深入jvm虚拟机--第一篇 void TemplateInterpreterGenerator::generate_and_dispatch(Template* t, TosState tos_out) 函数
今天第一次使用虚拟姐打断点,断点设置在了void TemplateInterpreterGenerator::generate_and_dispatch(Template* t, TosState tos_out) 了
在TemplateInterpreterGenerator.cpp中,这个函数之前看书就不太懂,现在debug时候就能分析的比较清楚了,这个函数的介绍在解密jvm的528页中有具体介绍
void TemplateInterpreterGenerator::generate_and_dispatch(Template* t, TosState tos_out) {
if (PrintBytecodeHistogram) histogram_bytecode(t);
#ifndef PRODUCT
// debugging code
if (CountBytecodes || TraceBytecodes || StopInterpreterAt > 0) count_bytecode();
if (PrintBytecodePairHistogram) histogram_bytecode_pair(t);
if (TraceBytecodes) trace_bytecode(t);
if (StopInterpreterAt > 0) stop_interpreter_at();
__ verify_FPU(1, t->tos_in());
#endif // !PRODUCT
int step = 0;
if (!t->does_dispatch()) {
step = t->is_wide() ? Bytecodes::wide_length_for(t->bytecode()) : Bytecodes::length_for(t->bytecode());
if (tos_out == ilgl) tos_out = t->tos_out();
// compute bytecode size
assert(step > 0, "just checkin'");
// setup stuff for dispatching next bytecode
if (ProfileInterpreter && VerifyDataPointer
&& MethodData::bytecode_has_profile(t->bytecode())) {
__ verify_method_data_pointer();
}
__ dispatch_prolog(tos_out, step);
}
// generate template
t->generate(_masm);
// advance
if (t->does_dispatch()) {
#ifdef ASSERT
// make sure execution doesn't go beyond this point if code is broken
__ should_not_reach_here();
#endif // ASSERT
} else {
// dispatch to next bytecode
__ dispatch_epilog(tos_out, step);
}
}
先看这个入参函数Template

这个是一个对象,在哪里定义的呢?得往上边查看
void TemplateInterpreterGenerator::set_entry_points(Bytecodes::Code code) {
CodeletMark cm(_masm, Bytecodes::name(code), code);
// initialize entry points
assert(_unimplemented_bytecode != NULL, "should have been generated before");
assert(_illegal_bytecode_sequence != NULL, "should have been generated before");
address bep = _illegal_bytecode_sequence;
address zep = _illegal_bytecode_sequence;
address cep = _illegal_bytecode_sequence;
address sep = _illegal_bytecode_sequence;
address aep = _illegal_bytecode_sequence;
address iep = _illegal_bytecode_sequence;
address lep = _illegal_bytecode_sequence;
address fep = _illegal_bytecode_sequence;
address dep = _illegal_bytecode_sequence;
address vep = _unimplemented_bytecode;
address wep = _unimplemented_bytecode;
// code for short & wide version of bytecode
if (Bytecodes::is_defined(code)) {
Template* t = TemplateTable::template_for(code);
assert(t->is_valid(), "just checking");
set_short_entry_points(t, bep, cep, sep, aep, iep, lep, fep, dep, vep);
}
if (Bytecodes::wide_is_defined(code)) {
Template* t = TemplateTable::template_for_wide(code);
assert(t->is_valid(), "just checking");
set_wide_entry_point(t, wep);
}
// set entry points
EntryPoint entry(bep, zep, cep, sep, aep, iep, lep, fep, dep, vep);
Interpreter::_normal_table.set_entry(code, entry);
Interpreter::_wentry_point[code] = wep;
}
是通过: Template* t = TemplateTable::template_for(code); 得到的; TemplateTable的定义
需要知道的是这个是个 静态类,理解是类似于java,能在全局通过类:成员,类:方法来调用(引用)
class TemplateTable: AllStatic {
public:
enum Operation { add, sub, mul, div, rem, _and, _or, _xor, shl, shr, ushr };
enum Condition { equal, not_equal, less, less_equal, greater, greater_equal };
enum CacheByte { f1_byte = 1, f2_byte = 2, f1_oop = 0x11 }; // byte_no codes
private:
static bool _is_initialized; // true if TemplateTable has been initialized
static Template _template_table [Bytecodes::number_of_codes];
static Template _template_table_wide[Bytecodes::number_of_codes];
static Template* _desc; // the current template to be generated
static Bytecodes::Code bytecode() { return _desc->bytecode(); }
static BarrierSet* _bs; // Cache the barrier set.
