[RH134] 8-磁盘管理
一、磁盘结构
我们以但磁盘的硬盘为例,如图所示:
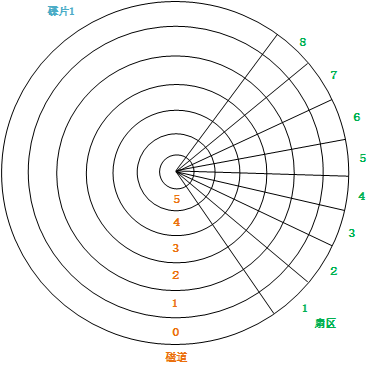
从内向往有很多的磁道(这里我们只画了5条,实际上非常多),这个磁盘被划分为很多扇区。每个扇区有一个固定的大小,例如512Bytes。
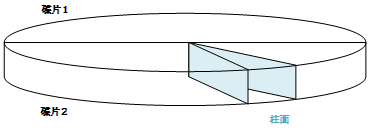
对于多磁盘的硬盘,同一个扇区,上下多个磁盘,可以组成柱面,如图:
二、分区(MBR结构)
如下图所示,我们将磁盘分成多个分区:

可以看到,C盘空间从2048扇区---4000扇区,D盘空间从4001扇区---8000扇区,E盘空间从8001扇区---10000扇区。
第一个扇区的512Byte用于记录磁盘的一些基本数据(MBR),例如bootloader(启动加载器)、分区表(记录主分区和扩展分区的信息)、结束符。
以上这种结构的磁盘叫做MBR结构磁盘。除了这种磁盘,还有另外一种叫做gpt结构磁盘(gpt结构磁盘可以支持更多的主分区,128个)。
三、分区表
分区表只记录主分区和扩展分区的信息(例如起始结束扇区等)。
分区的类别:
- 主分区:直接从硬盘划分,格式化后直接使用的分区叫主分区。
- 扩展分区:直接从硬盘划分,但不格式化直接使用,而是再将其分能更小的分区(逻辑分区)来使用。
- 逻辑分区:在扩展分区中逻辑划分的小分区。分区表不记录逻辑分区的信息。
注意:
在分区表中,每记录一个分区,需要消耗16Btye空间,所以以64Byte的总空间来算,主分区和扩展分区的总数不能超过4个(P+E<=4),而且规定扩展分区最多只能有一个(E<=1)。
所以,当我们需要划分超过4个分区的时候,我们就需要先划分一个扩展分区,然后在扩展分区上去划分逻辑分区。
四、磁盘管理
1.图形界面管理硬盘
1)添加一块硬盘
我们为虚拟机添加一个新的虚拟硬盘,相当于给物理机新添加一块硬盘。
2)打开图形化磁盘管理

如下图,可以看到,我们新添加的硬盘,大小为20G(这里显示21G,是因为Linux下计算的磁盘大小不是1024,而是1000)。

3)格式化硬盘
点击右上角的菜单,选择格式化磁盘:

第一项Erase,我们默认即可(速度更快,没必要初始化为0)。
第二项,就是让我们选择磁盘格式化的类别,MBR或GPT结构:
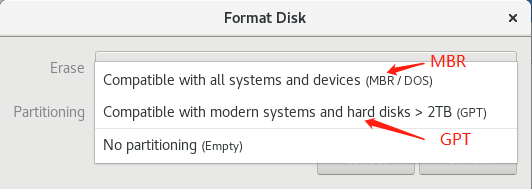
MBR的兼容性更好,GPT对大硬盘支持比较好。这里我们选择GPT结构。
格式化后,我们可以看到分区表为GUID分区表:
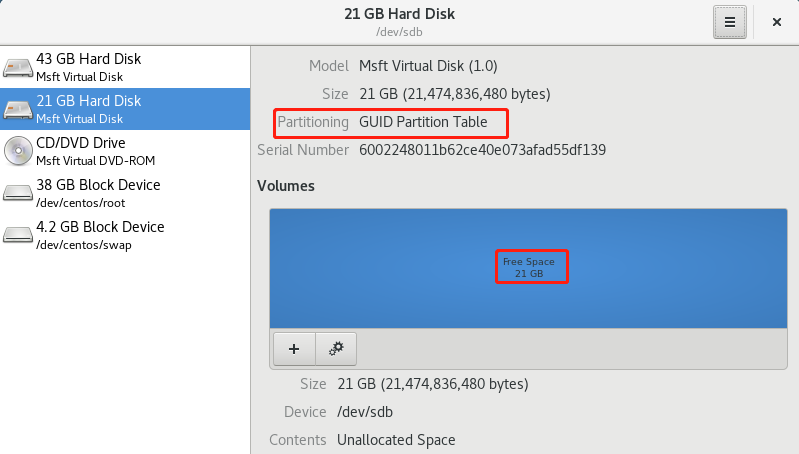
如果想将其变为MBR结构磁盘, 则再次格式化即可。
注意:
这个选择格式化磁盘类型的过程叫做"初始化磁盘标签"。
2.命令行磁盘管理
有以下三个命令可以用于磁盘管理:
- fdisk:用于管理MBR结构磁盘
- gdisk:用于管理GPT结构磁盘
- parted:兼而有之
1)parted命令修改磁盘标签
首先,我们要明确我们新添加的磁盘为 /dev/sdb
- [root@centos7 ~]# parted -s /dev/sdb mklabel msdos
"-s"表示忽略确认提示,/dev/sdb是我们要修改标签的磁盘,mklabel表示修改标签, msdos 表示MBR结构。
- [root@centos7 ~]# parted -s /dev/sdb mklabel gpt
从MBR修改回GPT结构。
如果想将磁盘恢复到既不是MBR也不是GPT结构:
- [root@centos7 ~]# parted -s /dev/sdb mklabel loop
2)fdisk查看所有磁盘信息
- [root@centos7 ~]# fdisk -l
- WARNING: fdisk GPT support is currently new, and therefore in an experimental phase. Use at your own discretion.
