使用BERT进行情感分类预测及代码实例
文章目录
0. BERT介绍
google 在2018年放出的大杀器, 作为当前NLP的最新技术,此模型在NLP的多个上游下游问题上都取得很好的成绩,刷新记录, 具体原理可以自行google, 这样一个新的技术, 值得我们学习一下, 下面我将给出一个使用BERT进行情感分类预测及代码实例, 供大家分享学习。
1. BERT配置
要求配置如下, tensorflow版本不能太低。
tensorflow >= 1.11.0 # CPU Version of TensorFlow.
tensorflow-gpu >= 1.11.0 # GPU version of TensorFlow.
1.1. clone BERT 代码
首先clone 官方代码,地址如下
https://github.com/google-research/bert.git
之后我们主要专注于run_classifier.py, 因为这个py文件是BERT的分类任务接口, 接下来我们主要就是对这个文件进行修改, 然后运行即可。 同理 其他任务则运行其他文件,例如问答训练是run_squad.py等
1.2. 数据处理
我们一共需要两种数据
- 数据是BERT开放的预训练模型
- 我们的数据集
1.2.1预训练模型
这是google花费大量资源训练出来的预训练模型, 我的数据集是英文句子, 所以我们使用 BERT-base,uncased
也就是基础版本+有大小写版本, 当然如果你用中文,google也提供了相应的数据集
下载地址如下: BERT-Base, Uncased下载地址
其他的可以在仓库的readme里找到相应的下载地址

然后随便放到一个地方,这里我放到了新建的uncased文件夹里, 路径不一样,模型运行参数会有一点点变化
1.2.2数据集
数据集介绍如下:
这是一个面向句子的情感分类问题。训练集和测试集已给出,使用训练集进行模型训练并对测试集中各句子进行情感预测。训练集包含10026行数据,测试集包含4850行数据。
训练集
训练集中,每一行代表一条训练语句,包括四部分内容,使用’\t’分隔符:
ID1 ID2 polarity text
其中ID1和ID2是爬取句子内容的定位信息,同学们无需使用。text是句子内容,polarity是句子对应情感类型,有positive、negative、neutral三种。
测试集
测试集中,每一行代表一条待预测语句,包括四部分内容,使用’\t’分隔符:
NA line_num unknwn text
以上是我得到的数据集, 但是我们需要从训练集里面挑10%作为开发集
开发集
开发集是由训练集得到的,我们使用pandas得到开发集, 代码如下, 开发集和训练集比例为9:1, 两个数据集数据不重合, 我们运行以下代码,得到训练集和开发集, 测试集不用重新划分, 用现成的即可
data_cut_off.py
import os
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
if __name__ == '__main__':
path = "glue/"
pd_all = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(path, "data.tsv"), sep='\t' )
pd_all = shuffle(pd_all)
dev_set = pd_all.iloc[0:int(pd_all.shape[0]/10)]
train_set = pd_all.iloc[int(pd_all.shape[0]/10): int(pd_all.shape[0])]
dev_set.to_csv("glue/dev.tsv", index=False, sep='\t')
train_set.to_csv("glue/train.tsv", index=False, sep='\t')
这样我们就得到我们的数据集合。
2. 修改代码
因为这次是分类问题, 所以我们需要修改run_classify.py
2.1 加入新的处理类
因为我们是做一个分类的任务, 里面自带4个任务的处理类, 其中ColaProcessor是单句分类,和我们的任务较为相近, 所以我们模仿这个类,写一个自己的处理类。
class EmloProcessor(DataProcessor):
"""Processor for the Emotion data set ."""
