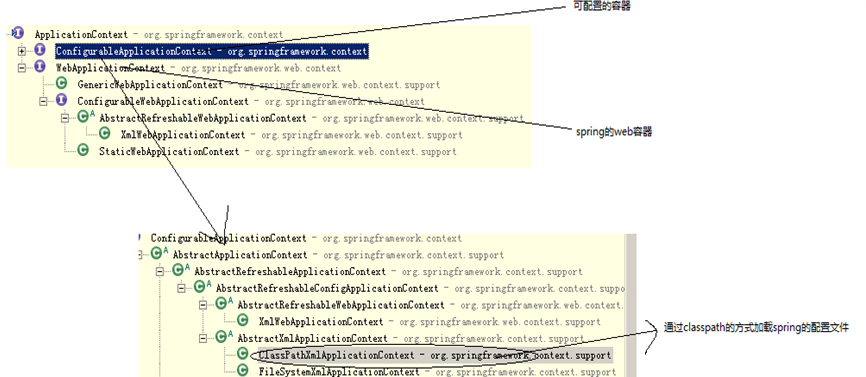
Spring容器的结构
创建对象
构造函数(用的最多)
静态工厂
关于静态工厂方法(https://www.jianshu.com/p/ceb5ec8f1174)

实例工厂

说明:
给工厂类创建了一个对象helloWorldFactory,再利用工厂对象调用工厂方法
别名

对象的创建时机
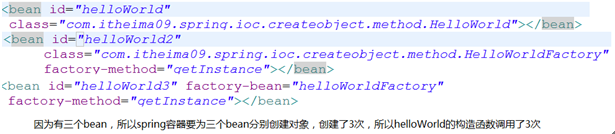
案例
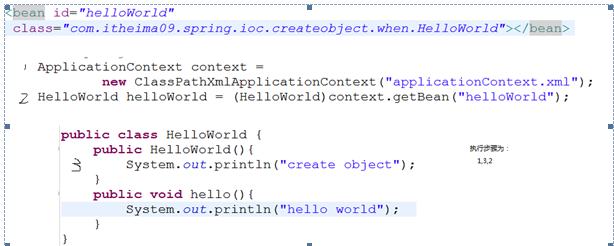
执行步骤为1,3,2
helloword构造函数为什么调用3次
以上两种情况是默认值,当spring容器启动的时候创建对象
在bean有这样一个属性
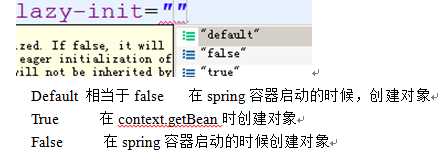
意义
如果把lazy-init设置为true,则当spring容器启动的时候,检测不到任何错误,这样会存在很大的安全性隐患,所以一般情况下应该设置lazy-init为default/false。但是如果一个bean中有一个属性,该属性含有大量的数据,这个时候不希望该bean过早的停留在内存中。
这个时候需要用到lazy-init为true。
对象的scope
默认情况(scope=singleton)

在默认情况下放入到spring中的bean是单例的
将来service层和dao层所有的类将放入到spring容器中,所以默认情况下这两个层的类的实例都是单例的,所以不能把数据声明到属性中。如果声明在属性中,将会成为共享的。
Scope为prototype

创建时机和scope的结合
Scope为prototype,lazy-init为true
在context.getBean时创建对象
Scopse为prototype,lazy-init为false
在context.getBean时创建对象,lazy-init为false失效
当scpose为prototype时,始终在context.getBean时创建对象
Scopse为singleton
是默认情况
Init和destroy
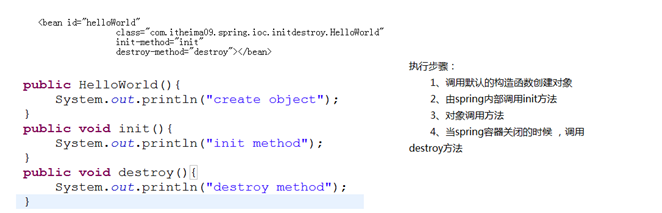
说明:
1、 init方法是由spring内部执行的
2、 只有当spring容器关闭以后才能执行destroy方法,spring容器一般情况下是不会关闭的。只有当web容器销毁掉的时候才可能关闭掉,所以只要一个对象在spring容器中,在spring容器关闭之前,会一直保留。
3、 如果一个bean的配置是scope为”prototype”,则spring容器不负责销毁。
Spring容器做的事情
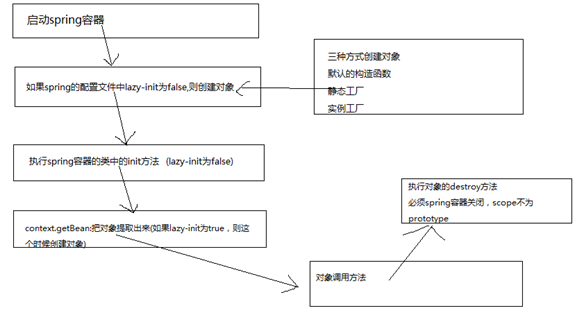
总结
创建对象
1、 对象的创建方式
2、 对象的创建时机
3、 对象的创建的模式
4、 Init和destroy
5、 创建时机和创建模式的结合
DI(依赖注入)
概念
给属性赋值