- Disk /dev/sda: 42.9 GB, bytes, sectors
- Units = sectors of * = bytes
- Sector size (logical/physical): bytes / bytes
- I/O size (minimum/optimal): bytes / bytes
- Disk label type: gpt
- Disk identifier: 6517A95B-8EB4--9FF6-9962100D1695
- # Start End Size Type Name
- 200M EFI System EFI System Partition
- 500M Microsoft basic
- .3G Linux LVM
- Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, bytes, sectors
- Units = sectors of * = bytes
- Sector size (logical/physical): bytes / bytes
- I/O size (minimum/optimal): bytes / bytes
- Disk label type: dos
- Disk identifier: 0x000b2546
- Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
- Disk /dev/mapper/centos-root: 38.0 GB, bytes, sectors
- Units = sectors of * = bytes
- Sector size (logical/physical): bytes / bytes
- I/O size (minimum/optimal): bytes / bytes
- Disk /dev/mapper/centos-swap: MB, bytes, sectors
- Units = sectors of * = bytes
- Sector size (logical/physical): bytes / bytes
- I/O size (minimum/optimal): bytes / bytes
可以看到,sda和sdb磁盘。
3)只查看某个磁盘的信息
- [root@centos7 ~]# fdisk -l /dev/sdb
- Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, bytes, sectors
- Units = sectors of * = bytes
- Sector size (logical/physical): bytes / bytes
- I/O size (minimum/optimal): bytes / bytes
- Disk label type: dos
- Disk identifier: 0x000b2546
- Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
3.使用fdisk对sdb进行分区
注意,这是是对sdb磁盘进行分区,分区后每个分区叫sdb1、sdb2等等。
1)查看所有actions
- [root@centos7 ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb
- The device presents a logical sector size that is smaller than
- the physical sector size. Aligning to a physical sector (or optimal
- I/O) size boundary is recommended, or performance may be impacted.
- Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.).
- Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
- Be careful before using the write command.
- Command (m for help): m # 查看所有action
- Command action
- a toggle a bootable flag
- b edit bsd disklabel
- c toggle the dos compatibility flag
- d delete a partition # 删除一个分区
- g create a new empty GPT partition table
- G create an IRIX (SGI) partition table
- l list known partition types # 查看分区类型
- m print this menu # 查看当前菜单
- n add a new partition # 创建一个新分区
- o create a new empty DOS partition table
- p print the partition table # 查看分区表
- q quit without saving changes # 相当于q!,不保存退出
- s create a new empty Sun disklabel
- t change a partition's system id
- u change display/entry units
- v verify the partition table
- w write table to disk and exit # 相当于wq,保存并退出
- x extra functionality (experts only)
- Command (m for help):
2)使用操作"p",查看分区表
- # 查看sda磁盘的分区信息
- Command (m for help): p
- Disk /dev/sda: 42.9 GB, bytes, sectors
- Units = sectors of * = bytes
- Sector size (logical/physical): bytes / bytes
- I/O size (minimum/optimal): bytes / bytes
- Disk label type: gpt
- Disk identifier: 6517A95B-8EB4--9FF6-9962100D1695
- # Start End Size Type Name
- 200M EFI System EFI System Partition
- 500M Microsoft basic
- .3G Linux LVM
可以看到在sda中,存在分区信息。
- # 查看sdb磁盘的分区信息
- Command (m for help): p
- Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, bytes, sectors
- Units = sectors of * = bytes
- Sector size (logical/physical): bytes / bytes
- I/O size (minimum/optimal): bytes / bytes
- Disk label type: dos
- Disk identifier: 0x000b2546
- Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
sdb暂时没有分区。
3)使用"n"新建分区
- Command (m for help): n
- Partition type:
- p primary ( primary, extended, free)
- e extended
- Select (default p):
可以看到,可以创建的分区有两种类型,primary主分区,和extended扩展分区(扩展分区可以创建逻辑分区)。
我们创建一个主分区:
- Command (m for help): n
- Partition type:
- p primary ( primary, extended, free)
- e extended
- Select (default p): p # 选择创建主分区
- Partition number (-, default ): 1 # 默认编号为1,即sdb1
- First sector (-, default ): 2048 # 开始扇区为2048
- Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (-, default ): 4196351 # 结束扇区为4196351,即从2048开始一共2G空间
- Partition of type Linux and of size GiB is set
- Command (m for help):
结束扇区的计算:2*1024*1024*2-1 + 2048 = 4196351,即2G = 2*1024M = 2*1024*1024K = 2*1024*1024*2扇区。
这样划分我们发现计算扇区很复杂,我们也可以直接使用+2G来实现:
- Command (m for help): n
- Partition type:
- p primary ( primary, extended, free)
- e extended
- Select (default p): p
- Partition number (-, default ):
- First sector (-, default ):
- Using default value
- Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (-, default ): +2G
- Partition of type Linux and of size GiB is set
当我们创建了4个分区后,则无法再创建了,因为前面说了,MBR分区表中只能保存最多4个分区的信息。
4)创建逻辑分区
假设我们已经创建了2个主分区:
- Command (m for help): p
- Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, bytes, sectors
- Units = sectors of * = bytes
- Sector size (logical/physical): bytes / bytes
- I/O size (minimum/optimal): bytes / bytes
- Disk label type: dos
- Disk identifier: 0x000b2546
- Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
- /dev/sdb1 Linux
- /dev/sdb2 Linux
