Pytorch实现UNet例子学习
参考:https://github.com/milesial/Pytorch-UNet
实现的是二值汽车图像语义分割,包括 dense CRF 后处理.
使用python3,我的环境是python3.6
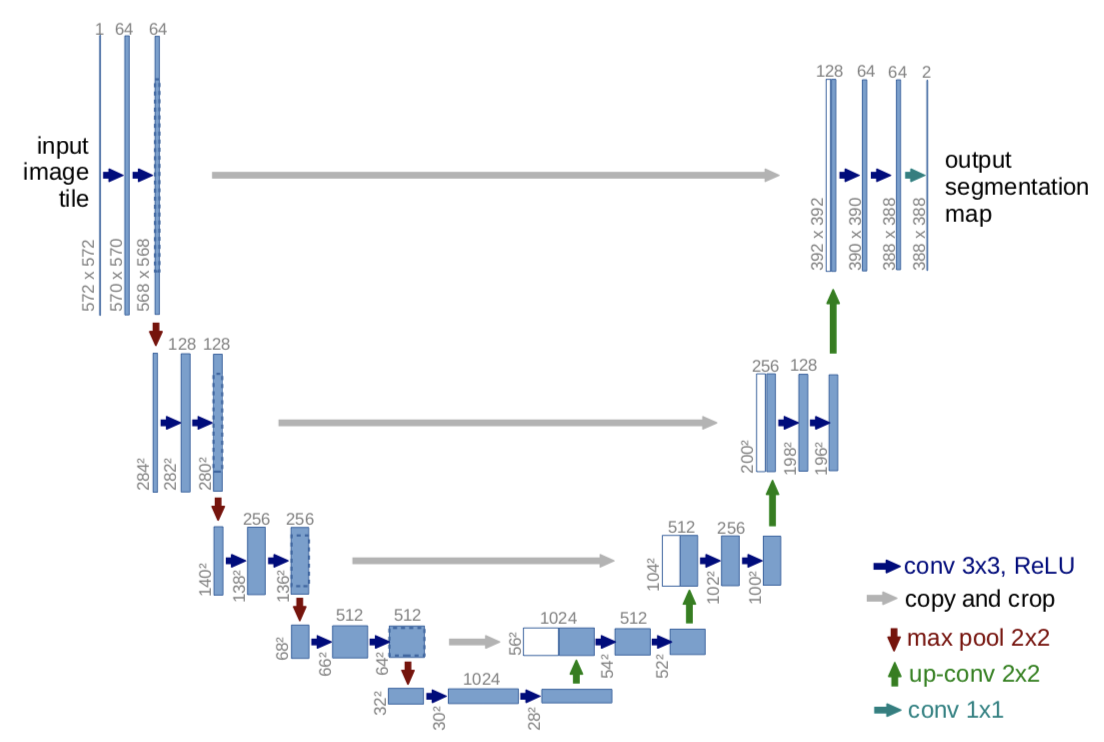
1.使用
1> 预测
1)查看所有的可用选项:
python predict.py -h
返回:
(deeplearning) userdeMBP:Pytorch-UNet-master user$ python predict.py -h
usage: predict.py [-h] [--model FILE] --input INPUT [INPUT ...]
[--output INPUT [INPUT ...]] [--cpu] [--viz] [--no-save]
[--no-crf] [--mask-threshold MASK_THRESHOLD] [--scale SCALE] optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--model FILE, -m FILE
Specify the file in which is stored the model (default
: 'MODEL.pth') #指明使用的训练好的模型文件,默认使用MODEL.pth
--input INPUT [INPUT ...], -i INPUT [INPUT ...] #指明要进行预测的图像文件,必须要有的值
filenames of input images
--output INPUT [INPUT ...], -o INPUT [INPUT ...] #指明预测后生成的图像文件的名字
filenames of ouput images
--cpu, -c Do not use the cuda version of the net #指明使用CPU,默认为false,即默认使用GPU
--viz, -v Visualize the images as they are processed #当图像被处理时,将其可视化,默认为false,即不可以可视化
--no-save, -n Do not save the output masks #不存储得到的预测图像到某图像文件中,和--viz结合使用,即可对预测结果可视化,但是不存储结果,默认为false,即会保存结果
--no-crf, -r Do not use dense CRF postprocessing #指明不使用CRF对输出进行后处理,默认为false,即使用CRF
--mask-threshold MASK_THRESHOLD, -t MASK_THRESHOLD
Minimum probability value to consider a mask pixel #最小化考虑掩模像素为白色的概率值,默认为0.5
white
--scale SCALE, -s SCALE
Scale factor for the input images #输入图像的比例因子,默认为0.5
2)预测单一图片image.jpg并存储结果到output.jpg的命令
python predict.py -i image.jpg -o output.jpg
测试一下:
(deeplearning) userdeMBP:Pytorch-UNet-master user$ python predict.py --cpu --viz -i image.jpg -o output.jpg
Loading model MODEL.pth
Using CPU version of the net, this may be very slow
Model loaded ! Predicting image image.jpg ...
/anaconda3/envs/deeplearning/lib/python3./site-packages/torch/nn/modules/upsampling.py:: UserWarning: nn.Upsample is deprecated. Use nn.functional.interpolate instead.
warnings.warn("nn.{} is deprecated. Use nn.functional.interpolate instead.".format(self.name))
/anaconda3/envs/deeplearning/lib/python3./site-packages/torch/nn/functional.py:: UserWarning: nn.functional.sigmoid is deprecated. Use torch.sigmoid instead.
warnings.warn("nn.functional.sigmoid is deprecated. Use torch.sigmoid instead.")
