Python奇技
本文目录
16.字符串格式化
来源:http://andrewliu.in/
作者:Andrew Liu
显示有限的接口到外部
当发布 python 第三方 package 时,并不希望代码中所有的函数或者 class 可以被外部import,在 __init__.py 中添加 __all__ 属性,该 list 中填写可以 import 的类或者函数名,可以起到限制的 import 的作用,防止外部import其他函数或者类
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from base import APIBase from client import Client from decorator import interface, export, stream from server import Server from storage import Storage from util import (LogFormatter, disable_logging_to_stderr, enable_logging_to_kids, info) __all__ = ['APIBase', 'Client', 'LogFormatter', 'Server', 'Storage', 'disable_logging_to_stderr',
'enable_logging_to_kids', 'export', 'info', 'interface', 'stream']
with的魔力
with语句需要支持 上下文管理协议的对象,上下文管理协议包含 __enter__ 和 __exit__ 两个方法。with语句建立运行时上下文需要通过这两个方法执行进入和退出操作。
其中 上下文表达式 是跟在 with 之后的表达式, 该表示大返回一个上下文管理对象
# 常见with使用场景
with open("test.txt", "r") as my_file: # 注意, 是__enter__()方法的返回值赋值给了my_file,
for line in my_file:
print line
知道具体原理,我们可以自定义支持上下文管理协议的类,类中实现 __enter__ 和 __exit__ 方法
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- class MyWith(object): def __init__(self): print "__init__ method" def __enter__(self): print "__enter__ method" return self # 返回对象给as后的变量 def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_value, exc_traceback): print "__exit__ method" if exc_traceback is None: print "Exited without Exception" return True else: print "Exited with Exception" return False def test_with(): with MyWith() as my_with: print "running my_with" print "------分割线-----" with MyWith() as my_with: print "running before Exception" raise Exception print "running after Exception" if __name__ == '__main__': test_with()
执行结果如下:
__init__ method __enter__ method running my_with __exit__ method Exited without Exception ------分割线----- __init__ method __enter__ method running before Exception __exit__ method Exited with Exception Traceback (most recent call last): File "bin/python", line 34, in <module> exec(compile(__file__f.read(), __file__, "exec")) File "test_with.py", line 33, in <module> test_with() File "test_with.py", line 28, in test_with raise Exception Exception
filter的用法
相对 filter 而言,map 和 reduce 使用的会更频繁一些,filter 正如其名字,按照某种规则过滤掉一些元素
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- lst = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] # 所有奇数都会返回True, 偶数会返回False被过滤掉 print filter(lambda x: x % 2 != 0, lst) #输出结果 [1, 3, 5]
当条件满足时,返回的为等号后面的变量,否则返回 else 后语句
lst = [1, 2, 3] new_lst = lst[0] if lst is not None else None print new_lst # 打印结果 1
装饰器之单例
使用装饰器实现简单的单例模式
# 单例装饰器 def singleton(cls): instances = dict() # 初始为空 def _singleton(*args, **kwargs): if cls not in instances: #如果不存在, 则创建并放入字典 instances[cls] = cls(*args, **kwargs) return instances[cls] return _singleton @singleton class Test(object): pass if __name__ == '__main__': t1 = Test() t2 = Test() # 两者具有相同的地址 print t1, t2
staticmethod装饰器
类中两种常用的装饰,首先区分一下他们
普通成员函数,其中第一个隐式参数为对象
classmethod装饰器,类方法(给人感觉非常类似于OC中的类方法),其中第一个隐式参数为类
staticmethod装饰器,没有任何隐式参数。python中的静态方法类似与C++中的静态方法
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
class A(object):
# 普通成员函数
def foo(self, x):
print "executing foo(%s, %s)" % (self, x)
@classmethod # 使用classmethod进行装饰
def class_foo(cls, x):
print "executing class_foo(%s, %s)" % (cls, x)
@staticmethod # 使用staticmethod进行装饰
def static_foo(x):
print "executing static_foo(%s)" % x
def test_three_method():
obj = A()
# 直接调用噗通的成员方法
obj.foo("para") # 此处obj对象作为成员函数的隐式参数, 就是self
