算法进阶面试题06——实现LFU缓存算法、计算带括号的公式、介绍和实现跳表结构
接着第四课的内容,主要讲LFU、表达式计算和跳表
第一题
上一题实现了LRU缓存算法,LFU也是一个著名的缓存算法
自行了解之后实现LFU中的set 和 get
要求:两个方法的时间复杂度都为O(1)
LFU根据get、set操作次数决定的优先级。
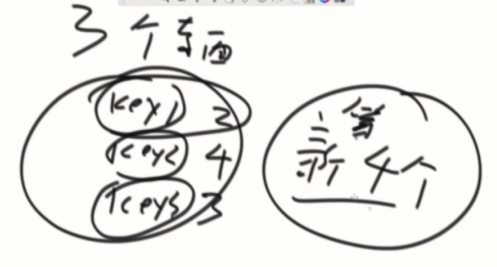
同样次数,最不经常访问的先出去。
实现思路:建立一个次数链,每个次数再链接上一个双向链。(两个双链表)

Put和Get的时候,先检查是否存在
如果没有,put就存在1的链表下,get就返回null。
如果有,找到属于哪个头,然后分离出来,查看头部的下一个是否次数+1的关系,有就插入,没有就建出来。每次挂都是挂在小链表的头部。
size满了,就删最左边底下的head。
看代码...(代码是把最近操作的放在头部)
public class Code_03_LFU {
//小链表的节点
public static class Node {
public Integer key;
public Integer value;
public Integer times;
public Node up;
public Node down;
public Node(int key, int value, int times) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.times = times;
}
}
public static class LFUCache {
//把次数相同的节点连在一起的链表
public static class NodeList {
//本链的头尾
public Node head;
public Node tail;
//前一个和后一个
public NodeList last;
public NodeList next;
public NodeList(Node node) {
head = node;
tail = node;
}
public void addNodeFromHead(Node newHead) {
newHead.down = head;
head.up = newHead;
head = newHead;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null;
}
//其中的任何节点都可能删,因为次数增加也要调整节点位置
//把节点从本环境中分离
public void deleteNode(Node node) {
if (head == tail) {
head = null;
tail = null;
} else {
if (node == head) {//头
head = node.down;
head.up = null;
} else if (node == tail) {//尾
tail = node.up;
tail.down = null;
} else {//其中
node.up.down = node.down;
node.down.up = node.up;
}
}
node.up = null;
node.down = null;
}
}
private int capacity;//容量
private int size;//当前大小
//通过key找Node
private HashMap<Integer, Node> records;
//找到Node的当前所在链表
private HashMap<Node, NodeList> heads;
private NodeList headList;
public LFUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.size = 0;
this.records = new HashMap<>();
this.heads = new HashMap<>();
headList = null;
}
public void set(int key, int value) {
if (records.containsKey(key)) {//存在
Node node = records.get(key);
node.value = value;
node.times++;
NodeList curNodeList = heads.get(node);
move(node, curNodeList);//帮node找新家
} else {
if (size == capacity) {//腾出空间
Node node = headList.tail;
headList.deleteNode(node);
modifyHeadList(headList);//检查是否要调整(有可能删光了)
records.remove(node.key);
heads.remove(node);
size--;
}
Node node = new Node(key, value, 1);
if (headList == null) {//第一次加
headList = new NodeList(node);
} else {
//检查是否存在专属的次数链表
if (headList.head.times.equals(node.times)) {
