”MySQL索引“学习总结
序
learn by doing 是最快的学习方式。在百度外卖研发中心,我每天工作接触数据库方面最多的就是“索引”,另外面试官在面试时也一定会考察到索引。
Part 1, Explain语法
The EXPLAIN statement provides information about the execution plan for a SELECT statement.
Here is the explanation of some Output Columns:
| Column | Meaning |
|---|---|
| id | Select identifier |
| select_type | select type |
| table | table for the output row |
| type | join type(联接类型) |
| possible_key | possible indexes to choosen |
| key | index actually choosen |
| key_len | length of choosen key |
| ref | colummns compared to the index(列比较的索引) |
| rows | Estimate of rows to be examined(估计被检查的行) |
| extra | additional information |
部分列的含义解释如下:
Select Type
The type of SELECT, which can be any of those shown in the following table.(可以是如下显示的任何一种类型)
| select_type Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| SIMPLE | Simple select, not using UNION or subqueries. |
| PRIMARY | 用到了主键的查询 |
| UNION | Second or later SELECT statement in a UNION |
| SUBQUERY | First SELECT in subquery |
type
The join type(联接类型).
The type column of EXPLAIN output describes how tables are joined. The following exceprpt(节选) list describes the join types, ordered from the best type to the worst:(从最快的联接类型到最差的)
1. const
The table has at most(至多) one matching row, which is read at the start of the query. Because there is only one row, values from the column in this row can be regarded as(视为) constants(常量) by the rest of(剩下的) the optimizer.
2. eq_ref
One row is read from this table for each combination of rows from the previous tables. Other than the system and const types, this is the best possible join type. It is used when all parts of an index are used by the join and the index is a PRIMARY KEY or UNIQUE NOT NULL index.(对于每个来自于前面的表的行组合,从该表中读取一行。这可能是最好的联接类型,除了const类型。它用在一个索引的所有部分被联接使用并且索引是UNIQUE或PRIMARY KEY。)
3. ref
All rows with matching index values are read from this table for each combination of rows from the previous tables. ref is used if the join uses only a leftmost prefix(最左前缀) of the key or if the key is not a PRIMARY KEY or UNIQUE index (in other words, if the join cannot select a single row based on the key value).
eq_ref 与 ref 的辨析
" for each combination of rows from the previous table " eq_ref 和 ref 都会 " read from this table ",但是也存在一点区别。如下表所示。
| join type | differences |
|---|---|
| eq_ref | one row |
| ref | All rows with matching index values |
eq_ref 是从本表读一行;ref 会从本表读所有命中索引的行。
4. index
The index join type is the same as ALL(全表扫描), except that the index tree is scanned. This occurs two ways:
If the index is a covering index for the queries and can be used to satisfy all data required from the table, only the index tree is scanned. In this case, the Extra column says
Using index.A full table scan is performed using reads from the index to look up data rows in index order.
Uses indexdoes not appear in the Extra column.
当查询只使用作为单索引一部分的列时,MySQL可以使用该联接类型。
5. ALL
A full table scan is done for each combination of rows from the previous tables. 如果该表是第一个没标记const的表,这通常不好,并且通常在其它情况下会很差.
possible_keys
The possible_keys column indicates which indexes MySQL can choose from use to find the rows in this table. Note that this column is totally independent of the order of the tables as displayed in the output from EXPLAIN. That means that some of the keys in possible_keys might not be usable in practice with the generated table order.
key
The key column indicates the key (index) that MySQL actually decided to use. If MySQL decides to use one of the possible_keys indexes to look up rows, that index is listed as the key value.
It is possible that key will name an index that is not present in the possible_keys value. This can happen if none of the possible_keys indexes are suitable for looking up rows, but all the columns selected by the query are columns of some other index. That is, the named index covers the selected columns, so although it is not used to determine which rows to retrieve, an index scan is more efficient than a data row scan.
ref
The ref column shows which columns or constants are compared to the index named in the key column to select rows from the table.
Extra
This column contains additional information about how MySQL resolves the query.
The Extra column of EXPLAIN output contains additional information about how MySQL resolves the query. The following list(节选) explains the values that can appear in this column. If you want to make your queries as fast as possible, look out for Extra values of Using filesort and Using temporary.
1.Using filesort
MySQL must do an extra pass to find out how to retrieve(检索) the rows in sorted order. The sort is done by going through all rows according to the join type and storing(储存) the sort key and pointer to the row for all rows that match the WHERE clause. The keys then are sorted and the rows are retrieved in sorted order.
2.Using index
The column information is retrieved from the table using only information in the index tree without having to do an additional seek to read the actual row. This strategy can be used when the query uses only columns that are part of a single index.
3.Using filesort
MySQL must do an extra pass to find out how to retrieve the rows in sorted order. The sort is done by going through all rows according to the join type and storing the sort key and pointer to the row for all rows that match the WHERE clause. The keys then are sorted and the rows are retrieved in sorted order.