public:
//%note templates_1
static InterpreterMacroAssembler* _masm; // the assembler used when generating templates
private:
// special registers
static inline Address at_bcp(int offset);
// helpers
static void unimplemented_bc();
static void patch_bytecode(Bytecodes::Code bc, Register bc_reg,
Register temp_reg, bool load_bc_into_bc_reg = true, int byte_no = -1);
// C calls
static void call_VM(Register oop_result, address entry_point);
static void call_VM(Register oop_result, address entry_point, Register arg_1);
static void call_VM(Register oop_result, address entry_point, Register arg_1, Register arg_2);
static void call_VM(Register oop_result, address entry_point, Register arg_1, Register arg_2, Register arg_3);
// these overloadings are not presently used on SPARC:
static void call_VM(Register oop_result, Register last_java_sp, address entry_point);
static void call_VM(Register oop_result, Register last_java_sp, address entry_point, Register arg_1);
static void call_VM(Register oop_result, Register last_java_sp, address entry_point, Register arg_1, Register arg_2);
static void call_VM(Register oop_result, Register last_java_sp, address entry_point, Register arg_1, Register arg_2, Register arg_3);
// bytecodes
static void nop();
static void aconst_null();
static void iconst(int value);
static void lconst(int value);
static void fconst(int value);
static void dconst(int value);
static void bipush();
static void sipush();
static void ldc(bool wide);
static void ldc2_w();
static void fast_aldc(bool wide);
static void locals_index(Register reg, int offset = 1);
static void iload();
static void fast_iload();
static void fast_iload2();
static void fast_icaload();
static void lload();
static void fload();
static void dload();
static void aload();
static void locals_index_wide(Register reg);
static void wide_iload();
static void wide_lload();
static void wide_fload();
static void wide_dload();
static void wide_aload();
static void iaload();
static void laload();
static void faload();
static void daload();
static void aaload();
static void baload();
static void caload();
static void saload();
static void iload(int n);
static void lload(int n);
static void fload(int n);
static void dload(int n);
static void aload(int n);
static void aload_0();
static void istore();
static void lstore();
static void fstore();
static void dstore();
static void astore();
};
那么试着摸索 能看到 _template_table,这个是一个数组,一共有239个,对应了239个字节码指令
static Template* template_for (Bytecodes::Code code) { Bytecodes::check (code); return &_template_table [code]; }

此时code值为01则返回对应的为_nop的指令,意思就是t=一个_nop字节码的信息,还接着看
step = t->is_wide() ? Bytecodes::wide_length_for(t->bytecode()) : Bytecodes::length_for(t->bytecode());
此为generate_and_dispatch函数中的,分析 t->bytecode(),值==01
//share/vm/interpreter/templateTable.cpp文件中
Bytecodes::Code Template::bytecode() const {
int i = this - TemplateTable::_template_table;
if (i < 0 || i >= Bytecodes::number_of_codes)
i = this - TemplateTable::_template_table_wide;
return Bytecodes::cast(i);
}
那么看_template_table,还是上面已经介绍的那个,接着分析
Bytecodes::wide_length_for(01)
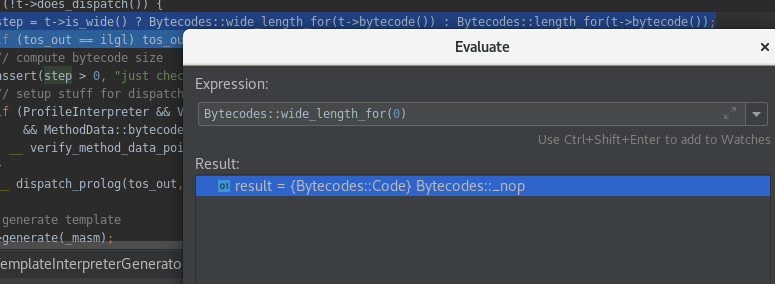
这里的用法就是静态方法调用,查看Bytecodes类
class Bytecodes: AllStatic {
public:
enum Code {
_illegal = -1,
// Java bytecodes
_nop = 0, // 0x00
_aconst_null = 1, // 0x01
_iconst_m1 = 2, // 0x02
_iconst_0 = 3, // 0x03
_iconst_1 = 4, // 0x04
_iconst_2 = 5, // 0x05
_iconst_3 = 6, // 0x06
_iconst_4 = 7, // 0x07
_iconst_5 = 8, // 0x08
_lconst_0 = 9, // 0x09
_lconst_1 = 10, // 0x0a
_fconst_0 = 11, // 0x0b
_fconst_1 = 12, // 0x0c
_fconst_2 = 13, // 0x0d
_dconst_0 = 14, // 0x0e
_dconst_1 = 15, // 0x0f
_bipush = 16, // 0x10
_sipush = 17, // 0x11
_ldc = 18, // 0x12
_ldc_w = 19, // 0x13
_ldc2_w = 20, // 0x14
_iload = 21, // 0x15
_lload = 22, // 0x16
_fload = 23, // 0x17
_dload = 24, // 0x18
_aload = 25, // 0x19
_iload_0 = 26, // 0x1a
_iload_1 = 27, // 0x1b
_iload_2 = 28, // 0x1c
_iload_3 = 29, // 0x1d
_lload_0 = 30, // 0x1e
_lload_1 = 31, // 0x1f
_lload_2 = 32, // 0x20
_lload_3 = 33, // 0x21
_fload_0 = 34, // 0x22
number_of_codes
};
// Flag bits derived from format strings, can_trap, can_rewrite, etc.:
enum Flags {
// semantic flags:
_bc_can_trap = 1<<0, // bytecode execution can trap or block
_bc_can_rewrite = 1<<1, // bytecode execution has an alternate form
// format bits (determined only by the format string):
_fmt_has_c = 1<<2, // constant, such as sipush "bcc"
_fmt_has_j = 1<<3, // constant pool cache index, such as getfield "bjj"
_fmt_has_k = 1<<4, // constant pool index, such as ldc "bk"
_fmt_has_i = 1<<5, // local index, such as iload
_fmt_has_o = 1<<6, // offset, such as ifeq
_fmt_has_nbo = 1<<7, // contains native-order field(s)
_fmt_has_u2 = 1<<8, // contains double-byte field(s)
_fmt_has_u4 = 1<<9, // contains quad-byte field
_fmt_not_variable = 1<<10, // not of variable length (simple or wide)
_fmt_not_simple = 1<<11, // either wide or variable length
_all_fmt_bits = (_fmt_not_simple*2 - _fmt_has_c),
// Example derived format syndromes:
_fmt_b = _fmt_not_variable,
_fmt_bc = _fmt_b | _fmt_has_c,
_fmt_bi = _fmt_b | _fmt_has_i,
_fmt_bkk = _fmt_b | _fmt_has_k | _fmt_has_u2,
_fmt_bJJ = _fmt_b | _fmt_has_j | _fmt_has_u2 | _fmt_has_nbo,
_fmt_bo2 = _fmt_b | _fmt_has_o | _fmt_has_u2,
_fmt_bo4 = _fmt_b | _fmt_has_o | _fmt_has_u4
};
private:
static bool _is_initialized;
static const char* _name [number_of_codes];
static BasicType _result_type [number_of_codes];
static s_char _depth [number_of_codes];
static u_char _lengths [number_of_codes];
static Code _java_code [number_of_codes];
static jchar _flags [(1<<BitsPerByte)*2]; // all second page for wide formats
static void def(Code code, const char* name, const char* format, const char* wide_format, BasicType result_type, int depth, bool can_trap);
static void def(Code code, const char* name, const char* format, const char* wide_format, BasicType result_type, int depth, bool can_trap, Code java_code);
static void pd_initialize(); // platform specific initialization
static Code pd_base_code_for(Code code); // platform specific base_code_for implementation
// Verify that bcp points into method
#ifdef ASSERT
static bool check_method(const methodOopDesc* method, address bcp);
#endif
static bool check_must_rewrite(Bytecodes::Code bc);
public:
// Conversion
static void check (Code code) { assert(is_defined(code), "illegal code"); }
static void wide_check (Code code) { assert(wide_is_defined(code), "illegal code"); }
static Code cast (int code) { return (Code)code; }
static Code code_at(const methodOopDesc* method, address bcp) {
assert(method == NULL || check_method(method, bcp), "bcp must point into method");
Code code = cast(*bcp);
assert(code != _breakpoint || method != NULL, "need methodOop to decode breakpoint");
return (code != _breakpoint) ? code : non_breakpoint_code_at(method, bcp);
}
static Code java_code_at(const methodOopDesc* method, address bcp) {
return java_code(code_at(method, bcp));
}
// Fetch a bytecode or a breakpoint:
static Code code_or_bp_at(address bcp) { return (Code)cast(*bcp); }
static Code code_at(methodOop method, int bci);
static bool is_active_breakpoint_at(address bcp) { return (Code)*bcp == _breakpoint; }
// find a bytecode, behind a breakpoint if necessary:
static Code non_breakpoint_code_at(const methodOopDesc* method, address bcp);
// Bytecode attributes
static bool is_defined (int code) { return 0 <= code && code < number_of_codes && flags(code, false) != 0; }
static bool wide_is_defined(int code) { return is_defined(code) && flags(code, true) != 0; }
static const char* name (Code code) { check(code); return _name [code]; }
static BasicType result_type (Code code) { check(code); return _result_type [code]; }
static int depth (Code code) { check(code); return _depth [code]; }
// Note: Length functions must return <=0 for invalid bytecodes.