obj.class_foo("para") # 此处类作为隐式参数被传入, 就是cls
A.class_foo("para") #更直接的类方法调用
obj.static_foo("para") # 静态方法并没有任何隐式参数, 但是要通过对象或者类进行调用
A.static_foo("para")
if __name__ == '__main__':
test_three_method()
# 函数输出
executing foo(<__main__.A object at 0x100ba4e10>, para)
executing class_foo(<class '__main__.A'>, para)
executing class_foo(<class '__main__.A'>, para)
executing static_foo(para)
executing static_foo(para)
property装饰器
定义私有类属性
将 property 与装饰器结合实现属性私有化( 更简单安全的实现get和set方法 )
#python内建函数 property(fget=None, fset=None, fdel=None, doc=None)
fget 是获取属性的值的函数,fset 是设置属性值的函数,fdel 是删除属性的函数,doc 是一个字符串(like a comment)。从实现来看,这些参数都是可选的
property有三个方法 getter(),setter() 和 delete() 来指定 fget,fset 和 fdel。这表示以下这行
class Student(object):
@property #相当于property.getter(score) 或者property(score)
def score(self):
return self._score
@score.setter #相当于score = property.setter(score)
def score(self, value):
if not isinstance(value, int):
raise ValueError('score must be an integer!')
if value < 0 or value > 100:
raise ValueError('score must between 0 ~ 100!')
self._score = value
iter魔法
通过 yield 和 __iter__ 的结合,我们可以把一个对象变成可迭代的
通过 __str__ 的重写,可以直接通过想要的形式打印对象
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- class TestIter(object): def __init__(self): self.lst = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] def read(self): for ele in xrange(len(self.lst)): yield ele def __iter__(self): return self.read() def __str__(self): return ','.join(map(str, self.lst)) __repr__ = __str__ def test_iter(): obj = TestIter() for num in obj: print num print obj if __name__ == '__main__': test_iter()
神奇partial
partial 使用上很像 C++ 中仿函数(函数对象)
在 stackoverflow 给出了类似与 partial 的运行方式
def partial(func, *part_args): def wrapper(*extra_args): args = list(part_args) args.extend(extra_args) return func(*args) return wrapper
利用用闭包的特性绑定预先绑定一些函数参数,返回一个可调用的变量,直到真正的调用执行
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from functools import partial def sum(a, b): return a + b def test_partial(): fun = partial(sum, 2) # 事先绑定一个参数, fun成为一个只需要一个参数的可调用变量 print fun(3) # 实现执行的即是sum(2, 3) if __name__ == '__main__': test_partial() # 执行结果 5
神秘eval
eval 我理解为一种内嵌的 python 解释器(这种解释可能会有偏差),会解释字符串为对应的代码并执行,并且将执行结果返回
看一下下面这个例子
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
def test_first():
return 3
def test_second(num):
return num
action = { # 可以看做是一个sandbox
"para": 5,
"test_first" : test_first,
"test_second": test_second
}
def test_eavl():
condition = "para == 5 and test_second(test_first) > 5"
res = eval(condition, action) # 解释condition并根据action对应的动作执行
print res
if __name__ == '_
exec
exec 在 Python 中会忽略返回值,总是返回 None,eval 会返回执行代码或语句的返回值
exec 和 eval 在执行代码时,除了返回值其他行为都相同
在传入字符串时,会使用 compile(source, '<string>', mode) 编译字节码。mode 的取值为 exec 和 eval
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
def test_first():
print "hello"
def test_second():
test_first()
print "second"
def test_third():
print "third"
action = {
"test_second": test_second,
"test_third": test_third
}
def test_exec():
exec "test_second" in action
if __name__ == '__main__':
test_exec() # 无法看到执行结果
getattr
getattr(object, name[, default]) Return the value of the named attribute of object. name must be a string. If the string is the name of one of the object’s attributes, the result is the value of that attribute. For example, getattr(x, ‘foobar’) is equivalent to x.foobar. If the named attribute does not exist, default is returned if provided, otherwise AttributeError is raised.