给pid和name赋值的过程就是di
Xml
Setter方法

说明:
1、 spring容器实例化person和student两个对象
2、 利用java的反射机制调用属性的setter方法赋值 property的 name属性由setter决定
3、 在客户端利用context.getBean方法把spring容器中的一个对象获取了。
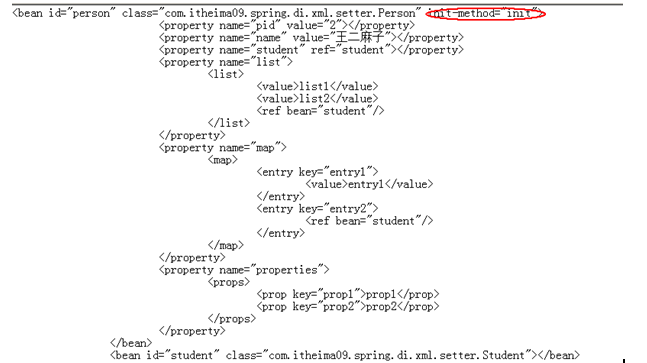
说明:
1、 启动spring容器
2、 实例化person对象和student对象
3、 给person中的属性赋值
4、 调用person的init方法初始化
5、 客户端利用context.getBean获取对象

说明:
1、 启动spring容器
2、 实例化person对象
3、 因为person对象依赖于student对象,所以在实例化person对象的时候必须实例化student对象,所以这个时候,在student对象上的lazy-init为true将失效。
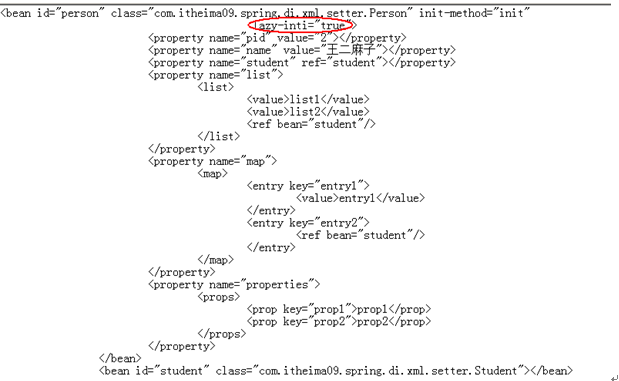
说明:
1、 启动spring容器
2、 实例化student
3、 在客户端执行context.getBean方法获取person对象
4、 实例化person对象,调用person的构造函数
5、 调用person中的setStudent方法,给person中的student赋值
6、 执行person中的init方法
7、 Person对象调用方法
构造器
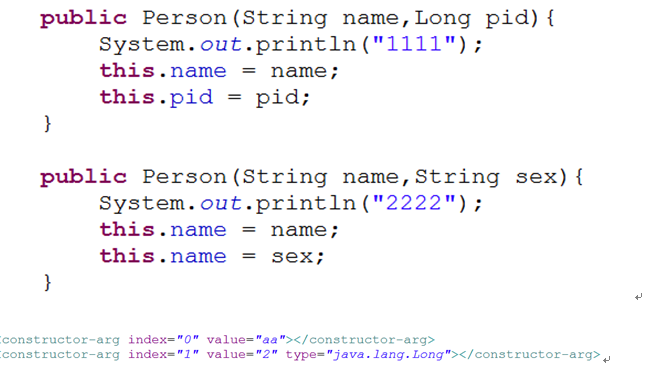
说明:
1、 constructor-arg代表指定的构造器函数的其中的一个参数
2、 可以利用index,ref,value,type来指定唯一的构造器
3、 如果一个bean的配置中没有constructor-arg属性,则必须利用默认的构造函数创建对象。
4、 所以在写一个javabean的时候,应该提供属性的setter方法,默认的构造器,带参数的构造器
IOC和DI的意义
案例1
需求
编写一个文档管理系统,在该系统中有如下的结构:
1、 Document:interface
readDocument方法
writeDocument方法
2、 WordDocument 是Document的实现类
readDocument
writeDocument
3、 ExcelDocument
readDocument
writerDocument
4、 PDFDocument
readDocument
writeDocument
5、 DocumentManager
Document document;
readDocument()
writeDocument()
做法1
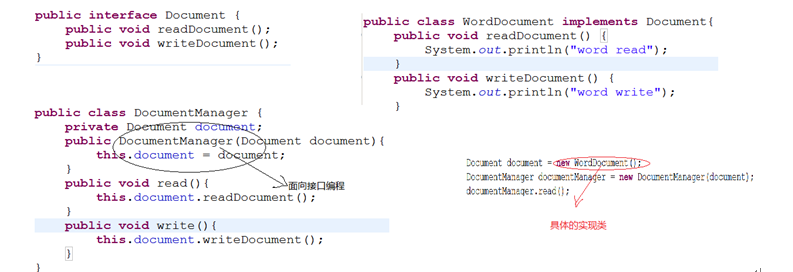
说明:
上述的代码是不完全的面向接口编程
做法2
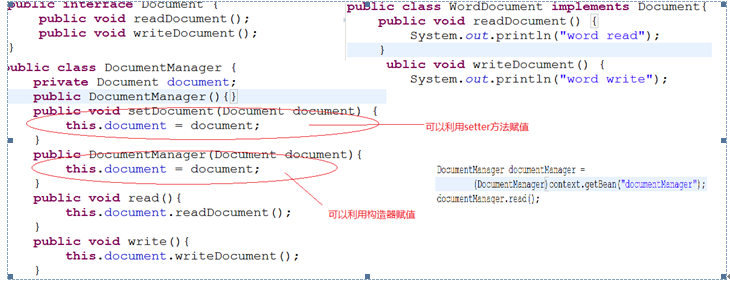
说明:
在代码端没有出现具体的类,完全的面向接口编程。
在spring容器的配置文件中决定了documentManager中的接口的实现类是什么。而这个过程和java代码端没有关系。
案例2
需求
把action调用service,service调用dao用spring来完成
实现
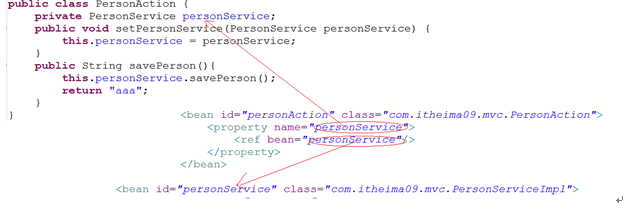
意义
实现了完全的面向接口编程,在代码端没有要关系一个接口的实现类是什么。
注解
概念
1、 用来解释说明
2、 注解必须作用在类的某一个部分
3、 注解的作用域范围(java,class,jvm)
4、 注解解析器
自定义的注解
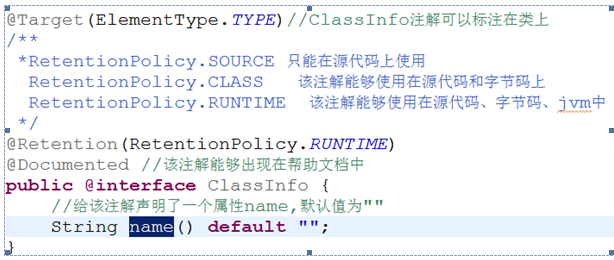
注解的使用