// Calling check(code) in length functions would throw an unwanted assert.
static int length_for (Code code) { /*no check*/ return _lengths [code] & 0xF; }
static int wide_length_for(Code code) { /*no check*/ return _lengths [code] >> 4; }
static bool can_trap (Code code) { check(code); return has_all_flags(code, _bc_can_trap, false); }
static Code java_code (Code code) { check(code); return _java_code [code]; }
static bool can_rewrite (Code code) { check(code); return has_all_flags(code, _bc_can_rewrite, false); }
static bool must_rewrite(Bytecodes::Code code) { return can_rewrite(code) && check_must_rewrite(code); }
static bool native_byte_order(Code code) { check(code); return has_all_flags(code, _fmt_has_nbo, false); }
static bool uses_cp_cache (Code code) { check(code); return has_all_flags(code, _fmt_has_j, false); }
// if 'end' is provided, it indicates the end of the code buffer which
// should not be read past when parsing.
static int special_length_at(Bytecodes::Code code, address bcp, address end = NULL);
static int special_length_at(methodOop method, address bcp, address end = NULL) { return special_length_at(code_at(method, bcp), bcp, end); }
static int raw_special_length_at(address bcp, address end = NULL);
static int length_for_code_at(Bytecodes::Code code, address bcp) { int l = length_for(code); return l > 0 ? l : special_length_at(code, bcp); }
static int length_at (methodOop method, address bcp) { return length_for_code_at(code_at(method, bcp), bcp); }
static int java_length_at (methodOop method, address bcp) { return length_for_code_at(java_code_at(method, bcp), bcp); }
static bool is_java_code (Code code) { return 0 <= code && code < number_of_java_codes; }
static bool is_aload (Code code) { return (code == _aload || code == _aload_0 || code == _aload_1
|| code == _aload_2 || code == _aload_3); }
static bool is_astore (Code code) { return (code == _astore || code == _astore_0 || code == _astore_1
|| code == _astore_2 || code == _astore_3); }
static bool is_zero_const (Code code) { return (code == _aconst_null || code == _iconst_0
|| code == _fconst_0 || code == _dconst_0); }
static bool is_invoke (Code code) { return (_invokevirtual <= code && code <= _invokedynamic); }
static int compute_flags (const char* format, int more_flags = 0); // compute the flags
static int flags (int code, bool is_wide) {
assert(code == (u_char)code, "must be a byte");
return _flags[code + (is_wide ? (1<<BitsPerByte) : 0)];
}
static int format_bits (Code code, bool is_wide) { return flags(code, is_wide) & _all_fmt_bits; }
static bool has_all_flags (Code code, int test_flags, bool is_wide) {
return (flags(code, is_wide) & test_flags) == test_flags;
}
// Initialization
static void initialize ();
};
#endif // SHARE_VM_INTERPRETER_BYTECODES_HPP
那么
static int wide_length_for(Code code) { /*no check*/ return _lengths [code] >> 4; }
这个静态类中的值

那么久能看到了 _lengths[01] 为1,
static int length_for (Code code) { /*no check*/ return _lengths [code] & 0xF; }
_lengths[01]为1 &1111111 还是为1;
今天先分析到这里,明天再续
现在准备执行
// generate template
t->generate(_masm);
还是要看Template这个东西,先看类的定义
//"interpreter/interpreterRuntime.hpp"
class Template VALUE_OBJ_CLASS_SPEC {
private:
enum Flags {
uses_bcp_bit, // set if template needs the bcp pointing to bytecode
does_dispatch_bit, // set if template dispatches on its own
calls_vm_bit, // set if template calls the vm
wide_bit // set if template belongs to a wide instruction
}; typedef void (*generator)(int arg); int _flags; // describes interpreter template properties (bcp unknown)
TosState _tos_in; // tos cache state before template execution
TosState _tos_out; // tos cache state after template execution
generator _gen; // template code generator
int _arg; // argument for template code generator void initialize(int flags, TosState tos_in, TosState tos_out, generator gen, int arg); friend class TemplateTable; public:
Bytecodes::Code bytecode() const;
bool is_valid() const { return _gen != NULL; }
bool uses_bcp() const { return (_flags & (1 << uses_bcp_bit )) != 0; }
bool does_dispatch() const { return (_flags & (1 << does_dispatch_bit)) != 0; }
bool calls_vm() const { return (_flags & (1 << calls_vm_bit )) != 0; }
bool is_wide() const { return (_flags & (1 << wide_bit )) != 0; }
TosState tos_in() const { return _tos_in; }
TosState tos_out() const { return _tos_out; }
void generate(InterpreterMacroAssembler* masm);
};
//进入函数内部
void Template::generate(InterpreterMacroAssembler* masm) {
// parameter passing
TemplateTable::_desc = this;
TemplateTable::_masm = masm;
// code generation
_gen(_arg); ///这个函数在 TemplateTable类中
masm->flush();
}
进入_gen(_arg)
//templateTable_x86.cpp
void TemplateTable::nop() {
transition(vtos, vtos);
// nothing to do
}
这里正是对应了templateTable

特别注意上边的类的调用: Template::generater ===>调用了 TemplateTable::nop函数
这nop函数啥也没做
void TemplateTable::transition(TosState tos_in, TosState tos_out) {
assert(_desc->tos_in() == tos_in , "inconsistent tos_in information");
assert(_desc->tos_out() == tos_out, "inconsistent tos_out information");
}
这样就结束了, t->generate(_masm);生成模板的函数调用,之前看过template是 在哪里 Template TemplateTable::_template_table [Bytecodes::number_of_codes];保存
那么他是怎么创造的呢?