Visualizing results for image image.jpg, close to continue ...
返回可视化图片为:
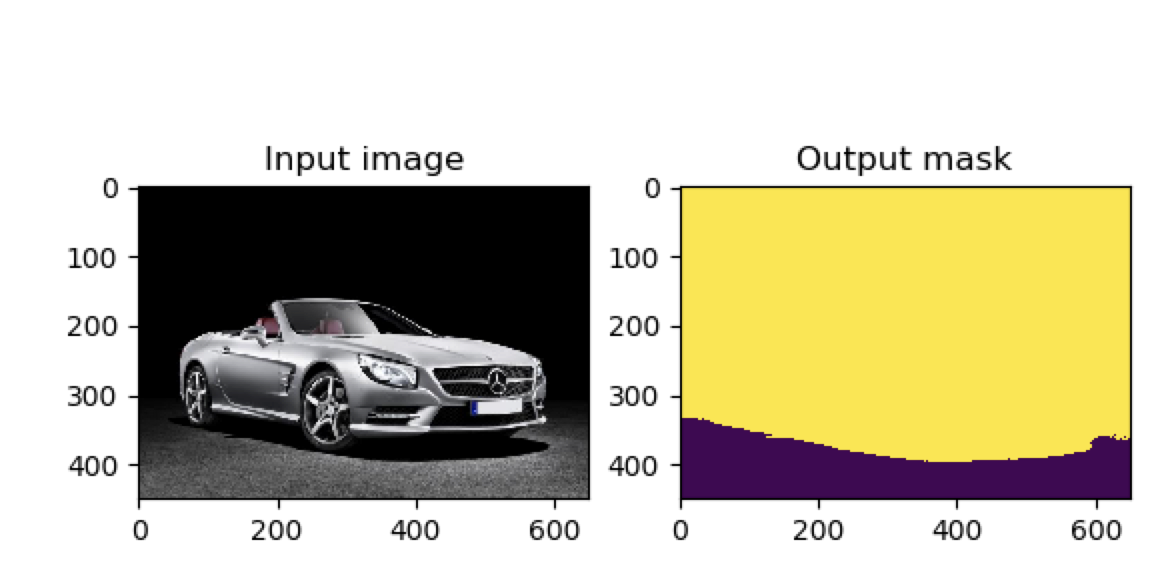
关闭该可视化图片命令就会运行结束:
Mask saved to output.jpg
(deeplearning) userdeMBP:Pytorch-UNet-master user$
并且在当前文件夹中生成名为output.jpg的文件,该图为:

3)预测多张图片并显示,预测结果不存储:
python predict.py -i image1.jpg image2.jpg --viz --no-save
测试:
先得到的是image1.jpg的可视化结果:
(deeplearning) userdeMBP:Pytorch-UNet-master user$ python predict.py -i image1.jpg image2.jpg --viz --no-save --cpu
Loading model MODEL.pth
Using CPU version of the net, this may be very slow
Model loaded ! Predicting image image1.jpg ...
/anaconda3/envs/deeplearning/lib/python3./site-packages/torch/nn/modules/upsampling.py:: UserWarning: nn.Upsample is deprecated. Use nn.functional.interpolate instead.
warnings.warn("nn.{} is deprecated. Use nn.functional.interpolate instead.".format(self.name))
/anaconda3/envs/deeplearning/lib/python3./site-packages/torch/nn/functional.py:: UserWarning: nn.functional.sigmoid is deprecated. Use torch.sigmoid instead.
warnings.warn("nn.functional.sigmoid is deprecated. Use torch.sigmoid instead.")
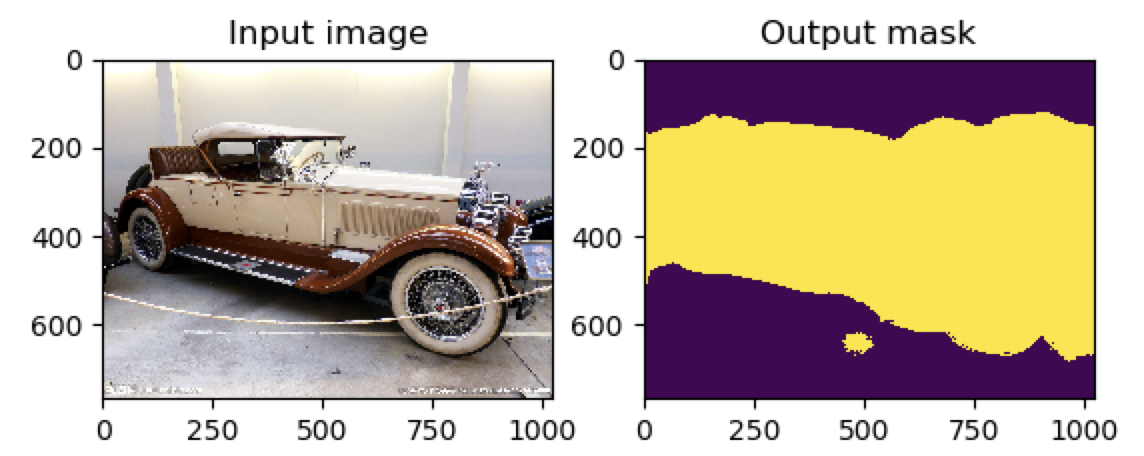
Visualizing results for image image1.jpg, close to continue ...
