深入详解美团点评CAT跨语言服务监控(九)CAT管理平台MVC框架
在第2章我们讲到,服务器在初始化CatServlet 之后, 会初始化 MVC,MVC也是继承自AbstractContainerServlet , 同样也是一个 Servlet 容器,这是一个非常古老的MVC框架,当时Spring MVC 还并不成熟,但是所有MVC框架的核心思想都是一致的。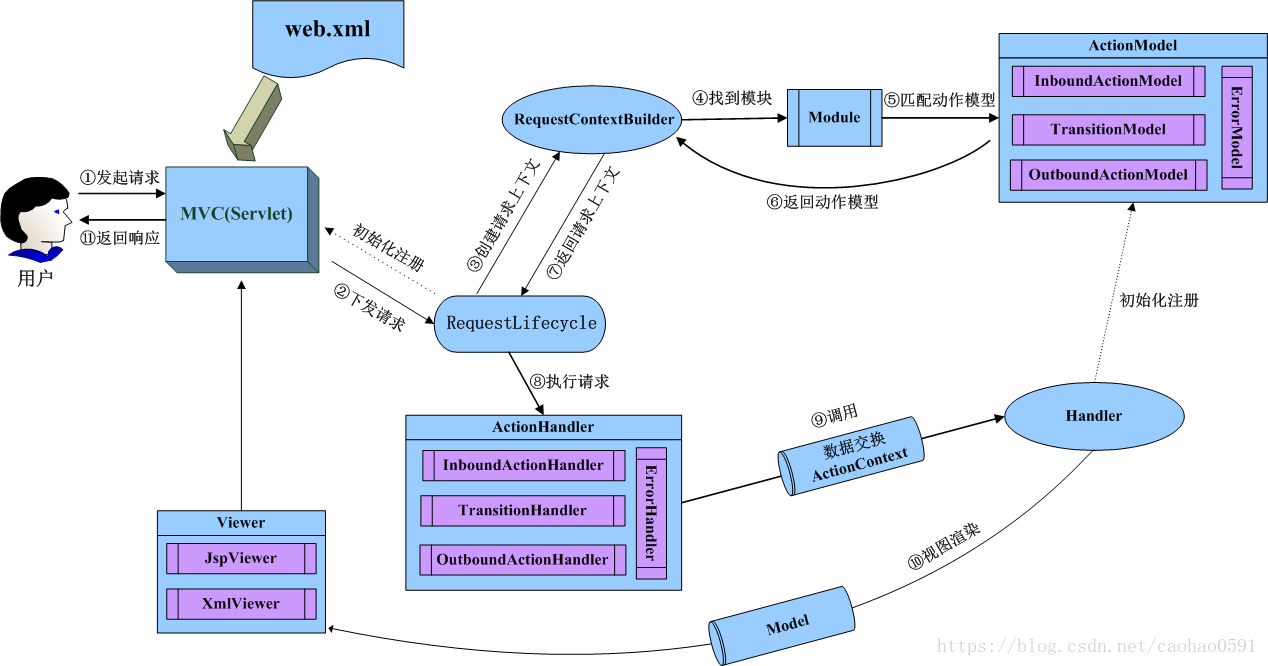
在初始化完CatServlet之后,我们就会调用 MVC 的父类 AbstractContainerServlet 去初始化MVC容器,初始化最核心的步骤是调用MVC子类的initComponents(...) 函数去创建请求周期管理器(RequestLifecycle),并将容器上下文(ServletContext)的指针传递给 RequestLifecycle。容器类RequestLifecycle 的配置信息位于文件 web-framework-4.0.0.jar/META-INF/plexus/components-web-framework.xml 中。
public class MVC extends AbstractContainerServlet {
protected void initComponents(ServletConfig config) throws Exception {
if(this.m_handler == null) {
String contextPath = config.getServletContext().getContextPath();
String path = contextPath != null && contextPath.length() != 0?contextPath:"/";
this.getLogger().info("MVC is starting at " + path);
this.initializeCat(config);
this.initializeModules(config);
this.m_handler = (RequestLifecycle)this.lookup(RequestLifecycle.class, "mvc");
this.m_handler.setServletContext(config.getServletContext());
config.getServletContext().setAttribute("mvc-servlet", this);
this.getLogger().info("MVC started at " + path);
}
}
}
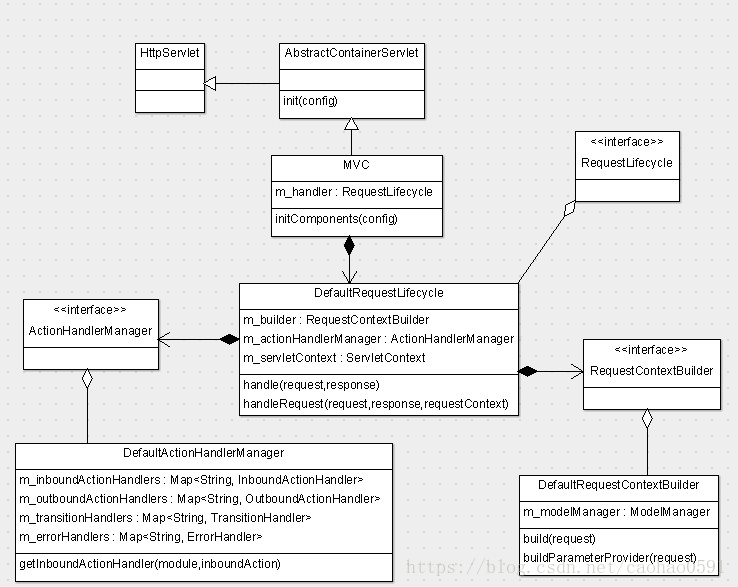
从上面类图, 我们看到MVC 拥有DefaultRequestLifecycle的一个实例,用于完成每次请求的生命周期内的所有工作,例如URL的解析,路由的实现,异常处理等等。DefaultRequestLifecycle 拥有3个重要的成员变量,m_servletContext 用于维护servlet容器的上下文,m_builder用于创建请求上下文,它是管理请求解析、路由的核心,m_actionHandlerManager 对象用于管理负责页面请求的动作执行器,他会被plexus容器实例化。
下面我展示下业务页面相关的类,如下,然后分析下 MVC 的核心逻辑。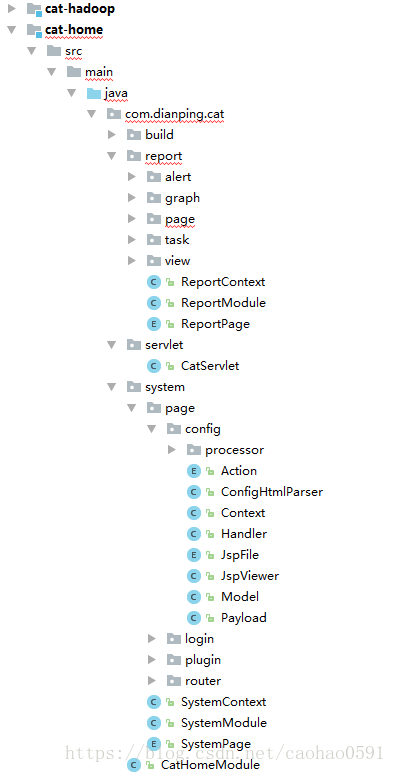
接下来我们先来具体看看 RequestContextBuilder 对象的功能以及初始化的逻辑,如下类图。
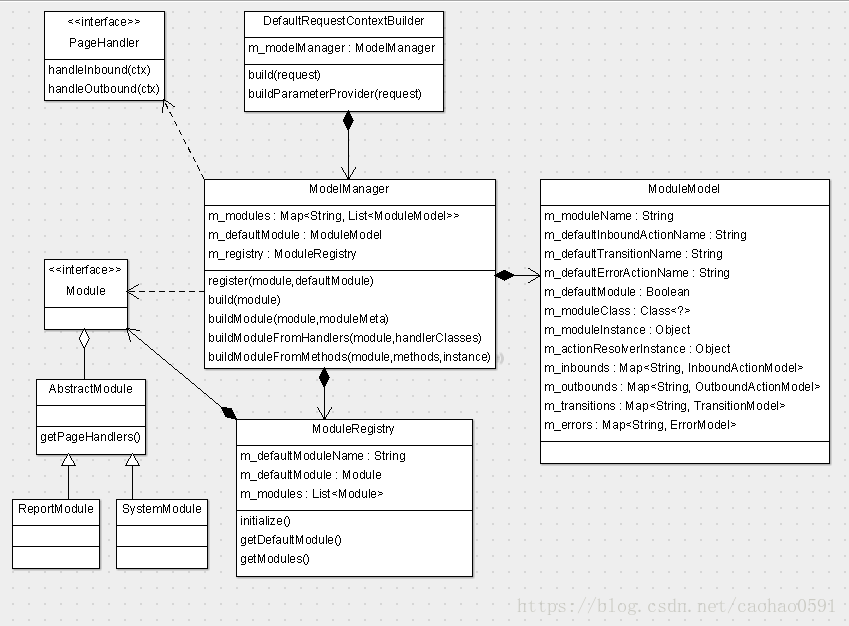
RequestContextBuilder 利用 ModelManager 来管理模块(Module)与动作模型(Model), 模块与动作模型是请求上下文中2个非常重要的概念,不要搞混淆,模块是大的页面分类,目前整个CAT页面平台只有2个模块,分别是报表模块(ReportModule)和系统模块(SystemModule),动作模型则是两大模块下面具体的页面路由信息,他维护具体页面处理器(Handler)的指针、以及处理的函数,以便在请求到来的时候,根据URL找到相应页面处理器,将控制权交给页面处理器(Handler),由页面处理器进行页面逻辑处理,比如获取报表数据、登录、配置修改、页面展示等等,Module对象的指针和动作模型的信息都会存在于ModuleModel对象中,ModuleModel相当于MVC框架的路由转发控制核心,而Handler相当于MVC中的Controller层。接下来我们详细剖析。
ModelManager 的 ModuleRegistry 对象负责对模块的实例化。ModuleRegistry类实现了Initializable方法,所以在plexus实例化ModuleRegistry之后,遍会调用他的initialize()方法实例化ReportModule和SystemModule对象了,如下:
public class ModuleRegistry extends ContainerHolder implements Initializable {
private String m_defaultModuleName;
private Module m_defaultModule;
private List<Module> m_modules;
@Override
public void initialize() throws InitializationException {
if (m_defaultModuleName != null) {
m_defaultModule = lookup(Module.class, m_defaultModuleName);
}
m_modules = lookupList(Module.class);
}
}
我们来看两个页面URL:
存储报表页面: http://localhost:8080/cat/r/t
配置管理页面:http://localhost:8080/cat/s/config
上面URL中的 "r" 代表的就是ReportModule,所有的报表相关的页面都在ReportModule中定义,"s" 则代表SystemModule,系统相关的页面都在SystemModule中定义,上面参数的"t"和"config"是路由动作(Action),后续将会详细讲解,这里的 "r"、"s" 实际上是模块名称,该参数在哪里定义的呢? 在模块(Module)的java定义文件中,我们看到模块元数据(ModuleMeta) 的定义如下:
@ModuleMeta(name = "s", defaultInboundAction = "config", defaultTransition = "default", defaultErrorAction = "default")
@ModuleMeta(name = "r", defaultInboundAction = "home", defaultTransition = "default", defaultErrorAction = "default")
在元数据中,就有名称信息,除此之外,元数据还定义了模块的默认路由动作,报表默认动作是"home",即我们一进去看到的首页, 而系统默认动作则是"config"。在两个模块的java定义文件中,除了Module元数据的定义之外,还有对该模块下所有页面处理器(Handler)的定义:
