一致性哈希算法(consistent hashing)PHP实现
一致性哈希算法在1997年由麻省理工学院提出的一种分布式哈希(DHT)实现算法,设计目标是为了解决因特网中的热点(Hot spot)问题,初衷和CARP十分类似。一致性哈希修正了CARP使用的简单哈希算法带来的问题,使得分布式哈希(DHT)可以在P2P环境中真正得到应用。
一致性hash算法提出了在动态变化的Cache环境中,判定哈希算法好坏的四个定义:
1、平衡性(Balance):平衡性是指哈希的结果能够尽可能分布到所有的缓冲中去,这样可以使得所有的缓冲空间都得到利用。很多哈希算法都能够满足这一条件。
2、单调性(Monotonicity):单调性是指如果已经有一些内容通过哈希分派到了相应的缓冲中,又有新的缓冲加入到系统中。哈希的结果应能够保证原有已分配的内容可以被映射到原有的或者新的缓冲中去,而不会被映射到旧的缓冲集合中的其他缓冲区。
3、分散性(Spread):在分布式环境中,终端有可能看不到所有的缓冲,而是只能看到其中的一部分。当终端希望通过哈希过程将内容映射到缓冲上时,由于不同终端所见的缓冲范围有可能不同,从而导致哈希的结果不一致,最终的结果是相同的内容被不同的终端映射到不同的缓冲区中。这种情况显然是应该避免的,因为它导致相同内容被存储到不同缓冲中去,降低了系统存储的效率。分散性的定义就是上述情况发生的严重程度。好的哈希算法应能够尽量避免不一致的情况发生,也就是尽量降低分散性。
4、负载(Load):负载问题实际上是从另一个角度看待分散性问题。既然不同的终端可能将相同的内容映射到不同的缓冲区中,那么对于一个特定的缓冲区而言,也可能被不同的用户映射为不同 的内容。与分散性一样,这种情况也是应当避免的,因此好的哈希算法应能够尽量降低缓冲的负荷。
在分布式集群中,对机器的添加删除,或者机器故障后自动脱离集群这些操作是分布式集群管理最基本的功能。如果采用常用的 hash(object)%N 算法,那么在有机器添加或者删除后,很多原有的数据就无法找到了,这样严重的违反了单调性原则。接下来主要讲解一下一致性哈希算法是如何设计的:
环形Hash空间
按照常用的hash算法来将对应的key哈希到一个具有 2^32次方 个桶的空间中,即0~(2^32)-1的数字空间中。现在我们可以将这些数字头尾相连,想象成一个闭合的环形。如下图
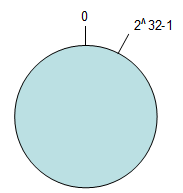
把数据通过一定的hash算法处理后映射到环上
现在我们将object1、object2、object3、object4四个对象通过特定的Hash函数计算出对应的key值,然后散列到Hash环上。如下图:
Hash(object1) = key1;
Hash(object2) = key2;
Hash(object3) = key3;
Hash(object4) = key4;
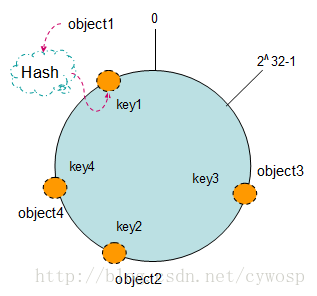
将机器通过hash算法映射到环上
在采用一致性哈希算法的分布式集群中将新的机器加入,其原理是通过使用与对象存储一样的Hash算法将机器也映射到环中(一般情况下对机器的hash计算是采用机器的IP或者机器唯一的别名作为输入值),然后以顺时针的方向计算,将所有对象存储到离自己最近的机器中。
假设现在有NODE1,NODE2,NODE3三台机器,通过Hash算法得到对应的KEY值,映射到环中,其示意图如下:
Hash(NODE1) = KEY1;
Hash(NODE2) = KEY2;
Hash(NODE3) = KEY3;
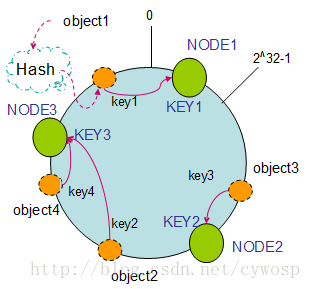