图为:

关闭这个后就会接着生成image2.jpg的可视化结果:
Predicting image image2.jpg ...
Visualizing results for image image2.jpg, close to continue ...
返回图为:
这时候关闭该可视化服务就会结束了,并且没有在本地保存生成的图片
4)如果你的计算机只有CPU,即CPU-only版本,使用选项--cpu指定
5)你可以指定你使用的训练好的模型文件,使用--mode MODEL.pth
6)如果使用上面的命令选项--no-crf:
(deeplearning) userdeMBP:Pytorch-UNet-master user$ python predict.py -i image1.jpg image2.jpg --viz --no-save --cpu --no-crf
返回的结果是:
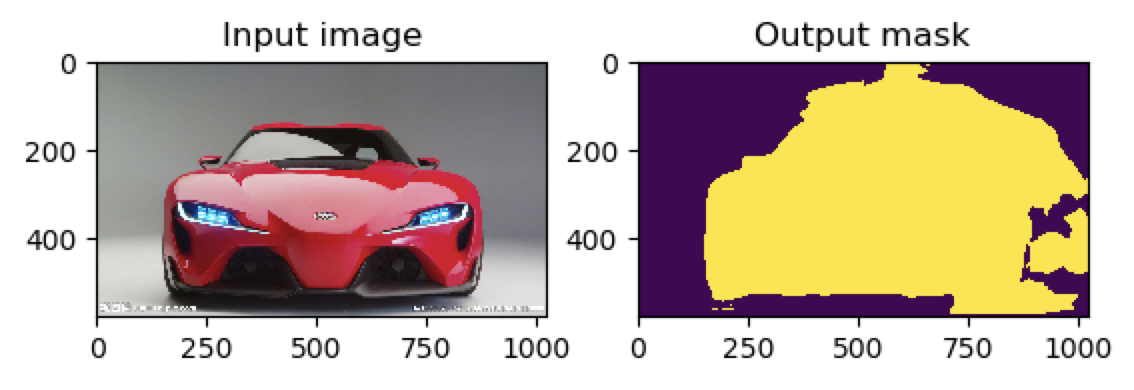
还有:

可见crf后处理后,可以将一些不符合事实的判断结果给剔除,使得结果更加精确
2〉训练
python train.py -h
首先需要安装模块pydensecrf,实现CRF条件随机场的模块:
pip install pydensecrf
但是出错:
pydensecrf/densecrf/include/Eigen/Core:22:10: fatal error: 'complex' file not found
#include <complex>
^~~~~~~~~
warning and error generated.
error: command 'gcc' failed with exit status ----------------------------------------
Failed building wheel for pydensecrf
Running setup.py clean for pydensecrf
Failed to build pydensecrf
解决办法,参考https://github.com/lucasb-eyer/pydensecrf:
先安装cython,需要0.22以上的版本:
(deeplearning) userdeMBP:Pytorch-UNet-master user$ pip install -U cython
Installing collected packages: cython
Successfully installed cython-0.29.
然后从git安装最新版本:
pip install git+https://github.com/lucasb-eyer/pydensecrf.git
但还是没有成功
后面找到了新的方法,使用conda来安装就成功了:
userdeMacBook-Pro:~ user$ conda install -n deeplearning -c conda-forge pydensecrf
-c指明从conda-forge下载模块
conda-forge是可以安装软件包的附加渠道,使用该conda-forge频道取代defaults
因为直接安装conda install -n deeplearning pydensecrf找不到该模块
这时候运行python train.py -h可见支持的选项的信息:
(deeplearning) userdeMBP:Pytorch-UNet-master user$ python train.py -h
Usage: train.py [options] Options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-e EPOCHS, --epochs=EPOCHS
number of epochs #指明迭代的次数
-b BATCHSIZE, --batch-size=BATCHSIZE
batch size #图像批处理的大小
-l LR, --learning-rate=LR
learning rate #使用的学习率
-g, --gpu use cuda #使用GPU进行训练
-c LOAD, --load=LOAD load file model #下载预训练的文件,在该基础上进行训练
-s SCALE, --scale=SCALE
downscaling factor of the images #图像的缩小因子
3>代码分析
1》unet定义网络
unet/unet_parts.py
# sub-parts of the U-Net model import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F #实现左边的横向卷积
class double_conv(nn.Module):
'''(conv => BN => ReLU) * 2'''
def __init__(self, in_ch, out_ch):
super(double_conv, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
#以第一层为例进行讲解
#输入通道数in_ch,输出通道数out_ch,卷积核设为kernal_size *,padding为1,stride为1,dilation=
#所以图中H*W能从572* 变为 *,计算为570 = (( + *padding - dilation*(kernal_size-) -) / stride ) +
nn.Conv2d(in_ch, out_ch, , padding=),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_ch), #进行批标准化,在训练时,该层计算每次输入的均值与方差,并进行移动平均
nn.ReLU(inplace=True), #激活函数
nn.Conv2d(out_ch, out_ch, , padding=), #再进行一次卷积,从570*570变为 *
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_ch),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
) def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
return x #实现左边第一行的卷积
class inconv(nn.Module):#
def __init__(self, in_ch, out_ch):
super(inconv, self).__init__()
self.conv = double_conv(in_ch, out_ch) # 输入通道数in_ch为3, 输出通道数out_ch为64 def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
return x #实现左边的向下池化操作,并完成另一层的卷积
class down(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_ch, out_ch):
super(down, self).__init__()
self.mpconv = nn.Sequential(
nn.MaxPool2d(),
double_conv(in_ch, out_ch)
) def forward(self, x):
x = self.mpconv(x)
return x #实现右边的向上的采样操作,并完成该层相应的卷积操作
class up(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_ch, out_ch, bilinear=True):
super(up, self).__init__() # would be a nice idea if the upsampling could be learned too,
# but my machine do not have enough memory to handle all those weights
if bilinear:#声明使用的上采样方法为bilinear——双线性插值,默认使用这个值,计算方法为 floor(H*scale_factor),所以由28*28变为56*