系统页面处理器:
@ModulePagesMeta({
com.dianping.cat.system.page.login.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.system.page.config.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.system.page.plugin.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.system.page.router.Handler.class
})
报表页面处理器:
@ModulePagesMeta({
com.dianping.cat.report.page.home.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.problem.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.transaction.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.event.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.heartbeat.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.logview.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.model.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.dashboard.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.matrix.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.cross.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.cache.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.state.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.metric.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.dependency.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.statistics.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.alteration.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.monitor.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.network.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.web.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.system.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.cdn.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.app.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.alert.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.overload.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.database.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.storage.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.activity.Handler.class,
com.dianping.cat.report.page.top.Handler.class
})
我们回过头来再看ModelManager的初始化过程,在两个模块被实例化之后 ModelManager 将调用 register() 方法注册模块(Module), 并放入 Map<String, List<ModuleModel>> 对象中, Map 的key是String类型,表示的就是Module名称, Map的 value 则是 ModuleModel 。
public class ModelManager extends ContainerHolder implements Initializable {
@Inject
private ModuleRegistry m_registry;
private Map<String, List<ModuleModel>> m_modules = new HashMap();
private ModuleModel m_defaultModule;
public void initialize() throws InitializationException {
Module defaultModule = this.m_registry.getDefaultModule();
List<Module> modules = this.m_registry.getModules();
Iterator i$ = modules.iterator();
while(i$.hasNext()) {
Module module = (Module)i$.next();
this.register(module, defaultModule == module);
}
}
void register(Module module, boolean defaultModule) {
ModuleModel model = this.build(module);
String name = model.getModuleName();
List<ModuleModel> list = (List)this.m_modules.get(name);
if(list == null) {
list = new ArrayList();
this.m_modules.put(name, list);
}
((List)list).add(model);
if(defaultModule) {
...
this.m_defaultModule = model;
}
}
}
ModuleModel在什么时候会被创建、初始化? 在模块注册函数regiter()中,注册的第一步,就是调用 build() 函数创建 ModuleModel,现在我们详细剖析整个build的流程,build函数首先提取Module元数据(ModuleMeta),然后调用 buildModule() 创建ModuleModel对象,并初始化ModuleModel信息, 例如设置模块名、模块类信息、默认动作、以及模块对象(Module)指针,然后调用 buildModuleFromMethods 创建路由动作模型(Model)。