注解解析器
package com.itheima09.annotation; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import org.junit.Test; /**
* 注解解析器
* @author zd
*
*/
public class AnnotationParse {
public static void parse(){
Class classt = Itheima09.class;
//在该类上存在ClassInfo注解
if(classt.isAnnotationPresent(ClassInfo.class)){
//从类上得到类的注解
ClassInfo classInfo = (ClassInfo)classt.getAnnotation(ClassInfo.class);
//输出该注解的name属性
System.out.println(classInfo.name());
}
//获取该类的所有的方法
Method[] methods = classt.getMethods();
for(Method method:methods){
//如果该方法上存在MethodInfo注解
if(method.isAnnotationPresent(MethodInfo.class)){
//获取该方法上面的methodinfo注解
MethodInfo methodInfo = method.getAnnotation(MethodInfo.class);
//输出注解中的value属性
System.out.println(methodInfo.value());
}
}
} @Test
public void test(){
AnnotationParse.parse();
}
}
Spring中的注解
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd">
<!--
把person和student放入到spring容器中
-->
<bean id="person" class="com.itheima09.spring.di.annotation.Person"></bean>
<bean id="student" class="com.itheima09.spring.di.annotation.Student"></bean>
<!--
启动依赖注入的注解解析器
-->
<context:annotation-config></context:annotation-config>
</beans>
applicationContext.xml
package com.itheima09.spring.di.annotation; import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class PersonTest {
@Test
public void testPerson(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Person person = (Person)context.getBean("person");
person.say();
}
}
PersonTest

在spring的配置文件中

说明:
1、 启动spring容器
2、 spring容器内部创建了两个对象person和student
3、 当spring容器解析到
启动依赖注入的注解解析器:
1、 spring容器在容器中查找所有的bean(prerson,student)
2、 看哪些bean的属性上面是否有Resource注解
3、 如果属性上面有该注解,再次检查是否有name属性
4、 如果没有name属性,则会把该注解标注的属性的名称获取到和spring容器中的id做匹配,如果匹配成功,则赋值,如果匹配不成功,则按照类型(注解的变量的类型 和 所有bean的class类型)进行匹配,如果匹配成功,则赋值(不推荐,类型匹配要求bean类型唯一出现,否则错误),如果匹配不成功,则报错。(赋值指的是person的private属性student的赋值,在Person类中对private属性student前面加上 Resource注解)
5、 如果有name属性,则把name属性的值解析出来和spring容器中的id做匹配,如果匹配成功,则赋值,如果匹配不成功,则报错。
6、 从上述的步骤可以看出注解的效率比较低,xml的效率比较高,注解书写比较简单,xml书写比较复杂。
Spring容器的关于di的注解(spring自己的注解)
按照类型匹配
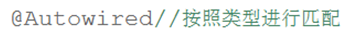
按照ID匹配