headList.addNodeFromHead(node);
} else {//没有就建
NodeList newList = new NodeList(node);
newList.next = headList;
headList.last = newList;
headList = newList;
}
}
//记录信息
records.put(key, node);
heads.put(node, headList);
size++;
}
}
private void move(Node node, NodeList oldNodeList) {
oldNodeList.deleteNode(node);//先从老家搬出
//搬出后老家有可能因为无住户而被拆除,所以前指向要判断下
NodeList preList = modifyHeadList(oldNodeList) ? oldNodeList.last
: oldNodeList;
NodeList nextList = oldNodeList.next;
if (nextList == null) {//新家不存在,建一个
NodeList newList = new NodeList(node);
if (preList != null) {//老家还在
preList.next = newList;
}
newList.last = preList;
//应对1---3的情况,删了1,后面没2,自然新建的2会变为新头
// ^a---^b
if (headList == null) {
headList = newList;
}
heads.put(node, newList);//加入记录
} else {
//新家合适,是老家+1的配套
if (nextList.head.times.equals(node.times)) {
nextList.addNodeFromHead(node);
heads.put(node, nextList);
} else {//新家不合适,建一个
NodeList newList = new NodeList(node);
if (preList != null) {//保证前一个节点不为空,不然下面代码报错
preList.next = newList;
}
newList.last = preList;
newList.next = nextList;
nextList.last = newList;
if (headList == nextList) {//判断头链表是否有变化
headList = newList;
}
heads.put(node, newList);//加入记录
}
}
}
// return whether delete this head
private boolean modifyHeadList(NodeList nodeList) {
if (nodeList.isEmpty()) {//如果房子没有住户,要进行拆除
if (headList == nodeList) {//如果是头节点
headList = nodeList.next;
if (headList != null) {//尾部的情况
headList.last = null;
}
} else {//普通节点
nodeList.last.next = nodeList.next;
if (nodeList.next != null) {//尾部的话就是null的
nodeList.next.last = nodeList.last;
}
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
public int get(int key) {
if (!records.containsKey(key)) {
return -1;
}
Node node = records.get(key);
node.times++;
NodeList curNodeList = heads.get(node);
move(node, curNodeList);//帮Node找新家
return node.value;
}
}
}
打完这代码,其他什么链表操作都是你孙子。
等同于面对真正对手前,练的打木桩和铁砂掌。
面试经验:
面试官问如果测试代码你会怎么测?
要把对数器的思路说上。
考察你是否想到一些极端的边界情况。
解决方法:
在写代码的过程中,出错点、代码边界点、需要讨论的东西,记下来,养成一种思维习惯。
写代码的时候,遇到特殊情况,纸笔记录下来,面试官问的时候,你都已经记录好了。
题目二:
给定一个字符串str,str表示一个公式,公式里可能有整数、加减乘除符号和左右括号,返回公式的计算结果。
【举例】
str="48*((70-65)-43)+8*1",返回-1816。
str="3+1*4",返回7。 str="3+(1*4)",返回7。
【说明】
1.可以认为给定的字符串一定是正确的公式,即不需要对str做公式有效性检查。
2.如果是负数,就需要用括号括起来,比如"4*(-3)"。但如果负数作为公式的开头或括号部分的开头,则可以没有括号,比如"-3*4"和"(-3)*4"都是合法的。
3.不用考虑计算过程中会发生溢出的情况
需要好的代码结构设计
思路:
分没有小括号和有小括号的计算方法。
没有小括号的情况:不是 * / 直接往里放,是就取出一个计算后再放回去。
