Vuex原理实现
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。
思考问题
- Vuex 只在更实例引入了,那么它是如何在每个子组件中都能使用的?
- Vuex 是一个插件,为什么更改了Vuex中的state,会触发视图的跟新?
vuex原理
vuex 是vue的状态管理工具,目的是为了更方便实现多个组件之间的状态共享
vuex的工作原理, Vuex 官方文档 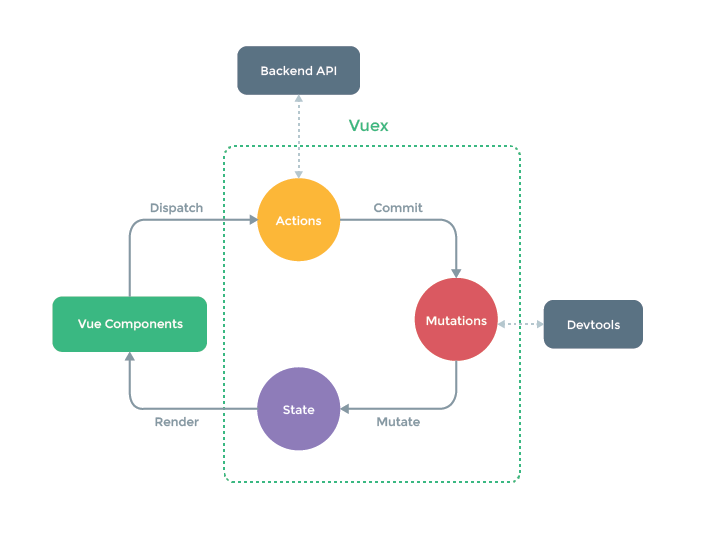
vuex实现
新建一个vuex文件,导出一个store对象
let Vue;
class Store { }
const install = (_Vue) => {
Vue = _Vue;
} export default {
// 这方法在use的时候默认会被调用
install,
Store
}使用混合,在创建组件之前,将vuex实例挂载到vue的实例上
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() {
// 需要拿到store,给每个组件都增加 $store 属性
// 为什么不直接给Vue.prototype 上增加?是因为可能会new 好多个Vue的实例,在别的实例上不需要store
if (this.$options && this.$options.store) {
this.$store = this.$options.store;
} else {
// 这里判断一下,如果单独创建了一个实例没有parent
this.$store = this.$parent && this.$parent.$store;
}
}
});获取
new Store传入的对象class Store {
constructor(options = {}) {
// 将用户的状态放入到 store 中
this.state = options.state; // 获取计算属性
let getters = options.getters;
this.getters = {};
Object.keys(getters).forEach(getterName => {
Object.defineProperty(this.getters, getterName, {
get: () => {
return getters[getterName](this.state);
}
});
});
}
}将
state的数据变成响应式的数据class Store {
constructor(options = {}) {
// Vuex 的核心,定义了响应式变化,数据更新之后更新视图
this._vm = new Vue({
data() {
return {
state: options.state
};
}
});
}
// 类的属性访问器
get state() {
return this._vm.state;
}
}通过触发
mutations更改状态// 通过 this.commit() 触发更改
mutations: {
syncAdd(state, payload) {
state.age += payload;
}
} // 通过发布订阅的模式
class Store {
constructor(options = {}) {
let mutations = options.mutations;
this.mutations = {};
Object.keys(mutations).forEach(mutationName => {
// 订阅所有的mutations
this.mutations[mutationName] = (payload) => {
// 内部的第一个参数是状态
mutations[mutationName](this.state, payload);
}
});
}
// 提交更改,会在当前的 store 上找到对应的函数执行
// 发布
commit = (mutationName, payload) => { // 保证this
this.mutations[mutationName](payload);
}
}内部封装的
forEach, 减少重复代码const forEachValue = (obj, fn) => {
Object.keys(obj).forEach(key => {
fn(key, obj[key]);
});
}; // 对上面的 getters 改造下
forEachValue(getters, (gettersName, fn) => {
Object.defineProperty(this.getters, getterName, {
get: () => {
return fn(this.state);
}
});
}); // 对上面的mutations 改造下
forEachValue(mutations, (mutationName, fn) => {
this.mutations[mutationName] = (payload) => {
fn(this.state, payload);
}
})通过触发
action异步跟新转态action 异步提交更改,异步操作完之后提交到mutation中
例:actions: {
asyncMinus({ commit }, payload) {
setTimeout(() => {
commit('syncMinus', payload);
}, 1000);
}
}
mutations: {
syncMinus(state, payload) {
state.age -= payload;
}
} // 也是一个发布订阅模式
class Store {
constructor(options ={}) {
let actions = options.actions;
this.actions = {};
forEachValue(actions, (actionName, fn) => {
this.actions[actionName] = (payload) => {
fn(this, payload);
}
});
}
dispatch = (actionName, payload) => {
// 源码里有一个变量,来控制是否是通过mutation 来更新的转态,不是会抛个警告
this.actions[actionName](payload);
}
}vuex简单实现
let Vue;
const forEachValue = (obj = {}, fn) => {
return Object.keys(obj || {}).forEach(key => {
fn(key, obj[key]);
})
}
class Store {
constructor(options = {}) {
this._vm = new Vue({
data() {
return {
state: options.state
}
}
}); let getters = options.getters;
this.getters = {};
forEachValue(getters, (getterName, fn) => {
Object.defineProperty(this.getters, getterName, {
get: () => {
return fn(this.state);
}
});
}); // mutations
let mutations = options.mutations;
this._mutations = {};
// 订阅
forEachValue(mutations, (mutationName, fn) => {