public class ModelManager extends ContainerHolder implements Initializable {
ModuleModel build(Module module) {
Class<?> moduleClass = module.getClass();
ModuleMeta moduleMeta = (ModuleMeta)moduleClass.getAnnotation(ModuleMeta.class);
if(moduleMeta == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(moduleClass + " must be annotated by " + ModuleMeta.class);
} else {
ModuleModel model = this.buildModule(module, moduleMeta);
this.validateModule(model);
return model;
}
}
private ModuleModel buildModule(Module module, ModuleMeta moduleMeta) {
ModuleModel model = new ModuleModel();
Class<?> moduleClass = module.getClass();
model.setModuleName(moduleMeta.name());
model.setModuleClass(moduleClass);
model.setDefaultInboundActionName(moduleMeta.defaultInboundAction());
model.setDefaultTransitionName(moduleMeta.defaultTransition());
model.setDefaultErrorActionName(moduleMeta.defaultErrorAction());
model.setActionResolverInstance(this.lookupOrNewInstance(moduleMeta.actionResolver()));
model.setModuleInstance(module);
this.buildModuleFromMethods(model, moduleClass.getMethods(), model.getModuleInstance());
Class<? extends PageHandler<?>>[] pageHandlers = module.getPageHandlers();
if(pageHandlers != null) {
this.buildModuleFromHandlers(model, pageHandlers);
}
return model;
}
}
路由动作模型(Model)分为4类,分别是InboundActionModel、OutboundActionModel、TransitionModel、ErrorModel,InboundActionModel主要负责变更,OutboundActionModel负责页面展示,绝大多数页面都是展示目的,TransitionModel负责转场,ErrorModel则负责异常处理。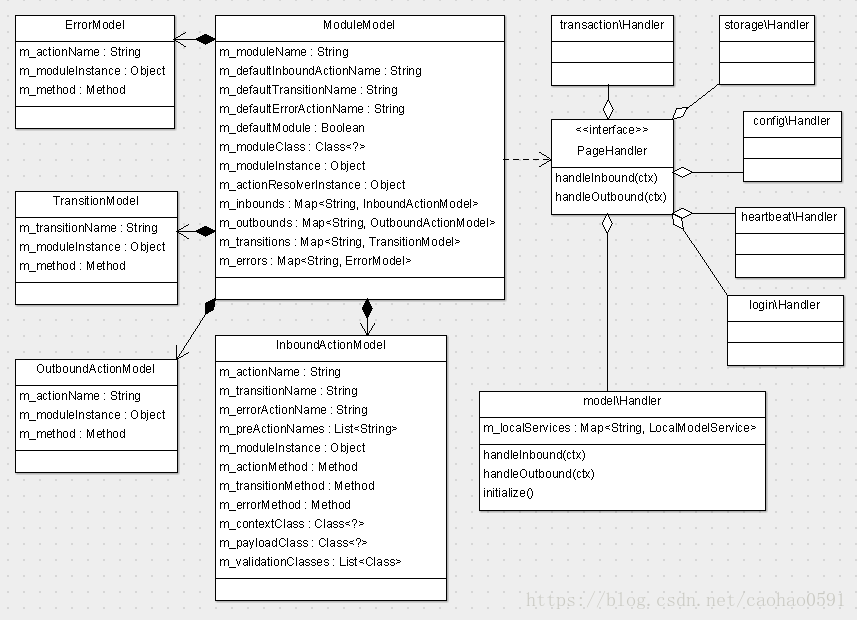
每个动作模型(Model) 中都包含路由页面处理器(Handler)的指针,上面类图尽列举了部分Handler,Handler对象的指针在Model中由 m_moduleInstance 变量维护、以及路由到页面处理器中的具体哪个方法(Method),在Model中由m_actionMethod 变量维护。路由规则由谁来定?在各个页面处理器类中,我们看到了四类注解,InboundActionMeta、OutboundActionMeta、TransitionMeta、ErrorActionMeta,他们将决定哪个页面处理器的哪个函数会被路由到。
public class ModelManager extends ContainerHolder implements Initializable {
private void buildModuleFromHandlers(ModuleModel module, Class<? extends PageHandler<?>>[] handlerClasses) {
Class[] arr$ = handlerClasses;
int len$ = handlerClasses.length;
for(int i$ = 0; i$ < len$; ++i$) {
Class<? extends PageHandler<?>> handlerClass = arr$[i$];
PageHandler<?> handler = (PageHandler)this.lookup(handlerClass);
this.buildModuleFromMethods(module, handlerClass.getMethods(), handler);
}
}
private void buildModuleFromMethods(ModuleModel module, Method[] methods, Object instance) {
Method[] arr$ = methods;
int len$ = methods.length;
for(int i$ = 0; i$ < len$; ++i$) {
Method method = arr$[i$];
int modifier = method.getModifiers();
if(!Modifier.isStatic(modifier) && !Modifier.isAbstract(modifier) && !method.isBridge() && !method.isSynthetic()) {
InboundActionMeta inMeta = (InboundActionMeta)method.getAnnotation(InboundActionMeta.class);
PreInboundActionMeta preInMeta = (PreInboundActionMeta)method.getAnnotation(PreInboundActionMeta.class);
OutboundActionMeta outMeta = (OutboundActionMeta)method.getAnnotation(OutboundActionMeta.class);
TransitionMeta transitionMeta = (TransitionMeta)method.getAnnotation(TransitionMeta.class);
ErrorActionMeta errorMeta = (ErrorActionMeta)method.getAnnotation(ErrorActionMeta.class);
int num = (inMeta == null?0:1) + (outMeta == null?0:1) + (transitionMeta == null?0:1) + (errorMeta == null?0:1);