最后全部放完只剩下加减运算。

相当于乘除所在区域合成一块。
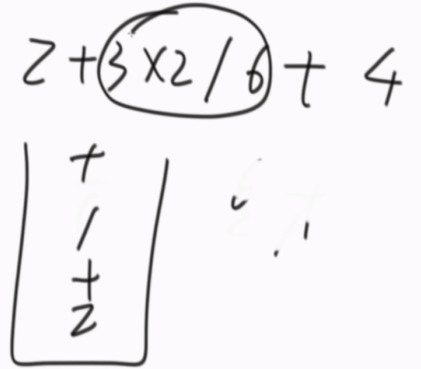
有小括号的情况:
定义一个函数。
str从index开始计算公式,遇到)或str结尾,过程结束。

遇到左括号后,后面的东西就不算了,直接扔给调子过程,碰到右括号再返回[结果和算到哪个位置]。
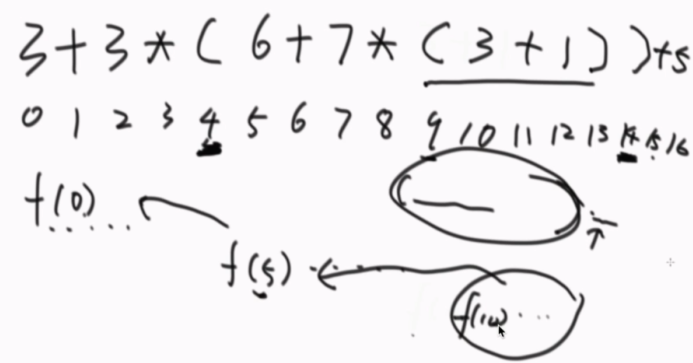
看到code
public class Code_07_ExpressionCompute {
public static int getValue(String str) {
return value(str.toCharArray(), 0)[0];
}
//返回数组[计算结果,计算到哪个位置]
public static int[] value(char[] str, int i) {
//双端队列
LinkedList<String> que = new LinkedList<String>();
int pre = 0;//收集数字
int[] bra = null;
while (i < str.length && str[i] != ')') {
if (str[i] >= '0' && str[i] <= '9') {//把数字重组,注意有=
pre = pre * 10 + str[i++] - '0';
} else if (str[i] != '(') {// + - * /
//收集数字和符号,数字+符号是一组
addNum(que, pre);
que.addLast(String.valueOf(str[i++]));
pre = 0;//注意清0
} else {// 当前i位置为(
bra = value(str, i + 1);//不管,直接递归
pre = bra[0];
i = bra[1] + 1;
}
}
addNum(que, pre);
return new int[] { getNum(que), i };
}
public static void addNum(LinkedList<String> que, int num) {
if (!que.isEmpty()) {
int cur = 0;
String top = que.pollLast();
if (top.equals("+") || top.equals("-")) {
que.addLast(top);//放回去
} else {
cur = Integer.valueOf(que.pollLast());
num = top.equals("*") ? (cur * num) : (cur / num);
}
}
que.addLast(String.valueOf(num));
}
//计算加减
public static int getNum(LinkedList<String> que) {
int res = 0;
boolean add = true;
String cur = null;
int num = 0;
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
cur = que.pollFirst();
if (cur.equals("+")) {
add = true;
} else if (cur.equals("-")) {
add = false;
} else {
num = Integer.valueOf(cur);
res += add ? num : (-num);
}
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String exp = "48*((70-65)-43)+8*1";
System.out.println(getValue(exp));
exp = "4*(6+78)+53-9/2+45*8";
System.out.println(getValue(exp));
exp = "10-5*3";
System.out.println(getValue(exp));
exp = "-3*4";
System.out.println(getValue(exp));
exp = "3+1*4";
System.out.println(getValue(exp));
}
}
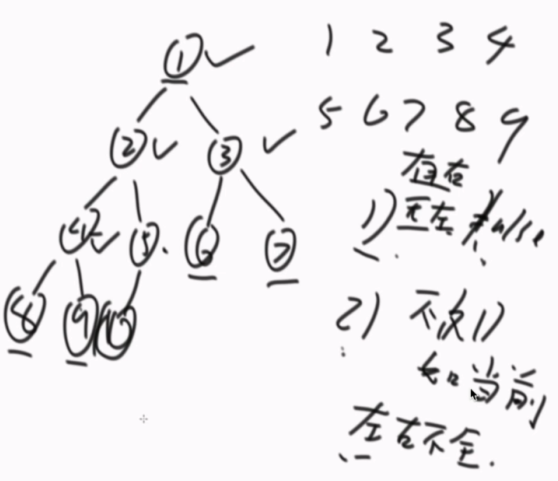
判断一棵二叉树是否是搜索二叉树
判断一棵二叉树是否是完全二叉树(基础班讲过)
按层遍历(队列)节点,
1、如果当前节点有右无左直接false
2、不违反1的情况,当前节点左右不全,剩下的全都要叶子节点。

public class Code_07_IsBSTAndCBT {
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
//Morris遍历
//左子树小、右子树大
public static boolean isBST(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
boolean res = true;
Node pre = null;
Node cur1 = head;
Node cur2 = null;