this._mutations[mutationName] = (paylod) => {
fn(this.state, paylod);
}
}); // actions
let actions = options.actions;
this._actions = {};
forEachValue(actions, (actionName, fn) => {
this._actions[actionName] = (paylod) => {
fn(this, paylod);
}
});
}
// 发布
commit = (mutationName, paylod) => {
this._mutations[mutationName](paylod);
}
dispatch = (actionName, paylod) => {
this._actions[actionName](paylod);
}
get state() {
return this._vm.state;
}
}
const install = (_Vue) => {
Vue = _Vue;
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() {
if (this.$options && this.$options.store) {
this.$store = this.$options.store;
} else {
this.$store = this.$parent && this.$parent.$store;
}
}
});
} export default {
install,
Store
};modules的实现
主要是将mosules里面的数据格式化成我们想要的格式
js { _modules: { root: state: {__ob__: Observer} _children: {} _rawModule: {modules: {…}, state: {…}, getters: {…}, mutations: {…}, actions: {…} } }- 数据格式化
// 在 Store 中定义modules
this._modules = new ModuleCollection(options); // 把数据格式化成我们想要的结构 class ModuleCollection {
constructor(options) { // 模块依赖的收集
this.register([], options); // 注册模块,将模块注册成树结构
}
register(path, rootModule) {
let module = { // 将模块格式化
_rawModule: rootModule,
_children: {},
state: rootModule.state
}
if (path.length === 0) { // 如何是根模块 将这个模块挂载到根实例上
this.root = module;
} else {
// 递归都用reduce方法, 通过_children 属性进行查找
let parent = path.slice(0, -1).reduce((root, current) => {
return root._children[current];
}, this.root);
parent._children[path[path.length - 1]] = module;
}
// 看当前模块是否有modules
if (rootModule.modules) { // 如果有modules 开始重新注册
forEachValue(rootModule.modules, (moduleName, module) => {
this.register(path.concat(moduleName), module);
})
}
}
}- 安装模块
installModule(this, this.state, [], this._modules.root); // 安装模块
const installModule = (store, rootState, path, rootModule) => {
// 将state 挂载到根上
if (path.length > 0) {
let parent = path.slice(0, -1).reduce((root, current) => {
return root[current];
}, rootState);
// vue 不能再对象上增加不存在的属性,否则视图不会更新
// parent.path[path.length - 1] = rootModule.state;
Vue.set(parent, path[path.length - 1], rootModule.state);
}
// getters
let getters = rootModule._rawModule.getters;
if (getters) {
forEachValue(getters, (getterName, fn) => {
Object.defineProperty(store.getters, getterName, {
get() {
// 让getters 执行,将自己的状态传入
return fn(rootModule.state); // 将对应的函数执行
}
});
});
}
// mutations
let mutations = rootModule._rawModule.mutations; // 拿到每个模块里的mutations
if (mutations) {
forEachValue(mutations, (mutationName, fn) => {
let mutations = store._mutations[mutationName] || [];
mutations.push((paylod) => {
fn.call(store, rootModule.state, paylod);
// 发布,让所有的订阅依次执行
store._subscribes.forEach(fn => fn({ type: mutationName, paylod }, rootState))
});
store._mutations[mutationName] = mutations;
});
}
// actions
let actions = rootModule._rawModule.actions; // 拿到每个模块里的mutations
if (actions) {
forEachValue(actions, (actionName, fn) => {
let actions = store._actions[actionName] || [];
actions.push((paylod) => {
fn.call(store, store, paylod);
});
store._actions[actionName] = actions;
});
}
// 循环挂载儿子
forEachValue(rootModule._children, (moduleName, module) => {
installModule(store, rootState, path.concat(moduleName), module);
});
}vuex完整实现
let Vue;
const forEachValue = (obj = {}, fn) => {
return Object.keys(obj || {}).forEach(key => {
fn(key, obj[key]);
});
}
class ModuleCollection {
constructor(options) { // 模块依赖的收集