def get_train_examples(self, data_dir):
"""定义开发集的数据是什么,data_dir会作为参数传进去, 这里就是加上你的文件名即可 """
return self._create_examples(
self._read_tsv(os.path.join(data_dir, "train.tsv"), ), "train")
def get_dev_examples(self, data_dir):
"""定义开发集的数据是什么,data_dir会作为参数传进去,模型训练的时候会用到,这里就是加上你的文件名即可 """
return self._create_examples(
self._read_tsv(os.path.join(data_dir, "dev.tsv")), "dev")
def get_test_examples(self, data_dir):
"""定义测试集的数据是什么, 用于预测数据 ,在训练时没有用到这个函数, 这里写预测的数据集"""
return self._create_examples(
self._read_tsv(os.path.join(data_dir, "test.tsv")), "test")
def get_labels(self):
""" 这里是显示你一共有几个分类标签, 在此任务中我有3个标签,如实写上 标签值和 csv里面存的值相同 """
return ["neutral", "positive", "negative"]
def _create_examples(self, lines, set_type):
"""这个函数是用来把数据处理, 把每一个例子分成3个部分,填入到InputExample的3个参数
text_a 是 第一个句子的文本
text_b 是 第二个句子的文本 但是由于此任务是单句分类, 所以 这里传入为None
guid 是一个二元组 第一个表示此数据是什么数据集类型(train dev test) 第二个表示数据标号
label 表示句子类别
"""
examples = []
for (i, line) in enumerate(lines):
guid = "%s-%s" % (set_type, i)
#print(line, i)
# 获取text 第三列和第四列分别是 类别 文本 所以分情况添加
text_a = tokenization.convert_to_unicode(line[3])
if set_type == "test":
#测试集的label 是要预测的 所以我们暂时先随便填一个类别即可 这里我选择都是neutral类
label = "neutral"
else:
label = tokenization.convert_to_unicode(line[2])
# 加入样本
examples.append(
InputExample(guid=guid, text_a=text_a, text_b=None, label=label))
return examples
有兴趣的盆友可以看看其他的3个类。
2.2 处理类注册
同样我们需要在主函数里把我们的类当做参数选项,给他加个选项, 也就是当参数填emlo时,使用的数据处理类是我们自己写的处理类
def main(_):
tf.logging.set_verbosity(tf.logging.INFO)
processors = {
"cola": ColaProcessor,
"mnli": MnliProcessor,
"mrpc": MrpcProcessor,
"xnli": XnliProcessor,
"emlo": EmloProcessor
}
3. 运行代码
运行代码需要提供参数, 这里我建议直接在pycharm编译器里加参数,或者直接命令行运行参数, 而不用按照官方教材 run xxx.sh
这里我给出我的编译参数, 如果你运行不了, 建议 改小max_seq_length, train_batch_size,
python
run_classifier.py
--task_name=emlo
--do_train=true
--do_eval=true
--data_dir=./glue
--vocab_file=./uncased/uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12/vocab.txt
--bert_config_file=./uncased/uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12/bert_config.json
--init_checkpoint=./uncased/uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12/bert_model.ckpt
--max_seq_length=128
--train_batch_size=32
--learning_rate=2e-5
--num_train_epochs=3.0
--output_dir=./tmp/emotion/
- task_name 表示我调用的是什么处理类 ,这里我们是用我们新的类所以选 emlo
- 文件dir 可以自己定义, 如果无定义到会出错, 我这里是有3个文件夹 uncased里面放预训练模型, glue放数据,tmp/emotion里面放结果
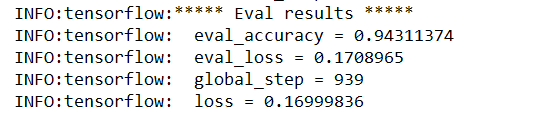
训练结果如下:
4. 分类预测
4.1 修改参数, 进行预测
预测的话, 将运行参数改为以下即可
python run_classifier.py
--task_name=emlo
--do_predict=true
--data_dir=./glue
--vocab_file=./uncased/uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12/vocab.txt
--bert_config_file=./uncased/uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12/bert_config.json
--init_checkpoint=./tmp/emotion/bert_model.ckpt
--max_seq_length=128
--output_dir=./tmp/emotion_out/
将会返回一个tsv, 每一列表示这一行的样本是这一类的概率

每一类代表的类别和 在run_classify.py里面定义的lab顺序相同

4.2 得到类别
结果不能是概率,而是类别, 所以我们写一个脚本进行转化
get_results.py
import os
import pandas as pd
if __name__ == '__main__':