我们将剩余的未分配空间创建为一个扩展分区:
- Command (m for help): n
- Partition type:
- p primary ( primary, extended, free)
- e extended
- Select (default p): e
- Partition number (,, default ):
- First sector (-, default ):
- Using default value
- Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (-, default ):
- Using default value
- Partition of type Extended and of size GiB is set
- Command (m for help): p
- Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, bytes, sectors
- Units = sectors of * = bytes
- Sector size (logical/physical): bytes / bytes
- I/O size (minimum/optimal): bytes / bytes
- Disk label type: dos
- Disk identifier: 0x000b2546
- Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
- /dev/sdb1 Linux
- /dev/sdb2 Linux
- /dev/sdb3 Extended
此时我们再次使用"n"创建分区:
- Command (m for help): n
- Partition type:
- p primary ( primary, extended, free)
- l logical (numbered from )
- Select (default p): p
- Selected partition
- No free sectors available
因为目前只有3个分区,而分区表可以支持4个分区,所以还可以让我们选择创建主分区,但是空间已经被三个分区占用完了,所以选择p的话,会提示没有剩余的扇区可用。
我们选择"l"来在sdb3上创建逻辑分区:
- Command (m for help): n
- Partition type:
- p primary ( primary, extended, free)
- l logical (numbered from )
- Select (default p): l
- Adding logical partition 5
- First sector (-, default ):
- Using default value
- Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (-, default ): +2G
- Partition of type Linux and of size GiB is set
这里注意,虽然我们只有2个主分区+1个扩展分区,但是逻辑分区的编号始终是从5开始的。也就是说我们的分区中不会存在sdb4这个分区。
我们多创建几个分区,并查看分区信息:
- Command (m for help): p
- Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, bytes, sectors
- Units = sectors of * = bytes
- Sector size (logical/physical): bytes / bytes
- I/O size (minimum/optimal): bytes / bytes
- Disk label type: dos
- Disk identifier: 0x000b2546
- Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
- /dev/sdb1 Linux # 主分区
- /dev/sdb2 Linux # 主分区
- /dev/sdb3 Extended # 扩展分区
- /dev/sdb5 Linux # 逻辑分区
- /dev/sdb6 Linux # 逻辑分区
- /dev/sdb7 Linux # 逻辑分区
- /dev/sdb8 Linux # 逻辑分区
上述信息中,分区除了分为主分区、扩展分区和逻辑分区,还有其他的分类方式,上述的ID就表示分类ID,System中的Linux类型表示可以直接格式化使用的分区(包含主分区和逻辑分区),Extended分区表示逻辑分区(不能直接格式化使用)。
5)分区类型与转换
那么这些类型有哪些呢?我们可以通过"l"来查看:
- Command (m for help): l
- Empty NEC DOS Minix / old Lin bf Solaris
- FAT12 Hidden NTFS Win Linux swap / So c1 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
- XENIX root Plan Linux c4 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
- XENIX usr 3c PartitionMagic OS/ hidden C: c6 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
- FAT16 <32M Venix Linux extended c7 Syrinx
- Extended PPC PReP Boot NTFS volume set da Non-FS data
- FAT16 SFS NTFS volume set db CP/M / CTOS / .
- HPFS/NTFS/exFAT 4d QNX4.x Linux plaintext de Dell Utility
- AIX 4e QNX4.x 2nd part 8e Linux LVM df BootIt
- AIX bootable 4f QNX4.x 3rd part Amoeba e1 DOS access
- a OS/ Boot Manag OnTrack DM Amoeba BBT e3 DOS R/O
- b W95 FAT32 OnTrack DM6 Aux 9f BSD/OS e4 SpeedStor
- c W95 FAT32 (LBA) CP/M a0 IBM Thinkpad hi eb BeOS fs
- e W95 FAT16 (LBA) OnTrack DM6 Aux a5 FreeBSD ee GPT
- f W95 Ext'd (LBA) 54 OnTrackDM6 a6 OpenBSD ef EFI (FAT-12/16/
- OPUS EZ-Drive a7 NeXTSTEP f0 Linux/PA-RISC b
- Hidden FAT12 Golden Bow a8 Darwin UFS f1 SpeedStor
- Compaq diagnost 5c Priam Edisk a9 NetBSD f4 SpeedStor
- Hidden FAT16 < SpeedStor ab Darwin boot f2 DOS secondary
- Hidden FAT16 GNU HURD or Sys af HFS / HFS+ fb VMware VMFS
- Hidden HPFS/NTF Novell Netware b7 BSDI fs fc VMware VMKCORE
- AST SmartSleep Novell Netware b8 BSDI swap fd Linux raid auto
- 1b Hidden W95 FAT3 DiskSecure Mult bb Boot Wizard hid fe LANstep
- 1c Hidden W95 FAT3 PC/IX be Solaris boot ff BBT
- 1e Hidden W95 FAT1 Old Minix
可以看到,这里有非常多的分区类别,我们还可以将分区的类型进行转化,例如将sdb5-sdb8的分区类型全部转化为Linux LVM逻辑卷类型(编号为8e):
- Command (m for help): t
- Partition number (-,-, default ):
- Hex code (type L to list all codes): 8e
- Changed type of partition 'Linux' to 'Linux LVM'
- Command (m for help): t
- Partition number (-,-, default ):
- Hex code (type L to list all codes): 8e
- Changed type of partition 'Linux' to 'Linux LVM'
- Command (m for help): t
- Partition number (-,-, default ):
- Hex code (type L to list all codes): 8e
- Changed type of partition 'Linux' to 'Linux LVM'
- Command (m for help): t
- Partition number (-,-, default ):
- Hex code (type L to list all codes): 8e
- Changed type of partition 'Linux' to 'Linux LVM'
- Command (m for help): p
- Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, bytes, sectors
- Units = sectors of * = bytes
- Sector size (logical/physical): bytes / bytes
- I/O size (minimum/optimal): bytes / bytes
- Disk label type: dos
- Disk identifier: 0x000b2546
- Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
- /dev/sdb1 Linux
- /dev/sdb2 Linux
- /dev/sdb3 Extended
- /dev/sdb5 8e Linux LVM
- /dev/sdb6 8e Linux LVM
- /dev/sdb7 8e Linux LVM
- /dev/sdb8 8e Linux LVM
6)保存分区配置
在我们划分好分区后,要进行保存:
- Command (m for help): w
- The partition table has been altered!
- Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
- Syncing disks.
- [root@centos7 ~]# partprobe /dev/sdb
使用"w"进行保存并退出,然后使用 partprobe /dev/sdb 刷新一个磁盘的分区表(应该是可选操作)。
4.格式化分区
1)在图形界面中查看分区后的磁盘
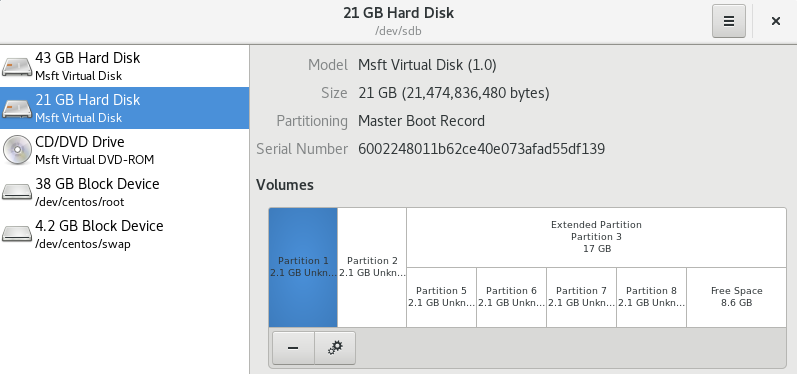
可以看到,我们做好分区后,所有的分区都是unknown状态的,也就是说未格式化。我们要使用的话,必须先格式化。
2)使用图形化界面格式化分区
当然,我们可以在图形界面中进行格式化,并选择格式化的文件系统类型,例如ext4、ntfs、xfs等:

3)使用命令行格式化分区
将sdb1格式化为xfs格式的文件系统:
- [root@centos7 ~]# mkfs -t xfs /dev/sdb1
- meta-data=/dev/sdb1 isize= agcount=, agsize= blks
- = sectsz= attr=, projid32bit=
- = crc= finobt=, sparse=
- data = bsize= blocks=, imaxpct=
- = sunit= swidth= blks
- naming =version bsize= ascii-ci= ftype=
- log =internal log bsize= blocks=, version=
- = sectsz= sunit= blks, lazy-count=
- realtime =none extsz= blocks=, rtextents=
注意在RHEL7或centos7中,默认使用的就是xfs文件系统。
如果我们再次格式化sdb1的话,会提示已经存在一个文件系统:
- [root@centos7 ~]# mkfs -t xfs /dev/sdb1
- mkfs.xfs: /dev/sdb1 appears to contain an existing filesystem (xfs).
- mkfs.xfs: Use the -f option to force overwrite.
这是使用"-f"选项来强制覆盖:
- [root@centos7 ~]# mkfs -t xfs -f /dev/sdb1
- meta-data=/dev/sdb1 isize= agcount=, agsize= blks
- = sectsz= attr=, projid32bit=
- = crc= finobt=, sparse=
- data = bsize= blocks=, imaxpct=
- = sunit= swidth= blks
- naming =version bsize= ascii-ci= ftype=
- log =internal log bsize= blocks=, version=
- = sectsz= sunit= blks, lazy-count=
- realtime =none extsz= blocks=, rtextents=
在格式化时指定文件系统的块大小(block size):
- [root@centos7 ~]# mkfs -t xfs -f -b size= /dev/sdb1
- specified blocksize is less than device physical sector size
- switching to logical sector size
- meta-data=/dev/sdb1 isize= agcount=, agsize= blks
- = sectsz= attr=, projid32bit=
- = crc= finobt=, sparse=
- data = bsize= blocks=, imaxpct=
- = sunit= swidth= blks
- naming =version bsize= ascii-ci= ftype=
- log =internal log bsize= blocks=, version=
- = sectsz= sunit= blks, lazy-count=
- realtime =none extsz= blocks=, rtextents=
可以看到,默认bsize为4096,即4k/block。我们将其修改为了1k/block。
当然,我们也可以使用其他类型的文件系统来格式化分区(例如ext4),操作是类似的(只是重复格式化不需要-f选项,设置block size直接使用-b 1024即可):
- [root@centos7 ~]# mkfs -t ext4 /dev/sdb1
- mke2fs 1.42. (-Dec-)
- Discarding device blocks: done
- Filesystem label=
- OS type: Linux
- Block size= (log=)
- Fragment size= (log=)
- Stride= blocks, Stripe width= blocks
- inodes, blocks
- blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
- First data block=
- Maximum filesystem blocks=
- block groups
- blocks per group, fragments per group
- inodes per group
- Superblock backups stored on blocks:
- , , , ,
- Allocating group tables: done
- Writing inode tables: done
- Creating journal ( blocks): done
- Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
- [root@centos7 ~]# mkfs -t ext4 -b /dev/sdb1
- mke2fs 1.42. (-Dec-)
- Warning: specified blocksize is less than device physical sectorsize
- Discarding device blocks: done
- Filesystem label=
- OS type: Linux
- Block size= (log=)
- Fragment size= (log=)
- Stride= blocks, Stripe width= blocks
- inodes, blocks
- blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
- First data block=
- Maximum filesystem blocks=
- block groups
- blocks per group, fragments per group
- inodes per group
- Superblock backups stored on blocks:
- , , , , , , , , ,
- ,
- Allocating group tables: done
- Writing inode tables: done
- Creating journal ( blocks): done
- Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
如果我们不记得文件系统的种类,则可以使用以下方式:
- [root@centos7 ~]# mkfs.
