4 基于优化的攻击——CW
CW攻击原论文地址——https://arxiv.org/pdf/1608.04644.pdf
1.CW攻击的原理
CW攻击是一种基于优化的攻击,攻击的名称是两个作者的首字母。首先还是贴出攻击算法的公式表达:
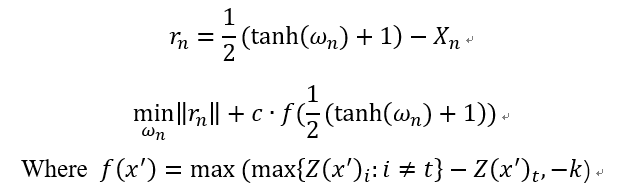
下面解释下算法的大概思想,该算法将对抗样本当成一个变量,那么现在如果要使得攻击成功就要满足两个条件:(1)对抗样本和对应的干净样本应该差距越小越好;(2)对抗样本应该使得模型分类错,且错的那一类的概率越高越好。
其实上述公式的两部分loss也就是基于这两点而得到的,首先说第一部分,rn对应着干净样本和对抗样本的差,但作者在这里有个小trick,他把对抗样本映射到了tanh空间里面,这样做有什么好处呢?如果不做变换,那么x只能在(0,1)这个范围内变换,做了这个变换 ,x可以在-inf到+inf做变换,有利于优化。
再来说说第二部分,公式中的Z(x)表示的是样本x通过模型未经过softmax的输出向量,对于干净的样本来说,这个这个向量的最大值对应的就是正确的类别(如果分类正确的话),现在我们将类别t(也就是我们最后想要攻击成的类别)所对应的逻辑值记为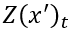 ,将最大的值(对应类别不同于t)记为
,将最大的值(对应类别不同于t)记为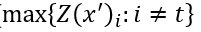 ,如果通过优化使得
,如果通过优化使得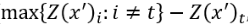 变小,攻击不就离成功了更近嘛。那么式子中的k是什么呢?k其实就是置信度(confidence),可以理解为,k越大,那么模型分错,且错成的那一类的概率越大。但与此同时,这样的对抗样本就更难找了。最后就是常数c,这是一个超参数,用来权衡两个loss之间的关系,在原论文中,作者使用二分查找来确定c值。
变小,攻击不就离成功了更近嘛。那么式子中的k是什么呢?k其实就是置信度(confidence),可以理解为,k越大,那么模型分错,且错成的那一类的概率越大。但与此同时,这样的对抗样本就更难找了。最后就是常数c,这是一个超参数,用来权衡两个loss之间的关系,在原论文中,作者使用二分查找来确定c值。
下面总结一下CW攻击:
CW是一个基于优化的攻击,主要调节的参数是c和k,看你自己的需要了。它的优点在于,可以调节置信度,生成的扰动小,可以破解很多的防御方法,缺点是,很慢~~~
最后在说一下,就是在某些防御论文中,它实现CW攻击,是直接用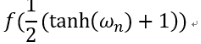 替换PGD中的loss,其余步骤和PGD一模一样。
替换PGD中的loss,其余步骤和PGD一模一样。
2.CW代码实现
class CarliniWagnerL2Attack(Attack, LabelMixin):
def __init__(self, predict, num_classes, confidence=0,
targeted=False, learning_rate=0.01,
binary_search_steps=9, max_iterations=10000,
abort_early=True, initial_const=1e-3,
clip_min=0., clip_max=1., loss_fn=None):
"""
Carlini Wagner L2 Attack implementation in pytorch
Carlini, Nicholas, and David Wagner. "Towards evaluating the
robustness of neural networks." 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and
Privacy (SP). IEEE, 2017.
https://arxiv.org/abs/1608.04644
learning_rate: the learning rate for the attack algorithm
max_iterations: the maximum number of iterations
binary_search_steps: number of binary search times to find the optimum
abort_early: if set to true, abort early if getting stuck in local min
confidence: confidence of the adversarial examples
targeted: TODO
"""
if loss_fn is not None:
import warnings
warnings.warn(
"This Attack currently do not support a different loss"
" function other than the default. Setting loss_fn manually"
" is not effective."
)
loss_fn = None
super(CarliniWagnerL2Attack, self).__init__(
predict, loss_fn, clip_min, clip_max)
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
self.max_iterations = max_iterations
self.binary_search_steps = binary_search_steps
self.abort_early = abort_early
self.confidence = confidence
self.initial_const = initial_const
self.num_classes = num_classes
# The last iteration (if we run many steps) repeat the search once.
self.repeat = binary_search_steps >= REPEAT_STEP
self.targeted = targeted
def _loss_fn(self, output, y_onehot, l2distsq, const):
# TODO: move this out of the class and make this the default loss_fn
# after having targeted tests implemented
real = (y_onehot * output).sum(dim=1)
# TODO: make loss modular, write a loss class
other = ((1.0 - y_onehot) * output - (y_onehot * TARGET_MULT)
).max(1)[0]
# - (y_onehot * TARGET_MULT) is for the true label not to be selected
if self.targeted:
loss1 = clamp(other - real + self.confidence, min=0.)