while (cur1 != null) {
cur2 = cur1.left;
if (cur2 != null) {
while (cur2.right != null && cur2.right != cur1) {
cur2 = cur2.right;
}
if (cur2.right == null) {
cur2.right = cur1;
cur1 = cur1.left;
continue;
} else {
cur2.right = null;
}
}
if (pre != null && pre.value > cur1.value) {
res = false;
}
pre = cur1;
cur1 = cur1.right;
}
return res;
}
public static boolean isCBT(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>();
boolean leaf = false;
Node l = null;
Node r = null;
queue.offer(head);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
head = queue.poll();
l = head.left;
r = head.right;
if ((leaf && (l != null || r != null)) || (l == null && r != null)) {
return false;
}
if (l != null) {
queue.offer(l);
}
if (r != null) {
queue.offer(r);
} else {//如果右子树为空,左子树不为空,接下来的都要是叶子节点
leaf = true;
}
}
return true;
}
// for test -- print tree
public static void printTree(Node head) {
System.out.println("Binary Tree:");
printInOrder(head, 0, "H", 17);
System.out.println();
}
public static void printInOrder(Node head, int height, String to, int len) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
printInOrder(head.right, height + 1, "v", len);
String val = to + head.value + to;
int lenM = val.length();
int lenL = (len - lenM) / 2;
int lenR = len - lenM - lenL;
val = getSpace(lenL) + val + getSpace(lenR);
System.out.println(getSpace(height * len) + val);
printInOrder(head.left, height + 1, "^", len);
}
public static String getSpace(int num) {
String space = " ";
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer("");
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
buf.append(space);
}
return buf.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(4);
head.left = new Node(2);
head.right = new Node(6);
head.left.left = new Node(1);
head.left.right = new Node(3);
head.right.left = new Node(5);
printTree(head);
System.out.println(isBST(head));
System.out.println(isCBT(head));
}
}
题目三:
回到第三课,讲跳表。
何为跳表?
完成功能(最大的k,比k小/大离他最近的key)和红色树、平衡搜索二叉树一样
代价也是longn,底层结构不是树结构。
Redis按序组织就是跳表结构。
每个数进去前,先random,0/1,直到1,就知道这个数是多少层。
如果L层没到最大层,从最高层开始找,如果最高的下一个大,往下走。如果小往右走。走到不能再走,往下走。
这个过程中,如果到了L层,在往下走之前,先把属于那个层的点先建上,然后往下走。依次建出属于新值的所有层的点。
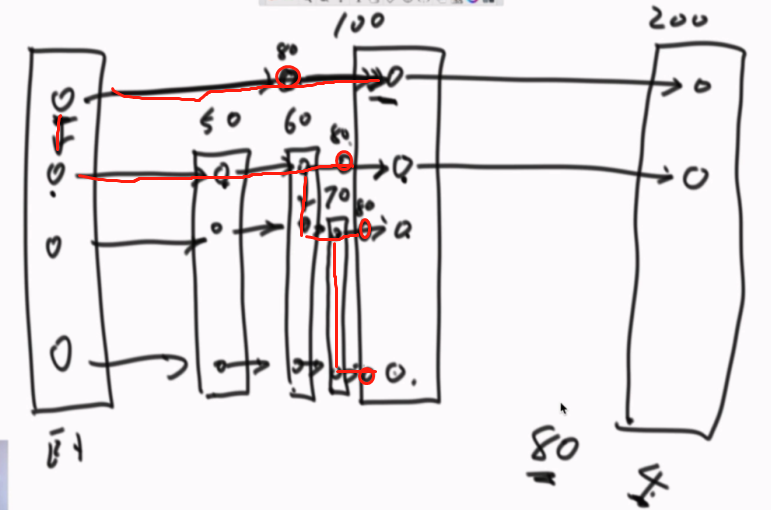
如果数据为N,第一层很多点,但是逐层上去会越来越少,在查询和建立的过程中,是从高层开始找的,一跨会跨过非常多的数。
用1/2概率这东西来优化效率。
从最高层开始找这个数(例如50万)该待的位置,只向下和向右那就跨过很多数了,每层都会跨过一定量的数(因为每个数的层数是1/2随机的),每层一次越过的位置,其实在底层看已经越过相当多的位置了,所以管他叫“跳表”。