- mkfs.btrfs mkfs.cramfs mkfs.ext2 mkfs.ext3 mkfs.ext4 mkfs.fat mkfs.minix mkfs.msdos mkfs.vfat mkfs.xfs
- [root@centos7 ~]# mkfs.xfs -b size= -f /dev/sdb1
- specified blocksize is less than device physical sector size
- switching to logical sector size
- meta-data=/dev/sdb1 isize= agcount=, agsize= blks
- = sectsz= attr=, projid32bit=
- = crc= finobt=, sparse=
- data = bsize= blocks=, imaxpct=
- = sunit= swidth= blks
- naming =version bsize= ascii-ci= ftype=
- log =internal log bsize= blocks=, version=
- = sectsz= sunit= blks, lazy-count=
- realtime =none extsz= blocks=, rtextents=
使用 mkfs. 按tab,可以看到区分文件系统种类的命令,我们直接使用对应的命令即可。其中mkfs.vfat主要用于U盘,
4)自动挂载分区时要注意文件系统类型
例如,我们要在开机时将sdb1自动挂载到/zz目录,需要修改 /etc/fstab 文件:
- #
- # /etc/fstab
- # Created by anaconda on Sun Mar ::
- #
- # Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
- # See man pages fstab(), findfs(), mount() and/or blkid() for more info
- #
- /dev/mapper/centos-root / xfs defaults
- UUID=01923e22---be98-c22b7ea968fb /boot xfs defaults
- UUID=7AB0-876A /boot/efi vfat umask=,shortname=winnt
- /dev/mapper/centos-swap swap swap defaults
- /dev/sdb1 /zz xfs defaults
可以看到,我们填写了一个xfs文件系统,这个文件系统类型一定要和我们挂载的分区真正的类型对应起来,不能乱写,否则可能启动不起来。
那么,如何来查看这个分区是什么文件系统类型呢?我们可以先手动挂载一下:
- [root@centos7 ~]# mount /dev/sdb1 /zz
- [root@centos7 ~]# df -hT
- Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
- devtmpfs devtmpfs .9G .9G % /dev
- tmpfs tmpfs .9G .9G % /dev/shm
- tmpfs tmpfs .9G 11M .9G % /run
- tmpfs tmpfs .9G .9G % /sys/fs/cgroup
- /dev/mapper/centos-root xfs 36G .1G 30G % /
- /dev/sda2 xfs 494M 165M 330M % /boot
- /dev/sda1 vfat 200M 12M 189M % /boot/efi
- tmpfs tmpfs 376M 40K 376M % /run/user/
- /dev/sr0 iso9660 603M 603M % /run/media/root/CentOS x86_64
- /dev/sdb1 xfs .0G 8.1M .0G % /zz
然后使用df -hT就能看到/dev/sdb1的文件系统类型,这时,我们就可以确认在/etc/fstab中的文件系统类型应该写什么了。
或者使用另外一个命令来直接查看某分区的文件系统类型:
- [root@centos7 ~]# blkid
- /dev/sr0: UUID="2015-12-09-23-03-16-00" LABEL="CentOS 7 x86_64" TYPE="iso9660" PTTYPE="dos"
- /dev/sda1: SEC_TYPE="msdos" UUID="7AB0-876A" TYPE="vfat" PARTLABEL="EFI System Partition" PARTUUID="fda2bd89-9fac-4cee-b8b5-780a6466315c"
- /dev/sda2: UUID="01923e22-2135-4842-be98-c22b7ea968fb" TYPE="xfs" PARTUUID="7c29241e-5889-4230-a40e-cffcc9197fd8"
- /dev/sda3: UUID="tsFdS0-5pvC-QqsQ-BwwB-3IAq-xhR8-bjVpiM" TYPE="LVM2_member" PARTUUID="6fe109b5-9b12-4ddf-828d-7b9cf63adbb1"
- /dev/sdb1: UUID="62ff7ea9-5d3d-4bfd-bedb-bcddf6e408f0" TYPE="xfs"
- /dev/sdb5: LABEL="my lvm 1" UUID="55aadc7b-b3ab-4f65-9efb-2d80f07721b2" TYPE="ext4"
- /dev/sdb6: LABEL="my lvm 2" UUID="9a231e33-0304-4009-b4e6-7bdd31b80fb6" TYPE="xfs"
- /dev/mapper/centos-root: UUID="5fed2a74-322a-4526-a222-8ae21f501cfb" TYPE="xfs"
- /dev/mapper/centos-swap: UUID="900351e0-6257-4ea6-a614-c9a30bead9f4" TYPE="swap"
5)如何查看分区文件系统信息(例如查看block size)
- [root@centos7 ~]# xfs # 按tab
- xfs_admin xfs_copy xfsdump xfs_freeze xfs_growfs xfsinvutil xfs_logprint xfs_metadump xfs_ncheck xfs_repair xfs_rtcp
- xfs_bmap xfs_db xfs_estimate xfs_fsr xfs_info xfs_io xfs_mdrestore xfs_mkfile xfs_quota xfsrestore
- [root@centos7 ~]# xfs_info /dev/sdb1 # 这里只用挂载点也可以查看
- meta-data=/dev/sdb1 isize= agcount=, agsize= blks
- = sectsz= attr=, projid32bit=
- = crc= finobt= spinodes=
- data = bsize= blocks=, imaxpct=
- = sunit= swidth= blks
- naming =version bsize= ascii-ci= ftype=
- log =internal bsize= blocks=, version=
- = sectsz= sunit= blks, lazy-count=
- realtime =none extsz= blocks=, rtextents=
当我们确定该分区的文件系统是xfs类型的,就可以使用xfs_*命令来进行相应的操作。
6)分区的UUID
每个分区格式化后都有一个UUID,我们可以通过blkid来查看:
- [root@centos7 ~]# blkid
- /dev/sr0: UUID="2015-12-09-23-03-16-00" LABEL="CentOS 7 x86_64" TYPE="iso9660" PTTYPE="dos"
- /dev/sda1: SEC_TYPE="msdos" UUID="7AB0-876A" TYPE="vfat" PARTLABEL="EFI System Partition" PARTUUID="fda2bd89-9fac-4cee-b8b5-780a6466315c"
- /dev/sda2: UUID="01923e22-2135-4842-be98-c22b7ea968fb" TYPE="xfs" PARTUUID="7c29241e-5889-4230-a40e-cffcc9197fd8"