//templateTable.cpp
void TemplateTable::initialize() {
if (_is_initialized) return; // Initialize table
TraceTime timer("TemplateTable initialization", TraceStartupTime); _bs = Universe::heap()->barrier_set(); // For better readability
const char _ = ' ';
const int ____ = 0;
const int ubcp = 1 << Template::uses_bcp_bit;
const int disp = 1 << Template::does_dispatch_bit;
const int clvm = 1 << Template::calls_vm_bit;
const int iswd = 1 << Template::wide_bit;
// interpr. templates
// Java spec bytecodes ubcp|disp|clvm|iswd in out generator argument
def(Bytecodes::_nop , ____|____|____|____, vtos, vtos, nop , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_aconst_null , ____|____|____|____, vtos, atos, aconst_null , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_iconst_m1 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, itos, iconst , -1 );
def(Bytecodes::_iconst_0 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, itos, iconst , 0 );
def(Bytecodes::_iconst_1 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, itos, iconst , 1 );
def(Bytecodes::_iconst_2 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, itos, iconst , 2 );
def(Bytecodes::_iconst_3 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, itos, iconst , 3 );
def(Bytecodes::_iconst_4 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, itos, iconst , 4 );
def(Bytecodes::_iconst_5 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, itos, iconst , 5 );
def(Bytecodes::_lconst_0 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, ltos, lconst , 0 );
def(Bytecodes::_lconst_1 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, ltos, lconst , 1 );
def(Bytecodes::_fconst_0 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, ftos, fconst , 0 );
def(Bytecodes::_fconst_1 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, ftos, fconst , 1 );
def(Bytecodes::_fconst_2 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, ftos, fconst , 2 );
def(Bytecodes::_dconst_0 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, dtos, dconst , 0 );
def(Bytecodes::_dconst_1 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, dtos, dconst , 1 );
def(Bytecodes::_bipush , ubcp|____|____|____, vtos, itos, bipush , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_sipush , ubcp|____|____|____, vtos, itos, sipush , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_ldc , ubcp|____|clvm|____, vtos, vtos, ldc , false );
def(Bytecodes::_ldc_w , ubcp|____|clvm|____, vtos, vtos, ldc , true );
def(Bytecodes::_ldc2_w , ubcp|____|____|____, vtos, vtos, ldc2_w , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_iload , ubcp|____|clvm|____, vtos, itos, iload , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_lload , ubcp|____|____|____, vtos, ltos, lload , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_fload , ubcp|____|____|____, vtos, ftos, fload , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_dload , ubcp|____|____|____, vtos, dtos, dload , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_aload , ubcp|____|clvm|____, vtos, atos, aload , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_iload_0 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, itos, iload , 0 );
def(Bytecodes::_iload_1 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, itos, iload , 1 );
def(Bytecodes::_iload_2 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, itos, iload , 2 );
def(Bytecodes::_iload_3 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, itos, iload , 3 );
def(Bytecodes::_lload_0 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, ltos, lload , 0 );
def(Bytecodes::_lload_1 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, ltos, lload , 1 );
def(Bytecodes::_lload_2 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, ltos, lload , 2 );
def(Bytecodes::_lload_3 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, ltos, lload , 3 );
def(Bytecodes::_fload_0 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, ftos, fload , 0 );
def(Bytecodes::_fload_1 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, ftos, fload , 1 );
def(Bytecodes::_fload_2 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, ftos, fload , 2 );
def(Bytecodes::_fload_3 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, ftos, fload , 3 );
def(Bytecodes::_dload_0 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, dtos, dload , 0 );
def(Bytecodes::_dload_1 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, dtos, dload , 1 );
def(Bytecodes::_dload_2 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, dtos, dload , 2 );
def(Bytecodes::_dload_3 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, dtos, dload , 3 );
def(Bytecodes::_aload_0 , ubcp|____|clvm|____, vtos, atos, aload_0 , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_aload_1 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, atos, aload , 1 );
def(Bytecodes::_aload_2 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, atos, aload , 2 );
def(Bytecodes::_aload_3 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, atos, aload , 3 );
def(Bytecodes::_iaload , ____|____|____|____, itos, itos, iaload , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_laload , ____|____|____|____, itos, ltos, laload , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_faload , ____|____|____|____, itos, ftos, faload , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_daload , ____|____|____|____, itos, dtos, daload , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_aaload , ____|____|____|____, itos, atos, aaload , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_baload , ____|____|____|____, itos, itos, baload , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_caload , ____|____|____|____, itos, itos, caload , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_saload , ____|____|____|____, itos, itos, saload , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_istore , ubcp|____|clvm|____, itos, vtos, istore , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_lstore , ubcp|____|____|____, ltos, vtos, lstore , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_fstore , ubcp|____|____|____, ftos, vtos, fstore , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_dstore , ubcp|____|____|____, dtos, vtos, dstore , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_astore , ubcp|____|clvm|____, vtos, vtos, astore , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_istore_0 , ____|____|____|____, itos, vtos, istore , 0 );