怎么插入,就怎么查。
public class Code_02_SkipList {
public static class SkipListNode {
public Integer value;
//长度为10,说明有10层,nextNodes[1]代表在1层上他的下一个节点是什么
//0层指向null,1指向第一层他的下一个结点是谁,以此类推
//从高层到下
public ArrayList<SkipListNode> nextNodes;
public SkipListNode(Integer value) {
this.value = value;
nextNodes = new ArrayList<SkipListNode>();
}
}
public static class SkipListIterator implements Iterator<Integer> {
SkipList list;
SkipListNode current;
public SkipListIterator(SkipList list) {
this.list = list;
this.current = list.getHead();
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return current.nextNodes.get(0) != null;
}
public Integer next() {
current = current.nextNodes.get(0);
return current.value;
}
}
public static class SkipList {
private SkipListNode head;//巨小,层数是最高的
private int maxLevel;
private int size;//加进来了多少个key
private static final double PROBABILITY = 0.5;
public SkipList() {
size = 0;
maxLevel = 0;
head = new SkipListNode(null);
head.nextNodes.add(null);
}
public SkipListNode getHead() {
return head;
}
public void add(Integer newValue) {
if (!contains(newValue)) {
size++;
int level = 0;
while (Math.random() < PROBABILITY) {
level++;
}
while (level > maxLevel) {
head.nextNodes.add(null);//头增加区域到最大层数
maxLevel++;
}
SkipListNode newNode = new SkipListNode(newValue);
SkipListNode current = head;//从头部往下移动
int levelAll = maxLevel;//从最高层开始找
do {
current = findNext(newValue, current, levelAll);
if (levelAll <= level){//达到应该加入节点的层
//前后环境接上
//当前层,建立指向刚好比自己大的节点的联系
//例如一共5层,由于是从高层开始插入,先把第五层加入0位置
//接着第四层的时候也是加到0位置,那就把原本第五层的挤到1位置
//...以此类推,加到最后一层就会是正常的0位置
// 最后一层也已经被挤到最后的位置上
newNode.nextNodes.add(0, current.nextNodes.get(level));
//把刚好比他小的节点,指向他。例如:7--->10 加入8 变成7--->8--->10
current.nextNodes.set(level, newNode);
level--;
}
} while (levelAll-- > 0);//当前层小了往右,大了往下
}
}
public void delete(Integer deleteValue) {
if (contains(deleteValue)) {
SkipListNode deleteNode = find(deleteValue);
size--;
int level = maxLevel;
SkipListNode current = head;
do {
current = findNext(deleteNode.value, current, level);
if (deleteNode.nextNodes.size() > level) {
current.nextNodes.set(level, deleteNode.nextNodes.get(level));
}
} while (level-- > 0);
}
}
// Returns the skiplist node with greatest value <= e
private SkipListNode find(Integer e) {
return find(e, head, maxLevel);
}
// Returns the skiplist node with greatest value <= e