self.up = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
else: #否则就使用转置卷积来实现上采样,计算式子为 (Height-)*stride - *padding -kernal_size +output_padding
self.up = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_ch//2, in_ch//2, 2, stride=2) self.conv = double_conv(in_ch, out_ch) def forward(self, x1, x2): #x2是左边特征提取传来的值
#第一次上采样返回56*,但是还没结束
x1 = self.up(x1) # input is CHW, []是batch_size, []是通道数,更改了下,与源码不同
diffY = x1.size()[] - x2.size()[] #得到图像x2与x1的H的差值,-=-
diffX = x1.size()[] - x2.size()[] #得到图像x2与x1的W差值,-=- #用第一次上采样为例,即当上采样后的结果大小与右边的特征的结果大小不同时,通过填充来使x2的大小与x1相同
#对图像进行填充(-,-,-,-),左右上下都缩小4,所以最后使得64*64变为56*
x2 = F.pad(x2, (diffX // 2, diffX - diffX//2,
diffY // 2, diffY - diffY//2)) # for padding issues, see
# https://github.com/HaiyongJiang/U-Net-Pytorch-Unstructured-Buggy/commit/0e854509c2cea854e247a9c615f175f76fbb2e3a
# https://github.com/xiaopeng-liao/Pytorch-UNet/commit/8ebac70e633bac59fc22bb5195e513d5832fb3bd #将最后上采样得到的值x1和左边特征提取的值进行拼接,dim=1即在通道数上进行拼接,由512变为1024
x = torch.cat([x2, x1], dim=)
x = self.conv(x)
return x #实现右边的最高层的最右边的卷积
class outconv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_ch, out_ch):
super(outconv, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_ch, out_ch, ) def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
return x
unet/unetmodel.py
# full assembly of the sub-parts to form the complete net import torch.nn.functional as F from .unet_parts import * class UNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_channels, n_classes): #图片的通道数,1为灰度图像,3为彩色图像
super(UNet, self).__init__()
self.inc = inconv(n_channels, ) #假设输入通道数n_channels为3,输出通道数为64
self.down1 = down(, )
self.down2 = down(, )
self.down3 = down(, )
self.down4 = down(, )
self.up1 = up(, )
self.up2 = up(, )
self.up3 = up(, )
self.up4 = up(, )
self.outc = outconv(, n_classes) def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.inc(x)
x2 = self.down1(x1)
x3 = self.down2(x2)
x4 = self.down3(x3)
x5 = self.down4(x4)
x = self.up1(x5, x4)
x = self.up2(x, x3)
x = self.up3(x, x2)
x = self.up4(x, x1)
x = self.outc(x)
return F.sigmoid(x) #进行二分类
2》utils
实现dense CRF的代码utils/crf.py:
详细可见pydensecrf的使用
#coding:utf-
import numpy as np
import pydensecrf.densecrf as dcrf def dense_crf(img, output_probs): #img为输入的图像,output_probs是经过网络预测后得到的结果
h = output_probs.shape[] #高度
w = output_probs.shape[] #宽度 output_probs = np.expand_dims(output_probs, )
output_probs = np.append( - output_probs, output_probs, axis=) d = dcrf.DenseCRF2D(w, h, ) #NLABELS=2两类标注,车和不是车
U = -np.log(output_probs) #得到一元势
U = U.reshape((, -)) #NLABELS=2两类标注
U = np.ascontiguousarray(U) #返回一个地址连续的数组
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img) d.setUnaryEnergy(U) #设置一元势 d.addPairwiseGaussian(sxy=, compat=) #设置二元势中高斯情况的值
d.addPairwiseBilateral(sxy=, srgb=, rgbim=img, compat=)#设置二元势众双边情况的值 Q = d.inference() #迭代5次推理
Q = np.argmax(np.array(Q), axis=).reshape((h, w)) #得列中最大值的索引结果 return Q
utils/utils.py
import random
import numpy as np #将图像分成左右两块
def get_square(img, pos):
"""Extract a left or a right square from ndarray shape : (H, W, C))"""
h = img.shape[]
if pos == :
return img[:, :h]
else:
return img[:, -h:] def split_img_into_squares(img):
return get_square(img, ), get_square(img, ) #对图像进行转置,将(H, W, C)变为(C, H, W)
def hwc_to_chw(img):
return np.transpose(img, axes=[, , ]) def resize_and_crop(pilimg, scale=0.5, final_height=None):
w = pilimg.size[] #得到图片的宽
h = pilimg.size[]#得到图片的高
#默认scale为0.,即将高和宽都缩小一半
newW = int(w * scale)
newH = int(h * scale) #如果没有指明希望得到的最终高度
if not final_height:
diff =
else:
diff = newH - final_height
#重新设定图片的大小
img = pilimg.resize((newW, newH))
#crop((left,upper,right,lower))函数,从图像中提取出某个矩形大小的图像。它接收一个四元素的元组作为参数,各元素为(left, upper, right, lower),坐标系统的原点(, )是左上角