- /dev/sda3: UUID="tsFdS0-5pvC-QqsQ-BwwB-3IAq-xhR8-bjVpiM" TYPE="LVM2_member" PARTUUID="6fe109b5-9b12-4ddf-828d-7b9cf63adbb1"
- /dev/sdb1: UUID="62ff7ea9-5d3d-4bfd-bedb-bcddf6e408f0" TYPE="xfs"
- /dev/sdb5: LABEL="my lvm 1" UUID="55aadc7b-b3ab-4f65-9efb-2d80f07721b2" TYPE="ext4"
- /dev/sdb6: LABEL="my lvm 2" UUID="9a231e33-0304-4009-b4e6-7bdd31b80fb6" TYPE="xfs"
- /dev/mapper/centos-root: UUID="5fed2a74-322a-4526-a222-8ae21f501cfb" TYPE="xfs"
- /dev/mapper/centos-swap: UUID="900351e0-6257-4ea6-a614-c9a30bead9f4" TYPE="swap"
也可以通过以下命令来查看:
- [root@centos7 ~]# xfs_admin -u /dev/sdb1
- UUID = 62ff7ea9-5d3d-4bfd-bedb-bcddf6e408f0
我们在进行自动挂载配置/etc/fstab时,也可以直接使用UUID进行配置:
- /dev/mapper/centos-root / xfs defaults
- UUID=01923e22---be98-c22b7ea968fb /boot xfs defaults
- UUID=7AB0-876A /boot/efi vfat umask=,shortname=winnt
- /dev/mapper/centos-swap swap swap defaults
- UUID=62ff7ea9-5d3d-4bfd-bedb-bcddf6e408f0 /zz xfs defaults
这样也可以将/dev/sdb1成功挂载到/zz下。
UUID也是可以被修改的:
- [root@centos7 ~]# uuidgen # 生成一个新的UUID
- 37f9713b-fb33-41da-9c9f-599d722523d2
- [root@centos7 ~]# umount /zz # 首先要卸载,才能修改UUID
- [root@centos7 ~]# xfs_admin -U 37f9713b-fb33-41da-9c9f-599d722523d2 /dev/sdb1 # 修改/dev/sdb1的UUID为新的UUID
- Clearing log and setting UUID
- writing all SBs
- new UUID = 37f9713b-fb33-41da-9c9f-599d722523d2
再次查看/dev/sdb1的UUID:
- [root@centos7 ~]# xfs_admin -u /dev/sdb1
- UUID = 37f9713b-fb33-41da-9c9f-599d722523d2
可以看到,UUID修改成功。
UUID一般什么使用?
·在我们使用网络设备的时候,例如iSCSI,磁盘有可能窜位,例如不同时间同一个设备的名字不一样,这是就要使用唯一的UUID来挂载这个设备。
5.什么是swap分区
swap叫交换分区,相当于windows中的虚拟内存。是一个比较老的技术,主要用于解决内存多小的问题。
什么使用使用swap:
虽然swap分区模拟内存,帮助内存存放一些不那么重要的实时数据,但并不是在内存完全使用完后才启用swap的,何时使用swap分区,是由一定策略的(例如物理内存使用比例,可以配置的)。
1)关于内存配置文件
- [root@centos7 ~]# ls /proc/sys/vm/
- admin_reserve_kbytes dirty_bytes extfrag_threshold lowmem_reserve_ratio min_slab_ratio nr_hugepages oom_dump_tasks page-cluster user_reserve_kbytes
- block_dump dirty_expire_centisecs hugepages_treat_as_movable max_map_count min_unmapped_ratio nr_hugepages_mempolicy oom_kill_allocating_task panic_on_oom vfs_cache_pressure
- compact_memory dirty_ratio hugetlb_shm_group memory_failure_early_kill mmap_min_addr nr_overcommit_hugepages overcommit_kbytes percpu_pagelist_fraction zone_reclaim_mode
- dirty_background_bytes dirty_writeback_centisecs laptop_mode memory_failure_recovery mmap_rnd_bits nr_pdflush_threads overcommit_memory stat_interval
- dirty_background_ratio drop_caches legacy_va_layout min_free_kbytes mmap_rnd_compat_bits numa_zonelist_order overcommit_ratio swappiness
这个目录中的文件都是关于内存的系统文件。
2)设置启用swap内存的时机
查看swap在内存使用多少比例的时候启用:
- [root@centos7 vm]# cat /proc/sys/vm/swappiness
当物理内存使用比例达到100-swappiness的值时,则启用swap,默认即70%。
3)是否可以不创建swap
我们应该要创建swap分区,因为系统能够分配的虚拟内存总大小,其中包含了swap分区的大小。
查看当前内存可分配总大小和已分配总大小:
- [root@centos7 vm]# watch -n . 'grep -i commit' /proc/meminfo
- Every .5s: grep -i commit /proc/meminfo Mon Mar ::
- CommitLimit: kB
- Committed_AS: kB
每0.5秒刷新一下数据,可以看到CommitLimit是当前内存可分配的总大小(我们实际物理内存是4G,swap分区是4G),但这里是6G。
已经分配出去的内存为Commited_AS,大小为3G+。
查看默认可分配物理内存比例:
- [root@centos7 vm]# cat overcommit_ratio
可分配内存总大小计算公式:
- CommitLimit = 物理内存总大小 * overcommit_ratio% + swap大小
这里计算出来就是:
- CommitLimit = 4G * % + 4G = 6G
当然我们可以对overcommit_ratio等内核参数进行调整,从而优化内存。如果要想使用全量的物理内存,则可以将overcommit_memory修改为1。
4)swap设置为多大比较合适
在企业中,一般都将swap设置得和物理内存一样大(硬盘成本比较低)。
当然我们应该根据具体的需求来设置swap的大小,如果大小不够,后期还可以调整(例如再添加一个swap分区)。
5)查看当前swap分区信息
查看当前swap分区:
- [root@centos7 vm]# swapon -s
- Filename Type Size Used Priority
- /dev/dm- partition -
- [root@centos7 vm]# cat /proc/swaps
- Filename Type Size Used Priority
- /dev/dm- partition -
这两种方式都可以查看当前swap分区的信息。我们看到当前swap分区的大小为4G。
6)添加一个swap分区
查看当前sdb磁盘上的分区:
- [root@centos7 vm]# fdisk -l
- WARNING: fdisk GPT support is currently new, and therefore in an experimental phase. Use at your own discretion.