4.Using temporary
To resolve the query, MySQL needs to create a temporary table to hold the result. This typically happens if the query contains GROUP BY and ORDER BY clauses that list columns differently.
5.Using where
A WHERE clause is used to restrict which rows to match against the next table or send to the client. Unless you specifically intend to fetch or examine all rows from the table, you may have something wrong in your query if the Extra value is not Using where and the table join type is ALL or index. Even if you are using an index for all parts of a WHERE clause, you may see Using where if the column can be NULL.
part 2, 索引命中原则
单一索引
关于单一索引的命中原则比较简单。有如下一张表
执行如下查询:
select * from test where name='name.1000'
然后,对这条查询执行一下 explain ,结果如下图所示。

由于key列为NULL可以得知,这条查询并没有使用到索引。
组合索引
1.全索引匹配
有另一张表,如下图所示。
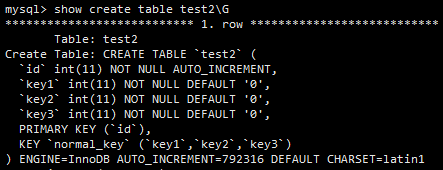
执行如下查询:
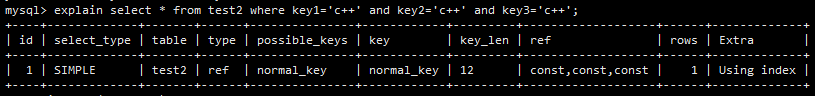
select * from test2 where key1=12 and key2=378 and key3=29
explain的结果如下图所示。
2.最左前缀原则
为了证明最左前缀原则,需要展示另外一张表,如下图所示。
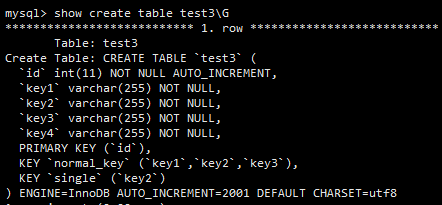
执行如下查询:
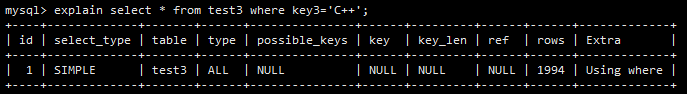
select * from test3 where key3='c++'
让我们看看这次查询的执行情况。explain 的结果如下图所示。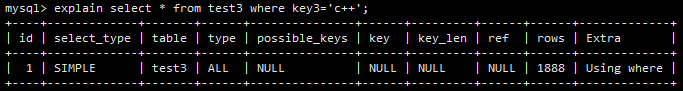
key3 是 normal_key 索引的一部分,但在这次查询中,normal_key 并不能派上用场,这是因为 mysql 组合索引数据结构(基于 B+ Tree )的原因。
3.最左前缀的特例——索引的副作用
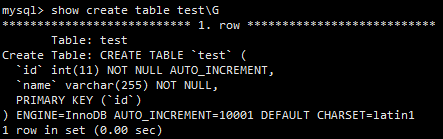
让我们还是关注在 test2 这张表上,其表结构如下所示。

让我们执行 explain 一条 SQL,结果如下所示。
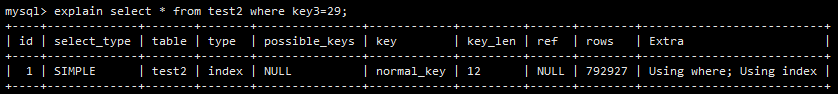
key 这一栏显示该条查询用到了 normal_key 这一索引,但是执行时间并不理想(280ms)。其原因在《构建高性能web站点》一书中已经讲过了:这条查询在并不适合自己的索引上苦苦寻找。
对于这种情况——组合索引的副作用——书上建议加入 order by id 下表是加入order by id 子句之后执行时间的对比。
Using order by id |
Not Using |
|---|---|
| 310ms | 350ms |
4. 当 type 是 index 时,Extra 何时会显示 Using Index
在上面 mysql 手册的摘录中,出现了如下一句话,让我没能读懂。
A full table scan is performed using reads from the index to look up data rows in index order.
Uses indexdoes not appear in the Extra column.
借助如下这张图并结合上面第3节(最左前缀的特例——索引的副作用)的实例,我大致明白了含义。
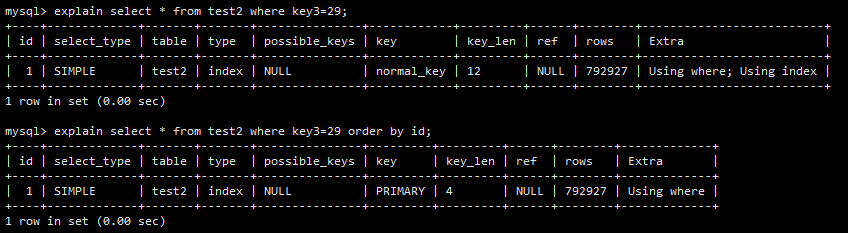
对于 select * from test2 where key3=29 order by id 这条语句,mysql 一定会全表扫描的,并且会按照 id 这一(主键)索引来排序,所以在 Extra 这一栏中,Using Index 并没有出现。
参考文献 MySQL 5.7 Reference Manual
(End)
”MySQL索引“学习总结的更多相关文章
- Mysql索引学习笔记
1.btree索引与hash索引 下列范围查询适用于 btree索引和hash索引: SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE key_col = 1 OR key_col IN (15,18,2 ...