注解只能应用与引用类型
类扫描的注解
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd">
<!--
把一个类放入到spring容器中,该类就是一个component
在base-package指定的包及子包中扫描所有的类
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima09.spring.scan.annotation">
</context:component-scan>
</beans>
xml
package com.itheima09.spring.scan.annotation;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("person")
public class Person {
@Resource(name="student")
private Student student;
public void say(){
this.student.say();
}
}
Person
步骤

说明:在指定的包及子包中扫描


流程分析
1、 启动spring容器
2、 Spring容器解析类扫描的注解解析器,在base-package指定的包及子包中查找所有的类
3、 查看哪些类上面是否含有@Component注解
4、 如果该注解的value的属性的值为空,则把类名的第一个字母变成小写,作为id值,放入到spring容器中
5、 如果该注解的value的属性的值不为空,则用value的属性的值作为id值,放入到spring容器中
6、 再次查找在spring容器中的类的所有的属性,按照@Resource的规则给属性赋值
说明
使用了类扫描机制的做法,配置文件中的配置很简单了,但是效率越来越低。
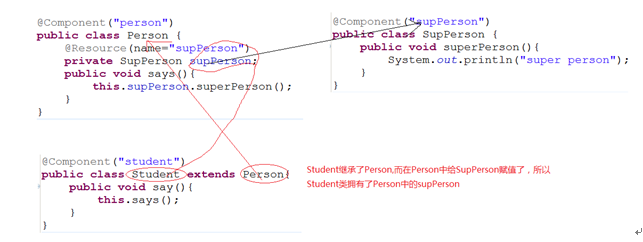
继承
Xml的继承

注解的继承
Aop
目的
让PersonDao的数据库的操作和Transaction事务的操作分离。
代理模式
静态代理模式
package com.itheima09.dao.proxy;
public interface PersonDao {
public void savePerson();
}
interface
package com.itheima09.dao.proxy;
public class PersonDaoImpl implements PersonDao{
public void savePerson() {
System.out.println("save person");
}
}
impl
package com.itheima09.dao.proxy;
import com.itheima09.dao.Transaction;
public class PersonDaoProxy implements PersonDao{
private PersonDao personDao;
private Transaction transaction;
public PersonDaoProxy(PersonDao personDao,Transaction transaction){
this.personDao = personDao;
this.transaction = transaction;
}
public void savePerson() {
/**
* 1、开启事务
* 2、进行save操作
* 3、事务提交
*/
this.transaction.beginTransaction();
this.personDao.savePerson();
this.transaction.commit();
}
}
proxy
package com.itheima09.dao.proxy;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.itheima09.dao.Transaction;
public class ProxyTest {
@Test
public void testProxy(){
/**
* 创建PersonDaoImpl对象
* 创建事务对象
* 创建PersonDaoProxy对象
*/
PersonDao personDao = new PersonDaoImpl();
Transaction transaction = new Transaction();
PersonDaoProxy personDaoProxy = new PersonDaoProxy(personDao, transaction);
personDaoProxy.savePerson();
}
}
proxytest

动态代理模式
Jdk动态代理
接口

目标类
拦截器

客户端

问题
1、 代理对象有多少方法,方法的名称是什么?
因为代理对象和目标类一样,同样的实现了接口,所以接口中有多少方法,代理对象中就有多少个方法,名称和接口中的方法的名称一样。
2、 拦截器中的invoke方法在什么时候执行的?
当在客户端,代理对象调用方法的时候,进入到了invoke方法
3、 拦截器中的invoke方法中的method参数在什么时候传递的值?
当在客户端,代理对象调用方法的时候,进入到了invoke方法,这个时候,method参数就是代理对象调用的方法。
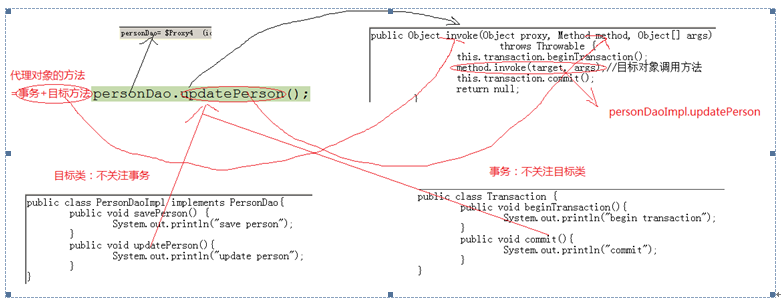
4、 代理对象的方法体的内容是什么?
代理对象的方法体的内容就是invoke方法体的内容
代理对象的方法体:
1、 开启事务
2、 目标方法
3、 事务的提交
4、 代理对象的方法体就把事务和目标方法结合在一起了,这样做的目的就是为了让目标类的目标方法和事务的方法松耦合。
流程图
案例

