04面向对象编程-02-原型继承 和 ES6的class继承
1、原型继承
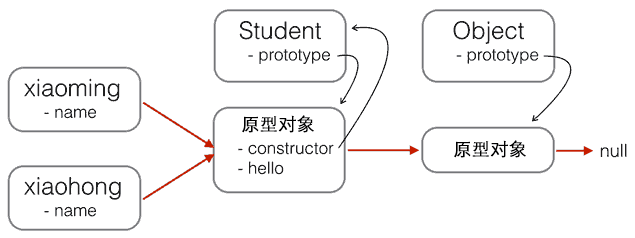
在上一篇中,我们提到,JS中原型继承的本质,实际上就是 “将构造函数的原型对象,指向由另一个构造函数创建的实例”。
function Student(props) {
this.name = props.name || 'Unnamed';
}
Student.prototype.hello = function () {
alert('Hello, ' + this.name + '!');
}function Student(props) {
this.name = props.name || 'Unnamed';
}
Student.prototype.hello = function () {
alert('Hello, ' + this.name + '!');
}
function PrimaryStudent(props) {
// 调用Student构造函数,绑定this变量
Student.call(this, props);
this.grade = props.grade || 1;
}function PrimaryStudent(props) {
// 调用Student构造函数,绑定this变量
Student.call(this, props);
this.grade = props.grade || 1;
}
new PrimaryStudent() ----> PrimaryStudent.prototype ----> Object.prototype ----> nullnew PrimaryStudent() ----> PrimaryStudent.prototype ----> Object.prototype ----> null
new PrimaryStudent() ----> PrimaryStudent.prototype ----> Student.prototype ----> Object.prototype ----> nullnew PrimaryStudent() ----> PrimaryStudent.prototype ----> Student.prototype ----> Object.prototype ----> null
new PrimaryStudent() ----> Student.prototype ----> Object.prototype ----> nullnew PrimaryStudent() ----> Student.prototype ----> Object.prototype ----> null
var bridge = {}; //创建一个没有内容的对象
bridge.__proto__ = Student.prototype; //让这个对象的原型对象是Student.prototype
bridge.constructor = PrimaryStudent; //让这个对象的构造函数为PrimaryStudent
PrimaryStudent.prototype = bridge; //让PrimaryStudent的原型对象指向bridge
这样一来,原型链就变成了:
new PrimaryStudent() ----> PrimaryStudent.prototype(bridge) ----> Student.prototype ----> Object.prototype ----> null
按照我们比喻的说法,就是:
- 让Student有个儿子bridge(bridge.__proto__ = Student.prototype;)
- 然后这个娃和PrimaryStudent结婚了(bridge.constructor = PrimaryStudent; PrimaryStudent.prototype = bridge;)
- 那么自然PrimaryStudent的子女(通过PrimaryStudent创建的对象),既会老爹bridge的技能,也会爷爷Student的技能”
//验证一下
bridge.do = function(){alert("hahaha")};
var xiaoming = new PrimaryStudent({name:'xiaoming', grade:2});
xiaoming.do(); // 弹框alert("hahaha");
//验证原型
xiaoming.__proto__ === PrimaryStudent.prototype; //true
xiaoming.__proto__.__proto__ === Student.prototype; //true
//验证继承关系
xiaoming instanceof PrimaryStudent; //true
xiaoming instanceof Student; //truevar bridge = {}; //创建一个没有内容的对象
bridge.__proto__ = Student.prototype; //让这个对象的原型对象是Student.prototype
bridge.constructor = PrimaryStudent; //让这个对象的构造函数为PrimaryStudent
PrimaryStudent.prototype = bridge; //让PrimaryStudent的原型对象指向bridge
这样一来,原型链就变成了:
new PrimaryStudent() ----> PrimaryStudent.prototype(bridge) ----> Student.prototype ----> Object.prototype ----> null
按照我们比喻的说法,就是:
- 让Student有个儿子bridge(bridge.__proto__ = Student.prototype;)
- 然后这个娃和PrimaryStudent结婚了(bridge.constructor = PrimaryStudent; PrimaryStudent.prototype = bridge;)
- 那么自然PrimaryStudent的子女(通过PrimaryStudent创建的对象),既会老爹bridge的技能,也会爷爷Student的技能”
//验证一下
bridge.do = function(){alert("hahaha")};
var xiaoming = new PrimaryStudent({name:'xiaoming', grade:2});
xiaoming.do(); // 弹框alert("hahaha");
//验证原型
xiaoming.__proto__ === PrimaryStudent.prototype; //true
xiaoming.__proto__.__proto__ === Student.prototype; //true
//验证继承关系
xiaoming instanceof PrimaryStudent; //true
xiaoming instanceof Student; //true
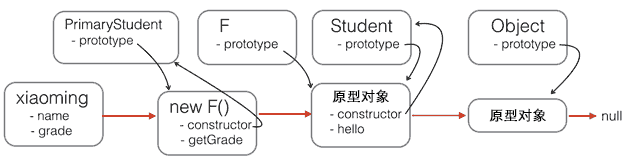
// PrimaryStudent构造函数:
function PrimaryStudent(props) {
Student.call(this, props);
this.grade = props.grade || 1;
}
// 空函数F,用于后面起桥接作用
function F() {
}
// 把F的原型指向Student.prototype,这样通过F创建的对象,其__proto__属性就是Student.prototype
F.prototype = Student.prototype;
// 把PrimaryStudent的原型指向一个新的F对象,F对象的原型正好指向Student.prototype
PrimaryStudent.prototype = new F();
// 把PrimaryStudent原型的构造函数修复为PrimaryStudent
PrimaryStudent.prototype.constructor = PrimaryStudent;