- MySQL索引学习记录
参考资料: http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/6530142http://blog.codinglabs.org/articles/theor ...
- mysql 索引学习--多条件等值查询,顺序不同也能应用联合索引啦
以前学习这一块的时候,是说:假设建立了联合索引a+b,那么查询语句也一定要是这个顺序才能应用该索引. 那么实际是怎样呢,经过mysql这么多次版本升级,相信mysql已经给我们做了某些优化. 下面是我 ...
- mysql索引学习
索引用于快速找出在某列中有一特定值的行. 如果不使用索引,MySQL必须从第一条记录开始读完整个表,直到找出相关的行. 表越大,查询数据所花费的时间越多. 如果表中查询的列有一个索引,MySQL能快速 ...
- mysql索引学习----2----创建索引、修改索引、删除索引的命令语句
查看表中已经存在 index:show index from table_name; 创建和删除索引索引的创建可以在CREATE TABLE语句中进行,也可以单独用CREATE INDEX或ALTER ...
- 4.直方图介绍和使用|MySQL索引学习
GreatSQL社区原创内容未经授权不得随意使用,转载请联系小编并注明来源. 目录 一.导读 二.步骤 2.1 SQL语句 2.2 直方图案例 2.3 查看直方图统计信息 2.3 直方图分类 2.4 ...
- 3.联合索引、覆盖索引及最左匹配原则|MySQL索引学习
GreatSQL社区原创内容未经授权不得随意使用,转载请联系小编并注明来源. 导语 在数据检索的过程中,经常会有多个列的匹配需求,今天介绍下联合索引的使用以及最左匹配原则的案例. 最左匹配原则作用在联 ...
- MySQL数据库学习笔记(六)----MySQL多表查询之外键、表连接、子查询、索引
本章主要内容: 一.外键 二.表连接 三.子查询 四.索引 一.外键: 1.什么是外键 2.外键语法 3.外键的条件 4.添加外键 5.删除外键 1.什么是外键: 主键:是唯一标识一条记录,不能有重复 ...
- Mysql数据库学习笔记之数据库索引(index)
什么是索引: SQL索引有两种,聚集索引和非聚集索引,索引主要目的是提高了SQL Server系统的性能,加快数据的查询速度与减少系统的响应时间. 聚集索引:该索引中键值的逻辑顺序决定了表中相应行的物 ...
随机推荐
- HDU 6343 - Problem L. Graph Theory Homework - [(伪装成图论题的)简单数学题]
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=6343 Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Li ...
- Dividing the Path POJ - 2373 dp
题意:你有无数个长度可变的区间d 满足 2a<=d<=2b且为偶数. 现在要你用这些区间填满一条长为L(L<1e6且保证是偶数)的长线段. 满足以下要求: 1.可变区间之间不能有 ...
- complexity_action
大话数据结构 /* 顺序存储的结构 */ #define MAXSIZE 20 //存储空间初始分配量 typedef int ElemType; //ElemType类型根据实际情况而定,这里假设为 ...
- In MySQL, a zero number equals any string
最近在做项目的过程中发现了一个问题 数据库表 test 有个字段是 target_id int(11),这个字段可能为零 使用如下查询 select * from test where targe ...
- Jquery获取元素的位置
$(".curr_play").position().left //元素距离父级元素左侧位置 $(".curr_play").offset().left //元 ...
- ARP报文
硬件类型:指明了发送方想知道的硬件接口类型,以太网的值为1: 协议类型:指明了发送方提供的高层协议类型,IP为0x0800(16进制): 硬件地址长度和协议长度:指明了硬件地址和高层协议地址的长度,这 ...
- Hibernate错误
1.Field 'id' doesn't have a default value 原来是我的数据设计的时候,把主键的类型定义为int的,原本想是用自增的方式来的,可是由于自己的粗心,写sql语句的时 ...
- 如何在 vue 项目里正确地引用 jquery 和 jquery-ui的插件
copy内容的网址: https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000007020623 使用vue-cli构建的vue项目,webpack的配置文件是分散在很多地方的,而我们需要 ...
- 远程调用Spark平台中的程序
用scala语言,开发好了在spark平台上可以一直运行的机器学习模型 现在有个需求: 要远程调用该模型的一些方法并获取结果 那么可以使用jetty在服务器端主节点占用一个端口然后对外提供http服务 ...
- How many Fibs?(poj 2413)大数斐波那契
http://acm.sdut.edu.cn:8080/vjudge/contest/view.action?cid=259#problem/C Description Recall the defi ...