if(num != 0) {
if(num > 1) {
throw new RuntimeException(method + " can only be annotated by one of " + InboundActionMeta.class + ", " + OutboundActionMeta.class + ", " + TransitionMeta.class + " or " + ErrorActionMeta.class);
}
if(inMeta != null) {
InboundActionModel inbound = this.buildInbound(module, method, inMeta, preInMeta);
inbound.setModuleInstance(instance);
module.addInbound(inbound);
} else if(outMeta != null) {
OutboundActionModel outbound = this.buildOutbound(module, method, outMeta);
outbound.setModuleInstance(instance);
module.addOutbound(outbound);
} else if(transitionMeta != null) {
TransitionModel transition = this.buildTransition(method, transitionMeta);
transition.setModuleInstance(instance);
if(!module.getTransitions().containsKey(transition.getTransitionName())) {
module.addTransition(transition);
}
} else {
if(errorMeta == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Internal error!");
}
ErrorModel error = this.buildError(method, errorMeta);
error.setModuleInstance(instance);
if(!module.getErrors().containsKey(error.getActionName())) {
module.addError(error);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
buildModule(...)函数将会从两个方面创建路由动作模型,一方面在 buildModule(...) 函数中,有一行代码: this.buildModuleFromMethods(model, moduleClass.getMethods(), model.getModuleInstance()); 这行代码他会遍历ReportModule和SystemModule类的所有成员函数,找到被注解的函数,仅有两个模块的父类 AbstractModule 拥有TransitionMeta、ErrorActionMeta 两类注解,所有Transition动作将被路由到handleTransition(...)函数内执行,异常将由onError(...)函数处理,事实上这两个动作没有做任何事情,如下:
public abstract class AbstractModule implements Module {
@TransitionMeta(name = "default")
public void handleTransition(ActionContext<?> ctx) {
// simple cases, nothing here
}
@ErrorActionMeta(name = "default")
public void onError(ActionContext<?> ctx) {
// ignore error, leave MVC to handle it
}
}
另一方面,在buildModule(...)函数中,module.getPageHandlers() 调用可以获取模块(Module)下的所有页面处理器(Handler),具体有哪些Handler在之前讲解 @ModulePagesMeta 的时候有列举,大家可以翻前面看看,然后去遍历这些Handler的成员函数,查看是否有上面讲过的那些注解,如果有,就将被注解的成员函数信息以及页面处理器的指针写入相应的动作模型(Model)中,不同动作模型会被分别加入ModuleModel的如下4个Map成员变量中,Map的 key 是 String类型,指代动作名称。
public class ModuleModel extends BaseEntity<ModuleModel> {
private Map<String, InboundActionModel> m_inbounds = new LinkedHashMap();
private Map<String, OutboundActionModel> m_outbounds = new LinkedHashMap();
private Map<String, TransitionModel> m_transitions = new LinkedHashMap();
private Map<String, ErrorModel> m_errors = new LinkedHashMap();
}
例如下面的Transaction报表页面处理器(transaction\Handler) 的handleInbound和handleOutbound 函数,分别被InboundActionMeta 和 OutboundActionMeta 注解了, 那么对于url : http://localhost:8080/cat/r/t,我们就可以根据 "r" 找到对应的ModuleModel对象,然后根据动作名称 "t" ,找到对应的路由动作模型, 然后程序控制权将会先后交给InboundActionModel、TransitionModel、OutboundActionModel 维护的页面处理器(Handler)的执行函数。捕获的异常将由 ErrorModel 维护的执行函数处理。下面transaction\Handler 的成员函数 handleInbound(...) 和 handleOutbound(...) ,将会先后被执行。
package com.dianping.cat.report.page.transaction;
public class Handler implements PageHandler<Context> {
@Override
@PayloadMeta(Payload.class)
@InboundActionMeta(name = "t")
public void handleInbound(Context ctx) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
@Override
@OutboundActionMeta(name = "t")
public void handleOutbound(Context ctx) throws ServletException, IOException {
...