- Disk /dev/sda: 42.9 GB, bytes, sectors
- Units = sectors of * = bytes
- Sector size (logical/physical): bytes / bytes
- I/O size (minimum/optimal): bytes / bytes
- Disk label type: gpt
- Disk identifier: 6517A95B-8EB4--9FF6-9962100D1695
- # Start End Size Type Name
- 200M EFI System EFI System Partition
- 500M Microsoft basic
- .3G Linux LVM
- Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, bytes, sectors
- Units = sectors of * = bytes
- Sector size (logical/physical): bytes / bytes
- I/O size (minimum/optimal): bytes / bytes
- Disk label type: dos
- Disk identifier: 0x000b2546
- Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
- /dev/sdb1 Linux
- /dev/sdb2 Linux swap / Solaris
- /dev/sdb3 Extended
- /dev/sdb5 Linux
- /dev/sdb6 Linux
- /dev/sdb7 8e Linux LVM
- /dev/sdb8 8e Linux LVM
- Disk /dev/mapper/centos-root: 38.0 GB, bytes, sectors
- Units = sectors of * = bytes
- Sector size (logical/physical): bytes / bytes
- I/O size (minimum/optimal): bytes / bytes
- Disk /dev/mapper/centos-swap: MB, bytes, sectors
- Units = sectors of * = bytes
- Sector size (logical/physical): bytes / bytes
- I/O size (minimum/optimal): bytes / bytes
我们将sdb2分区的类型修改为Linux swap类型。然后将其启用为swap分区:
- [root@centos7 vm]# mkswap /dev/sdb2
- Setting up swapspace version , size = KiB
- no label, UUID=d8a1c50b-ff7d-435b--5906513a1300
mkswap相当于格式化,将其作为swap分区。
启用该swap分区:
- [root@centos7 vm]# swapon /dev/sdb2
查看当前swap分区:
- [root@centos7 vm]# swapon -s
- Filename Type Size Used Priority
- /dev/dm- partition -
- /dev/sdb2 partition -
可以看到,/dev/sdb2已经被作为swap分区使用,目前的swap分区总大小为6G。
这里注意这两个swap分区的优先级,分别为-2和-3,值越大的优先被使用,这里-2大于-3,所以/dev/dm-1优先使用。当然我们也可以修改其优先级,自定义哪个先被使用。
7)调整swap分区的使用优先级
首先要关闭需要调整的swap分区:
- [root@centos7 vm]# swapoff /dev/sdb2
然后重新启动它时,指定优先级数值:
- [root@centos7 vm]# swapon -p /dev/sdb2
再次查看:
- [root@centos7 vm]# swapon -s
- Filename Type Size Used Priority
- /dev/dm- partition -
- /dev/sdb2 partition 1
这是/dev/sdb2的优先级大于/dev/dm-1的优先级,所有/dev/sdb2优先被使用。
8)自动挂载swap分区
前面我们使用swapon将/dev/sdb2作为swap分区使用,但这个配置是临时生效的,当重启后就失效了。
想要让其自动生效,则还是配置/etc/fstab文件:
- /dev/mapper/centos-root / xfs defaults
- UUID=01923e22---be98-c22b7ea968fb /boot xfs defaults
- UUID=7AB0-876A /boot/efi vfat umask=,shortname=winnt
- /dev/mapper/centos-swap swap swap defaults
- UUID=62ff7ea9-5d3d-4bfd-bedb-bcddf6e408f0 /zz xfs defaults
- /dev/sdb2 swap swap defaults,pri=1
参考前面系统默认配置的swap分区,我们添加一条在最后即可。这里使用 pri= 来指定优先级。
手工触发以下自动挂载:
- # mount -a 自动挂载普通分区
- swapon -a # 自动挂载swap分区
9)将一个文件作为swap分区
当我们swap不够用的时候,但是又没有新的分区可以用来扩展。此时就可以创建一个文件来充当swap分区。
首先创建一个文件:
- [root@centos7 /]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/swpfile bs=1M count=
- + records in
- + records out
- bytes ( MB) copied, 0.0591268 s, 3.5 GB/s
创建了一个200M的文件空间。
修改权限为600:
- [root@centos7 /]# chmod /swpfile
初始化并使用:
- [root@centos7 /]# mkswap /swpfile
- Setting up swapspace version , size = KiB
- no label, UUID=e60b4a09-5c5a--abdf-b336addaab96
- [root@centos7 /]# swapon /swpfile
这样就将一个文件作为swap分区使用了。注意这个文件是位于根目录下的,也就是说这部分空间位于逻辑卷 /dev/mapper/centos-root (该逻辑卷挂载到根目录"/"下的)。
其实,在windows下就是以这种方式使用的虚拟内存。在windows下有一个文件叫 pagefile.sys ,这个文件就是充当swap交换分区(虚拟内存)的效果。
windows移动该文件参考:https://jingyan.baidu.com/article/5d368d1e8d4b0c3f61c05764.html
====
[RH134] 8-磁盘管理的更多相关文章
- liunx 磁盘管理命令记录
Linux磁盘管理好坏管理直接关系到整个系统的性能问题. Linux磁盘管理常用三个命令为df.du和fdisk. df:列出文件系统的整体磁盘使用量 du:检查磁盘空间使用量 fdisk:用于磁盘分 ...