通过上图可以看出对象与机器处于同一哈希空间中,这样按顺时针转动object1存储到了NODE1中,object3存储到了NODE2中,object2、object4存储到了NODE3中。在这样的部署环境中,hash环是不会变更的,因此,通过算出对象的hash值就能快速的定位到对应的机器中,这样就能找到对象真正的存储位置了。
机器的删除与添加
普通hash求余算法最为不妥的地方就是在有机器的添加或者删除之后会照成大量的对象存储位置失效,这样就大大的不满足单调性了。下面来分析一下一致性哈希算法是如何处理的。
1. 节点(机器)的删除
以上面的分布为例,如果NODE2出现故障被删除了,那么按照顺时针迁移的方法,object3将会被迁移到NODE3中,这样仅仅是object3的映射位置发生了变化,其它的对象没有任何的改动。如下图:
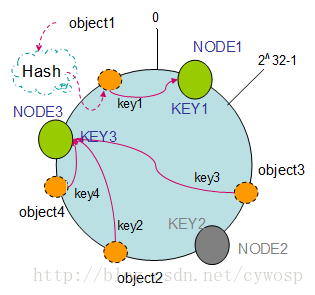
2. 节点(机器)的添加
如果往集群中添加一个新的节点NODE4,通过对应的哈希算法得到KEY4,并映射到环中,如下图:
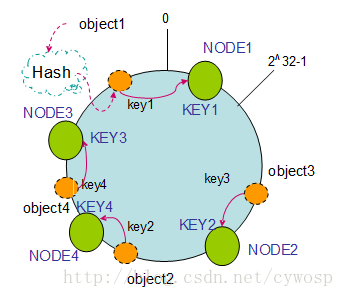
通过按顺时针迁移的规则,那么object2被迁移到了NODE4中,其它对象还保持这原有的存储位置。通过对节点的添加和删除的分析,一致性哈希算法在保持了单调性的同时,还是数据的迁移达到了最小,这样的算法对分布式集群来说是非常合适的,避免了大量数据迁移,减小了服务器的的压力。
平衡性
根据上面的图解分析,一致性哈希算法满足了单调性和负载均衡的特性以及一般hash算法的分散性,但这还并不能当做其被广泛应用的原由,因为还缺少了平衡性。下面将分析一致性哈希算法是如何满足平衡性的。hash算法是不保证平衡的,如上面只部署了NODE1和NODE3的情况(NODE2被删除的图),object1存储到了NODE1中,而object2、object3、object4都存储到了NODE3中,这样就照成了非常不平衡的状态。在一致性哈希算法中,为了尽可能的满足平衡性,其引入了虚拟节点。
“虚拟节点”( virtual node )是实际节点(机器)在 hash 空间的复制品( replica ),一实际个节点(机器)对应了若干个“虚拟节点”,这个对应个数也成为“复制个数”,“虚拟节点”在 hash 空间中以hash值排列。
以上面只部署了NODE1和NODE3的情况(NODE2被删除的图)为例,之前的对象在机器上的分布很不均衡,现在我们以2个副本(复制个数)为例,这样整个hash环中就存在了4个虚拟节点,最后对象映射的关系图如下:
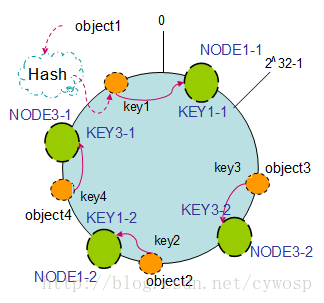
根据上图可知对象的映射关系:object1->NODE1-1,object2->NODE1-2,object3->NODE3-2,object4->NODE3-1。通过虚拟节点的引入,对象的分布就比较均衡了。那么在实际操作中,正真的对象查询是如何工作的呢?对象从hash到虚拟节点到实际节点的转换如下图:
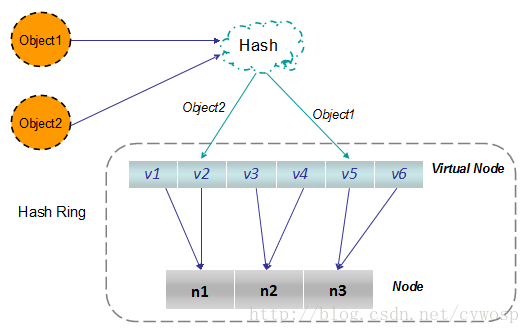
“虚拟节点”的hash计算可以采用对应节点的IP地址加数字后缀的方式。例如假设NODE1的IP地址为192.168.1.100。引入“虚拟节点”前,计算 cache A 的 hash 值:
Hash(“192.168.1.100”);
引入“虚拟节点”后,计算“虚拟节”点NODE1-1和NODE1-2的hash值:
Hash(“192.168.1.100#1”); // NODE1-1
Hash(“192.168.1.100#2”); // NODE1-2
一致性hash算法的PHP实现
<?php
/**
* Flexihash - A simple consistent hashing implementation for PHP.
