深度学习中的Data Augmentation方法(转)基于keras
在深度学习中,当数据量不够大时候,常常采用下面4中方法:
2. Regularization. 数据量比较小会导致模型过拟合, 使得训练误差很小而测试误差特别大. 通过在Loss Function 后面加上正则项可以抑制过拟合的产生. 缺点是引入了一个需要手动调整的hyper-parameter. 详见 https://www.wikiwand.com/en/Regularization_(mathematics)
3. Dropout. 这也是一种正则化手段. 不过跟以上不同的是它通过随机将部分神经元的输出置零来实现. 详见 http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~hinton/absps/JMLRdropout.pdf
4. Unsupervised Pre-training. 用Auto-Encoder或者RBM的卷积形式一层一层地做无监督预训练, 最后加上分类层做有监督的Fine-Tuning. 参考 http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.207.1102&rep=rep1&type=pdf
不同的任务背景下, 我们可以通过图像的几何变换, 使用以下一种或多种组合数据增强变换来增加输入数据的量. 这里具体的方法都来自数字图像处理的内容, 相关的知识点介绍, 网上都有, 就不一一介绍了.
- 旋转 | 反射变换(Rotation/reflection): 随机旋转图像一定角度; 改变图像内容的朝向;
- 翻转变换(flip): 沿着水平或者垂直方向翻转图像;
- 缩放变换(zoom): 按照一定的比例放大或者缩小图像;
- 平移变换(shift): 在图像平面上对图像以一定方式进行平移;
可以采用随机或人为定义的方式指定平移范围和平移步长, 沿水平或竖直方向进行平移. 改变图像内容的位置; - 尺度变换(scale): 对图像按照指定的尺度因子, 进行放大或缩小; 或者参照SIFT特征提取思想, 利用指定的尺度因子对图像滤波构造尺度空间. 改变图像内容的大小或模糊程度;
- 对比度变换(contrast): 在图像的HSV颜色空间,改变饱和度S和V亮度分量,保持色调H不变. 对每个像素的S和V分量进行指数运算(指数因子在0.25到4之间), 增加光照变化;
- 噪声扰动(noise): 对图像的每个像素RGB进行随机扰动, 常用的噪声模式是椒盐噪声和高斯噪声;
- 颜色变换(color): 在训练集像素值的RGB颜色空间进行PCA, 得到RGB空间的3个主方向向量,3个特征值, p1, p2, p3, λ1, λ2, λ3. 对每幅图像的每个像素Ixy=[IRxy,IGxy,IBxy]T进行加上如下的变化:
[p1,p2,p3][α1λ1,α2λ2,α3λ3]T
其中:αi是满足均值为0,方差为0.1的随机变量.
代码实现
作为实现部分, 这里介绍一下在python 环境下, 利用已有的开源代码库Keras作为实践:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__author__ = 'Administrator' # import packages
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator, array_to_img, img_to_array, load_img datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rotation_range=0.2,
width_shift_range=0.2,
height_shift_range=0.2,
shear_range=0.2,
zoom_range=0.2,
horizontal_flip=True,
fill_mode='nearest') img = load_img('C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\dataA\lena.jpg') # this is a PIL image, please replace to your own file path
x = img_to_array(img) # this is a Numpy array with shape (3, 150, 150)
x = x.reshape((1,) + x.shape) # this is a Numpy array with shape (1, 3, 150, 150) # the .flow() command below generates batches of randomly transformed images
# and saves the results to the `preview/` directory i = 0
for batch in datagen.flow(x,
batch_size=1,
save_to_dir='C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\dataA\pre',#生成后的图像保存路径
save_prefix='lena',
save_format='jpg'):
i += 1
if i > 20: #这个20指出要扩增多少个数据
break # otherwise the generator would loop indefinitely
主要函数:ImageDataGenerator 实现了大多数上文中提到的图像几何变换方法.
- rotation_range: 旋转范围, 随机旋转(0-180)度;
- width_shift and height_shift: 随机沿着水平或者垂直方向,以图像的长宽小部分百分比为变化范围进行平移;
- rescale: 对图像按照指定的尺度因子, 进行放大或缩小, 设置值在0 - 1之间,通常为1 / 255;
- shear_range: 水平或垂直投影变换, 参考这里 https://keras.io/preprocessing/image/
- zoom_range: 按比例随机缩放图像尺寸;
- horizontal_flip: 水平翻转图像;
- fill_mode: 填充像素, 出现在旋转或平移之后.