path = "tmp/emotion_out/"
pd_all = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(path, "test_results.tsv") ,sep='\t',header=None)
data = pd.DataFrame(columns=['polarity'])
print(pd_all.shape)
for index in pd_all.index:
neutral_score = pd_all.loc[index].values[0]
positive_score = pd_all.loc[index].values[1]
negative_score = pd_all.loc[index].values[2]
if max(neutral_score, positive_score, negative_score) == neutral_score:
# data.append(pd.DataFrame([index, "neutral"],columns=['id','polarity']),ignore_index=True)
data.loc[index+1] = ["neutral"]
elif max(neutral_score, positive_score, negative_score) == positive_score:
#data.append(pd.DataFrame([index, "positive"],columns=['id','polarity']),ignore_index=True)
data.loc[index+1] = [ "positive"]
else:
#data.append(pd.DataFrame([index, "negative"],columns=['id','polarity']),ignore_index=True)
data.loc[index+1] = [ "negative"]
#print(negative_score, positive_score, negative_score)
data.to_csv(os.path.join(path, "pre_sample.tsv"),sep = '\t')
#print(data)
得到最终预测结果

5. 运行问题
5.1 出现内存不够
官方解释影响内存大小的参数
The factors that affect memory usage are:
max_seq_length: The released models were trained with sequence lengths
up to 512, but you can fine-tune with a shorter max sequence length to save
substantial memory. This is controlled by themax_seq_lengthflag in our
example code.train_batch_size: The memory usage is also directly proportional to
the batch size.- Model type,
BERT-Basevs.BERT-Large: TheBERT-Largemodel
requires significantly more memory thanBERT-Base. - Optimizer: The default optimizer for BERT is Adam, which requires a lot
of extra memory to store themandvvectors. Switching to a more memory
efficient optimizer can reduce memory usage, but can also affect the
results. We have not experimented with other optimizers for fine-tuning.
Using the default training scripts (run_classifier.py and run_squad.py), we
benchmarked the maximum batch size on single Titan X GPU (12GB RAM) with
TensorFlow 1.11.0:
| System | Seq Length | Max Batch Size |
|---|---|---|
BERT-Base |
64 | 64 |
| … | 128 | 32 |
| … | 256 | 16 |
| … | 320 | 14 |
| … | 384 | 12 |
| … | 512 | 6 |
BERT-Large |
64 | 12 |
| … | 128 | 6 |
| … | 256 | 2 |
| … | 320 | 1 |
| … | 384 | 0 |
| … | 512 | 0 |
- 对于参数max_seq_length, train_batch_size 越小, 内存使用越小
- 对于使用的预训练集 BERT-Base 使用内存比 BERT-Large小
- 使用不同的优化器也会造成一定的影响
作者给出了一些他使用的12g显存的搭配, 可以参考使用
6. 源码 GITHUB 地址
特意直接开放源码, 供大家参考
https://github.com/wangjiwu/BERT-emotion-classification
使用BERT进行情感分类预测及代码实例的更多相关文章
- 使用bert进行情感分类
2018年google推出了bert模型,这个模型的性能要远超于以前所使用的模型,总的来说就是很牛.但是训练bert模型是异常昂贵的,对于一般人来说并不需要自己单独训练bert,只需要加载预训练模型, ...
- Bert实战---情感分类
1.情感分析语料预处理 使用酒店评论语料,正面评论和负面评论各5000条,用BERT参数这么大的模型, 训练会产生严重过拟合,,泛化能力差的情况, 这也是我们下面需要解决的问题; 2.sigmoid二 ...
- 基于Bert的文本情感分类
详细代码已上传到github: click me Abstract: Sentiment classification is the process of analyzing and reaso ...
- 关于情感分类(Sentiment Classification)的文献整理
最近对NLP中情感分类子方向的研究有些兴趣,在此整理下个人阅读的笔记(持续更新中): 1. Thumbs up? Sentiment classification using machine lear ...
