[Python & Machine Learning] 学习笔记之scikit-learn机器学习库
1. scikit-learn介绍
scikit-learn是Python的一个开源机器学习模块,它建立在NumPy,SciPy和matplotlib模块之上。值得一提的是,scikit-learn最先是由David Cournapeau在2007年发起的一个Google Summer of Code项目,从那时起这个项目就已经拥有很多的贡献者了,而且该项目目前为止也是由一个志愿者团队在维护着。
scikit-learn最大的特点就是,为用户提供各种机器学习算法接口,可以让用户简单、高效地进行数据挖掘和数据分析。
scikit-learn主页:scikit-learn homepage
2. scikit-learn安装
scikit-learn的安装方法有很多种,而且也是适用于各种主流操作系统,scikit-learn主页上也分别详细地介绍了在不同操作系统下的三种安装方法,具体安装详情请移步至 installing scikit-learn。
在这里,首先向大家推荐一款学习Python的强大的开发环境python(x,y)。python(x,y)是一个基于python的科学计算软件包,它包含集成开发环境Eclipse和Python开发插件pydev、数据交互式编辑和可视化工具spyder,而且还内嵌了Python的基础数据库numpy和高级数学库scipy、3D可视化工具集MayaVi、Python界面开发库PyQt、Python与C/C++混合编译器SWIG。除此之外,python(x,y)配备了丰富齐全的帮助文档,非常方便科研人员使用。
对于像楼主这样,在学校习惯了用Matlab仿真搞科研的学生而言,python(x,y)是学习Python的一个绝佳选择,其中内嵌的spyder提供了类似于Matlab的交互界面,可以很方便地使用。python(x,y)的下载请点击这里:python(x,y)下载。
由于scikit-learn是基于NumPy、SciPy和matplotlib模块的,所以在安装scikit-learn之前必须要安装这3个模块,这就很麻烦。但是,如果你提前像楼主这样安装了python(x,y),它本身已经包含上述的模块,你只需下载与你匹配的scikit-learn版本,直接点击安装即可。
scikit-learn各种版本下载:scikit-learn下载。
3. scikit-learn载入数据集
scikit-learn内包含了常用的机器学习数据集,比如做分类的iris和digit数据集,用于回归的经典数据集Boston house prices。
scikit-learn载入数据集实例:
from sklearn import datasets
iris = datasets.load_iris()
scikit-learn载入的数据集是以类似于字典的形式存放的,该对象中包含了所有有关该数据的数据信息(甚至还有参考文献)。其中的数据值统一存放在.data的成员中,比如我们要将iris数据显示出来,只需显示iris的data成员:
print iris.data
数据都是以n维(n个特征)矩阵形式存放和展现,iris数据中每个实例有4维特征,分别为:sepal length、sepal width、petal length和petal width。显示iris数据:
[[ 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2]
[ 4.9 3. 1.4 0.2]
... ...
[ 5.9 3. 5.1 1.8]]
如果是对于监督学习,比如分类问题,数据中会包含对应的分类结果,其存在.target成员中:
print iris.target
对于iris数据而言,就是各个实例的分类结果:
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2]
4. scikit-learn学习和预测
scikit-learn提供了各种机器学习算法的接口,允许用户可以很方便地使用。每个算法的调用就像一个黑箱,对于用户来说,我们只需要根据自己的需求,设置相应的参数。
比如,调用最常用的支撑向量分类机(SVC):
from sklearn import svm
clf = svm.SVC(gamma=0.001, C=100.) #不希望使用默认参数,使用用户自己给定的参数
print clf
分类器的具体信息和参数:
SVC(C=100.0, cache_size=200, class_weight=None, coef0=0.0, degree=3,
gamma=0.001, kernel='rbf', max_iter=-1, probability=False,
random_state=None, shrinking=True, tol=0.001, verbose=False)
分类器的学习和预测可以分别利用 fit(X,Y) 和 predict(T) 来实现。
例如,将digit数据划分为训练集和测试集,前n-1个实例为训练集,最后一个为测试集(这里只是举例说明fit和predict函数的使用)。然后利用fit和predict分别完成学习和预测,代码如下:
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn import svm
clf = svm.SVC(gamma=0.001, C=100.)