*
* The MIT License
*
* Copyright (c) 2008 Paul Annesley
*
* Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
* of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
* in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
* to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
* copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
* furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
*
* The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
* all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
*
* THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
* IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
* AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
* LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
* OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
* THE SOFTWARE.
*
* @author Paul Annesley
* @link http://paul.annesley.cc/
* @copyright Paul Annesley, 2008
* @comment by MyZ (http://blog.csdn.net/mayongzhan)
*/ /**
* A simple consistent hashing implementation with pluggable hash algorithms.
*
* @author Paul Annesley
* @package Flexihash
* @licence http://www.opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.php
*/
class Flexihash
{
/**
* The number of positions to hash each target to.
*
* @var int
* @comment 虚拟节点数,解决节点分布不均的问题
*/
private $_replicas = 64; /**
* The hash algorithm, encapsulated in a Flexihash_Hasher implementation.
* @var object Flexihash_Hasher
* @comment 使用的hash方法 : md5,crc32
*/
private $_hasher; /**
* Internal counter for current number of targets.
* @var int
* @comment 节点记数器
*/
private $_targetCount = 0; /**
* Internal map of positions (hash outputs) to targets
* @var array { position => target, ... }
* @comment 位置对应节点,用于lookup中根据位置确定要访问的节点
*/
private $_positionToTarget = array(); /**
* Internal map of targets to lists of positions that target is hashed to.
* @var array { target => [ position, position, ... ], ... }
* @comment 节点对应位置,用于删除节点
*/
private $_targetToPositions = array(); /**
* Whether the internal map of positions to targets is already sorted.
* @var boolean
* @comment 是否已排序
*/
private $_positionToTargetSorted = false; /**
* Constructor
* @param object $hasher Flexihash_Hasher
* @param int $replicas Amount of positions to hash each target to.
* @comment 构造函数,确定要使用的hash方法和需拟节点数,虚拟节点数越多,分布越均匀,但程序的分布式运算越慢
*/
public function __construct(Flexihash_Hasher $hasher = null, $replicas = null)
{
$this->_hasher = $hasher ? $hasher : new Flexihash_Crc32Hasher();
if (!empty($replicas)) $this->_replicas = $replicas;
} /**
* Add a target.
* @param string $target
* @chainable
* @comment 添加节点,根据虚拟节点数,将节点分布到多个虚拟位置上
*/
public function addTarget($target)
{
if (isset($this->_targetToPositions[$target]))
{
throw new Flexihash_Exception("Target '$target' already exists.");
} $this->_targetToPositions[$target] = array(); // hash the target into multiple positions
for ($i = 0; $i < $this->_replicas; $i++)
{
$position = $this->_hasher->hash($target . $i);
$this->_positionToTarget[$position] = $target; // lookup
$this->_targetToPositions[$target] []= $position; // target removal
} $this->_positionToTargetSorted = false;
$this->_targetCount++; return $this;
} /**
* Add a list of targets.
* @param array $targets
* @chainable
*/
public function addTargets($targets)
{
foreach ($targets as $target)
{
$this->addTarget($target);
} return $this;
} /**
* Remove a target.
* @param string $target
* @chainable
*/
public function removeTarget($target)
{
if (!isset($this->_targetToPositions[$target]))
{
throw new Flexihash_Exception("Target '$target' does not exist.");
} foreach ($this->_targetToPositions[$target] as $position)
{
unset($this->_positionToTarget[$position]);
} unset($this->_targetToPositions[$target]); $this->_targetCount--; return $this;
} /**
* A list of all potential targets
* @return array
*/
public function getAllTargets()
{
return array_keys($this->_targetToPositions);
} /**
* A list of all potential targets
* @return array
*/
public function getAll()
{
return array(
"targers"=>$this->_positionToTarget,
"positions"=>$this->_targetToPositions);
} /**
* Looks up the target for the given resource.