else:
loss1 = clamp(real - other + self.confidence, min=0.)
loss2 = (l2distsq).sum()
loss1 = torch.sum(const * loss1)
loss = loss1 + loss2
return loss
def _is_successful(self, output, label, is_logits):
# determine success, see if confidence-adjusted logits give the right
# label
if is_logits:
output = output.detach().clone()
if self.targeted:
output[torch.arange(len(label)), label] -= self.confidence
else:
output[torch.arange(len(label)), label] += self.confidence
pred = torch.argmax(output, dim=1)
else:
pred = output
if pred == INVALID_LABEL:
return pred.new_zeros(pred.shape).byte()
return is_successful(pred, label, self.targeted)
def _forward_and_update_delta(
self, optimizer, x_atanh, delta, y_onehot, loss_coeffs):
optimizer.zero_grad()
adv = tanh_rescale(delta + x_atanh, self.clip_min, self.clip_max)
transimgs_rescale = tanh_rescale(x_atanh, self.clip_min, self.clip_max)
output = self.predict(adv)
l2distsq = calc_l2distsq(adv, transimgs_rescale)
loss = self._loss_fn(output, y_onehot, l2distsq, loss_coeffs)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
return loss.item(), l2distsq.data, output.data, adv.data
def _get_arctanh_x(self, x):
result = clamp((x - self.clip_min) / (self.clip_max - self.clip_min),
min=self.clip_min, max=self.clip_max) * 2 - 1
return torch_arctanh(result * ONE_MINUS_EPS)
def _update_if_smaller_dist_succeed(
self, adv_img, labs, output, l2distsq, batch_size,
cur_l2distsqs, cur_labels,
final_l2distsqs, final_labels, final_advs):
target_label = labs
output_logits = output
_, output_label = torch.max(output_logits, 1)
mask = (l2distsq < cur_l2distsqs) & self._is_successful(
output_logits, target_label, True)
cur_l2distsqs[mask] = l2distsq[mask] # redundant
cur_labels[mask] = output_label[mask]
mask = (l2distsq < final_l2distsqs) & self._is_successful(
output_logits, target_label, True)
final_l2distsqs[mask] = l2distsq[mask]
final_labels[mask] = output_label[mask]
final_advs[mask] = adv_img[mask]
def _update_loss_coeffs(
self, labs, cur_labels, batch_size, loss_coeffs,
coeff_upper_bound, coeff_lower_bound):
# TODO: remove for loop, not significant, since only called during each
# binary search step
for ii in range(batch_size):
cur_labels[ii] = int(cur_labels[ii])
if self._is_successful(cur_labels[ii], labs[ii], False):
coeff_upper_bound[ii] = min(
coeff_upper_bound[ii], loss_coeffs[ii])
if coeff_upper_bound[ii] < UPPER_CHECK:
loss_coeffs[ii] = (
coeff_lower_bound[ii] + coeff_upper_bound[ii]) / 2
else:
coeff_lower_bound[ii] = max(
coeff_lower_bound[ii], loss_coeffs[ii])
if coeff_upper_bound[ii] < UPPER_CHECK:
loss_coeffs[ii] = (
coeff_lower_bound[ii] + coeff_upper_bound[ii]) / 2
else:
loss_coeffs[ii] *= 10
def perturb(self, x, y=None):
x, y = self._verify_and_process_inputs(x, y)
# Initialization
if y is None:
y = self._get_predicted_label(x)
x = replicate_input(x)
batch_size = len(x)
coeff_lower_bound = x.new_zeros(batch_size)
coeff_upper_bound = x.new_ones(batch_size) * CARLINI_COEFF_UPPER
loss_coeffs = torch.ones_like(y).float() * self.initial_const
final_l2distsqs = [CARLINI_L2DIST_UPPER] * batch_size
final_labels = [INVALID_LABEL] * batch_size
final_advs = x
x_atanh = self._get_arctanh_x(x)
y_onehot = to_one_hot(y, self.num_classes).float()
final_l2distsqs = torch.FloatTensor(final_l2distsqs).to(x.device)
final_labels = torch.LongTensor(final_labels).to(x.device)
# Start binary search
for outer_step in range(self.binary_search_steps):
delta = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros_like(x))
optimizer = optim.Adam([delta], lr=self.learning_rate)
cur_l2distsqs = [CARLINI_L2DIST_UPPER] * batch_size
cur_labels = [INVALID_LABEL] * batch_size
cur_l2distsqs = torch.FloatTensor(cur_l2distsqs).to(x.device)
cur_labels = torch.LongTensor(cur_labels).to(x.device)
prevloss = PREV_LOSS_INIT
if (self.repeat and outer_step == (self.binary_search_steps - 1)):
loss_coeffs = coeff_upper_bound
for ii in range(self.max_iterations):
loss, l2distsq, output, adv_img = \
self._forward_and_update_delta(
optimizer, x_atanh, delta, y_onehot, loss_coeffs)
if self.abort_early:
if ii % (self.max_iterations // NUM_CHECKS or 1) == 0:
if loss > prevloss * ONE_MINUS_EPS:
break
prevloss = loss
self._update_if_smaller_dist_succeed(
adv_img, y, output, l2distsq, batch_size,
cur_l2distsqs, cur_labels,
final_l2distsqs, final_labels, final_advs)
self._update_loss_coeffs(
y, cur_labels, batch_size,
loss_coeffs, coeff_upper_bound, coeff_lower_bound)
return final_advs
4 基于优化的攻击——CW的更多相关文章
- 5.基于优化的攻击——CW
CW攻击原论文地址——https://arxiv.org/pdf/1608.04644.pdf 1.CW攻击的原理 CW攻击是一种基于优化的攻击,攻击的名称是两个作者的首字母.首先还是贴出攻击算法的公 ...