目标接口
public interface SalaryManager {
public void showSalary();
}
目标类
package com.heima.dao.jdkproxy.salary;
public class SalaryManagerImpl implements SalaryManager{
@Override
public void showSalary() {
System.out.println("正在查看工资");
}
}
日志
package com.heima.dao.jdkproxy.salary;
public class Logger {
public void logging(){
System.out.println("logging");
}
}
安全性框架
package com.heima.dao.jdkproxy.salary;
public class Security {
public void security(){
System.out.println("security");
}
}
权限类
package com.heima.dao.jdkproxy.salary;
public class Privilege {
private String access;
public void setAccess(String access) {
this.access = access;
}
public String getAccess() {
return access;
}
}
拦截器
package com.heima.dao.jdkproxy.salary; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class SalaryManagerInterceptor implements InvocationHandler{
private Object target;
private Logger logger;
private Security security;
private Privilege privilege; public SalaryManagerInterceptor(Object target, Logger logger,
Security security, Privilege privilege) { this.target = target;
this.logger = logger;
this.security = security;
this.privilege = privilege;
} @Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
this.logger.logging();
this.security.security();
if(this.privilege.getAccess().equals("admin")){
method.invoke(target, args);
}else{
System.out.println("权限不足");
}
return null;
} }
拦截器把这些内容全部结合在一起了。
改进
可以把日志、安全性框架等作为一个接口出现
日志:
在拦截器中:

Cglib代理
1、 产生的代理类是目标类的子类
2、 是用字节码增强技术产生的代理类
案例
jdkProxy缺点, 通知和目标方法结合在一起的过程,放在拦截器中,需要程序员自己指定(耦合性高),所以引入aop,可以再xml中配置,提高松耦合
Aop的概念
切面
事务、日志、安全性的框架,权限等就是切面
通知
切面中的方法就是通知
切入点
只有符合(表达式)切入点的条件,才能让通知和目标方法结合在一起
连接点
客户端调用的方法
织入
形成代理对象方法体的过程