// 继续在PrimaryStudent原型(就是new F()对象)上定义方法
PrimaryStudent.prototype.getGrade = function () {
return this.grade;
};
// 创建xiaoming
var xiaoming = new PrimaryStudent({
name: '小明',
grade: 2
});
xiaoming.name; // '小明'
xiaoming.grade; // 2
// 验证原型
xiaoming.__proto__ === PrimaryStudent.prototype; // true
xiaoming.__proto__.__proto__ === Student.prototype; // true
// 验证继承关系
xiaoming instanceof PrimaryStudent; // true
xiaoming instanceof Student; // true// PrimaryStudent构造函数:
function PrimaryStudent(props) {
Student.call(this, props);
this.grade = props.grade || 1;
}
// 空函数F,用于后面起桥接作用
function F() {
}
// 把F的原型指向Student.prototype,这样通过F创建的对象,其__proto__属性就是Student.prototype
F.prototype = Student.prototype;
// 把PrimaryStudent的原型指向一个新的F对象,F对象的原型正好指向Student.prototype
PrimaryStudent.prototype = new F();
// 把PrimaryStudent原型的构造函数修复为PrimaryStudent
PrimaryStudent.prototype.constructor = PrimaryStudent;
// 继续在PrimaryStudent原型(就是new F()对象)上定义方法
PrimaryStudent.prototype.getGrade = function () {
return this.grade;
};
// 创建xiaoming
var xiaoming = new PrimaryStudent({
name: '小明',
grade: 2
});
xiaoming.name; // '小明'
xiaoming.grade; // 2
// 验证原型
xiaoming.__proto__ === PrimaryStudent.prototype; // true
xiaoming.__proto__.__proto__ === Student.prototype; // true
// 验证继承关系
xiaoming instanceof PrimaryStudent; // true
xiaoming instanceof Student; // true
function inherits(Child, Parent) {
var F = function () {};
F.prototype = Parent.prototype;
Child.prototype = new F();
Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
}function inherits(Child, Parent) {
var F = function () {};
F.prototype = Parent.prototype;
Child.prototype = new F();
Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
}
function Student(props) {
this.name = props.name || 'Unnamed';
}
Student.prototype.hello = function () {
alert('Hello, ' + this.name + '!');
}
function PrimaryStudent(props) {
Student.call(this, props);
this.grade = props.grade || 1;
}
// 实现原型继承链:
inherits(PrimaryStudent, Student);
// 绑定其他方法到PrimaryStudent原型:
PrimaryStudent.prototype.getGrade = function () {
return this.grade;
};function Student(props) {
this.name = props.name || 'Unnamed';
}
Student.prototype.hello = function () {
alert('Hello, ' + this.name + '!');
}
function PrimaryStudent(props) {
Student.call(this, props);
this.grade = props.grade || 1;
}
// 实现原型继承链:
inherits(PrimaryStudent, Student);
// 绑定其他方法到PrimaryStudent原型:
PrimaryStudent.prototype.getGrade = function () {
return this.grade;
};
- 定义新的构造函数,并在内部用call()调用希望“继承”的构造函数,并绑定this
- 借助中间函数F实现原型链继承,最好通过封装的inherits函数完成
- 继续在新的构造函数的原型上定义新方法
2、class继承(ES6)
class Student {
// 定义构造函数
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
//定义在原型上的函数,没有function关键字,相当于 Student.prototype.hello = function(){...}
hello() {
alert('Hello, ' + this.name + '!');
}
}class Student {
// 定义构造函数
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
//定义在原型上的函数,没有function关键字,相当于 Student.prototype.hello = function(){...}
hello() {
alert('Hello, ' + this.name + '!');
}
}
var xiaoming = new Student('小明');
xiaoming.hello();var xiaoming = new Student('小明');
xiaoming.hello();
class PrimaryStudent extends Student {
constructor(name, grade) {
super(name); // 记得用super调用父类的构造方法!
this.grade = grade;
}
myGrade() {
alert('I am at grade ' + this.grade);
}
}class PrimaryStudent extends Student {
constructor(name, grade) {
super(name); // 记得用super调用父类的构造方法!
this.grade = grade;
}
myGrade() {
alert('I am at grade ' + this.grade);
}
}
04面向对象编程-02-原型继承 和 ES6的class继承的更多相关文章
- 04面向对象编程-01-创建对象 和 原型理解(prototype、__proto__)
1.JS中对象的"不同":原型概念 从Java中我们可以很好地去理解 "类" 和 "实例" 两个概念,可是在JavaScript中,这个概念 ...