* @param string $resource
* @return string
*/
public function lookup($resource)
{
$targets = $this->lookupList($resource, 1);
if (empty($targets)) throw new Flexihash_Exception('No targets exist');
return $targets[0]; //0表示返回离资源位置最近的机器节点
} /**
* Get a list of targets for the resource, in order of precedence.
* Up to $requestedCount targets are returned, less if there are fewer in total.
*
* @param string $resource
* @param int $requestedCount The length of the list to return
* @return array List of targets
* @comment 查找当前的资源对应的节点,
* 节点为空则返回空,节点只有一个则返回该节点,
* 对当前资源进行hash,对所有的位置进行排序,在有序的位置列上寻找当前资源的位置
* 当全部没有找到的时候,将资源的位置确定为有序位置的第一个(形成一个环)
* 返回所找到的节点
*/
public function lookupList($resource, $requestedCount)
{
if (!$requestedCount)
throw new Flexihash_Exception('Invalid count requested'); // handle no targets
if (empty($this->_positionToTarget))
return array(); // optimize single target
if ($this->_targetCount == 1)
return array_unique(array_values($this->_positionToTarget)); // hash resource to a position
$resourcePosition = $this->_hasher->hash($resource); $results = array();
$collect = false; $this->_sortPositionTargets(); // search values above the resourcePosition
foreach ($this->_positionToTarget as $key => $value)
{
// start collecting targets after passing resource position
if (!$collect && $key > $resourcePosition)
{
$collect = true;
} // only collect the first instance of any target
if ($collect && !in_array($value, $results))
{
$results []= $value;
//var_dump($results);
}
// return when enough results, or list exhausted
//var_dump(count($results));
//var_dump($requestedCount);
if (count($results) == $requestedCount || count($results) == $this->_targetCount)
{
return $results;
}
} // loop to start - search values below the resourcePosition
foreach ($this->_positionToTarget as $key => $value)
{
if (!in_array($value, $results))
{
$results []= $value;
} // return when enough results, or list exhausted
if (count($results) == $requestedCount || count($results) == $this->_targetCount)
{
return $results;
}
} // return results after iterating through both "parts"
return $results;
} public function __toString()
{
return sprintf(
'%s{targets:[%s]}',
get_class($this),
implode(',', $this->getAllTargets())
);
} // ----------------------------------------
// private methods /**
* Sorts the internal mapping (positions to targets) by position
*/
private function _sortPositionTargets()
{
// sort by key (position) if not already
if (!$this->_positionToTargetSorted)
{
ksort($this->_positionToTarget, SORT_REGULAR);
$this->_positionToTargetSorted = true;
}
} } /**
* Hashes given values into a sortable fixed size address space.
*
* @author Paul Annesley
* @package Flexihash
* @licence http://www.opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.php
*/
interface Flexihash_Hasher
{ /**
* Hashes the given string into a 32bit address space.
*
* Note that the output may be more than 32bits of raw data, for example
* hexidecimal characters representing a 32bit value.
*
* The data must have 0xFFFFFFFF possible values, and be sortable by
* PHP sort functions using SORT_REGULAR.
*
* @param string
* @return mixed A sortable format with 0xFFFFFFFF possible values
*/
public function hash($string); } /**
* Uses CRC32 to hash a value into a signed 32bit int address space.
* Under 32bit PHP this (safely) overflows into negatives ints.
*
* @author Paul Annesley
* @package Flexihash
* @licence http://www.opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.php
*/
class Flexihash_Crc32Hasher
implements Flexihash_Hasher
{ /* (non-phpdoc)
* @see Flexihash_Hasher::hash()
*/
public function hash($string)
{
return crc32($string);
} } /**
* Uses CRC32 to hash a value into a 32bit binary string data address space.
*
* @author Paul Annesley
* @package Flexihash
* @licence http://www.opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.php
*/
class Flexihash_Md5Hasher
implements Flexihash_Hasher
{ /* (non-phpdoc)
* @see Flexihash_Hasher::hash()
*/
public function hash($string)
{
return substr(md5($string), 0, 8); // 8 hexits = 32bit // 4 bytes of binary md5 data could also be used, but
// performance seems to be the same.