Aop的意义
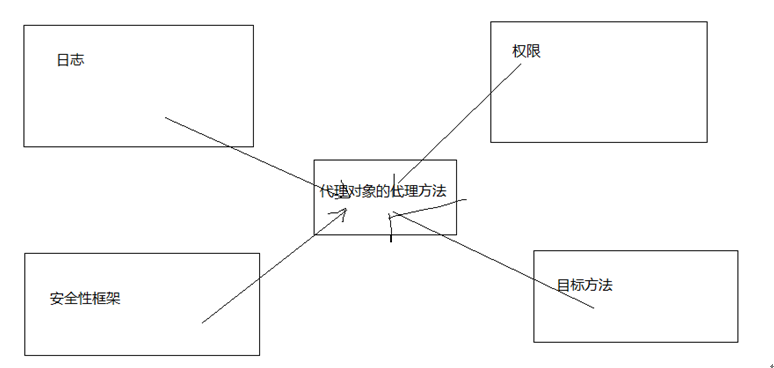
说明:
1、 在开发的过程中,日志、权限、安全性的框架、目标方法完全是松耦合的
2、 在形成代理对象的方法的过程中就把这几个结合在一起了
切入点表达式
3.1 execution
由于Spring切面粒度最小是达到方法级别,而execution表达式可以用于明确指定方法返回类型,类名,方法名和参数名等与方法相关的部件,并且在Spring中,大部分需要使用AOP的业务场景也只需要达到方法级别即可,因而execution表达式的使用是最为广泛的。如下是execution表达式的语法: execution(modifiers-pattern? ret-type-pattern declaring-type-pattern?name-pattern(param-pattern) throws-pattern?)
这里问号表示当前项可以有也可以没有,其中各项的语义如下: modifiers-pattern:方法的可见性,如public,protected;
ret-type-pattern:方法的返回值类型,如int,void等;
declaring-type-pattern:方法所在类的全路径名,如com.spring.Aspect;
name-pattern:方法名类型,如buisinessService();
param-pattern:方法的参数类型,如java.lang.String;
throws-pattern:方法抛出的异常类型,如java.lang.Exception;
如下是一个使用execution表达式的例子: execution(public * com.spring.service.BusinessObject.businessService(java.lang.String,..))
上述切点表达式将会匹配使用public修饰,返回值为任意类型,并且是com.spring.BusinessObject类中名称为businessService的方法,方法可以有多个参数,但是第一个参数必须是java.lang.String类型的方法。上述示例中我们使用了..通配符,关于通配符的类型,主要有两种: *通配符,该通配符主要用于匹配单个单词,或者是以某个词为前缀或后缀的单词。
如下示例表示返回值为任意类型,在com.spring.service.BusinessObject类中,并且参数个数为零的方法: execution(* com.spring.service.BusinessObject.*())
下述示例表示返回值为任意类型,在com.spring.service包中,以Business为前缀的类,并且是类中参数个数为零方法: execution(* com.spring.service.Business*.*())
..通配符,该通配符表示0个或多个项,主要用于declaring-type-pattern和param-pattern中,如果用于declaring-type-pattern中,则表示匹配当前包及其子包,如果用于param-pattern中,则表示匹配0个或多个参数。
如下示例表示匹配返回值为任意类型,并且是com.spring.service包及其子包下的任意类的名称为businessService的方法,而且该方法不能有任何参数: execution(* com.spring.service..*.businessService())
这里需要说明的是,包路径service..*.businessService()中的..应该理解为延续前面的service路径,表示到service路径为止,或者继续延续service路径,从而包括其子包路径;后面的*.businessService(),这里的*表示匹配一个单词,因为是在方法名前,因而表示匹配任意的类。 如下示例是使用..表示任意个数的参数的示例,需要注意,表示参数的时候可以在括号中事先指定某些类型的参数,而其余的参数则由..进行匹配: execution(* com.spring.service.BusinessObject.businessService(java.lang.String,..))
execution
https://www.cnblogs.com/zhangxufeng/p/9160869.html
execution(modifiers-pattern? ret-type-pattern declaring-type-pattern?name-pattern(param-pattern) throws-pattern?)这里问号表示当前项可以有也可以没有,其中各项的语义如下:
- modifiers-pattern:方法的可见性,如public,protected;
- ret-type-pattern:方法的返回值类型,如int,void等;
- declaring-type-pattern:方法所在类的全路径名,如com.spring.Aspect;
- name-pattern:方法名类型,如buisinessService();
- param-pattern:方法的参数类型,如java.lang.String;
- throws-pattern:方法抛出的异常类型,如java.lang.Exception;
- ..通配符,该通配符表示0个或多个项,主要用于declaring-type-pattern和param-pattern中,如果用于declaring-type-pattern中,则表示匹配当前包及其子包,如果用于param-pattern中,则表示匹配0个或多个参数。
- *通配符,该通配符主要用于匹配单个单词,或者是以某个词为前缀或后缀的单词。
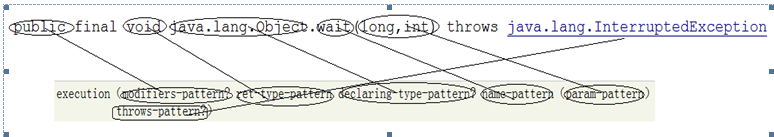
?表示可选可不选 可以不填
必须写 有2个: 1 ret-type-pattern:方法的返回值类型,如int,void等;
2
- name-pattern:方法名类型,如buisinessService();
- param-pattern:方法的参数类型,如java.lang.String;
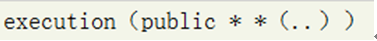
代表所有的公共方法
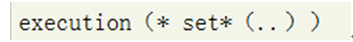
代表所有的以set开头的方法
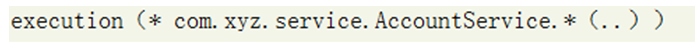
代表com.xyz.service包下的AccoutService类的所有的方法

代表com.xyz.service包下的所有的类的所有的方法

代表com.xyz.service包及子包下的所有的类的所有的方法
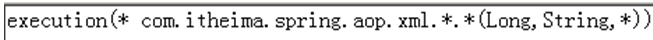
代表com.itheima.spring.aop.xml包下的所有的类的有三个参数,第一个参数为Long,第二个参数为String,第三个参数为任意类型的所有的方法


(1)Aspect(切面):通常是一个类,里面可以定义切入点和通知
(2)JointPoint(连接点):程序执行过程中明确的点,一般是方法的调用
(3)Advice(通知):AOP在特定的切入点上执行的增强处理,有before,after,afterReturning,afterThrowing,around
(4)Pointcut(切入点):就是带有通知的连接点,在程序中主要体现为书写切入点表达式
(5)AOP代理:AOP框架创建的对象,代理就是目标对象的加强。Spring中的AOP代理可以使JDK动态代理,也可以是CGLIB代理,前者基于接口,后者基于子类
Spring的aop
步骤
目标接口

目标类

切面

Spring的配置文件

执行流程
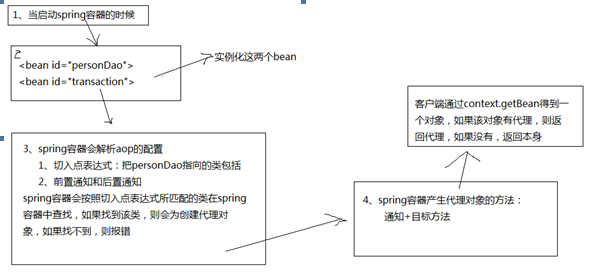
1、 context.getBean时,如果该类没有生成代理对象,则返回对象本身
2、 如果产生了代理对象,则返回代理对象
如果目标类实现了接口,则采用jdkproxy生成代理对象,如果目标类没有实现接口,则采用cglibproxy生成代理对象,而生成代理对象是由spring容器内部完成的。
通知
前置通知
在目标方法执行之前执行。
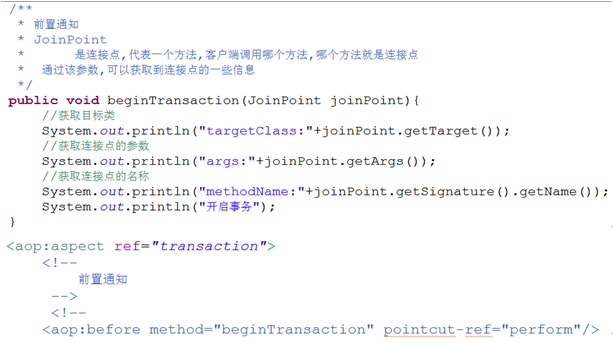
后置通知
在目标方法执行之后执行
可以获取目标方法的返回值
当目标方法遇到异常,不执行