def(Bytecodes::_istore_1 , ____|____|____|____, itos, vtos, istore , 1 );
def(Bytecodes::_istore_2 , ____|____|____|____, itos, vtos, istore , 2 );
def(Bytecodes::_istore_3 , ____|____|____|____, itos, vtos, istore , 3 );
def(Bytecodes::_lstore_0 , ____|____|____|____, ltos, vtos, lstore , 0 );
def(Bytecodes::_lstore_1 , ____|____|____|____, ltos, vtos, lstore , 1 );
def(Bytecodes::_lstore_2 , ____|____|____|____, ltos, vtos, lstore , 2 );
def(Bytecodes::_lstore_3 , ____|____|____|____, ltos, vtos, lstore , 3 );
def(Bytecodes::_fstore_0 , ____|____|____|____, ftos, vtos, fstore , 0 );
def(Bytecodes::_fstore_1 , ____|____|____|____, ftos, vtos, fstore , 1 );
def(Bytecodes::_fstore_2 , ____|____|____|____, ftos, vtos, fstore , 2 );
def(Bytecodes::_fstore_3 , ____|____|____|____, ftos, vtos, fstore , 3 );
def(Bytecodes::_dstore_0 , ____|____|____|____, dtos, vtos, dstore , 0 );
def(Bytecodes::_dstore_1 , ____|____|____|____, dtos, vtos, dstore , 1 );
def(Bytecodes::_dstore_2 , ____|____|____|____, dtos, vtos, dstore , 2 );
def(Bytecodes::_dstore_3 , ____|____|____|____, dtos, vtos, dstore , 3 );
def(Bytecodes::_astore_0 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, vtos, astore , 0 );
def(Bytecodes::_astore_1 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, vtos, astore , 1 );
def(Bytecodes::_astore_2 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, vtos, astore , 2 );
def(Bytecodes::_astore_3 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, vtos, astore , 3 );
def(Bytecodes::_iastore , ____|____|____|____, itos, vtos, iastore , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_lastore , ____|____|____|____, ltos, vtos, lastore , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_fastore , ____|____|____|____, ftos, vtos, fastore , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_dastore , ____|____|____|____, dtos, vtos, dastore , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_aastore , ____|____|clvm|____, vtos, vtos, aastore , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_bastore , ____|____|____|____, itos, vtos, bastore , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_castore , ____|____|____|____, itos, vtos, castore , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_sastore , ____|____|____|____, itos, vtos, sastore , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_pop , ____|____|____|____, vtos, vtos, pop , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_pop2 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, vtos, pop2 , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_dup , ____|____|____|____, vtos, vtos, dup , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_dup_x1 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, vtos, dup_x1 , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_dup_x2 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, vtos, dup_x2 , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_dup2 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, vtos, dup2 , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_dup2_x1 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, vtos, dup2_x1 , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_dup2_x2 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, vtos, dup2_x2 , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_swap , ____|____|____|____, vtos, vtos, swap , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_iadd , ____|____|____|____, itos, itos, iop2 , add );
def(Bytecodes::_ladd , ____|____|____|____, ltos, ltos, lop2 , add );
def(Bytecodes::_fadd , ____|____|____|____, ftos, ftos, fop2 , add );
def(Bytecodes::_dadd , ____|____|____|____, dtos, dtos, dop2 , add );
def(Bytecodes::_isub , ____|____|____|____, itos, itos, iop2 , sub );
def(Bytecodes::_lsub , ____|____|____|____, ltos, ltos, lop2 , sub );
def(Bytecodes::_fsub , ____|____|____|____, ftos, ftos, fop2 , sub );
def(Bytecodes::_dsub , ____|____|____|____, dtos, dtos, dop2 , sub );
def(Bytecodes::_imul , ____|____|____|____, itos, itos, iop2 , mul );
def(Bytecodes::_lmul , ____|____|____|____, ltos, ltos, lmul , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_fmul , ____|____|____|____, ftos, ftos, fop2 , mul );
def(Bytecodes::_dmul , ____|____|____|____, dtos, dtos, dop2 , mul );
def(Bytecodes::_idiv , ____|____|____|____, itos, itos, idiv , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_ldiv , ____|____|____|____, ltos, ltos, ldiv , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_fdiv , ____|____|____|____, ftos, ftos, fop2 , div );
def(Bytecodes::_ddiv , ____|____|____|____, dtos, dtos, dop2 , div );
def(Bytecodes::_irem , ____|____|____|____, itos, itos, irem , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_lrem , ____|____|____|____, ltos, ltos, lrem , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_frem , ____|____|____|____, ftos, ftos, fop2 , rem );
def(Bytecodes::_drem , ____|____|____|____, dtos, dtos, dop2 , rem );
def(Bytecodes::_ineg , ____|____|____|____, itos, itos, ineg , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_lneg , ____|____|____|____, ltos, ltos, lneg , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_fneg , ____|____|____|____, ftos, ftos, fneg , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_dneg , ____|____|____|____, dtos, dtos, dneg , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_ishl , ____|____|____|____, itos, itos, iop2 , shl );
def(Bytecodes::_lshl , ____|____|____|____, itos, ltos, lshl , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_ishr , ____|____|____|____, itos, itos, iop2 , shr );
def(Bytecodes::_lshr , ____|____|____|____, itos, ltos, lshr , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_iushr , ____|____|____|____, itos, itos, iop2 , ushr );
def(Bytecodes::_lushr , ____|____|____|____, itos, ltos, lushr , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_iand , ____|____|____|____, itos, itos, iop2 , _and );
def(Bytecodes::_land , ____|____|____|____, ltos, ltos, lop2 , _and );
def(Bytecodes::_ior , ____|____|____|____, itos, itos, iop2 , _or );
def(Bytecodes::_lor , ____|____|____|____, ltos, ltos, lop2 , _or );
def(Bytecodes::_ixor , ____|____|____|____, itos, itos, iop2 , _xor );
def(Bytecodes::_lxor , ____|____|____|____, ltos, ltos, lop2 , _xor );