// Starts at node start and level
private SkipListNode find(Integer e, SkipListNode current, int level) {
do {
current = findNext(e, current, level);
} while (level-- > 0);
return current;
}
// Returns the node at a given level with highest value less than e
private SkipListNode findNext(Integer e, SkipListNode current, int level) {
//获得当前节点所在层中连接的下一个节点(例如cur在第七层中的下一个)
SkipListNode next = current.nextNodes.get(level);
while (next != null) {
Integer value = next.value;
if (lessThan(e, value)) { // e < value
break;//如果下一个数比新增值大了,就找到接入位置。
//cur就是这一层中,最后一个小于当前数的值。
}
//向右动
current = next;
next = current.nextNodes.get(level);
}
return current;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
public boolean contains(Integer value) {
SkipListNode node = find(value);
return node != null && node.value != null && equalTo(node.value, value);
}
public Iterator<Integer> iterator() {
return new SkipListIterator(this);
}
/******************************************************************************
* Utility Functions *
******************************************************************************/
private boolean lessThan(Integer a, Integer b) {
return a.compareTo(b) < 0;
}
private boolean equalTo(Integer a, Integer b) {
return a.compareTo(b) == 0;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
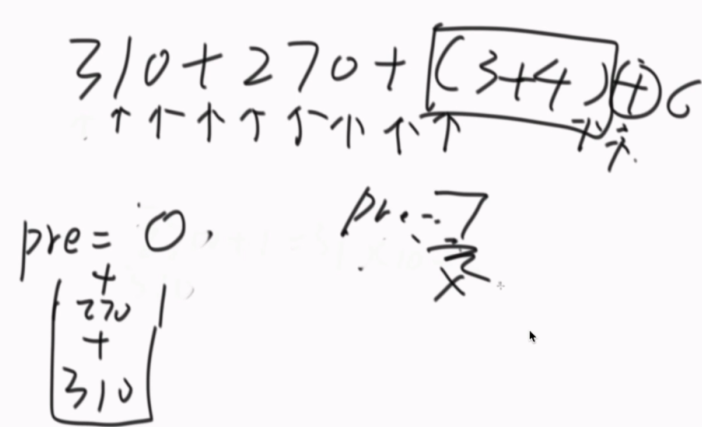
add操作图解
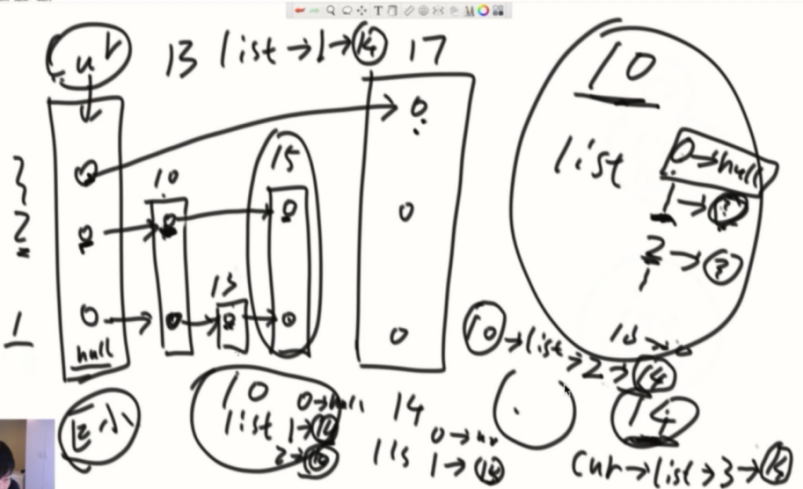
证明算法复杂度:
可以研究下他的分布,不管输入规律是什么,基本上就是一颗二叉树的样子,概率是0.5,那下一层基本是本层数量的两倍,所以是logn的代价,一跳,跳过很多节点,一共跳多少层就是代价,逻辑概念可以等同于一颗二叉树,但是他是以概率完成的。
add方法存在问题,应该是从最高层开始找的,现在是从random出来的level开始找。应该是从最高层向下向右找到相应的位置,达到level层后再开始加入。(例如random出了第一层,如果从第一层开始遍历,就不是longn的算法了)(上面展示的代码已经修正)
算法进阶面试题06——实现LFU缓存算法、计算带括号的公式、介绍和实现跳表结构的更多相关文章
- -实现 LFU 缓存算法
-实现 LFU 缓存算法, 设计一个类 LFUCache,实现下面三个函数 + 构造函数: 传入 Cache 内最多能存储的 key 的数量 + get(key):如果 Cache 中存在该 key, ...
- 算法进阶面试题05——树形dp解决步骤、返回最大搜索二叉子树的大小、二叉树最远两节点的距离、晚会最大活跃度、手撕缓存结构LRU
接着第四课的内容,加入部分第五课的内容,主要介绍树形dp和LRU 第一题: 给定一棵二叉树的头节点head,请返回最大搜索二叉子树的大小 二叉树的套路 统一处理逻辑:假设以每个节点为头的这棵树,他的最 ...
- 算法进阶面试题07——求子数组的最大异或和(前缀树)、换钱的方法数(递归改dp最全套路解说)、纸牌博弈、机器人行走问题
主要讲第五课的内容前缀树应用和第六课内容暴力递归改动态规划的最全步骤 第一题 给定一个数组,求子数组的最大异或和. 一个数组的异或和为,数组中所有的数异或起来的结果. 简单的前缀树应用 暴力方法: 先 ...
- 算法进阶面试题04——平衡二叉搜索树、AVL/红黑/SB树、删除和调整平衡的方法、输出大楼轮廓、累加和等于num的最长数组、滴滴Xor
接着第三课的内容和讲了第四课的部分内容 1.介绍二叉搜索树 在二叉树上,何为一个节点的后继节点? 何为搜索二叉树? 如何实现搜索二叉树的查找?插入?删除? 二叉树的概念上衍生出的. 任何一个节点,左比 ...