通过 string 类型的 name,返回对象的 name 属性(方法)对应的值,如果属性不存在,则返回默认值,相当于 object.name
# 使用范例 class TestGetAttr(object): test = "test attribute" def say(self): print "test method" def test_getattr(): my_test = TestGetAttr() try: print getattr(my_test, "test") except AttributeError: print "Attribute Error!" try: getattr(my_test, "say")() except AttributeError: # 没有该属性, 且没有指定返回值的情况下 print "Method Error!" if __name__ == '__main__': test_getattr() # 输出结果 test attribute test method
命令行处理
def process_command_line(argv):
"""
Return a 2-tuple: (settings object, args list).
`argv` is a list of arguments, or `None` for ``sys.argv[1:]``.
"""
if argv is None:
argv = sys.argv[1:]
# initialize the parser object:
parser = optparse.OptionParser(
formatter=optparse.TitledHelpFormatter(width=78),
add_help_option=None)
# define options here:
parser.add_option( # customized description; put --help last
'-h', '--help', action='help',
help='Show this help message and exit.')
settings, args = parser.parse_args(argv)
# check number of arguments, verify values, etc.:
if args:
parser.error('program takes no command-line arguments; '
'"%s" ignored.' % (args,))
# further process settings & args if necessary
return settings, args
def main(argv=None):
settings, args = process_command_line(argv)
# application code here, like:
# run(settings, args)
return 0 # success
if __name__ == '__main__':
status = main()
sys.exit(status)
读写csv文件
# 从csv中读取文件, 基本和传统文件读取类似
import csv
with open('data.csv', 'rb') as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
for row in reader:
print row
# 向csv文件写入
import csv
with open( 'data.csv', 'wb') as f:
writer = csv.writer(f)
writer.writerow(['name', 'address', 'age']) # 单行写入
data = [
( 'xiaoming ','china','10'),
( 'Lily', 'USA', '12')]
writer.writerows(data) # 多行写入
各种时间形式转换
只发一张网上的图,然后差文档就好了,这个是记不住的
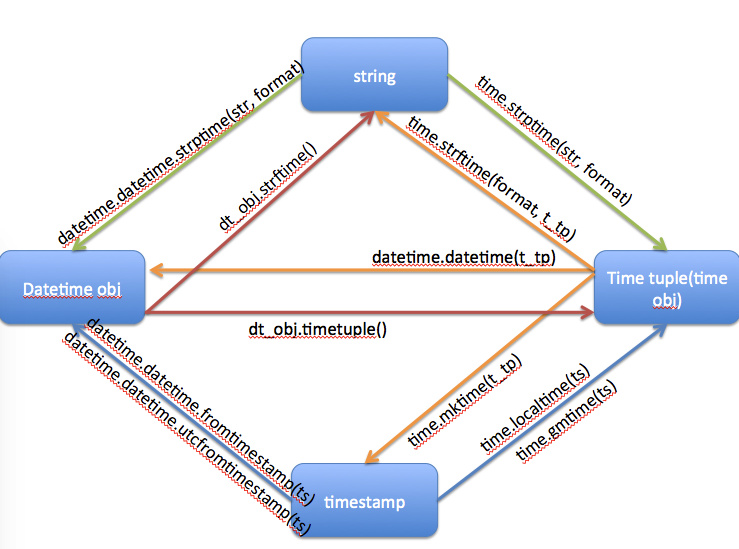
字符串格式化
一个非常好用, 很多人又不知道的功能
>>> name = "andrew"
>>> "my name is {name}".format(name=name)
'my name is andrew'

微信扫一扫
关注该公众号
Python奇技的更多相关文章
- [转]倍数提高工作效率的 Android Studio 奇技
转自:http://android.jobbole.com/81687/ 倍数提高工作效率的 Android Studio 奇技 2015/10/08 · 技术分享 · 4 评论· Android S ...