def(Bytecodes::_iinc , ubcp|____|clvm|____, vtos, vtos, iinc , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_i2l , ____|____|____|____, itos, ltos, convert , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_i2f , ____|____|____|____, itos, ftos, convert , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_i2d , ____|____|____|____, itos, dtos, convert , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_l2i , ____|____|____|____, ltos, itos, convert , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_l2f , ____|____|____|____, ltos, ftos, convert , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_l2d , ____|____|____|____, ltos, dtos, convert , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_f2i , ____|____|____|____, ftos, itos, convert , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_f2l , ____|____|____|____, ftos, ltos, convert , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_f2d , ____|____|____|____, ftos, dtos, convert , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_d2i , ____|____|____|____, dtos, itos, convert , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_d2l , ____|____|____|____, dtos, ltos, convert , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_d2f , ____|____|____|____, dtos, ftos, convert , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_i2b , ____|____|____|____, itos, itos, convert , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_i2c , ____|____|____|____, itos, itos, convert , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_i2s , ____|____|____|____, itos, itos, convert , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_lcmp , ____|____|____|____, ltos, itos, lcmp , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_fcmpl , ____|____|____|____, ftos, itos, float_cmp , -1 );
def(Bytecodes::_fcmpg , ____|____|____|____, ftos, itos, float_cmp , 1 );
def(Bytecodes::_dcmpl , ____|____|____|____, dtos, itos, double_cmp , -1 );
def(Bytecodes::_dcmpg , ____|____|____|____, dtos, itos, double_cmp , 1 );
def(Bytecodes::_ifeq , ubcp|____|clvm|____, itos, vtos, if_0cmp , equal );
def(Bytecodes::_ifne , ubcp|____|clvm|____, itos, vtos, if_0cmp , not_equal );
def(Bytecodes::_iflt , ubcp|____|clvm|____, itos, vtos, if_0cmp , less );
def(Bytecodes::_ifge , ubcp|____|clvm|____, itos, vtos, if_0cmp , greater_equal);
def(Bytecodes::_ifgt , ubcp|____|clvm|____, itos, vtos, if_0cmp , greater );
def(Bytecodes::_ifle , ubcp|____|clvm|____, itos, vtos, if_0cmp , less_equal );
def(Bytecodes::_if_icmpeq , ubcp|____|clvm|____, itos, vtos, if_icmp , equal );
def(Bytecodes::_if_icmpne , ubcp|____|clvm|____, itos, vtos, if_icmp , not_equal );
def(Bytecodes::_if_icmplt , ubcp|____|clvm|____, itos, vtos, if_icmp , less );
def(Bytecodes::_if_icmpge , ubcp|____|clvm|____, itos, vtos, if_icmp , greater_equal);
def(Bytecodes::_if_icmpgt , ubcp|____|clvm|____, itos, vtos, if_icmp , greater );
def(Bytecodes::_if_icmple , ubcp|____|clvm|____, itos, vtos, if_icmp , less_equal );
def(Bytecodes::_if_acmpeq , ubcp|____|clvm|____, atos, vtos, if_acmp , equal );
def(Bytecodes::_if_acmpne , ubcp|____|clvm|____, atos, vtos, if_acmp , not_equal );
def(Bytecodes::_goto , ubcp|disp|clvm|____, vtos, vtos, _goto , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_jsr , ubcp|disp|____|____, vtos, vtos, jsr , _ ); // result is not an oop, so do not transition to atos
def(Bytecodes::_ret , ubcp|disp|____|____, vtos, vtos, ret , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_tableswitch , ubcp|disp|____|____, itos, vtos, tableswitch , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_lookupswitch , ubcp|disp|____|____, itos, itos, lookupswitch , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_ireturn , ____|disp|clvm|____, itos, itos, _return , itos );
def(Bytecodes::_lreturn , ____|disp|clvm|____, ltos, ltos, _return , ltos );
def(Bytecodes::_freturn , ____|disp|clvm|____, ftos, ftos, _return , ftos );
def(Bytecodes::_dreturn , ____|disp|clvm|____, dtos, dtos, _return , dtos );
def(Bytecodes::_areturn , ____|disp|clvm|____, atos, atos, _return , atos );
def(Bytecodes::_return , ____|disp|clvm|____, vtos, vtos, _return , vtos );
def(Bytecodes::_getstatic , ubcp|____|clvm|____, vtos, vtos, getstatic , f1_byte );
def(Bytecodes::_putstatic , ubcp|____|clvm|____, vtos, vtos, putstatic , f2_byte );
def(Bytecodes::_getfield , ubcp|____|clvm|____, vtos, vtos, getfield , f1_byte );
def(Bytecodes::_putfield , ubcp|____|clvm|____, vtos, vtos, putfield , f2_byte );
def(Bytecodes::_invokevirtual , ubcp|disp|clvm|____, vtos, vtos, invokevirtual , f2_byte );
def(Bytecodes::_invokespecial , ubcp|disp|clvm|____, vtos, vtos, invokespecial , f1_byte );
def(Bytecodes::_invokestatic , ubcp|disp|clvm|____, vtos, vtos, invokestatic , f1_byte );
def(Bytecodes::_invokeinterface , ubcp|disp|clvm|____, vtos, vtos, invokeinterface , f1_byte );
def(Bytecodes::_invokedynamic , ubcp|disp|clvm|____, vtos, vtos, invokedynamic , f1_oop );
def(Bytecodes::_new , ubcp|____|clvm|____, vtos, atos, _new , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_newarray , ubcp|____|clvm|____, itos, atos, newarray , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_anewarray , ubcp|____|clvm|____, itos, atos, anewarray , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_arraylength , ____|____|____|____, atos, itos, arraylength , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_athrow , ____|disp|____|____, atos, vtos, athrow , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_checkcast , ubcp|____|clvm|____, atos, atos, checkcast , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_instanceof , ubcp|____|clvm|____, atos, itos, instanceof , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_monitorenter , ____|disp|clvm|____, atos, vtos, monitorenter , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_monitorexit , ____|____|clvm|____, atos, vtos, monitorexit , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_wide , ubcp|disp|____|____, vtos, vtos, wide , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_multianewarray , ubcp|____|clvm|____, vtos, atos, multianewarray , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_ifnull , ubcp|____|clvm|____, atos, vtos, if_nullcmp , equal );
def(Bytecodes::_ifnonnull , ubcp|____|clvm|____, atos, vtos, if_nullcmp , not_equal );
def(Bytecodes::_goto_w , ubcp|____|clvm|____, vtos, vtos, goto_w , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_jsr_w , ubcp|____|____|____, vtos, vtos, jsr_w , _ ); // wide Java spec bytecodes