- Windows Server 2012 磁盘管理之 简单卷、跨区卷、带区卷、镜像卷和RAID-5卷
今天给客户配置故障转移群集,在Windows Server 2012 R2的系统上,通过iSCSI连接上DELL的SAN存储后,在磁盘管理里面发现可以新建 简单卷.跨区卷.带区卷.镜像卷.RAID-5 ...
- Linux常用命令学习7---(磁盘管理df du、磁盘的分区和格式化fdisk parted)
1.磁盘管理 在服务器的维护中,我们需要关心服务器的磁盘使用了多少.还有多少的剩余空间.某个文件有多大.某个文件夹内的所有文件在一起一共占用的多少空间……问题.以便我们在合适的时机为服务器添加硬 ...
- LINUX的磁盘管理du命令详解
LINUX的磁盘管理du命令详解 du(disk usage)命令可以计算文件或目录所占的磁盘空间.没有指定任何选项时, 它会测量当前工作目录与其所有子目录,分别显示各个目录所占的快数,最后才显示工作 ...
- 用Win7自带的磁盘管理工具给硬盘分区
最近新买了一台笔记本,要给硬盘分几个区,心想还是用个工具方便点,于是就上网准备下个“硬盘分区魔术师”,但是看到有一篇文章介绍Win7系统也自带了硬盘分区工具,这我以前倒没听说过,试了一下,还挺方便好用 ...
- Linux_磁盘管理
一.linux磁盘管理 命令:fdisk -l brwx-rw--- 其中b(占位符)代表block,块设备文件 sda,sdb... --> 硬盘 其中sda1,sda2..sdb1,sdb2 ...
- Linux 磁盘管理
Linux磁盘管理好坏管理直接关系到整个系统的性能问题. Linux磁盘管理常用三个命令为df.du和fdisk. df:列出文件系统的整体磁盘使用量 du:检查磁盘空间使用量 fdisk:用于磁盘分 ...
- Linux_06------Linux的磁盘管理
进制编码 * 3.格式化交换分区 * 4.启用交换分区 * * 1.2. * fdisk /dev/sdb * p * t * 6(分区编号) * L(查看编码列表),找到SWAP交换分区标号 * 8 ...
- Linux 系统常用命令汇总(五) 磁盘管理
磁盘管理 命令 选项 注解 示例 df [选项] 显示磁盘空间使用情况 显示磁盘空间是员工情况,以M显示: df -m -i 使用inodes显示结果 -k(m) 使用KB(MB)显示结果 du ...
- Linux命令工具基础04 磁盘管理
Linux命令工具基础04 磁盘管理 日程磁盘管理中,我们最常用的有查看当前磁盘使用情况,查看当前目录所占大小,以及打包压缩与解压缩: 查看磁盘空间 查看磁盘空间利用大小 df -h -h: huma ...
随机推荐
- jQuery学习笔记——jQuery基础核心
代码风格 在jQuery程序中,不管是页面元素的选择.内置的功能函数,都是美元符号“$”来起始的.而这个“$”就是jQuery当中最重要且独有的对象:jQuery对象,所以我们在页面元素选择或执行功能 ...
- hdu4035 Maze 题解
/* 设 E[i]表示在结点i处,要走出迷宫所要走的边数的期望. E[i] = ki*E[1] + (1-ki-ei)*E[fa[i]] + (1-ki-ei); E[i] = ki*E[1] + ( ...
- .Net Core3.0 WebApi 项目框架搭建 四:JWT权限验证
.Net Core3.0 WebApi 项目框架搭建:目录 什么是JWT 根据维基百科定义,JWT(读作 [/dʒɒt/]),即JSON Web Tokens,是一种基于JSON的.用于在网络上声明某 ...
- Java Mail 发送带有附件的邮件
1.小编用的是163邮箱发送邮件,所以要先登录163邮箱开启POP3/SMTP/IMAP服务方法: 2.下载所需的java-mail 包 https://maven.java.net/content/ ...
- Django之forms.Form
django中的form组件提供了普通表单提交及验证数据的主要功能: 1. 生成页面可用的HTML标签 2. 对用户提交的数据进行验证 3. 可保留用户上次提交的数据 django中 ...
- STM32 HAL库学习系列---定时器TIM 输入捕获功能
基本方法 1.设置TIM2 CH1为输入捕获功能: 2.设置上升沿捕获: 3.使能TIM2 CH1捕获功能: 4.捕获到上升沿后,存入capture_buf[0],改为捕获下降沿: 5.捕获到下降沿后 ...
- 存储系列之 Linux ext2 概述
引言:学习经典永不过时. 我们之前介绍过存储介质主要是磁盘,先介绍过物理的,后又介绍了虚拟的.保存在磁盘上的信息一般采用文件(file)为单位,磁盘上的文件必须是持久的,同时文件是通过操作系统管理的, ...
- Java——用程序编译一个文件夹下所有java文件到另一个文件夹下
package com.java.test.a; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Ar ...
- 关于mobileSelect.js日期数据获取封装,动态时间,封装
传入起始年份和起始月份 得到 插件的标准格式放到 效果 let getAllDatas = (stime, etime) => { //接收传进来的参数月份 var data_M = etime ...
- js 滚动条滑动
toTop() { let top = document.documentElement.scrollTop || document.body.scrollTop; // 实现滚动效果 const t ...