}
}
除此之外,从代码中我们还看到一个PreInboundActionMeta注解,有些动作可能会包含一个或者多个前置动作。而 PreInboundActionMeta 注解就用于标识某个动作的前置动作。
请求处理流程
当有http请求过来,请进入 DefaultRequestLifecycle 的handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) 进行处理,该函数首先调用 RequestContextBuilder 的 build 函数创建请求上下文, 然后将请求上下文交给动作执行管理对象(ActionHandlerManager) 管理的 InboundActionHandler、TransitionHandler、OutboundActionHandler先后执行,如果捕获到异常交给 ErrorHandler 处理。
public class DefaultRequestLifecycle implements RequestLifecycle, LogEnabled {
private RequestContextBuilder m_builder;
private ActionHandlerManager m_actionHandlerManager;
private ServletContext m_servletContext;
public void handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
RequestContext context = this.m_builder.build(request);
try {
if(context == null) {
this.showPageNotFound(request, response);
} else {
this.handleRequest(request, response, context);
}
} finally {
if(context != null) {
this.m_builder.reset(context);
}
}
}
}
先看看build(...)函数中上下文的创建逻辑,首先将url请求参数放入请求参数提供对象(ParameterProvider),然后从参数中提取模块名,随后创建动作解析器,通过解析请求参数。
例如URL:http://localhost:8080/cat/r/e?domain=cat&ip=All&date=2018041918&reportType=day&op=view 解析之后得到如下参数,其中,模块名就是"r",对应ReportModule,动作名是 "t"。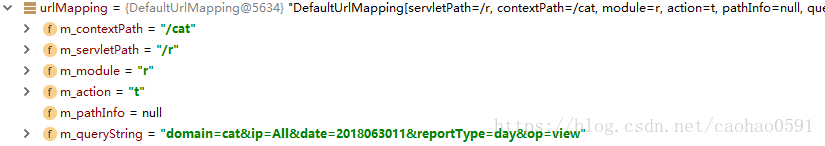
我们通过解析获得的模块名称、动作名称,就可以找到对应的ModuleModel,从中获取路由动作模型InboundActionModel、TransitionModel、OutboundActionModel、ErrorModel的指针,我们将参数信息、模块信息、动作模型信息全部放入请求上下文(RequestContext) 中, 交给相应的动作执行器去执行。
public class DefaultRequestContextBuilder extends ContainerHolder implements RequestContextBuilder {
@Override
public RequestContext build(HttpServletRequest request) {
ParameterProvider provider = buildParameterProvider(request);
String requestModuleName = provider.getModuleName();
ActionResolver actionResolver = (ActionResolver) m_modelManager.getActionResolver(requestModuleName);
UrlMapping urlMapping = actionResolver.parseUrl(provider);
String action = urlMapping.getAction();
InboundActionModel inboundAction = m_modelManager.getInboundAction(requestModuleName, action);
if (inboundAction == null) {
return null;
}
RequestContext context = new RequestContext();
ModuleModel module = m_modelManager.getModule(requestModuleName, action);
urlMapping.setModule(module.getModuleName());
context.setActionResolver(actionResolver);
context.setParameterProvider(provider);
context.setUrlMapping(urlMapping);
context.setModule(module);
context.setInboundAction(inboundAction);
context.setTransition(module.findTransition(inboundAction.getTransitionName()));
context.setError(module.findError(inboundAction.getErrorActionName()));
return context;
}
}
现在我们回到DefaultRequestLifecycle 的请求处理函数handle(...),在创建完成请求上下文之后,我们便调用handleRequest(...)函数来处理请求了,当然,如果请求上下文为空,我们会调用showPageNotFound展示404页面。在handleRequest(...)函数中,我们首先从请求上下文中获取ModuleModel,以及InboundActionModel,然后创建动作上下文(ActionContext)。