def(Bytecodes::_iload , ubcp|____|____|iswd, vtos, itos, wide_iload , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_lload , ubcp|____|____|iswd, vtos, ltos, wide_lload , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_fload , ubcp|____|____|iswd, vtos, ftos, wide_fload , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_dload , ubcp|____|____|iswd, vtos, dtos, wide_dload , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_aload , ubcp|____|____|iswd, vtos, atos, wide_aload , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_istore , ubcp|____|____|iswd, vtos, vtos, wide_istore , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_lstore , ubcp|____|____|iswd, vtos, vtos, wide_lstore , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_fstore , ubcp|____|____|iswd, vtos, vtos, wide_fstore , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_dstore , ubcp|____|____|iswd, vtos, vtos, wide_dstore , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_astore , ubcp|____|____|iswd, vtos, vtos, wide_astore , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_iinc , ubcp|____|____|iswd, vtos, vtos, wide_iinc , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_ret , ubcp|disp|____|iswd, vtos, vtos, wide_ret , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_breakpoint , ubcp|disp|clvm|____, vtos, vtos, _breakpoint , _ ); // JVM bytecodes
def(Bytecodes::_fast_agetfield , ubcp|____|____|____, atos, atos, fast_accessfield , atos );
def(Bytecodes::_fast_bgetfield , ubcp|____|____|____, atos, itos, fast_accessfield , itos );
def(Bytecodes::_fast_cgetfield , ubcp|____|____|____, atos, itos, fast_accessfield , itos );
def(Bytecodes::_fast_dgetfield , ubcp|____|____|____, atos, dtos, fast_accessfield , dtos );
def(Bytecodes::_fast_fgetfield , ubcp|____|____|____, atos, ftos, fast_accessfield , ftos );
def(Bytecodes::_fast_igetfield , ubcp|____|____|____, atos, itos, fast_accessfield , itos );
def(Bytecodes::_fast_lgetfield , ubcp|____|____|____, atos, ltos, fast_accessfield , ltos );
def(Bytecodes::_fast_sgetfield , ubcp|____|____|____, atos, itos, fast_accessfield , itos ); def(Bytecodes::_fast_aputfield , ubcp|____|____|____, atos, vtos, fast_storefield , atos );
def(Bytecodes::_fast_bputfield , ubcp|____|____|____, itos, vtos, fast_storefield , itos );
def(Bytecodes::_fast_zputfield , ubcp|____|____|____, itos, vtos, fast_storefield , itos );
def(Bytecodes::_fast_cputfield , ubcp|____|____|____, itos, vtos, fast_storefield , itos );
def(Bytecodes::_fast_dputfield , ubcp|____|____|____, dtos, vtos, fast_storefield , dtos );
def(Bytecodes::_fast_fputfield , ubcp|____|____|____, ftos, vtos, fast_storefield , ftos );
def(Bytecodes::_fast_iputfield , ubcp|____|____|____, itos, vtos, fast_storefield , itos );
def(Bytecodes::_fast_lputfield , ubcp|____|____|____, ltos, vtos, fast_storefield , ltos );
def(Bytecodes::_fast_sputfield , ubcp|____|____|____, itos, vtos, fast_storefield , itos ); def(Bytecodes::_fast_aload_0 , ____|____|____|____, vtos, atos, aload , 0 );
def(Bytecodes::_fast_iaccess_0 , ubcp|____|____|____, vtos, itos, fast_xaccess , itos );
def(Bytecodes::_fast_aaccess_0 , ubcp|____|____|____, vtos, atos, fast_xaccess , atos );
def(Bytecodes::_fast_faccess_0 , ubcp|____|____|____, vtos, ftos, fast_xaccess , ftos ); def(Bytecodes::_fast_iload , ubcp|____|____|____, vtos, itos, fast_iload , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_fast_iload2 , ubcp|____|____|____, vtos, itos, fast_iload2 , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_fast_icaload , ubcp|____|____|____, vtos, itos, fast_icaload , _ ); def(Bytecodes::_fast_invokevfinal , ubcp|disp|clvm|____, vtos, vtos, fast_invokevfinal , f2_byte ); def(Bytecodes::_fast_linearswitch , ubcp|disp|____|____, itos, vtos, fast_linearswitch , _ );
def(Bytecodes::_fast_binaryswitch , ubcp|disp|____|____, itos, vtos, fast_binaryswitch , _ ); def(Bytecodes::_fast_aldc , ubcp|____|clvm|____, vtos, atos, fast_aldc , false );
def(Bytecodes::_fast_aldc_w , ubcp|____|clvm|____, vtos, atos, fast_aldc , true ); def(Bytecodes::_return_register_finalizer , ____|disp|clvm|____, vtos, vtos, _return , vtos ); def(Bytecodes::_shouldnotreachhere , ____|____|____|____, vtos, vtos, shouldnotreachhere , _ );
// platform specific bytecodes
pd_initialize(); _is_initialized = true;
}
看这个函数:TemplateTable::initialize(),这里为每个字节码指令进行了一次def(....)命令,
def(Bytecodes::_nop , ____|____|____|____, vtos, vtos, nop , _ );
def就是定义的意思,关注这个nop参数,他是一个函数位于templateTable.cpp
void TemplateTable::nop() {
transition(vtos, vtos);
// nothing to do
}
看def函数
void TemplateTable::def(Bytecodes::Code code, int flags, TosState in, TosState out, void (*gen)(int arg), int arg) {
// should factor out these constants
const int ubcp = 1 << Template::uses_bcp_bit;
const int disp = 1 << Template::does_dispatch_bit;
const int clvm = 1 << Template::calls_vm_bit;
const int iswd = 1 << Template::wide_bit;
// determine which table to use
bool is_wide = (flags & iswd) != 0;
// make sure that wide instructions have a vtos entry point
// (since they are executed extremely rarely, it doesn't pay out to have an
// extra set of 5 dispatch tables for the wide instructions - for simplicity
// they all go with one table)
assert(in == vtos || !is_wide, "wide instructions have vtos entry point only");
Template* t = is_wide ? template_for_wide(code) : template_for(code);
// setup entry
t->initialize(flags, in, out, gen, arg);
assert(t->bytecode() == code, "just checkin'");
}
关键点就在 Template* t = is_wide ? template_for_wide(code) : template_for(code);
之前分析过t=? : template_for(code);是在 static Template _template_table [];数组中保存的
那么这句话就是获取一个得到数组中的一个引用,应该这个t不能是null,否则就会空指针异常了,应该在哪里初始化过了,那么接下了
生成具体内容 t->initialize(flags, in, out, gen, arg);
// Implementation of Template
void Template::initialize(int flags, TosState tos_in, TosState tos_out, generator gen, int arg) {
_flags = flags;
_tos_in = tos_in;
_tos_out = tos_out;
_gen = gen;
_arg = arg;
}
也没干别的就是把 templateTable中的函数指针,数据等赋值给了 Template对象(模板对象)
接着分析 dispatch_epilog(tos_out, step);

__ dispatch_epilog 其中的开头__ 代表 masm 这在揭秘虚拟机中有解释,
void InterpreterMacroAssembler::dispatch_epilog(TosState state, int step) {
dispatch_next(state, step);
}
void InterpreterMacroAssembler::dispatch_next(TosState state, int step, bool generate_poll) {
// load next bytecode (load before advancing _bcp_register to prevent AGI)
load_unsigned_byte(rbx, Address(_bcp_register, step));
// advance _bcp_register
increment(_bcp_register, step);
dispatch_base(state, Interpreter::dispatch_table(state), true, generate_poll);
}
对应的

那么今天就结束了,下次再续
深入jvm虚拟机--第一篇 void TemplateInterpreterGenerator::generate_and_dispatch(Template* t, TosState tos_out) 函数的更多相关文章
- JVM学习第一篇思考:一个Java代码是怎么运行起来的-上篇
JVM学习第一篇思考:一个Java代码是怎么运行起来的-上篇 作为一个使用Java语言开发的程序员,我们都知道,要想运行Java程序至少需要安装JRE(安装JDK也没问题).我们也知道我们Java程序 ...