最终通知
无论目标方法是否遇到异常都会执行,相当于代码中的finnaly
异常通知
获取目标方法抛出的异常

环绕通知
能够控制目标方法的执行


package com.heima.spring.aop.xml.advice; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; public class Transaction {
public void begeinTransaction(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println(joinPoint.getTarget());
System.out.println(joinPoint.getArgs());
System.out.println(joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println("begin transaction");
}
public void commit(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object val){
System.out.println(val);
System.out.println("commit");
}
public void finalyMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){ System.out.println("finaly method");
}
public void throwingMethod(JoinPoint jp,Throwable ex){
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
System.out.println("异常"); }
public void arroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp)throws Throwable{
System.out.println("环绕通知aaa");
pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕通知bbbb");
}
}
xml
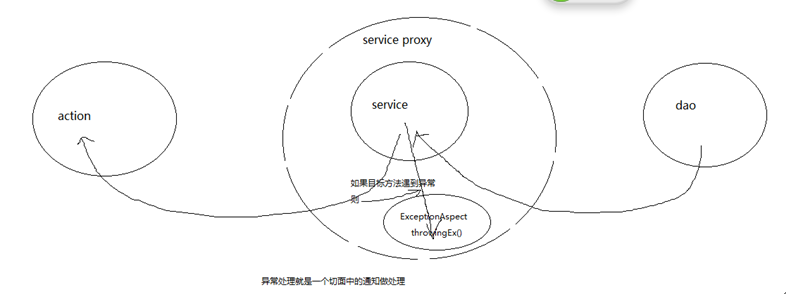
案例:异常处理
技术图
实现
切面