- Python 炫技操作:安装包的八种方法,你知道吗?
本文的文字及图片来源于网络,仅供学习.交流使用,不具有任何商业用途,如有问题请及时联系我们以作处理 1. 使用 easy_install easy_install 这应该是最古老的包安装方式了,目前基 ...
- 很多人不知道的Python 炫技操作:条件语句的写法
有的人说 Python 是一门 入门容易,但是精通难的语言,这一点我非常赞同. Python 语言里有许多(而且是越来越多)的高级特性,是 Python 发烧友们非常喜欢的.在这些人的眼里,能够写出那 ...
- Python炫技操作:五种Python 转义表示法
1. 为什么要有转义? ASCII 表中一共有 128 个字符.这里面有我们非常熟悉的字母.数字.标点符号,这些都可以从我们的键盘中输出.除此之外,还有一些非常特殊的字符,这些字符,我通常很难用键盘上 ...
- 倍数提高工作效率的 Android Studio 奇技
来源:JeremyHe 链接:http://zlv.me/posts/2015/07/13/14_android-studio-tips/ 这是从Philippe Breault的系列文章<An ...
- Android Studio 提高工作效率的奇技
1.ctrl+f12 ctrl+f12此快捷键可以调出当前文件的大纲,并通过模糊匹配快速跳转至指定的方法.勾选上“show anonymous classes”后其功能相当于Eclipse中的ctrl ...
- Python 小技之实现的鲜花盛宴,你准备好了吗?
前言 本文的文字及图片来源于网络,仅供学习.交流使用,不具有任何商业用途,版权归原作者所有,如有问题请及时联系我们以作处理. 作者:派森酱 PS:如有需要Python学习资料的小伙伴可以加点击下方链接 ...
- 很多人不知道的Python 炫技操作:海象运算符的三种用法
Python 版本发展非常快,如今最新的版本已经是 Pyhton 3.9,即便如此,有很多人甚至还停留在 3.6 或者 3.7,连 3.8 还没用上. 很多 Python 3.8 的特性还没来得及了解 ...
- JACASCRIPT--的奇技技巧的44招
JavaScript是一个绝冠全球的编程语言,可用于Web开发.移动应用开发(PhoneGap.Appcelerator).服务器端开发(Node.js和Wakanda)等等.JavaScript还是 ...
随机推荐
- python--网络通信协议
一 . osi七层协议 互联网协议按照功能不同分为osi七层或tcp/ip五层或tcp/ip四层 二 . tcp三次握手和四次挥手 我们知道网络层,可以实现两个主机之间的通信.但是这并不具体,因为,真 ...
- int long long 的范围
unsigned int 0-4294967295 (10位数,4e9) int -2147483648-2147483647 (10位 ...
- Linux文件管理类命令及命令别名
文件查看类命令: cat: tac: 从文件尾部开始显示 分屏显示: more [option] 文件名: 查看至文件尾部会退出 空格为翻页 less [option] 文件名: 查看至文件尾部不退出 ...
- 数据库---大数据+hadoop
大数据:hadoop:大数据和hadoop的关系
- JAVA连接MYSQL8.0问题
title: java连接mysql8.0问题 date: 2018-07-08 19:27:38 updated: tags: description: keywords: comments: im ...
- log4net.dll配置以及在项目中应用
1,首先在项目中引用log4net.dll,然后项目中添加一个配置文件log4net.config <?xml version="1.0" encoding="ut ...
- appium之android_uiautomator定位
前言 appium就是封装android的uiautomator这个框架来的,所以uiautomator的一些定位方法也可以用 text 1.通过text文本定位语法 new UiSelector() ...
- Codeforces Round #265 (Div. 1)
D. World of Darkraft - 2 time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input sta ...
- POJ 1606 Jugs
Jugs Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 4280 Accepted: 2533 Special Ju ...
- MySQL容量规划之tcpcopy应用之道
官方文档:https://github.com/session-replay-tools/mysql-replay-module tcpcopy可以将正式环境上来自客户端的请求复制一份到测试端并复现, ...

 加载中
加载中