效果如下图所示:

转载于:http://blog.csdn.net/mduanfire/article/details/51674098
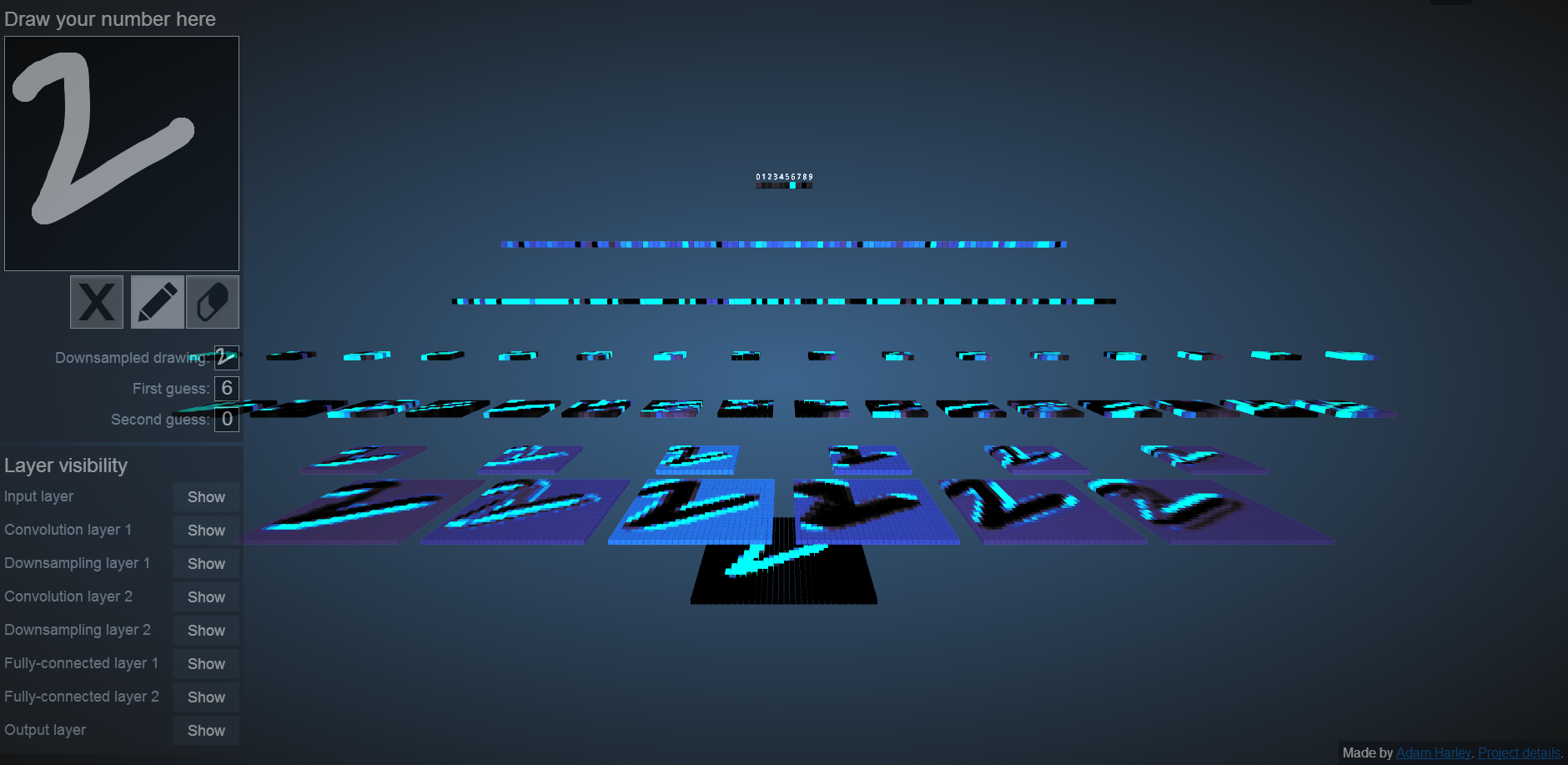
为什么要做变形,或者说数据增强。从这个网站可以看出 http://scs.ryerson.ca/~aharley/vis/conv/ 手写字符稍微变形点,就有可能识别出错,因此数据增强可以生成一些变形的数据,让网络提前适应
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__author__ = 'Administrator' # import packages
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator, array_to_img, img_to_array, load_img datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rotation_range=0.2,
width_shift_range=0.2,
height_shift_range=0.2,
shear_range=0.2,
zoom_range=0.2,
horizontal_flip=True,
fill_mode='nearest') for k in range(33):
numstr = "{0:d}".format(k);
filename='C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\bad\\'+numstr+'.jpg';
ufilename = unicode(filename , "utf8")
img = load_img(ufilename) # this is a PIL image, please replace to your own file path
x = img_to_array(img) # this is a Numpy array with shape (3, 150, 150)
x = x.reshape((1,) + x.shape) # this is a Numpy array with shape (1, 3, 150, 150) # the .flow() command below generates batches of randomly transformed images
# and saves the results to the `preview/` directory i = 0 for batch in datagen.flow(x,
batch_size=1,
save_to_dir='C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\dataA\\',#生成后的图像保存路径
save_prefix=numstr,
save_format='jpg'):
i += 1
if i > 20:
break # otherwise the generator would loop indefinitely
end
# -*- coding: utf- -*-
__author__ = 'Administrator' # import packages
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator, array_to_img, img_to_array, load_img datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rotation_range=,
width_shift_range=0.2,
height_shift_range=0.2,
rescale=./,
shear_range=0.2,
zoom_range=0.2,
horizontal_flip=True,
fill_mode='nearest')
import os import sys
reload(sys)
sys.setdefaultencoding('utf8') ufilename = unicode("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\测试" , "utf8") for filename in os.listdir(ufilename): #listdir的参数是文件夹的路径
print ( filename) #此时的filename是文件夹中文件的名称
pathname='C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\测试\\'+filename;
#ufilename = unicode(pathname , "utf8")
img = load_img(pathname) # this is a PIL image, please replace to your own file path
x = img_to_array(img) # this is a Numpy array with shape (, , )