- 2.基于梯度的攻击——FGSM
FGSM原论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6572 1.FGSM的原理 FGSM的全称是Fast Gradient Sign Method(快速梯度下降法),在白盒环境 ...
- 1 基于梯度的攻击——FGSM
FGSM原论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6572 1.FGSM的原理 FGSM的全称是Fast Gradient Sign Method(快速梯度下降法),在白盒环境 ...
- 4.基于梯度的攻击——MIM
MIM攻击原论文地址——https://arxiv.org/pdf/1710.06081.pdf 1.MIM攻击的原理 MIM攻击全称是 Momentum Iterative Method,其实这也是 ...
- 3.基于梯度的攻击——PGD
PGD攻击原论文地址——https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.06083.pdf 1.PGD攻击的原理 PGD(Project Gradient Descent)攻击是一种迭代攻击,可 ...
- 3 基于梯度的攻击——MIM
MIM攻击原论文地址——https://arxiv.org/pdf/1710.06081.pdf 1.MIM攻击的原理 MIM攻击全称是 Momentum Iterative Method,其实这也是 ...
- 2 基于梯度的攻击——PGD
PGD攻击原论文地址——https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.06083.pdf 1.PGD攻击的原理 PGD(Project Gradient Descent)攻击是一种迭代攻击,可 ...
- uva live 6190 Beautiful Spacing (二分法+dp试 基于优化的独特性质)
I - Beautiful Spacing Time Limit:8000MS Memory Limit:65536KB 64bit IO Format:%lld & %llu ...
- 京东云与AI 10 篇论文被AAAI 2020 收录,京东科技实力亮相世界舞台
美国时间2月7-12日,AAAI 2020大会在纽约正式拉开序幕,AAAI作为全球人工智能领域的顶级学术会议,每年评审并收录来自全球最顶尖的学术论文,这些学术研究引领着技术的趋势和未来.京东云与AI在 ...
随机推荐
- 一步一步理解线段树——转载自JustDoIT
一步一步理解线段树 目录 一.概述 二.从一个例子理解线段树 创建线段树 线段树区间查询 单节点更新 区间更新 三.线段树实战 -------------------------- 一 概述 线段 ...
- Java的当中的泛型
Java当中的泛型 01 import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class Demo{ public static voi ...
- 微信小程序_(校园视)开发视频的展示页_上
微信小程序_(校园视) 开发用户注册登陆 传送门 微信小程序_(校园视) 开发上传视频业务 传送门 微信小程序_(校园视) 开发视频的展示页-上 传送门 微信小程序_(校园视) 开发视频的展示页-下 ...
- Eclipse在线安装插件进度缓慢问题
最近在学习Maven的过程中需要安装m2e 插件,在线安装的缓慢速度实在是让人抓狂,故将自己最后的解决方案记录下来,以供其他人参考. 最终的原因是安装时同时检查更新了其他插件的最新版,所以安装插件时注 ...
- Linux-expect脚本-编写一个expect脚本
1.声明expect #!/usr/bin/expect -f 2.设置超时时间,获取参数 set ip [lindex $argv 0 ] //接收第一个参数,并设置IP set password ...
- 邻居子系统 之 邻居项查找neigh_lookup、___neigh_lookup_noref
概述 邻居项查找是通过neigh_lookup相关函数来进行的: ___neigh_lookup_noref,该函数根据输出设备和主键值(IPv4为下一跳ip地址)在邻居项hash表中查找,找到则返回 ...
- 【编程漫谈】PHP
PHP是个很古老的脚本技术了,当年CGI比较让人诟病,于是PHP横空出世.PHP即写即用特性,吸引了一大批粉丝,而且类似C语言的编程风格,让那些C程序员非常容易地转到这个平台上来.当然PHP刚出来的时 ...
- 卸载阿里云盾(安骑士)监控&屏蔽云盾IP
卸载阿里云盾监控 wget http://update.aegis.aliyun.com/download/uninstall.sh chmod +x uninstall.sh ./uninstall ...
- 【makefile】make程序的命令行选项和参数
Make命令参数的典型序列如下所示: make [-f makefile文件名][选项][宏定义][目标] 这里用[]括起来的表示是可选的.命令行选项由破折号“–”指明,后面跟选项,如: make – ...
- 连续子数组的最大和 java实现
package findMax; /** * 连续子数组的最大和 * @author root * */ public class FindMax { static int[] data = {1,- ...