digits = datasets.load_digits()
clf.fit(digits.data[:-1], digits.target[:-1])
result=clf.predict(digits.data[-1])
print result
预测结果为:[8]
我们可以通过程序来查看测试集中的手写体实例到底长什么样来简单验证一下分类效果,代码和结果如下所示:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plot
plot.figure(1, figsize=(3, 3))
plot.imshow(digits.images[-1], cmap=plot.cm.gray_r, interpolation='nearest')
plot.show()
最后一个手写体实例为:
我们可以看到,这就是一个手写的数字“8”的,实际上正确的分类也是“8”。我们通过这个简单的例子,就是为了简单的学习如何来使用scikit-learn来解决分类问题,实际上这个问题要复杂得多。(PS:学习就是循序渐进,弄懂一个例子,就会弄懂第二个,... ,然后就是第n个,最后就会形成自己的知识和理论,你就可以轻松掌握,来解决各种遇到的复杂问题。)
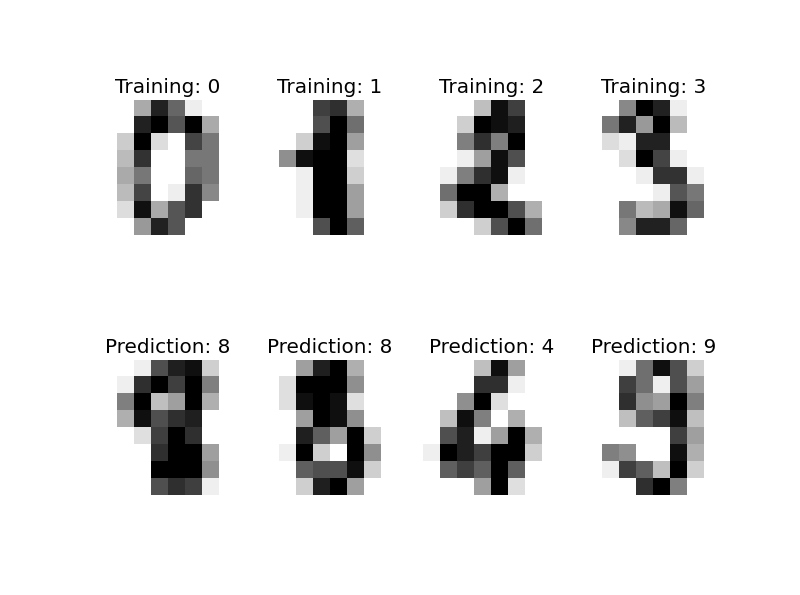
再为各位展示一个scikit-learn解决digit分类(手写体识别)的程序(by Gael Varoquaux),相信看过这个程序大家一定会对scikit-learn机器学习库有了一定的了解和认识。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Import datasets, classifiers and performance metrics
from sklearn import datasets, svm, metrics # The digits dataset
digits = datasets.load_digits() # The data that we are interested in is made of 8x8 images of digits, let's
# have a look at the first 3 images, stored in the `images` attribute of the
# dataset. If we were working from image files, we could load them using
# pylab.imread. Note that each image must have the same size. For these
# images, we know which digit they represent: it is given in the 'target' of
# the dataset.
images_and_labels = list(zip(digits.images, digits.target))
for index, (image, label) in enumerate(images_and_labels[:4]):
plt.subplot(2, 4, index + 1)
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation='nearest')
plt.title('Training: %i' % label) # To apply a classifier on this data, we need to flatten the image, to
# turn the data in a (samples, feature) matrix:
n_samples = len(digits.images)
data = digits.images.reshape((n_samples, -1)) # Create a classifier: a support vector classifier
classifier = svm.SVC(gamma=0.001) # We learn the digits on the first half of the digits
classifier.fit(data[:n_samples / 2], digits.target[:n_samples / 2]) # Now predict the value of the digit on the second half:
expected = digits.target[n_samples / 2:]
predicted = classifier.predict(data[n_samples / 2:]) print("Classification report for classifier %s:\n%s\n"
% (classifier, metrics.classification_report(expected, predicted)))
print("Confusion matrix:\n%s" % metrics.confusion_matrix(expected, predicted)) images_and_predictions = list(zip(digits.images[n_samples / 2:], predicted))
for index, (image, prediction) in enumerate(images_and_predictions[:4]):
plt.subplot(2, 4, index + 5)
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation='nearest')
plt.title('Prediction: %i' % prediction) plt.show()
输出结果:
Classification report for classifier SVC(C=1.0, cache_size=200, class_weight=None, coef0=0.0, degree=3,
gamma=0.001, kernel='rbf', max_iter=-1, probability=False,
random_state=None, shrinking=True, tol=0.001, verbose=False):
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 0.99 0.99 88
1 0.99 0.97 0.98 91
2 0.99 0.99 0.99 86
3 0.98 0.87 0.92 91
4 0.99 0.96 0.97 92
5 0.95 0.97 0.96 91
6 0.99 0.99 0.99 91
7 0.96 0.99 0.97 89
8 0.94 1.00 0.97 88
9 0.93 0.98 0.95 92 avg / total 0.97 0.97 0.97 899 Confusion matrix:
[[87 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 88 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1]
[ 0 0 85 1 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 79 0 3 0 4 5 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 88 0 0 0 0 4]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 88 1 0 0 2]
[ 0 1 0 0 0 0 90 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 88 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 88 0]
[ 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 90]]
5. 总结
1)scikit-learn的介绍和安装;
2)对scikit-learn有个概括的了解,能够尝试利用scikit-learn来进行数据挖掘和分析。
6. 参考内容
[1] An introduction to machine learning with scikit-learn
[2] 机器学习实战
[Python & Machine Learning] 学习笔记之scikit-learn机器学习库的更多相关文章
- [Machine Learning]学习笔记-Logistic Regression
[Machine Learning]学习笔记-Logistic Regression 模型-二分类任务 Logistic regression,亦称logtic regression,翻译为" ...