public class DefaultRequestLifecycle implements RequestLifecycle, LogEnabled {
private void handleRequest(final HttpServletRequest request, final HttpServletResponse response,
RequestContext requestContext) throws IOException {
ModuleModel module = requestContext.getModule();
InboundActionModel inboundAction = requestContext.getInboundAction();
ActionContext<?> actionContext = createActionContext(request, response, requestContext, inboundAction);
request.setAttribute(CatConstants.CAT_PAGE_URI, actionContext.getRequestContext().getActionUri(inboundAction.getActionName()));
try {
InboundActionHandler handler = m_actionHandlerManager.getInboundActionHandler(module, inboundAction);
handler.preparePayload(actionContext);
if (!handlePreActions(request, response, module, requestContext, inboundAction, actionContext)) {
return;
}
handleInboundAction(module, actionContext);
if (actionContext.isProcessStopped()) {
return;
}
handleTransition(module, actionContext);
handleOutboundAction(module, actionContext);
} catch (Throwable e) {
handleException(request, e, actionContext);
}
}
}
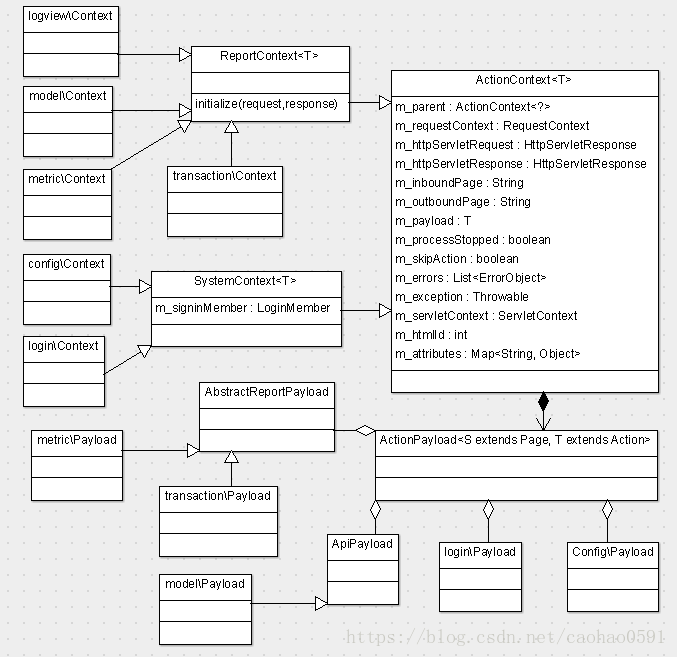
动作上下文(ActionContext) 会携带一些与该动作相关的信息, 包含HttpServletRequest、HttpServletResponse、请求上下文(RequestContext)、Servlet上下文(ServletContext)、Payload,Payload是URL后面带的参数,是一种数据传输对象(DTO),例如上面URL的 domain=cat&ip=All&date=2018041918&reportType=day&op=view,具体生成哪个DTO类,由InboundActionModel的一个成员变量 m_payloadClass决定,这个成员变量在MVC初始化时,创建动作模型InboundActionModel的时候,即在buildInbound(...)函数内被赋值,如下代码,在下方inbound 函数上,被 PayloadMeta 注解的类就是该上下文的DTO类,上面类图仅列举了部分Payload。
每个动作,都有对应的动作上下文,具体生成哪个上下文类,是由InboundActionModel的一个成员变量 m_contextClass 决定,也是在buildInbound(...)函数内被赋值,如下代码,他将inbound函数的第一个参数的类型赋给m_contextClass,即再下面代码中handleInbound(Context ctx) 函数的参数类型Context, outbound函数与inbound函数参数相同,就这样,Handler通过上下文 Context 与 MVC 容器之间交换参数数据、请求、应答等信息。
public class ModelManager extends ContainerHolder implements Initializable {
private Class<?> m_contextClass;
private Class<?> m_payloadClass;
private InboundActionModel buildInbound(ModuleModel module, Method method, InboundActionMeta inMeta, PreInboundActionMeta preInMeta) {
...
inbound.setContextClass(method.getParameterTypes()[0]);
if (preInMeta != null) {
inbound.setPreActionNames(preInMeta.value());
}
PayloadMeta payloadMeta = method.getAnnotation(PayloadMeta.class);
if (payloadMeta != null) {
inbound.setPayloadClass(payloadMeta.value());
}
...
}
}
public class Handler implements PageHandler<Context> {
@Override
@PayloadMeta(Payload.class)
@InboundActionMeta(name = "t")
public void handleInbound(Context ctx) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
@Override
@OutboundActionMeta(name = "t")
public void handleOutbound(Context ctx) throws ServletException, IOException {
...