x = x.reshape((,) + x.shape) # this is a Numpy array with shape (, , , )
# the .flow() command below generates batches of randomly transformed images
# and saves the results to the `preview/` directory
i =
for batch in datagen.flow(x,
batch_size=,
save_to_dir='C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\result\\',#生成后的图像保存路径
save_prefix=filename,
save_format='jpg'):
i +=
if i > :
break # otherwise the generator would loop indefinitely # datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
# rotation_range=0.2,
# width_shift_range=0.2,
# height_shift_range=0.2,
# rescale=./,
# shear_range=0.1,
# zoom_range=0.4,
# horizontal_flip=True,
# fill_mode='nearest')
#
# ufilename = unicode("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\训练" , "utf8")
# for filename in os.listdir(ufilename): #listdir的参数是文件夹的路径
# print ( filename) #此时的filename是文件夹中文件的名称
# pathname='C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\训练\\'+filename;
# # ufilename = unicode(pathname , "utf8")
# img = load_img(pathname) # this is a PIL image, please replace to your own file path
# x = img_to_array(img) # this is a Numpy array with shape (, , )
# x = x.reshape((,) + x.shape) # this is a Numpy array with shape (, , , )
#
# # the .flow() command below generates batches of randomly transformed images
# # and saves the results to the `preview/` directory
#
# i =
#
# for batch in datagen.flow(x,
# batch_size=,
# save_to_dir='C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\result\\',#生成后的图像保存路径
# save_prefix=filename,
# save_format='jpg'):
# i +=
# if i > :
# break # otherwise the generator would loop indefinitely
https://github.com/mdbloice/Augmentor
深度学习中的Data Augmentation方法(转)基于keras的更多相关文章
- 深度学习中数据的augmentation
为了提高模型的泛化能力,同时也为了增大数据集,我们往往需要对数据进行augmentation,在这篇博客中,将总结一下可以对数据进行的augmentation. 1.颜色数据增强,对图像亮度.饱和度. ...
- 深度学习中dropout策略的理解
现在有空整理一下关于深度学习中怎么加入dropout方法来防止测试过程的过拟合现象. 首先了解一下dropout的实现原理: 这些理论的解释在百度上有很多.... 这里重点记录一下怎么实现这一技术 参 ...
- 深度学习中Dropout原理解析
1. Dropout简介 1.1 Dropout出现的原因 在机器学习的模型中,如果模型的参数太多,而训练样本又太少,训练出来的模型很容易产生过拟合的现象. 在训练神经网络的时候经常会遇到过拟合的问题 ...
- Hebye 深度学习中Dropout原理解析
1. Dropout简介 1.1 Dropout出现的原因 在机器学习的模型中,如果模型的参数太多,而训练样本又太少,训练出来的模型很容易产生过拟合的现象. 在训练神经网络的时候经常会遇到过拟合的问题 ...
- 深度学习中正则化技术概述(附Python代码)
欢迎大家关注我们的网站和系列教程:http://www.tensorflownews.com/,学习更多的机器学习.深度学习的知识! 磐石 介绍 数据科学研究者们最常遇见的问题之一就是怎样避免过拟合. ...