} } /**
* An exception thrown by Flexihash.
*
* @author Paul Annesley
* @package Flexihash
* @licence http://www.opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.php
*/
class Flexihash_Exception extends Exception
{
}
测试代码
$hash = new Flexihash();
$targets=array(
"192.168.1.1:11011",
"192.168.1.1:11012",
"192.168.1.1:11013",
"192.168.1.1:11014",
"192.168.1.1:11015",
);
$hash->addTargets($targets);
for ($i=0; $i < 25; $i++) {
$resource = sprintf("format %d",$i);
var_dump($resource." --> ".$hash->lookup($resource));
}
输出
string(30) "format 0 --> 192.168.1.1:11015"
string(30) "format 1 --> 192.168.1.1:11015"
string(30) "format 2 --> 192.168.1.1:11015"
string(30) "format 3 --> 192.168.1.1:11015"
string(30) "format 4 --> 192.168.1.1:11011"
string(30) "format 5 --> 192.168.1.1:11011"
string(30) "format 6 --> 192.168.1.1:11011"
string(30) "format 7 --> 192.168.1.1:11011"
string(30) "format 8 --> 192.168.1.1:11012"
string(30) "format 9 --> 192.168.1.1:11013"
string(31) "format 10 --> 192.168.1.1:11013"
string(31) "format 11 --> 192.168.1.1:11011"
string(31) "format 12 --> 192.168.1.1:11012"
string(31) "format 13 --> 192.168.1.1:11011"
string(31) "format 14 --> 192.168.1.1:11014"
string(31) "format 15 --> 192.168.1.1:11014"
string(31) "format 16 --> 192.168.1.1:11014"
string(31) "format 17 --> 192.168.1.1:11014"
string(31) "format 18 --> 192.168.1.1:11012"
string(31) "format 19 --> 192.168.1.1:11012"
string(31) "format 20 --> 192.168.1.1:11013"
string(31) "format 21 --> 192.168.1.1:11012"
string(31) "format 22 --> 192.168.1.1:11012"
string(31) "format 23 --> 192.168.1.1:11014"
string(31) "format 24 --> 192.168.1.1:11012"
[Finished in 0.1s]
redis分布式代码设计
<?php
require_once("Flexihash.php");
$config=array(
"127.0.0.1:6371",
"127.0.0.1:6372",
"127.0.0.1:6373",
"127.0.0.1:6374",
);
class RedisCollect {
//redis实例
private $_redis = null;
//hash实例
private $_hash = null;
//初始化
public function __construct() {
global $config;
$this->_redis = new Redis();
$this->_hash = new Flexihash();
$this->_hash->addTargets($config);
}
public function set($key="", $value="") {
$m = $this->switchConncetion($key);
return $m->set($key, $value);
}
public function get($key) {
$m = $this->switchConncetion($key);
return $m->get($key);
}
private function switchConncetion($key) {
$hostinfo = $this->_hash->lookup($key);
$m = $this->connect($hostinfo);
return $m;
}
private function connect($hostinfo) {
list($host, $port) = explode(":", $hostinfo);
//printf("host = %s, port = %s\n",$host,$port);
if(empty($host) || empty($port)) {
return false;
}
try {
$this->_redis->connect($host, $port);
return $this->_redis;
} catch(Exception $e) {
die($e->getMessage());
}
}
}
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/cywosp/article/details/23397179
一致性哈希算法(consistent hashing)PHP实现的更多相关文章
- (转)每天进步一点点——五分钟理解一致性哈希算法(consistent hashing)
背景:在redis集群中,有关于一致性哈希的使用. 一致性哈希:桶大小0~(2^32)-1 哈希指标:平衡性.单调性.分散性.负载性 为了提高平衡性,引入“虚拟节点” 每天进步一点点——五分钟理解一致 ...
- 一致性哈希算法(consistent hashing)(转)
原文链接:每天进步一点点——五分钟理解一致性哈希算法(consistent hashing) 一致性哈希算法在1997年由麻省理工学院提出的一种分布式哈希(DHT)实现算法,设计目标是为了解决因特网 ...
- 一致性哈希算法(Consistent Hashing Algorithm)
一致性哈希算法(Consistent Hashing Algorithm) 浅谈一致性Hash原理及应用 在讲一致性Hash之前我们先来讨论一个问题. 问题:现在有亿级用户,每日产生千万级订单,如 ...