目标类

配置

从配置中可以看出,把service层所有的类当成目标类,只要service层所有的类的所有的方法抛出异常,则exceptionAspect中的异常通知就会获取到目标方法抛出的异常,所以在这里异常通知就是用来处理异常的,而且只有一个方法。并且该切面和所有的其他类都是松耦合的。
案例:权限的处理
技术图
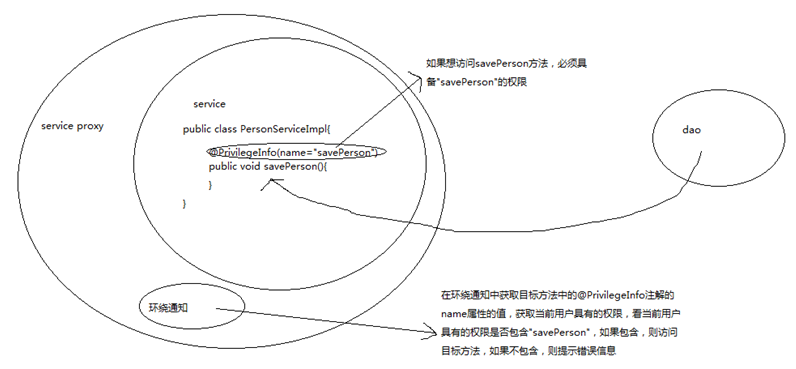
组成
1、 写dao层和service层的类和接口
2、 自定义的注解@PrivilegeInfo
3、 注解解析器:解析目标方法上面的注解的name属性的值
4、 写一个权限类Privilege(name)
5、 写一个关于权限的判断的切面,在切面中写一个环绕通知
实现
参照:/day03-02-itheima09-springAOP-xml-ex-privilege
扩展作业
利用spring的aop的环绕通知,记录如下的信息:
目标类 目标方法 执行时间 方法的起始时间 方法的结束时间
把上述的几个内容保存在数据库中,用jfreechar或者用table显示出来
AOP注解(了解)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima09.springaop.annotation.transaction"></context:component-scan>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
</beans>
xml
package com.itheima09.springaop.annotation.transaction; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /**
* @Aspect
* ==
* <aop:config>
* <aop:pointcut
expression="execution(* com.itheima09.springaop.annotation.transaction.PersonDaoImpl.*(..))"
id="aa()"/>
* </aop:config>
* @author zd
*
*/
@Component("transaction")
@Aspect//说明该注解标注的类是一个切面类
public class Transaction { @Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima09.springaop.annotation.transaction.PersonDaoImpl.*(..))")
private void aa(){} //方法标签 修饰符最好是private 返回值必须是void @Before("aa()")
public void beginTransaction(){
System.out.println("begin transaction");
}
@AfterReturning(value="aa()",returning="ex")
public void commit(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object ex){
System.out.println("commit");
}
}
transaction
黑马-Spring(IOC&DI) AOP的更多相关文章
- Spring+IOC(DI)+AOP概念及优缺点
Spring pring是一个轻量级的DI和AOP容器框架. 说它轻量级有一大部分原因是相对与EJB的(虽然本人从没有接触过EJB的应用),重要的是,Spring是非侵入式的,基于spring开发的应 ...
- spring IOC DI AOP MVC 事务, mybatis 源码解读
demo https://gitee.com/easybao/aop.git spring DI运行时序 AbstractApplicationContext类的 refresh()方法 1: pre ...
- Spring IOC DI AOP 的简单理解及应用
Spring两大特性:IOC 和AOP.IOC 控制反转,AOP 面向切面编程 spring 核心容器的主要组件时Bean工厂(BeanFactory) ,Bean 工厂使用控制反转模式来降低程序代码 ...
- spring+IOC+DI+AOP优点分析(一)
Spring是什么: Spring是一个轻量级的DI和AOP容器框架. 说它轻量级有一大部分原因是相对与EJB的(虽然本人从没有接触过EJB的应用),重要的是,Spring是非侵入式的,基于sprin ...
- Spring ioc与aop的理解
一 spring的特点 1.降低了组件之间的耦合性 ,实现了软件各层之间的解耦 2.可以使用容易提供的众多服务,如事务管理,消息服务等 3.容器提供单例模式支持 4.容器提供了AOP技术,利用它很容易 ...
- J2EE进阶(十四)超详细的Java后台开发面试题之Spring IOC与AOP
J2EE进阶(十四)超详细的Java后台开发面试题之Spring IOC与AOP 前言 搜狐畅游笔试题中有一道问答题涉及到回答谈谈对Spring IOC与AOP的理解.特将相关内容进行整理. ...
- 【转】spring - ioc和aop
[转]spring - ioc和aop 1.程序中为什么会用到spring的ioc和aop 2.什么是IOC,AOP,以及使用它们的好处,即详细回答了第一个问题 3.原理 关于1: a:我们平常使用对 ...
- Spring 学习教程(二): IOC/DI+AOP
1. IOC / DI Spring是一个基于IOC和AOP的结构J2EE系统的框架 IOC 反转控制 是Spring的基础,Inversion Of Control 简单说就是创建对象由以前的程序员 ...
- 零基础学习java------37---------mybatis的高级映射(单表查询,多表(一对一,一对多)),逆向工程,Spring(IOC,DI,创建对象,AOP)
一. mybatis的高级映射 1 单表,字段不一致 resultType输出映射: 要求查询的字段名(数据库中表格的字段)和对应的java类型的属性名一致,数据可以完成封装映射 如果字段和jav ...
随机推荐
- It is never too late!
整理着过去的学习笔记,零零碎碎的,偶尔夹杂着当时的心境. 泛泛的学着东西,不很系统,不很深入,倒像是在拾海,有时捡捡贝壳,有时抓抓螃蟹.叹服大海的神奇,还没来得及深钻某个领域. (以下内容写于2016 ...
- Cracking The Coding Interview 9.6
//原文: // // Given a matrix in which each row and each column is sorted, write a method to find an el ...
- windows下安装cygwin及配置(转)
reference:https://cygwin.com/install.html 对比:MinGW vs. CygWin https://www.cnblogs.com/findumars/p ...
- fabric运维
fabric中文文档:http://fabric-chs.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/chs/ 视频教程:http://study.163.com/course/courseMain.h ...
- 201621123001 《Java程序设计》第11周学习总结
1. 本周学习总结 1.1 以你喜欢的方式(思维导图或其他)归纳总结多线程相关内容. 一个进程可以同时运行多个不同线程,不同的线程执行不同的任务 Java线程是通过java.lang包中定义的Thre ...
- 20165214 实验二 Java面向对象程序设计
一.实验报告封面 课程:Java程序设计 班级:1652班 姓名:朱文远 学号:20165214 指导教师:娄嘉鹏 实验日期:2018年4月16日 实验时间:13:45 - 15:25 实验序号:二 ...
- L304 What Is Death?
How should we define the death of a person? Philosophers and physicians have long pondered this ques ...
- day 34 进程线程排序 抢票 初级生产者消费者
# 实现的内容 模拟购票 20个人买,就有一张购票查,的时候大家都看到,但是购买只能一人购买成功#利用互斥锁# from multiprocessing import Process,Lock# im ...
- vnode的挂载和更新流程 -- 简介.
来源 vnode原理 diff图解 <div id="app"> {{someVar}} </div> <script type="text ...
- elasticsearch内存优化设置
1.禁用交换分区 最简单的选项是完全禁用交换,通常elasticsearch是在框上运行的唯一服务,内存由ES_HEAP_SIZE环境变量控制,设有必要启用交换分区 linux:swapoff -a ...