- Javascript面向对象编程(三):非构造函数的继承(对象的深拷贝与浅拷贝)
Javascript面向对象编程(三):非构造函数的继承 作者: 阮一峰 日期: 2010年5月24日 这个系列的第一部分介绍了"封装",第二部分介绍了使用构造函数实现&quo ...
- 使用类进行面向对象编程 Class 实例化 和 ES5实例化 对比,继承
ES5 写法 function Book(title, pages, isbn) { this.title = title; this.pages = pages; this.isbn = isbn; ...
- es5继承和es6类和继承
es6新增关键字class,代表类,其实相当于代替了es5的构造函数 通过构造函数可以创建一个对象实例,那么通过class也可以创建一个对象实列 /* es5 创建一个person 构造函数 */ f ...
- python04 面向对象编程02
为啥要用类而不用函数呢 记住两个原则: 减少重复代码 代码会经常变更 2 会对变量或字符串的合法性检测(在实例初始化的时候能够统一初始化各个实例的变量,换做函数来说,要弄出同样的变量那么在初始化 ...
- Javascript面向对象编程(三):非构造函数的继承 by 阮一峰
今天是最后一个部分,介绍不使用构造函数实现"继承". 一.什么是"非构造函数"的继承? 比如,现在有一个对象,叫做"中国人". var Ch ...
- (转)Javascript面向对象编程(三):非构造函数的继承(作者:阮一峰)
不使用构造函数实现"继承". 一.什么是"非构造函数"的继承? 比如,现在有一个对象,叫做"中国人". var Chinese = { na ...
- Javascript面向对象编程(三):非构造函数的继承
转载自:http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2010/05/object-oriented_javascript_inheritance_continued.html 一.什 ...
- JS面向对象编程(三):非构造函数的继承
一.什么是"非构造函数"的继承? 现在有一个对象,叫"中国人". var Chinese = { ...
随机推荐
- SLF4J源码解析-LoggerFactory(一)
slf4j的含义为Simple logging facade for Java,其为简单的为java实现的日志打印工具,本文则对其源码进行简单的分析 JAVA调用SLF4J public class ...
- C3P0数据库连接池使用中的问题
java.io.FileNotFoundException: D:\javaStudy\javaee\.metadata\.plugins\org.eclipse.wst.server.core\tm ...
- github+hexo搭建自己的博客网站(三)主题之外的一些基本配置(图片位置,文章目录功能)
使用的yilia主题之后,还需要进行自己的定制配置 1.图片的位置 比如打赏的支付宝二维码图片,是在当前博客的source/assets/img/下 (不是当前主题) 配置:(在yilia主题下文件里 ...
- ubuntu常见错误--Could not get lock /var/lib/dpkg/lock解决
通过终端安装程序sudo apt-get install xxx时出错: E: Could not get lock /var/lib/dpkg/lock - open (11: Resource t ...
- Java重载重写与实现方法的规则
这几天在实训过程中做到了一个题,这个题目问的是 非抽象类实现接口后,必须实现接口中的所有抽象方法,除了abstract外,方法头必须完全一致.这句话是错误的.然后在做错以后自己总结一下重载 重写 和实 ...
- RedHat 7 常用命令总结
Linux RedHat 7常用命令总结... ----------------------- 征服Linux从终端开始 ------------------------------------- 在 ...
- vue-cli脚手架npm相关文件解读(7)dev-server.js
系列文章传送门: 1.build/webpack.base.conf.js 2.build/webpack.prod.conf.js 3.build/webpack.dev.conf.js 4.bui ...
- 关于原根的存在性及个数(Primitive Root Theorem)
我在RSA学习总结的第三部分关于Mille-Rabin素数测试的正确性证明里需要用到此定理,由于证明太长,故另开一章于此.(为啥我说话突然文绉绉了Orz,可能是这周辩论打多了) 结论是对素数p,mod ...
- Java入门——学会使用API
API是什么? API(Application Programming Interface)就是别人写的代码使用说明书. 下面是中文版API的使用具体截图. 1.左上角有个显示(图中"隐藏& ...
- uva11991 Easy Problem from Rujia Liu?
Though Rujia Liu usually sets hard problems for contests (for example, regional contests like Xi'an ...