- Machine Learning 学习笔记
点击标题可转到相关博客. 博客专栏:机器学习 PDF 文档下载地址:Machine Learning 学习笔记 机器学习 scikit-learn 图谱 人脸表情识别常用的几个数据库 机器学习 F1- ...
- Machine Learning 学习笔记1 - 基本概念以及各分类
What is machine learning? 并没有广泛认可的定义来准确定义机器学习.以下定义均为译文,若以后有时间,将补充原英文...... 定义1.来自Arthur Samuel(上世纪50 ...
- Coursera 机器学习 第6章(上) Advice for Applying Machine Learning 学习笔记
这章的内容对于设计分析假设性能有很大的帮助,如果运用的好,将会节省实验者大量时间. Machine Learning System Design6.1 Evaluating a Learning Al ...
- python网络爬虫学习笔记(二)BeautifulSoup库
Beautiful Soup库也称为beautiful4库.bs4库,它可用于解析HTML/XML,并将所有文件.字符串转换为'utf-8'编码.HTML/XML文档是与“标签树一一对应的.具体地说, ...
- python网络爬虫学习笔记(一)Request库
一.Requests库的基本说明 引入Rquests库的代码如下 import requests 库中支持REQUEST, GET, HEAD, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE共7个 ...
- machine learning学习笔记
看到Max Welling教授主页上有不少学习notes,收藏一下吧,其最近出版了一本书呢还,还没看过. http://www.ics.uci.edu/~welling/classnotes/clas ...
- 吴恩达Machine Learning学习笔记(一)
机器学习的定义 A computer program is said to learn from experience E with respect to some class of tasks T ...
- [Machine Learning]学习笔记-线性回归
模型 假定有i组输入输出数据.输入变量可以用\(x^i\)表示,输出变量可以用\(y^i\)表示,一对\(\{x^i,y^i\}\)名为训练样本(training example),它们的集合则名为训 ...
随机推荐
- WPF系列 Style
参考 WPF: Customize your Application with Styles and Control Templates (Part 2 of 2)
- C#学习笔记-数据的传递以及ToolStripProgressBar
代码: 方法一:窗体的代码-->可以直接通过预设的Click事件来实现控制进度条. public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { In ...
- ffmbc——广播电视以及专业用途量身定制的FFmpeg
做项目遇到针对于mpegts多节目流转码的问题,看遍了ffmpeg的参数都得不到解决办法,最后在雷神的博客中看到了ffmbc: 结果,还是没解决问题,但是看起来改改ffmbc的代码还是相对简单一些,抽 ...
- JS组件系列——Bootstrap寒冬暖身篇:弹出框和提示框效果以及代码展示
前言:对于Web开发人员,弹出框和提示框的使用肯定不会陌生,比如常见的表格新增和编辑功能,一般常见的主要有两种处理方式:行内编辑和弹出框编辑.在增加用户体验方面,弹出框和提示框起着重要的作用,如果你的 ...
- 您还在招聘网上海量投简历然后等面试机会吗?那你已经OUT了。
工作也可以来找我们.不行看完这篇. 从毕业到现在,换了2次工作.每次都在为招工组烦恼.找工作这个问题,不管是应届生还是职场老手.都面临一个问题就是找工作的平台.纵观目前的找工作的形式,主流的不外乎就两 ...
- Jquery自定义插件之$.extend()、$.fn和$.fn.extend()
jquery插件的种类: 1.对象级别的插件开发,即给jQuery对象添加方法,封装对象方法的插件,如:parent().appendTo() 2.一种是类级别的插件开发,即给jQuery添加新的全局 ...
- Jquery揭秘系列:实现 ready和bind事件
讲这一节之前,先回顾之前的一篇<小谈Jquery>里面的代码: (function (win) { var _$ = function (selector, context) { retu ...
- C 语言学习 第五次作业总结
第五次作业,主要学习和复习的是几种循环结构的使用. 在前一次的课堂上,同学们已经学习了分支语句的使用.分支语句和循环语句配合使用,就可以写出更多的,逻辑功能丰富的代码了. 逻辑功能的丰富,也意味着学习 ...
- python基础-函数式编程
python基础-函数式编程 高阶函数:map , reduce ,filter,sorted 匿名函数: lambda 1.1函数式编程 面向过程编程:我们通过把大段代码拆成函数,通过一层一层 ...
- 【51Nod 1622】【算法马拉松 19C】集合对
http://www.51nod.com/onlineJudge/questionCode.html#!problemId=1622 简单题..直接暴力快速幂 #include<cstdio&g ...