- 算法进阶面试题03——构造数组的MaxTree、最大子矩阵的大小、2017京东环形烽火台问题、介绍Morris遍历并实现前序/中序/后序
接着第二课的内容和带点第三课的内容. (回顾)准备一个栈,从大到小排列,具体参考上一课.... 构造数组的MaxTree [题目] 定义二叉树如下: public class Node{ public ...
- 算法进阶面试题02——BFPRT算法、找出最大/小的K个数、双向队列、生成窗口最大值数组、最大值减最小值小于或等于num的子数组数量、介绍单调栈结构(找出临近的最大数)
第二课主要介绍第一课余下的BFPRT算法和第二课部分内容 1.BFPRT算法详解与应用 找到第K小或者第K大的数. 普通做法:先通过堆排序然后取,是n*logn的代价. // O(N*logK) pu ...
- 算法进阶面试题01——KMP算法详解、输出含两次原子串的最短串、判断T1是否包含T2子树、Manacher算法详解、使字符串成为最短回文串
1.KMP算法详解与应用 子序列:可以连续可以不连续. 子数组/串:要连续 暴力方法:逐个位置比对. KMP:让前面的,指导后面. 概念建设: d的最长前缀与最长后缀的匹配长度为3.(前缀不能到最后一 ...
- 缓存算法(FIFO 、LRU、LFU三种算法的区别)
FIFO算法 FIFO 算法是一种比较容易实现的算法.它的思想是先进先出(FIFO,队列),这是最简单.最公平的一种思想,即如果一个数据是最先进入的,那么可以认为在将来它被访问的可能性很小.空间满的时 ...
- 【缓存算法】FIFO,LFU,LRU
一.FIFO算法 FIFO(First in First out),先进先出.其实在操作系统的设计理念中很多地方都利用到了先进先出的思想,比如作业调度(先来先服务),为什么这个原则在很多地方都会用到呢 ...
随机推荐
- drozer工具的安装与使用:之二使用篇
如果英文好的同学可以直接查看官方文档 官方文档连接:https://labs.mwrinfosecurity.com/assets/BlogFiles/mwri-drozer-user-guide ...
- ubuntu14.04 VIM for python 一键配置
# 超强vim配置文件 [](https://travis-ci. ...
- Linux内存管理--物理内存分配【转】
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/myarrow/article/details/8682819 1. First Fit分配器 First Fit分配器是最基本的内存分配器,它使用bi ...
- Python3学习笔记26-unittest模块
unittest单元测试框架,主要由四部分组成:测试固件.测试用例.测试套件.测试执行器 测试固件(test fixture) 测试固件有两部分,执行测试前的准备部分setUp(),测试执行完后的清扫 ...
- (常用)subprocess模块 详情官方
subprocess包中定义有数个创建子进程的函数,这些函数分别以不同的方式创建子进程,所以我们可以根据需要来从中选取一个使用.另外subprocess还提供了一些管理标准流(standard str ...
- nagios系列(六)之nagios实现对服务器cpu温度的监控
1.安装硬件传感器监控软件sensors yum install -y lm_sensors* 2.运行sensors-detect进行传感器检测 ##一路回车即可 Do you want to ov ...
- ocos2d-x 3.0坐标系详解--透彻篇 ---- convertToWorldSpace:把基于当前节点的本地坐标系下的坐标转换到世界坐标系中。
convertToWorldSpace:把基于当前节点的本地坐标系下的坐标转换到世界坐标系中.重点说明:基于... 不一定要是真实的, convertToWorldSpace 的结果也只是一个新 ...
- C#面向对象(继承)
- 数论-质数 poj2689,阶乘分解,求阶乘的尾零hdu1124, 求尾零为x的最小阶乘
/* 要求出[1,R]之间的质数会超时,但是要判断[L,R]之间的数是否是素数却不用筛到R 因为要一个合数n的最大质因子不会超过sqrt(n) 所以只要将[2,sqrt(R)]之间的素数筛出来,再用这 ...
- 性能测试十八:jmeter分布式
一台压力机产生得压力是有限的,尤其是jmeter,java本来性能就不是很好,并发特别多的时候,jmeter的性能会急剧下降,正常的接口,若单台压力机,超过1000并发以后,jmeter的性能就不怎么 ...