- zz详解深度学习中的Normalization,BN/LN/WN
详解深度学习中的Normalization,BN/LN/WN 讲得是相当之透彻清晰了 深度神经网络模型训练之难众所周知,其中一个重要的现象就是 Internal Covariate Shift. Ba ...
- 深度学习中交叉熵和KL散度和最大似然估计之间的关系
机器学习的面试题中经常会被问到交叉熵(cross entropy)和最大似然估计(MLE)或者KL散度有什么关系,查了一些资料发现优化这3个东西其实是等价的. 熵和交叉熵 提到交叉熵就需要了解下信息论 ...
- 卷积在深度学习中的作用(转自http://timdettmers.com/2015/03/26/convolution-deep-learning/)
卷积可能是现在深入学习中最重要的概念.卷积网络和卷积网络将深度学习推向了几乎所有机器学习任务的最前沿.但是,卷积如此强大呢?它是如何工作的?在这篇博客文章中,我将解释卷积并将其与其他概念联系起来,以帮 ...
- 深度学习中 --- 解决过拟合问题(dropout, batchnormalization)
过拟合,在Tom M.Mitchell的<Machine Learning>中是如何定义的:给定一个假设空间H,一个假设h属于H,如果存在其他的假设h’属于H,使得在训练样例上h的错误率比 ...
随机推荐
- ZABBIX冗余架构构筑(Centos6.4+pacemaker+corosync+drbd)
基本构成: 用pacemaker+corosync控制心跳和资源迁移 用drbd同步zabbix配置文件和mysql数据库 所有软件都用yum安装至默认路径 主机的drbd领域挂载至/drbd,备机不 ...
- SQL语言分类
SQL语言共分为四大类:数据查询语言DQL,数据操纵语言DML, 数据定义语言DDL,数据控制语言DCL. 1 数据查询语言DQL数据查询语言DQL基本结构是由SELECT子句,FROM子句,WHER ...
- Chrome开发者工具不完全指南(六、插件篇)
本篇是Chrome开发者工具的结尾篇,最后为大家介绍几款功能强大的插件.在chrome商店里面有很多插件,没事建议大家去逛逛.不过需要FQ,所以诸位请自备神器.一.皮肤插件 首先是大家期盼已久,翘首以 ...
- listview(3、动态刷新)
listview的动态刷新主要是调用adapter的notifyDataSetChanged. 在下面的例子中除了记录正常的刷新外,还记录一种错误的情况(注释掉的),作为备忘. notifyDataS ...
- 【情人节来一发】网站添加QQ客服功能
今年的元宵节遇到情人节,挺不自量力的,呵呵,开篇给各位讲个段子,早上一美女同学在空间发说说道:“开工大吉 起床啦,卖元宵,卖玫瑰,卖避孕套啦-有木有一起去发财的小伙伴?Let’s go…”,对于此种长 ...
- [51单片机] 以从0开始做4位8段共阴数码管3461AS驱动谈细节决定高质量DIY
目录 1)问题产生 2)失败尝试 3)最终方案 4)使用方法 5)知识共享 1)问题产生 在上一篇“以PWM控制直流电机为例建一个简单的51工程框架”中已向大家介绍了一个封装好的8位8段数码管的驱动( ...
- 把 Notepad++ 打造成一款易用的C#脚本编辑器
以前一直用Linqpad在写小程序脚本,但是Linqpad自动完成功能要收费,且不开源,这样的话就不方便扩展了.今天在 http://csscriptnpp.codeplex.com/ 发现了一款C# ...
- 让Redis在你的系统中发挥更大作用的几点建议
转载于:http://www.itxuexiwang.com/a/shujukujishu/redis/2016/0216/105.html?1455868313 Redis在很多方面与其他数据库解决 ...
- Beats数据采集---Packetbeat\Filebeat\Topbeat\WinlogBeat使用指南
Beats是elastic公司的一款轻量级数据采集产品,它包含了几个子产品: packetbeat(用于监控网络流量). filebeat(用于监听日志数据,可以替代logstash-input-fi ...
- 简单总结java 语法
通过学习慢慢的爱上了这门语言,在Java的学习过程中,可能会遇到形形色色的问题不容易解决,应多去专业论坛了解相关的知识,书本上的知识有限.要会从网上搜索有用的信息加以整理,促进学习的深入和知识水平的提 ...