#如果没有设置final_height,其实就是取整个图片
#如果设置了final_height,就是取一个上下切掉diff // 2,最后高度为final_height的图片
img = img.crop((, diff // 2, newW, newH - diff // 2))
return np.array(img, dtype=np.float32) def batch(iterable, batch_size):
"""批量处理列表"""
b = []
for i, t in enumerate(iterable):
b.append(t)
if (i + ) % batch_size == :
yield b
b = [] if len(b) > :
yield b #然后将数据分为训练集和验证集两份
def split_train_val(dataset, val_percent=0.05):
dataset = list(dataset)
length = len(dataset) #得到数据集大小
n = int(length * val_percent) #验证集的数量
random.shuffle(dataset) #将数据打乱
return {'train': dataset[:-n], 'val': dataset[-n:]} #对像素值进行归一化,由[,]变为[,]
def normalize(x):
return x / #将两个图片合并起来
def merge_masks(img1, img2, full_w):
h = img1.shape[] new = np.zeros((h, full_w), np.float32)
new[:, :full_w // 2 + 1] = img1[:, :full_w // 2 + 1]
new[:, full_w // 2 + 1:] = img2[:, -(full_w // 2 - 1):] return new # credits to https://stackoverflow.com/users/6076729/manuel-lagunas
def rle_encode(mask_image):
pixels = mask_image.flatten()
# We avoid issues with '' at the start or end (at the corners of
# the original image) by setting those pixels to '' explicitly.
# We do not expect these to be non-zero for an accurate mask,
# so this should not harm the score.
pixels[] =
pixels[-] =
runs = np.where(pixels[:] != pixels[:-])[] +
runs[::] = runs[::] - runs[:-:]
return runs
utils/data_vis.py实现结果的可视化:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def plot_img_and_mask(img, mask):
fig = plt.figure()
a = fig.add_subplot(, , ) #先是打印输入的图片
a.set_title('Input image')
plt.imshow(img) b = fig.add_subplot(, , ) #然后打印预测得到的结果图片
b.set_title('Output mask')
plt.imshow(mask)
plt.show()
utils/load.py
#
# load.py : utils on generators / lists of ids to transform from strings to
# cropped images and masks import os import numpy as np
from PIL import Image from .utils import resize_and_crop, get_square, normalize, hwc_to_chw def get_ids(dir):
"""返回目录中的id列表"""
return (f[:-] for f in os.listdir(dir)) #图片名字的后4位为数字,能作为图片id def split_ids(ids, n=):
"""将每个id拆分为n个,为每个id创建n个元组(id, k)"""
#等价于for id in ids:
# for i in range(n):
# (id, i)
#得到元祖列表[(id1,),(id1,),(id2,),(id2,),...,(idn,),(idn,)]
#这样的作用是后面会通过后面的0,1作为utils.py中get_square函数的pos参数,pos=0的取左边的部分,pos=1的取右边的部分
return ((id, i) for id in ids for i in range(n)) def to_cropped_imgs(ids, dir, suffix, scale):
"""从元组列表中返回经过剪裁的正确img"""
for id, pos in ids:
im = resize_and_crop(Image.open(dir + id + suffix), scale=scale) #重新设置图片大小为原来的scale倍
yield get_square(im, pos) #然后根据pos选择图片的左边或右边 def get_imgs_and_masks(ids, dir_img, dir_mask, scale):
"""返回所有组(img, mask)""" imgs = to_cropped_imgs(ids, dir_img, '.jpg', scale) # need to transform from HWC to CHW
imgs_switched = map(hwc_to_chw, imgs) #对图像进行转置,将(H, W, C)变为(C, H, W)
imgs_normalized = map(normalize, imgs_switched) #对像素值进行归一化,由[,]变为[,] masks = to_cropped_imgs(ids, dir_mask, '_mask.gif', scale) #对图像的结果也进行相同的处理 return zip(imgs_normalized, masks) #并将两个结果打包在一起 def get_full_img_and_mask(id, dir_img, dir_mask):
im = Image.open(dir_img + id + '.jpg')
mask = Image.open(dir_mask + id + '_mask.gif')
return np.array(im), np.array(mask)
3》预测
predict.py使用训练好的U-net网络对图像进行预测,使用dense CRF进行后处理:
#coding:utf-
import argparse
import os import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F from PIL import Image from unet import UNet
from utils import resize_and_crop, normalize, split_img_into_squares, hwc_to_chw, merge_masks, dense_crf
from utils import plot_img_and_mask from torchvision import transforms def predict_img(net,
full_img,
scale_factor=0.5,
out_threshold=0.5,
use_dense_crf=True,
use_gpu=False): net.eval() #进入网络的验证模式,这时网络已经训练好了
img_height = full_img.size[] #得到图片的高