}
}
接下来,通过 InboundActionHandler 去执行 inbound 逻辑,我们将会在首次使用 InboundActionHandler 的时候实例化,每个模块的每个动作都对应一个InboundActionHandler,如下:
public class DefaultActionHandlerManager extends ContainerHolder implements ActionHandlerManager {
public InboundActionHandler getInboundActionHandler(ModuleModel module, InboundActionModel inboundAction) {
String key = module.getModuleName() + ":" + inboundAction.getActionName();
InboundActionHandler actionHandler = (InboundActionHandler)this.m_inboundActionHandlers.get(key);
if(actionHandler == null) {
... //线程安全
actionHandler = (InboundActionHandler)this.lookup(InboundActionHandler.class);
actionHandler.initialize(inboundAction);
this.m_inboundActionHandlers.put(key, actionHandler);
}
return actionHandler;
}
}
实例化之后便调用 InboundActionHandler 的 initialize(...) 函数初始化,初始化的核心,在于通过PayloadProvider注册PayloadModel,之前提到,Payload是一种数据传输对象(DTO),每个页面动作都有各自的Payload,我们会通过 PayloadProvider 将各个Payload描述信息,加载到 PayloadModel对象中,然后写入DefaultPayloadProvider的成员变量 m_payloadModels中,该变量是个 Map 类型, Map的 key 是类通配泛型Class<?>,表示Payload类,具体是哪个类,之前有说明过。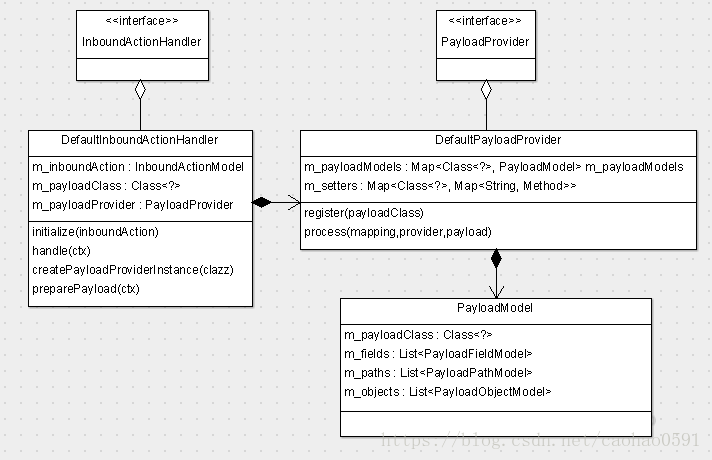
每个Payload都有可能由3种类型的字段组成,普通字段(Field), 对象字段(Object)和路径(Path), 分别由 FieldMeta、ObjectMeta、PathMeta 三个注解所描述,如下config页面的Payload数据(实际上这个Payload没有Path,为了示范我加了进来),他们的描述信息将会被分别写入 PayloadModel 的 m_fields、m_objects、m_paths 三个列表里。
package com.dianping.cat.system.page.config;
public class Payload implements ActionPayload<SystemPage, Action> {
@FieldMeta("op")
private Action m_action;
private SystemPage m_page;
@ObjectMeta("project")
private Project m_project = new Project();
@ObjectMeta("patternItem")
private PatternItem m_patternItem = new PatternItem();
...
@FieldMeta("domain")
private String m_domain;
@FieldMeta("domains")
private String[] m_domains = new String[100];
@FieldMeta("from")
private String m_from;
@FieldMeta("id")
private int m_id;
...
@PathMeta("path")
private String[] m_path;
}
在InboundActionHandler 被初始化之后,我们将首先用它来调用她的 preparePayload(...) 函数处理URL参数信息,如domain=cat&ip=All&date=2018041918&reportType=day&op=view,PayloadProvider 的process 方法会遍历InboundActionHandler初始化时注册的PayloadModel中的m_fields、m_objects、m_paths 三个列表,按照描述信息,将URL参数信息写入Payload对象,之后将 payload 装入动作上下文(ActionContext),带入Action函数。
public class DefaultInboundActionHandler extends ContainerHolder implements InboundActionHandler, LogEnabled {
@Override
public void preparePayload(ActionContext ctx) {
if (m_payloadClass != null) {
RequestContext requestContext = ctx.getRequestContext();
ActionPayload payload = createInstance(m_payloadClass);
payload.setPage(requestContext.getAction());
m_payloadProvider.process(requestContext.getUrlMapping(), requestContext.getParameterProvider(), payload);
payload.validate(ctx);
ctx.setPayload(payload);
}
}
}
加载Payload之后,RequestLifecycle 会调用 handlePreActions(...) 去执行 inbound 动作的前置动作,但是仅配置(config)相关的页面会有前置动作(login),如下,即必须是已登陆的用户才可以修改配置,这里我不做详细讲解,
public class Handler implements PageHandler<Context> {
@Override
@PreInboundActionMeta("login")
@PayloadMeta(Payload.class)
@InboundActionMeta(name = "config")
public void handleInbound(Context ctx) throws ServletException, IOException {
// display only, no action here
}
@Override
@PreInboundActionMeta("login")
@OutboundActionMeta(name = "config")
public void handleOutbound(Context ctx) throws ServletException, IOException {
...
}
}
然后RequestLifecycle将会通过inbound动作执行器去执行inbound方法,这个过程有很多的校验工作,其实最核心的就是下面一行代码,他利用java反射机制,去调用在 InboundActionModel 中注册的 Handler 对象的 inbound 方法,并将动作上下文(ActionContext) 作为参数传递过去。接下来的transition、outbound动作的调用,异常处理的 ErrorAction 也都是这种方式。
public class DefaultInboundActionHandler extends ContainerHolder implements InboundActionHandler, LogEnabled {
private InboundActionModel m_inboundAction;
public void handle(ActionContext ctx) throws ActionException {
...
ReflectUtils.invokeMethod(this.m_inboundAction.getActionMethod(), this.m_inboundAction.getModuleInstance(), new Object[]{ctx});
...
}
}
最后在Handler处理完成之后,DefaultRequestLifecycle将调用 this.m_builder.reset(context) 来重置请求上下文。
页面处理器Handler
深入详解美团点评CAT跨语言服务监控(九)CAT管理平台MVC框架的更多相关文章
- 深入详解美团点评CAT跨语言服务监控(一) CAT简介与部署
前言: CAT是一个实时和接近全量的监控系统,它侧重于对Java应用的监控,除了与点评RPC组件融合的很好之外,他将会能与Spring.MyBatis.Dubbo 等框架以及Log4j 等结合,支持P ...