this.register([], options); // 注册模块,将模块注册成树结构
}
register(path, rootModule) {
let module = { // 将模块格式化
_rawModule: rootModule,
_children: {},
state: rootModule.state
}
if (path.length === 0) { // 如何是根模块 将这个模块挂载到根实例上
this.root = module;
} else {
// 递归都用reduce方法, 通过_children 属性进行查找
let parent = path.slice(0, -1).reduce((root, current) => {
return root._children[current];
}, this.root);
parent._children[path[path.length - 1]] = module;
}
// 看当前模块是否有modules
if (rootModule.modules) { // 如果有modules 开始重新注册
forEachValue(rootModule.modules, (moduleName, module) => {
this.register(path.concat(moduleName), module);
})
}
}
}
// 安装模块
const installModule = (store, rootState, path, rootModule) => {
// 将state 挂载到根上
if (path.length > 0) {
let parent = path.slice(0, -1).reduce((root, current) => {
return root[current];
}, rootState);
// vue 不能再对象上增加不存在的属性,否则视图不会更新
// parent.path[path.length - 1] = rootModule.state;
Vue.set(parent, path[path.length - 1], rootModule.state);
}
// getters
let getters = rootModule._rawModule.getters;
if (getters) {
forEachValue(getters, (getterName, fn) => {
Object.defineProperty(store.getters, getterName, {
get() {
// 让getters 执行,将自己的状态传入
return fn(rootModule.state); // 将对应的函数执行
}
});
});
}
// mutations
let mutations = rootModule._rawModule.mutations; // 拿到每个模块里的mutations
if (mutations) {
forEachValue(mutations, (mutationName, fn) => {
let mutations = store._mutations[mutationName] || [];
mutations.push((paylod) => {
fn.call(store, rootModule.state, paylod);
// 发布,让所有的订阅依次执行
store._subscribes.forEach(fn => fn({ type: mutationName, paylod }, rootState))
});
store._mutations[mutationName] = mutations;
});
}
// actions
let actions = rootModule._rawModule.actions; // 拿到每个模块里的mutations
if (actions) {
forEachValue(actions, (actionName, fn) => {
let actions = store._actions[actionName] || [];
actions.push((paylod) => {
fn.call(store, store, paylod);
});
store._actions[actionName] = actions;
});
}
// 循环挂载儿子
forEachValue(rootModule._children, (moduleName, module) => {
installModule(store, rootState, path.concat(moduleName), module);
});
}
class Store {
constructor(options = {}) {
this._vm = new Vue({
data() {
return {
state: options.state
}
}
});
this.getters = {};
this._mutations = {};
this._actions = {};
this._subscribes = [];
this._modules = new ModuleCollection(options); // 把数据格式化成一个想要的数据结构 // 递归将结果分类
// this 整个store
// this.state 当前的根状态,把模块中的状态放在根上
// [] 是为了递归的初始值
// this._modules.root 是为了从跟模块开始安装
installModule(this, this.state, [], this._modules.root); // plugins
if (!Array.isArray(options.plugins)) {
throw new TypeError('plugins is not Array');
}
options.plugins.forEach(fn => fn(this));
}
// 发布
commit = (mutationName, paylod) => {
this._mutations[mutationName].forEach(fn => fn(paylod));
}
dispatch = (actionName, paylod) => {
this._actions[actionName].forEach(fn => fn(paylod));
}
// 订阅所有的plugins
subscribe = (fn) => {
this._subscribes.push(fn);
}
get state() {
return this._vm.state;
}
}
const install = (_Vue) => {
Vue = _Vue;
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() {
if (this.$options && this.$options.store) {
this.$store = this.$options.store;
} else {
this.$store = this.$parent && this.$parent.$store;
}
}
});
} export default {
install,
Store
};
Vuex原理实现的更多相关文章
- 举个例子去理解vuex(状态管理),通俗理解vuex原理,通过vue例子类比
通俗理解vuex原理---通过vue例子类比 本文主要通过简单的理解来解释下vuex的基本流程,而这也是vuex难点之一. 首先我们先了解下vuex的作用vuex其实是集中的数据管理仓库,相当于数 ...