- 文本情感分类:分词 OR 不分词(3)
为什么要用深度学习模型?除了它更高精度等原因之外,还有一个重要原因,那就是它是目前唯一的能够实现“端到端”的模型.所谓“端到端”,就是能够直接将原始数据和标签输入,然后让模型自己完成一切过程——包括特 ...
- NLP(十九) 双向LSTM情感分类模型
使用IMDB情绪数据来比较CNN和RNN两种方法,预处理与上节相同 from __future__ import print_function import numpy as np import pa ...
- 贝叶斯--旧金山犯罪分类预测和电影评价好坏 demo
来源引用:https://blog.csdn.net/han_xiaoyang/article/details/50629608 1.引言 贝叶斯是经典的机器学习算法,朴素贝叶斯经常运用于机器学习的案 ...
- kaggle——Bag of Words Meets Bags of Popcorn(IMDB电影评论情感分类实践)
kaggle链接:https://www.kaggle.com/c/word2vec-nlp-tutorial/overview 简介:给出 50,000 IMDB movie reviews,进行0 ...
- 基于机器学习和TFIDF的情感分类算法,详解自然语言处理
摘要:这篇文章将详细讲解自然语言处理过程,基于机器学习和TFIDF的情感分类算法,并进行了各种分类算法(SVM.RF.LR.Boosting)对比 本文分享自华为云社区<[Python人工智能] ...
随机推荐
- CentOS开机启动不了修复
1,如果启动时进度条,先修改为日志启动 启动后快速按任何键(Enter除外)进入如下界面 在按e进入 选择第二个选项卡 在按e进入将红色部分 rhgb quiet 删除,然后按Enter,在按b重启 ...
- Python Ethical Hacking - WEB PENETRATION TESTING(3)
CRAWLING SUMMARY Our crawler so far can guess: Subdomains. Directories. Files. Advantages: ->Disc ...
- Ubuntu18.04安装Docker并部署(编译、发布、构建镜像)Asp.NetCore项目全过程笔记
环境准备:阿里云Ubuntu18.04 全新安装 一.安装Docker 1.删除旧版本并更新包索引: sudo apt-get remove docker docker-engine dock ...
- 浅谈6种JS数组遍历方法的区别
本篇文章给大家介绍一下6种JS数组遍历方法:for.foreach.for in.for of.. each. ().each的区别.有一定的参考价值,有需要的朋友可以参考一下,希望对大家有所帮助. ...
- [leetcode/lintcode 题解] 一致性哈希 II · Consistent Hashing II
[题目描述] 在 Consistent Hashing I 中我们介绍了一个比较简单的一致性哈希算法,这个简单的版本有两个缺陷: 增加一台机器之后,数据全部从其中一台机器过来,这一台机器的读负载过大, ...
- jmeter 命令行模式(非GUI)运行脚本,察看结果树结果为空,解决办法;
jmeter的bin目录下,打开命令窗口,执行jmeter -n -t jmeter脚本 -l 结果: 执行结束后,聚合报告打开结果,显示错误率100%:察看结果树中打开结果,显示无数据: 解决办法: ...
- Day09_商品管理
学于黑马和传智播客联合做的教学项目 感谢 黑马官网 传智播客官网 微信搜索"艺术行者",关注并回复关键词"乐优商城"获取视频和教程资料! b站在线视频 0.学习 ...
- PHP serialize() 函数
serialize() 函数用于序列化对象或数组,并返回一个字符串.高佣联盟 www.cgewang.com serialize() 函数序列化对象后,可以很方便的将它传递给其他需要它的地方,且其类型 ...
- PDOStatement::fetchAll
PDOStatement::fetchAll — 返回一个包含结果集中所有行的数组(PHP 5 >= 5.1.0, PECL pdo >= 0.1.0)高佣联盟 www.cgewang.c ...
- MySQL(版本8.0.19)服务的启动/停止、登录/登出、修改密码
[先说明一点 ,windows系统下,英文字母不分大小写.] MySQL 服务的 启动 / 停止 方式一: (我的系统是windows10) 找到 此电脑 图标 右键点击,选择"管理&q ...