- SQL&EF优化第一篇 各种情况下的性能测试之count函数篇
测试环境 mssql 08 +win7 数据 30W条 二〇一六年十月二十九日 09:04:43 结论:1>主键> *>可空列 推测未论证: 根据情况优先选择 顺便提 ...
- JVM学习篇-第一篇
JVM学习篇-第一篇 JDK( Java Development Kit): Java程序设计语言.Java虚拟机.Java类库三部分统称为JDK,JDK是用于支持Java程序开发的最小环境** ...
- 深入理解Java虚拟机之JVM内存布局篇
内存布局**** JVM内存布局规定了Java在运行过程中内存申请.分配.管理的策略,保证了JVM的稳定高效运行.不同的JVM对于内存的划分方式和管理机制存在部分差异.结合JVM虚拟机规范,一起来 ...
- [转帖]java架构之路-(面试篇)JVM虚拟机面试大全
java架构之路-(面试篇)JVM虚拟机面试大全 https://www.cnblogs.com/cxiaocai/p/11634918.html 下文连接比较多啊,都是我过整理的博客,很多答案都 ...
- 【JVM第三篇--运行时数据区】程序计数器、虚拟机栈、本地方法栈
写在前面的话:本文是在观看尚硅谷JVM教程后,整理的学习笔记.其观看地址如下:尚硅谷2020最新版宋红康JVM教程 一.运行时数据区 我们在编写Java程序时,使用JVM的流程主要如下所示: 虚拟机在 ...
- 【JVM虚拟机】(9)-- JVM是如何处理异常的
[JVM虚拟机](9)-- JVM是如何处理异常的 上篇博客我们简单说过异常信息是存放在属性表集合中的Code属性表里,那么这篇博客就单独讲Code属性表中的exception_table. 在讲之前 ...
- 【JVM虚拟机】(8)--深入理解Class中--方法、属性表集合
#[JVM虚拟机](8)--深入理解Class中--方法.属性表集合 之前有关class文件已经写了两篇博客: 1.[JVM虚拟机](5)---深入理解JVM-Class中常量池 2.[JVM虚拟机] ...
- 【JVM虚拟机】(7)---深入理解Class中-属性集合
#[JVM虚拟机](7)---深入理解Class中-属性集合 之前有关class文件已经写了两篇博客: 1.[JVM虚拟机](5)---深入理解JVM-Class中常量池 2.[JVM虚拟机](6)- ...
随机推荐
- Java知识,面试总会问到虚拟机,虚拟机类加载机制你懂吗?
虚拟机把描述类的数据从Class文件文件加载到内存,并对数据进行校验.转换解析和初始化,最终形成可以被虚拟机直接使用的Java类型,这就是虚拟机的类加载机制. 与那些在编译时需要进行连接工作的语言不同 ...
- MySQL的启动选项和系统变量该如何配置?
MySQL的配置信息可以通过两种方式实现,一种是命令行形式,在启动MySQL服务时后边带上相关配置参数,此种方式会在MySQL重启后失效.另外一种是通过写入配置文件,如my.cnf,启动或者重启MyS ...
- 一文带你.Net混合锁和lock语句
本文主要讲解.Net基于Monitor.Enter和lock实现互斥锁 Monitor.Enter实现 相比前面的锁来说,混合锁的性能更高,任何引用类型的对象都可以做为锁对象,不需要事先创建指定类型的 ...
- SpringBoot实战:10分钟快速搞定环境
什么是 springboot Spring Boot是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化新Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程. 该框架使用了特定的方式来进行配置,从而使开发人 ...
- html中各种标签和属性(最基础的基本都有)
1.标题标签: h1~h6 ctrl+1~6 2.段落标签: p ctrl+shift+p 3.换行标签: br shift+回车 4.水平线: hr 5.加粗标签: stro ...
- Golang去除字符串前后空格
Golang去除字符串前后空格 实现Demo package main import "fmt" func DeletePreAndSufSpace(str string) str ...
- hive学习笔记之五:分桶
欢迎访问我的GitHub https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos 内容:所有原创文章分类汇总及配套源码,涉及Java.Docker.Kubernetes.DevOPS ...
- 41.1、shell编程案例
1.案例1(表达式案例): 开发shell脚本分别实现以定义变量,脚本传参以及read读入的方式比较2个整数大小.用条件表达式(禁if) 进行判断并以屏幕输出的方式提醒用户比较结果: [root@ba ...
- OpenMVG 系列 (1):入门简介
1 OpenMVG 简介 全称 Open Multiple View Geometry,是法国人 Pierre Moulon 读博期间开源的一个 C++ 库 最早版本 OpenMVG 0.1 是 ...
- PostgreSQL角色问题
角色 PostgreSQL使用角色的概念管理数据库访问权限. 根据角色自身的设置不同,一个角色可以看做是一个数据库用户,或者一组数据库用户. 角色可以拥有数据库对象(比如表)以及可以把这些对象上的权限 ...