img_width = full_img.size[] #得到图片的宽 img = resize_and_crop(full_img, scale=scale_factor) #在utils文件夹的utils.py中定义的函数,重新定义图像大小并进行切割,然后将图像转为数组np.array
img = normalize(img) #对像素值进行归一化,由[,]变为[,] left_square, right_square = split_img_into_squares(img)#将图像分成左右两块,来分别进行判断 left_square = hwc_to_chw(left_square) #对图像进行转置,将(H, W, C)变为(C, H, W),便于后面计算
right_square = hwc_to_chw(right_square) X_left = torch.from_numpy(left_square).unsqueeze() #将(C, H, W)变为(, C, H, W),因为网络中的输入格式第一个还有一个batch_size的值
X_right = torch.from_numpy(right_square).unsqueeze() if use_gpu:
X_left = X_left.cuda()
X_right = X_right.cuda() with torch.no_grad(): #不计算梯度
output_left = net(X_left)
output_right = net(X_right) left_probs = output_left.squeeze()
right_probs = output_right.squeeze() tf = transforms.Compose(
[
transforms.ToPILImage(), #重新变成图片
transforms.Resize(img_height), #恢复原来的大小
transforms.ToTensor() #然后再变成Tensor格式
]
) left_probs = tf(left_probs.cpu())
right_probs = tf(right_probs.cpu()) left_mask_np = left_probs.squeeze().cpu().numpy()
right_mask_np = right_probs.squeeze().cpu().numpy() full_mask = merge_masks(left_mask_np, right_mask_np, img_width)#将左右两个拆分后的图片合并起来 #对得到的结果根据设置决定是否进行CRF处理
if use_dense_crf:
full_mask = dense_crf(np.array(full_img).astype(np.uint8), full_mask) return full_mask > out_threshold def get_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--model', '-m', default='MODEL.pth', #指明使用的训练好的模型文件,默认使用MODEL.pth
metavar='FILE',
help="Specify the file in which is stored the model"
" (default : 'MODEL.pth')")
parser.add_argument('--input', '-i', metavar='INPUT', nargs='+', #指明要进行预测的图像文件
help='filenames of input images', required=True) parser.add_argument('--output', '-o', metavar='INPUT', nargs='+', #指明预测后生成的图像文件的名字
help='filenames of ouput images')
parser.add_argument('--cpu', '-c', action='store_true', #指明使用CPU
help="Do not use the cuda version of the net",
default=False)
parser.add_argument('--viz', '-v', action='store_true',
help="Visualize the images as they are processed", #当图像被处理时,将其可视化
default=False)
parser.add_argument('--no-save', '-n', action='store_true', #不存储得到的预测图像到某图像文件中,和--viz结合使用,即可对预测结果可视化,但是不存储结果
help="Do not save the output masks",
default=False)
parser.add_argument('--no-crf', '-r', action='store_true', #指明不使用CRF对输出进行后处理
help="Do not use dense CRF postprocessing",
default=False)
parser.add_argument('--mask-threshold', '-t', type=float,
help="Minimum probability value to consider a mask pixel white", #最小概率值考虑掩模像素为白色
default=0.5)
parser.add_argument('--scale', '-s', type=float,
help="Scale factor for the input images", #输入图像的比例因子
default=0.5) return parser.parse_args() def get_output_filenames(args):#从输入的选项args值中得到输出文件名
in_files = args.input
out_files = [] if not args.output: #如果在选项中没有指定输出的图片文件的名字,那么就会根据输入图片文件名,在其后面添加'_OUT'后缀来作为输出图片文件名
for f in in_files:
pathsplit = os.path.splitext(f) #将文件名和扩展名分开,pathsplit[]是文件名,pathsplit[]是扩展名
out_files.append("{}_OUT{}".format(pathsplit[], pathsplit[])) #得到输出图片文件名
elif len(in_files) != len(args.output): #如果设置了output名,查看input和output的数量是否相同,即如果input是两张图,那么设置的output也必须是两个,否则报错
print("Error : Input files and output files are not of the same length")
raise SystemExit()
else:
out_files = args.output return out_files def mask_to_image(mask):
return Image.fromarray((mask * ).astype(np.uint8)) #从数组array转成Image if __name__ == "__main__":
args = get_args() #得到输入的选项设置的值
in_files = args.input #得到输入的图像文件
out_files = get_output_filenames(args) #从输入的选项args值中得到输出文件名 net = UNet(n_channels=, n_classes=) #定义使用的model为UNet,调用在UNet文件夹下定义的unet_model.py,定义图像的通道为3,即彩色图像,判断类型设为1种 print("Loading model {}".format(args.model)) #指定使用的训练好的model if not args.cpu: #指明使用GPU
print("Using CUDA version of the net, prepare your GPU !")