- 转 白话解析:一致性哈希算法 consistent hashing
摘要: 本文首先以一个经典的分布式缓存的应用场景为铺垫,在了解了这个应用场景之后,生动而又不失风趣地介绍了一致性哈希算法,同时也明确给出了一致性哈希算法的优点.存在的问题及其解决办法. 声明与致谢: ...
- 白话解析:一致性哈希算法 consistent hashing【转】
学习一致性哈希算法原理的时候看到博主朱双印的一片文章,看完就懂,大佬! 白话解析:一致性哈希算法 consistent hashing
- _00013 一致性哈希算法 Consistent Hashing 新的讨论,并出现相应的解决
笔者博文:妳那伊抹微笑 博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/u012185296 个性签名:世界上最遥远的距离不是天涯,也不是海角,而是我站在妳的面前.妳却感觉不到我的存在 技术方向: ...
- 五分钟理解一致性哈希算法(consistent hashing)
转载请说明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/cywosp/article/details/23397179 一致性哈希算法在1997年由麻省理工学院提出的一种分布式哈希(DHT)实现算法 ...
- 每天进步一点点——五分钟理解一致性哈希算法(consistent hashing)
转载请说明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/cywosp/article/details/23397179 一致性哈希算法在1997年由麻省理工学院提出的一种分布式哈希(DHT) ...
- 一致性哈希算法(consistent hashing)【转】
一致性哈希算法 来自:http://blog.csdn.net/cywosp/article/details/23397179 一致性哈希算法在1997年由麻省理工学院提出的一种分布式哈希 ...
随机推荐
- 架构之道(3) - 令後端的吐血和喊FUCK的次数锐减
「那个产品经理不会技术,整天在需求,真操他妈的.」 这是很多产品经理遇到的一句话,如果你把顾客阶段完成了,回到自己的团队,遇到个技术大牛这麽说,那就表示,自己作为产品经理的功力还不够. 等我慢现解释, ...
- 17.3.15---C语言详解FILE文件操作
FILE 是 C语言文件结构定义, 打开文件和文件操作要用到这类结构.可以看成变量类型,用于变量声明.这个是一种数据结构类型,用来表示一个文件的相关信息,如果定义了一个文件指针,就用这个指针来指向某个 ...
- 唐顿庄园S01E01观看感悟
刚刚看了唐顿庄园的第一季第一集.看第一遍的时候,主要是看剧情,看看有没有什么吸引人的.我是一带而过的.等到看第二遍的时候,仔细观察画面,欣赏画面的美感,琢磨人物的台词对话.不断的倒退回放,越看越有滋味 ...
- remove_if 的效率测试
#include <iostream> #include <functional> #include <vector> #include <algorithm ...
- day32-socketserver
#socketserver 是在socket基础上进行了封装,它让server可以实时跟多个client进行通信. #thread线程:一个程序有一个线程,一个线程是调度cpu的最小单位.程序运行才产 ...
- Nginx的下载与安装
.创建文件输入网页中需要复制的 cat >/etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo<<EOF [nginx-stable] name=nginx stable repo ...
- java高并发之线程池
Java高并发之线程池详解 线程池优势 在业务场景中, 如果一个对象创建销毁开销比较大, 那么此时建议池化对象进行管理. 例如线程, jdbc连接等等, 在高并发场景中, 如果可以复用之前销毁的对 ...
- 直击LG曲面OLED首发现场,高端品质更出众
简直是太棒了,我可以去看LG曲面OLED电视新品发布会了.这可是LG向中国首次推出的曲面OLED电视.在网上我就已经看到其实曲面OLED电视已经在韩国.美国还有欧洲都上市了,听说现在反响还挺不错.真没 ...
- python之接口自动化测试框架
梳理python+unittest接口自动化测试框架的思路: 1.确定目录: cases:存放测试用例的py文件:config:存放一些数据库,环境地址等固定不变的信息: core:核心的文件, ca ...
- HQL语句简单介绍
HQL查询:Criteria查询对查询条件进行了面向对象封装,符合编程人员的思维方式,不过HQL(Hibernate Query Lanaguage)查询提供了更加丰富的和灵活的查询特性,因此 Hib ...