- vuex原理
Vuex 框架原理与源码分析 vuex状态管理到底是怎样一个原理? 状态管理 Vuex框架原理与源码分析 Vuex实现原理解析 Vue刚出不久,Vuex 就出来了,想请教下Vuex做了什么事情? 个人 ...
- 通俗理解vuex原理---通过vue例子类比
本文主要通过简单的理解来解释下vuex的基本流程,而这也是vuex难点之一. 首先我们先了解下vuex的作用 vuex其实是集中的数据管理仓库,相当于数据库mongoDB,MySQL等,任何组件都可以 ...
- 快速理解 VUEX 原理
1. vuex 的作用: vuex其实是集中的数据管理仓库,相当于数据库mongoDB,MySQL等,任何组件都可以存取仓库中的数据. 2. vuex 流程和 vue 类比: 我们看一下一个简单的vu ...
- Vuex 原理
1.Vuex是什么? 学院派:Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式:集中存储和管理应用的所有组件状态. 理解:以上这4个词是我们理解的关键.状态:什么是状态,我们可以通俗的理 ...
- vuex原理笔记
本文总结自: https://tech.meituan.com/vuex-code-analysis.html, 将要点提炼为笔记,以便不时之需,安不忘危. 核心可分为两部分: 1.vue.use(V ...
- Vuex原理详解
一.Vuex是什么 Vuex是专门为Vuejs应用程序设计的状态管理工具.它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生改变.它集中于MVC模式中的Model层 ...
- 初识vuex
1.简介 vuex是 vue官方推荐的一个状态管理器.当我们遇到很多状态改变时,组件之间的通信就会变得复杂,这时候vuex的强大就展现出来. 我们从vuex的原理以及vuex的api两个部分介绍vue ...
- vuex的学习和理解
初识Vuex: vuex是 vue官方推荐的一个状态管理器,也是vue专用的一个插件.当我们遇到很多状态改变时,组件之间的通信就会变得复杂,这时候vuex的强大就体现出来了. Vuex 应用的核心就是 ...
随机推荐
- java线程池原理解析
五一假期大雄看了一本<java并发编程艺术>,了解了线程池的基本工作流程,竟然发现线程池工作原理和互联网公司运作模式十分相似. 线程池处理流程 原理解析 互联网公司与线程池的关系 这里用一 ...
- LeetCode--Sort Array By Parity && N-Repeated Element in Size 2N Array (Easy)
905. Sort Array By Parity (Easy)# Given an array A of non-negative integers, return an array consist ...
- 在windows环境里,用Docker搭建Redis开发环境(新书第一个章节)
大家都知道高并发分布式组件的重要性,而且如果要进大厂,这些技术不可或缺.但这些技术的学习难点在于,大多数项目里的分布式组件,都是搭建在Linux系统上,在自己的windows机器上很难搭建开发环境,如 ...
- 【Kafka】Producer API
Producer API Kafka官网文档给了基本格式 地址:http://kafka.apachecn.org/10/javadoc/index.html?org/apache/kafka/cli ...
- js 调用webservice及nigix解决跨域问题
前言 我们写一些简单的爬虫的时候会遇到跨域问题,难道我们一定要用后台代理去解决吗? 答案是否定的.python之所以适应爬虫,是因为库真的很好用. 好吧python不是今天的主角,今天的主角是js. ...
- CentOS7 Installing Python3
最近开始学习python. python火了这么久,我终于还是跪舔它了,我是一个跟风的人,学过C.C#.JAVA.PHP,无一例外的浅尝即止,不知道我这双已经近视的眼,确认过的眼神还对不对,希望pyt ...
- hive经典练习题
一.建表和加载数据 1.student表 create table if not exists student(s_id int,s_name string,s_birth string,s_sex ...
- 宽字节XSS跨站攻击
简介 宽字节跨站漏洞多发生在GB系统编码. 对于GBK编码,字符是由两个字节构成,在%df遇到%5c时,由于%df的ascii大于128,所以会自动拼接%5c,吃掉反斜线.而%27 %20小于asci ...
- angular 实现依赖注入
1:首先获取module对象var myAppModule = angular.module('myApp', []); 2:定义对象(类似spring中xml声明bean对象<bean id= ...
- 十分钟看懂AES加密
十分钟看懂AES加密算法 今天看了Moserware的<A Stick Figure Guide to the Advanced Encryption Standard(AES)>收获了不 ...