net.cuda()
net.load_state_dict(torch.load(args.model))
else: #否则使用CPU
net.cpu()
net.load_state_dict(torch.load(args.model, map_location='cpu'))
print("Using CPU version of the net, this may be very slow") print("Model loaded !") for i, fn in enumerate(in_files): #对图片进行预测
print("\nPredicting image {} ...".format(fn)) img = Image.open(fn)
if img.size[] < img.size[]: #(W, H, C)
print("Error: image height larger than the width") mask = predict_img(net=net,
full_img=img,
scale_factor=args.scale,
out_threshold=args.mask_threshold,
use_dense_crf= not args.no_crf,
use_gpu=not args.cpu) if args.viz: #可视化输入的图片和生成的预测图片
print("Visualizing results for image {}, close to continue ...".format(fn))
plot_img_and_mask(img, mask) if not args.no_save:#设置为False,则保存
out_fn = out_files[i]
result = mask_to_image(mask) #从数组array转成Image
result.save(out_files[i]) #然后保存 print("Mask saved to {}".format(out_files[i]))
4》训练
import sys
import os
from optparse import OptionParser
import numpy as np import torch
import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
import torch.nn as nn
from torch import optim from eval import eval_net
from unet import UNet
from utils import get_ids, split_ids, split_train_val, get_imgs_and_masks, batch def train_net(net,
epochs=,
batch_size=,
lr=0.1,
val_percent=0.05,
save_cp=True,
gpu=False,
img_scale=0.5): dir_img = 'data/train/' #训练图像文件夹
dir_mask = 'data/train_masks/' #图像的结果文件夹
dir_checkpoint = 'checkpoints/' #训练好的网络保存文件夹 ids = get_ids(dir_img)#图片名字的后4位为数字,能作为图片id #得到元祖列表为[(id1,),(id1,),(id2,),(id2,),...,(idn,),(idn,)]
#这样的作用是后面重新设置生成器时会通过后面的0,1作为utils.py中get_square函数的pos参数,pos=0的取左边的部分,pos=1的取右边的部分
#这样图片的数量就会变成2倍
ids = split_ids(ids) iddataset = split_train_val(ids, val_percent) #将数据分为训练集和验证集两份 print('''
Starting training:
Epochs: {}
Batch size: {}
Learning rate: {}
Training size: {}
Validation size: {}
Checkpoints: {}
CUDA: {}
'''.format(epochs, batch_size, lr, len(iddataset['train']),
len(iddataset['val']), str(save_cp), str(gpu))) N_train = len(iddataset['train']) #训练集长度 optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), #定义优化器
lr=lr,
momentum=0.9,
weight_decay=0.0005) criterion = nn.BCELoss()#损失函数 for epoch in range(epochs): #开始训练
print('Starting epoch {}/{}.'.format(epoch + , epochs))
net.train() #设置为训练模式 # reset the generators重新设置生成器
# 对输入图片dir_img和结果图片dir_mask进行相同的图片处理,即缩小、裁剪、转置、归一化后,将两个结合在一起,返回(imgs_normalized, masks)
train = get_imgs_and_masks(iddataset['train'], dir_img, dir_mask, img_scale)
val = get_imgs_and_masks(iddataset['val'], dir_img, dir_mask, img_scale) epoch_loss = for i, b in enumerate(batch(train, batch_size)):
imgs = np.array([i[] for i in b]).astype(np.float32) #得到输入图像数据
true_masks = np.array([i[] for i in b]) #得到图像结果数据 imgs = torch.from_numpy(imgs)
true_masks = torch.from_numpy(true_masks) if gpu:
imgs = imgs.cuda()
true_masks = true_masks.cuda() masks_pred = net(imgs) #图像输入的网络后得到结果masks_pred,结果为灰度图像
masks_probs_flat = masks_pred.view(-) #将结果压扁 true_masks_flat = true_masks.view(-) loss = criterion(masks_probs_flat, true_masks_flat) #对两个结果计算损失
epoch_loss += loss.item() print('{0:.4f} --- loss: {1:.6f}'.format(i * batch_size / N_train, loss.item())) optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step() print('Epoch finished ! Loss: {}'.format(epoch_loss / i)) #一次迭代后得到的平均损失 if :
val_dice = eval_net(net, val, gpu)
print('Validation Dice Coeff: {}'.format(val_dice)) if save_cp:
torch.save(net.state_dict(),
dir_checkpoint + 'CP{}.pth'.format(epoch + ))
print('Checkpoint {} saved !'.format(epoch + )) def get_args():
parser = OptionParser()
parser.add_option('-e', '--epochs', dest='epochs', default=, type='int', #设置迭代数
help='number of epochs')
parser.add_option('-b', '--batch-size', dest='batchsize', default=, #设置训练批处理数
type='int', help='batch size')
parser.add_option('-l', '--learning-rate', dest='lr', default=0.1, #设置学习率
type='float', help='learning rate')
parser.add_option('-g', '--gpu', action='store_true', dest='gpu', #是否使用GPU,默认是不使用
default=False, help='use cuda')
parser.add_option('-c', '--load', dest='load', #下载之前预训练好的模型
default=False, help='load file model')
parser.add_option('-s', '--scale', dest='scale', type='float', #图像的缩小因子,用来重新设置图片大小
default=0.5, help='downscaling factor of the images') (options, args) = parser.parse_args()
return options if __name__ == '__main__':
args = get_args() #得到设置的所有参数信息 net = UNet(n_channels=, n_classes=) if args.load: #是否加载预先训练好的模型
net.load_state_dict(torch.load(args.load))
print('Model loaded from {}'.format(args.load)) if args.gpu: #是否使用GPU,设置为True,则使用
net.cuda()
# cudnn.benchmark = True # faster convolutions, but more memory try: #开始训练
train_net(net=net,
epochs=args.epochs,
batch_size=args.batchsize,
lr=args.lr,
gpu=args.gpu,
img_scale=args.scale)
except KeyboardInterrupt: #如果键盘输入ctrl+c停止,则会将结果保存在INTERRUPTED.pth中
torch.save(net.state_dict(), 'INTERRUPTED.pth')
print('Saved interrupt')
try:
sys.exit()
except SystemExit:
os._exit()
Pytorch实现UNet例子学习的更多相关文章
- pytorch例子学习-DATA LOADING AND PROCESSING TUTORIAL
参考:https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/data_loading_tutorial.html DATA LOADING AND PROCESSING TUT ...