- 深入详解美团点评CAT跨语言服务监控(七)消息分析器与报表(二)
CrossAnalyzer-调用链分析 在分布式环境中,应用是运行在独立的进程中的,有可能是不同的机器,或者不同的服务器进程.那么他们如果想要彼此联系在一起,形成一个调用链,在Cat中,CrossAn ...
- 深入详解美团点评CAT跨语言服务监控(六)消息分析器与报表(一)
大众点评CAT微服务监控架构对于消息的具体处理,是由消息分析器完成的,消息分析器会轮训读取PeriodTask中队列的消息来处理,一共有12类消息分析器,处理后的结果就是生成各类报表. 消息分析器的构 ...
- 深入详解美团点评CAT跨语言服务监控(四)服务端消息分发
这边首先介绍下大众点评CAT消息分发大概的架构如下: 图4 消息分发架构图 分析管理器的初始化 我们在第一章讲到服务器将接收到的消息交给解码器(MessageDecoder)去做解码最后交给具体的消费 ...
- 深入详解美团点评CAT跨语言服务监控(三)CAT客户端原理
cat客户端部分核心类 message目录下面有消息相关的部分接口 internal目录包含主要的CAT客户端内部实现类: io目录包含建立服务端连接.重连.消息队列监听.上报等io实现类: spi目 ...
- 深入详解美团点评CAT跨语言服务监控(二) CAT服务端初始化
Cat模块 Cat-client : cat客户端,编译后生成 cat-client-2.0.0.jar ,用户可以通过它来向cat-home上报统一格式的日志信息,可以集成到 mybatis.spr ...
- 深入详解美团点评CAT跨语言服务监控(五)配置与数据库操作
CAT配置 在CAT中,有非常多的配置去指导监控的行为,每个配置都有相应的配置管理类来管理,都有一个配置名, 配置在数据库或者配置文件中都是以xml格式存储,在运行时会被解析到具体实体类存储.我们选取 ...
- 深入详解美团点评CAT跨语言服务监控(八)报表持久化
周期结束 我们从消息分发章节知道,RealtimeConsumer在初始化的时候,会启动一个线程,每隔1秒钟就去从判断是否需要开启或结束一个周期(Period),如下源码,如果 value < ...
- 一阶RC高通滤波器详解(仿真+matlab+C语言实现)
文章目录 预备知识 关于电容 HPF的推导 simulink 仿真 simulink 运行结果 matlab 实现 matlab 运行结果 C语言实现 如果本文帮到了你,帮忙点个赞: 如果本文帮到了你 ...
随机推荐
- SQL-14 从titles表获取按照title进行分组,每组个数大于等于2,给出title以及对应的数目t。 注意对于重复的emp_no进行忽略。
题目描述 从titles表获取按照title进行分组,每组个数大于等于2,给出title以及对应的数目t.注意对于重复的emp_no进行忽略.CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS &q ...
- freemarker中的null异常处理以及!与??的使用(转)
原文链接: https://blog.csdn.net/mexican_jacky/article/details/50638062 阅读数:6304 如工程包含: 在user中我们有个角色,那么我们 ...
- 70 多表查询的分组F 聚合 Q 查询
聚合查询和分组查询 聚合 aggregate()是QuerySet 的一个终止子句,意思是说,它返回一个包含一些键值对的字典.键的名称是聚合值的标识符,值是计算出来的聚合值.键的名称是按照字段和聚合函 ...
- hibernate中基于主键映射1-1关联关系和基于外键映射1-1关联关系的不同
基于主键映射1-1关联关系和基于外键映射1-1关联关系的不同,主要区别是在配置映射文件上会有区别 两个持久化类为Manager和Department 1:基于主键映射1-1关联关系 1)使用其他持久化 ...
- PMP基本概念
项目是为创造独特的产品,服务或成果而进行的临时性的工作.项目的三个特点是:临时,独特,渐进明细. 运营是遵循组织有流程的重复性工作. 项目组合是为了实现战略目标而组合在一起管理的项目,项目集,子项目组 ...
- VMware虚拟机与主机共享文件夹
VMware也可以像docker容器那样"挂载"主机上的目录给虚拟机,在虚拟机上访问共享目录就跟访问自己的目录一样方便. 1. 虚拟机(M) -> 设置(S)-> 选项 ...
- 【转载】 如何看待 2019 年 CS PhD 现扎堆申请且大部分为 AI 方向?未来几年 AI 泡沫会破裂吗?
原贴地址: https://www.zhihu.com/question/316135639 作为一个 AI 方向的在读博士生,实在是过的蛮闹心,无意中逛知乎发现了这个帖子,发现很适合现在的自己,于是 ...
- 【leetcode】13-Roman2Integer
problem Roman to Integer 每个Roman表示一个数字,可以进行一一映射: 左边字符表示的数字小于右边字符时,减去对应的数字,否则加上: 注意左右字符比较时,最后一个字符不能比较 ...
- Java中的IO流大体介绍
由于Java中的IO流是在是知识点繁多,所以我大约花了1周的时间将其整理起来.但是整理起来后并不是将完事了,我还是要分字节流和字符流来讲述.然后字节流和字符流中还有是否带有缓冲流. 讲述完IO流后我将 ...
- PYTHON 定时器简单封装,基于SCHED
python fresher,轻拍. 在写后台服务时经常会遇到很多定时器的场景,threading.Timer类每实例化一个定时器会有一个新线程去执行,在客户端使用倒是没有问题,如果是服务器端定时器数 ...