- 深度学习框架PyTorch一书的学习-第五章-常用工具模块
https://github.com/chenyuntc/pytorch-book/blob/v1.0/chapter5-常用工具/chapter5.ipynb 希望大家直接到上面的网址去查看代码,下 ...
- 深度学习框架PyTorch一书的学习-第一/二章
参考https://github.com/chenyuntc/pytorch-book/tree/v1.0 希望大家直接到上面的网址去查看代码,下面是本人的笔记 pytorch的设计遵循tensor- ...
- PyTorch如何构建深度学习模型?
简介 每过一段时间,就会有一个深度学习库被开发,这些深度学习库往往可以改变深度学习领域的景观.Pytorch就是这样一个库. 在过去的一段时间里,我研究了Pytorch,我惊叹于它的操作简易.Pyto ...
- 数百个 HTML5 例子学习 HT 图形组件 – 3D建模篇
http://www.hightopo.com/demo/pipeline/index.html <数百个 HTML5 例子学习 HT 图形组件 – WebGL 3D 篇>里提到 HT 很 ...
- 数百个 HTML5 例子学习 HT 图形组件 – 3D 建模篇
http://www.hightopo.com/demo/pipeline/index.html <数百个 HTML5 例子学习 HT 图形组件 – WebGL 3D 篇>里提到 HT 很 ...
- 数百个 HTML5 例子学习 HT 图形组件 – WebGL 3D 篇
<数百个 HTML5 例子学习 HT 图形组件 – 拓扑图篇>一文让读者了解了 HT的 2D 拓扑图组件使用,本文将对 HT 的 3D 功能做个综合性的介绍,以便初学者可快速上手使用 HT ...
- 数百个 HTML5 例子学习 HT 图形组件 – 拓扑图篇
HT 是啥:Everything you need to create cutting-edge 2D and 3D visualization. 这口号是当年心目中的产品方向,接着就朝这个方向慢慢打 ...
- HTML5 例子学习 HT 图形组件
HTML5 例子学习 HT 图形组件 HT 是啥:Everything you need to create cutting-edge 2D and 3D visualization. 这口号是当年心 ...
随机推荐
- Java面向对象概述及三大特征(封装,继承和多态)
一.面向对象思想 Java是面向对象的高级语言,对于Java语言来说,万事万物皆对象! 它的基本思想是使用类,对象,继承,封装,消息等基本概念进行程序设计.面向对象程序的最小单元是类,类代表了客观世界 ...
- 每日分享!~ JavaScript(拖拽事件)
浏览器的拖拉事件 拖拉(drag)指的是,用户在某个对象上按下鼠标键不放,拖动它到另一个位置,然后释放鼠标键,将该对象放在那里. 拖拉的对象有好几种,包括元素节点.图片.链接.选中的文字等等.在网页中 ...
- Nginx安装与代理
1.第一步 - 添加Nginx存储库 要添加CentOS 7 EPEL存储库,请打开终端并使用以下命令: sudo yum install epel-release 2.第二步 - 安装Nginx 现 ...
- Docker Machine搭建并加入节点
对于集群服务器来讲,要在每台机器上手动安装Docker是一件及其痛苦的事情,还好有Docker Machine这一工具,Docker三剑客中的一角. 一.Docker Machine介绍 这个工具已经 ...
- Nginx学习笔记~目录索引
回到占占推荐博客索引 前几天整理了<Docker的学习笔记索引>,受到了很多朋友的关注,今天把Nginx的文章也整理一下,以后将永久更新,像大叔之前的<EF文章系列>,< ...
- 小议 localStorage
前言 什么是 localStorage? 在HTML5中,新加入了一个localStorage特性,这个特性主要是用来作为本地存储来使用的,解决了cookie存储空间不足的问题(cookie中每条co ...
- SpringBoot简单打包部署(附工程)
前言 本文主要介绍SpringBoot的一些打包事项和项目部署以及在其中遇到一些问题的解决方案. SpringBoot打包 在SpringBoot打包这块,我们就用之前的一个web项目来进行打包. 首 ...
- 微信公众号开发C#系列-2、微信公众平台接入指南
概述 微信公众平台消息接口的工作原理大概可以这样理解:从用户端到公众号端一个流程是这样的,用户发送消息到微信服务器,微信服务器将接收到的消息post到用户接入时填写的url中,在url处理程序中,首先 ...
- 从PRISM开始学WPF(六)MVVM(二)Command-更新至Prism7.1
命令绑定(Command) [7.1updated]这一节除了基础app部分,并没有什么变化 什么是Command? 先看下微软官方的说明: Commanding is an input mechan ...
- 在HTML页面中有jQuery实现实现拼图小游戏
1.用jQuery实现拼图小游戏 2.首先获得td的点击事件.再进行交换位置 3.下面这种仅供参考 4.下面这些是HTMl标签 当这个世界变得越来越复杂的时候,内心最需保持一份简单一份纯真:
