沉淀再出发:java中的HashMap、ConcurrentHashMap和Hashtable的认识
沉淀再出发:java中的HashMap、ConcurrentHashMap和Hashtable的认识
一、前言
很多知识在学习或者使用了之后总是会忘记的,但是如果把这些只是背后的原理理解了,并且记忆下来,这样我们就不会忘记了,常用的方法有对比记忆,将几个易混的概念放到一起进行比较,对我们的学习和生活有很大的帮助,比如hashmap和hashtab这两个概念的对比和记忆。
二、HashMap的基础知识
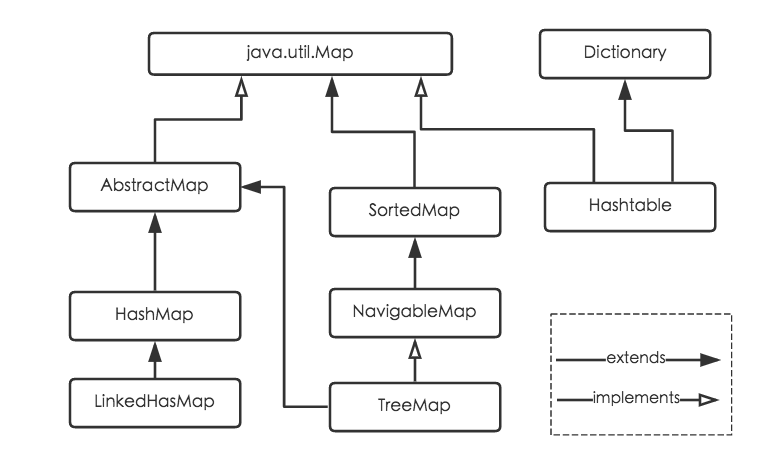
2.1、HashMap的介绍
HashMap 是一个散列表,它存储的内容是键值对(key-value)映射。
HashMap 继承于AbstractMap类,实现了Map、Cloneable、java.io.Serializable接口。
HashMap 的实现不是同步的,这意味着它不是线程安全的。它的key、value都可以为null。此外,HashMap中的映射不是有序的。
HashMap 的实例有两个参数影响其性能:“初始容量” 和 “加载因子”。容量是哈希表中桶的数量,初始容量是哈希表在创建时的容量。加载因子是哈希表在其容量自动增加之前可以达到多满的一种尺度。当哈希表中的条目数超出了加载因子与当前容量的乘积时,则要对该哈希表进行 rehash 操作(即重建内部数据结构),从而哈希表将具有大约两倍的桶数。通常,默认加载因子是 0.75, 这是在时间和空间成本上寻求一种折衷。加载因子过高虽然减少了空间开销,但同时也增加了查询成本(在大多数 HashMap 类的操作中,包括 get 和 put 操作,都反映了这一点)。在设置初始容量时应该考虑到映射中所需的条目数及其加载因子,以便最大限度地减少 rehash 操作次数。如果初始容量大于最大条目数除以加载因子,则不会发生 rehash 操作。
2.2、HashMap源码解读
package java.util;
import java.io.*; public class HashMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
{ // 默认的初始容量是16,必须是2的幂。
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16; // 最大容量(必须是2的幂且小于2的30次方,传入容量过大将被这个值替换)
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; // 默认加载因子
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; // 存储数据的Entry数组,长度是2的幂。
// HashMap是采用拉链法实现的,每一个Entry本质上是一个单向链表
transient Entry[] table; // HashMap的大小,它是HashMap保存的键值对的数量
transient int size; // HashMap的阈值,用于判断是否需要调整HashMap的容量(threshold = 容量*加载因子)
int threshold; // 加载因子实际大小
final float loadFactor; // HashMap被改变的次数
transient volatile int modCount; // 指定“容量大小”和“加载因子”的构造函数
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
// HashMap的最大容量只能是MAXIMUM_CAPACITY
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor); // 找出“大于initialCapacity”的最小的2的幂
int capacity = 1;
while (capacity < initialCapacity)
capacity <<= 1; // 设置“加载因子”
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
// 设置“HashMap阈值”,当HashMap中存储数据的数量达到threshold时,就需要将HashMap的容量加倍。
threshold = (int)(capacity * loadFactor);
// 创建Entry数组,用来保存数据
table = new Entry[capacity];
init();
} // 指定“容量大小”的构造函数
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
} // 默认构造函数。
public HashMap() {
// 设置“加载因子”
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
// 设置“HashMap阈值”,当HashMap中存储数据的数量达到threshold时,就需要将HashMap的容量加倍。
threshold = (int)(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY * DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
// 创建Entry数组,用来保存数据
table = new Entry[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY];
init();
} // 包含“子Map”的构造函数
public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this(Math.max((int) (m.size() / DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR) + 1,
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY), DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
// 将m中的全部元素逐个添加到HashMap中
putAllForCreate(m);
} static int hash(int h) {
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
} // 返回索引值
// h & (length-1)保证返回值的小于length
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h & (length-1);
} public int size() {
return size;
} public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
} // 获取key对应的value
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
// 获取key的hash值
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
// 在“该hash值对应的链表”上查找“键值等于key”的元素
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k)))
return e.value;
}
return null;
} // 获取“key为null”的元素的值
// HashMap将“key为null”的元素存储在table[0]位置!
private V getForNullKey() {
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null)
return e.value;
}
return null;
} // HashMap是否包含key
public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
return getEntry(key) != null;
} // 返回“键为key”的键值对
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
// 获取哈希值
// HashMap将“key为null”的元素存储在table[0]位置,“key不为null”的则调用hash()计算哈希值
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key.hashCode());
// 在“该hash值对应的链表”上查找“键值等于key”的元素
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
}
return null;
} // 将“key-value”添加到HashMap中
public V put(K key, V value) {
// 若“key为null”,则将该键值对添加到table[0]中。
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
// 若“key不为null”,则计算该key的哈希值,然后将其添加到该哈希值对应的链表中。
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
// 若“该key”对应的键值对已经存在,则用新的value取代旧的value。然后退出!
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
} // 若“该key”对应的键值对不存在,则将“key-value”添加到table中
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
} // putForNullKey()的作用是将“key为null”键值对添加到table[0]位置
private V putForNullKey(V value) {
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
// 这里的完全不会被执行到!
modCount++;
addEntry(0, null, value, 0);
return null;
} // 创建HashMap对应的“添加方法”,
// 它和put()不同。putForCreate()是内部方法,它被构造函数等调用,用来创建HashMap
// 而put()是对外提供的往HashMap中添加元素的方法。
private void putForCreate(K key, V value) {
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); // 若该HashMap表中存在“键值等于key”的元素,则替换该元素的value值
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
} // 若该HashMap表中不存在“键值等于key”的元素,则将该key-value添加到HashMap中
createEntry(hash, key, value, i);
} // 将“m”中的全部元素都添加到HashMap中。
// 该方法被内部的构造HashMap的方法所调用。
private void putAllForCreate(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
// 利用迭代器将元素逐个添加到HashMap中
for (Iterator<? extends Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V>> i = m.entrySet().iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) {
Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e = i.next();
putForCreate(e.getKey(), e.getValue());
}
} // 重新调整HashMap的大小,newCapacity是调整后的单位
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
} // 新建一个HashMap,将“旧HashMap”的全部元素添加到“新HashMap”中,
// 然后,将“新HashMap”赋值给“旧HashMap”。
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
transfer(newTable);
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);
} // 将HashMap中的全部元素都添加到newTable中
void transfer(Entry[] newTable) {
Entry[] src = table;
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (int j = 0; j < src.length; j++) {
Entry<K,V> e = src[j];
if (e != null) {
src[j] = null;
do {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
} while (e != null);
}
}
} // 将"m"的全部元素都添加到HashMap中
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
// 有效性判断
int numKeysToBeAdded = m.size();
if (numKeysToBeAdded == 0)
return; // 计算容量是否足够,
// 若“当前实际容量 < 需要的容量”,则将容量x2。
if (numKeysToBeAdded > threshold) {
int targetCapacity = (int)(numKeysToBeAdded / loadFactor + 1);
if (targetCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
targetCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
int newCapacity = table.length;
while (newCapacity < targetCapacity)
newCapacity <<= 1;
if (newCapacity > table.length)
resize(newCapacity);
} // 通过迭代器,将“m”中的元素逐个添加到HashMap中。
for (Iterator<? extends Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V>> i = m.entrySet().iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) {
Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e = i.next();
put(e.getKey(), e.getValue());
}
} // 删除“键为key”元素
public V remove(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> e = removeEntryForKey(key);
return (e == null ? null : e.value);
} // 删除“键为key”的元素
final Entry<K,V> removeEntryForKey(Object key) {
// 获取哈希值。若key为null,则哈希值为0;否则调用hash()进行计算
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
Entry<K,V> prev = table[i];
Entry<K,V> e = prev; // 删除链表中“键为key”的元素
// 本质是“删除单向链表中的节点”
while (e != null) {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
modCount++;
size--;
if (prev == e)
table[i] = next;
else
prev.next = next;
e.recordRemoval(this);
return e;
}
prev = e;
e = next;
} return e;
} // 删除“键值对”
final Entry<K,V> removeMapping(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return null; Map.Entry<K,V> entry = (Map.Entry<K,V>) o;
Object key = entry.getKey();
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
Entry<K,V> prev = table[i];
Entry<K,V> e = prev; // 删除链表中的“键值对e”
// 本质是“删除单向链表中的节点”
while (e != null) {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
if (e.hash == hash && e.equals(entry)) {
modCount++;
size--;
if (prev == e)
table[i] = next;
else
prev.next = next;
e.recordRemoval(this);
return e;
}
prev = e;
e = next;
} return e;
} // 清空HashMap,将所有的元素设为null
public void clear() {
modCount++;
Entry[] tab = table;
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; i++)
tab[i] = null;
size = 0;
} // 是否包含“值为value”的元素
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
// 若“value为null”,则调用containsNullValue()查找
if (value == null)
return containsNullValue(); // 若“value不为null”,则查找HashMap中是否有值为value的节点。
Entry[] tab = table;
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length ; i++)
for (Entry e = tab[i] ; e != null ; e = e.next)
if (value.equals(e.value))
return true;
return false;
} // 是否包含null值
private boolean containsNullValue() {
Entry[] tab = table;
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length ; i++)
for (Entry e = tab[i] ; e != null ; e = e.next)
if (e.value == null)
return true;
return false;
} // 克隆一个HashMap,并返回Object对象
public Object clone() {
HashMap<K,V> result = null;
try {
result = (HashMap<K,V>)super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// assert false;
}
result.table = new Entry[table.length];
result.entrySet = null;
result.modCount = 0;
result.size = 0;
result.init();
// 调用putAllForCreate()将全部元素添加到HashMap中
result.putAllForCreate(this); return result;
} // Entry是单向链表。
// 它是 “HashMap链式存储法”对应的链表。
// 它实现了Map.Entry 接口,即实现getKey(), getValue(), setValue(V value), equals(Object o), hashCode()这些函数
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final K key;
V value;
// 指向下一个节点
Entry<K,V> next;
final int hash; // 构造函数。
// 输入参数包括"哈希值(h)", "键(k)", "值(v)", "下一节点(n)"
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
} public final K getKey() {
return key;
} public final V getValue() {
return value;
} public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
} // 判断两个Entry是否相等
// 若两个Entry的“key”和“value”都相等,则返回true。
// 否则,返回false
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o;
Object k1 = getKey();
Object k2 = e.getKey();
if (k1 == k2 || (k1 != null && k1.equals(k2))) {
Object v1 = getValue();
Object v2 = e.getValue();
if (v1 == v2 || (v1 != null && v1.equals(v2)))
return true;
}
return false;
} // 实现hashCode()
public final int hashCode() {
return (key==null ? 0 : key.hashCode()) ^
(value==null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
} public final String toString() {
return getKey() + "=" + getValue();
} // 当向HashMap中添加元素时,绘调用recordAccess()。
// 这里不做任何处理
void recordAccess(HashMap<K,V> m) {
} // 当从HashMap中删除元素时,绘调用recordRemoval()。
// 这里不做任何处理
void recordRemoval(HashMap<K,V> m) {
}
} // 新增Entry。将“key-value”插入指定位置,bucketIndex是位置索引。
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
// 保存“bucketIndex”位置的值到“e”中
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
// 设置“bucketIndex”位置的元素为“新Entry”,
// 设置“e”为“新Entry的下一个节点”
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
// 若HashMap的实际大小 不小于 “阈值”,则调整HashMap的大小
if (size++ >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
} // 创建Entry。将“key-value”插入指定位置,bucketIndex是位置索引。
// 它和addEntry的区别是:
// (01) addEntry()一般用在 新增Entry可能导致“HashMap的实际容量”超过“阈值”的情况下。
// 例如,我们新建一个HashMap,然后不断通过put()向HashMap中添加元素;
// put()是通过addEntry()新增Entry的。
// 在这种情况下,我们不知道何时“HashMap的实际容量”会超过“阈值”;
// 因此,需要调用addEntry()
// (02) createEntry() 一般用在 新增Entry不会导致“HashMap的实际容量”超过“阈值”的情况下。
// 例如,我们调用HashMap“带有Map”的构造函数,它绘将Map的全部元素添加到HashMap中;
// 但在添加之前,我们已经计算好“HashMap的容量和阈值”。也就是,可以确定“即使将Map中
// 的全部元素添加到HashMap中,都不会超过HashMap的阈值”。
// 此时,调用createEntry()即可。
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
// 保存“bucketIndex”位置的值到“e”中
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
// 设置“bucketIndex”位置的元素为“新Entry”,
// 设置“e”为“新Entry的下一个节点”
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
} // HashIterator是HashMap迭代器的抽象出来的父类,实现了公共了函数。
// 它包含“key迭代器(KeyIterator)”、“Value迭代器(ValueIterator)”和“Entry迭代器(EntryIterator)”3个子类。
private abstract class HashIterator<E> implements Iterator<E> {
// 下一个元素
Entry<K,V> next;
// expectedModCount用于实现fast-fail机制。
int expectedModCount;
// 当前索引
int index;
// 当前元素
Entry<K,V> current; HashIterator() {
expectedModCount = modCount;
if (size > 0) { // advance to first entry
Entry[] t = table;
// 将next指向table中第一个不为null的元素。
// 这里利用了index的初始值为0,从0开始依次向后遍历,直到找到不为null的元素就退出循环。
while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null)
;
}
} public final boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
} // 获取下一个元素
final Entry<K,V> nextEntry() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
Entry<K,V> e = next;
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException(); // 注意!!!
// 一个Entry就是一个单向链表
// 若该Entry的下一个节点不为空,就将next指向下一个节点;
// 否则,将next指向下一个链表(也是下一个Entry)的不为null的节点。
if ((next = e.next) == null) {
Entry[] t = table;
while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null)
;
}
current = e;
return e;
} // 删除当前元素
public void remove() {
if (current == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
Object k = current.key;
current = null;
HashMap.this.removeEntryForKey(k);
expectedModCount = modCount;
} } // value的迭代器
private final class ValueIterator extends HashIterator<V> {
public V next() {
return nextEntry().value;
}
} // key的迭代器
private final class KeyIterator extends HashIterator<K> {
public K next() {
return nextEntry().getKey();
}
} // Entry的迭代器
private final class EntryIterator extends HashIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public Map.Entry<K,V> next() {
return nextEntry();
}
} // 返回一个“key迭代器”
Iterator<K> newKeyIterator() {
return new KeyIterator();
}
// 返回一个“value迭代器”
Iterator<V> newValueIterator() {
return new ValueIterator();
}
// 返回一个“entry迭代器”
Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> newEntryIterator() {
return new EntryIterator();
} // HashMap的Entry对应的集合
private transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet = null; // 返回“key的集合”,实际上返回一个“KeySet对象”
public Set<K> keySet() {
Set<K> ks = keySet;
return (ks != null ? ks : (keySet = new KeySet()));
} // Key对应的集合
// KeySet继承于AbstractSet,说明该集合中没有重复的Key。
private final class KeySet extends AbstractSet<K> {
public Iterator<K> iterator() {
return newKeyIterator();
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return containsKey(o);
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return HashMap.this.removeEntryForKey(o) != null;
}
public void clear() {
HashMap.this.clear();
}
} // 返回“value集合”,实际上返回的是一个Values对象
public Collection<V> values() {
Collection<V> vs = values;
return (vs != null ? vs : (values = new Values()));
} // “value集合”
// Values继承于AbstractCollection,不同于“KeySet继承于AbstractSet”,
// Values中的元素能够重复。因为不同的key可以指向相同的value。
private final class Values extends AbstractCollection<V> {
public Iterator<V> iterator() {
return newValueIterator();
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return containsValue(o);
}
public void clear() {
HashMap.this.clear();
}
} // 返回“HashMap的Entry集合”
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
return entrySet0();
} // 返回“HashMap的Entry集合”,它实际是返回一个EntrySet对象
private Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet0() {
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> es = entrySet;
return es != null ? es : (entrySet = new EntrySet());
} // EntrySet对应的集合
// EntrySet继承于AbstractSet,说明该集合中没有重复的EntrySet。
private final class EntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
return newEntryIterator();
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<K,V> e = (Map.Entry<K,V>) o;
Entry<K,V> candidate = getEntry(e.getKey());
return candidate != null && candidate.equals(e);
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return removeMapping(o) != null;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
public void clear() {
HashMap.this.clear();
}
} // java.io.Serializable的写入函数
// 将HashMap的“总的容量,实际容量,所有的Entry”都写入到输出流中
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws IOException
{
Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> i =
(size > 0) ? entrySet0().iterator() : null; // Write out the threshold, loadfactor, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultWriteObject(); // Write out number of buckets
s.writeInt(table.length); // Write out size (number of Mappings)
s.writeInt(size); // Write out keys and values (alternating)
if (i != null) {
while (i.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<K,V> e = i.next();
s.writeObject(e.getKey());
s.writeObject(e.getValue());
}
}
} private static final long serialVersionUID = 362498820763181265L; // java.io.Serializable的读取函数:根据写入方式读出
// 将HashMap的“总的容量,实际容量,所有的Entry”依次读出
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
{
// Read in the threshold, loadfactor, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultReadObject(); // Read in number of buckets and allocate the bucket array;
int numBuckets = s.readInt();
table = new Entry[numBuckets]; init(); // Give subclass a chance to do its thing. // Read in size (number of Mappings)
int size = s.readInt(); // Read the keys and values, and put the mappings in the HashMap
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
K key = (K) s.readObject();
V value = (V) s.readObject();
putForCreate(key, value);
}
} // 返回“HashMap总的容量”
int capacity() { return table.length; }
// 返回“HashMap的加载因子”
float loadFactor() { return loadFactor; }
}
HashMap源码解读(jdk1.6)
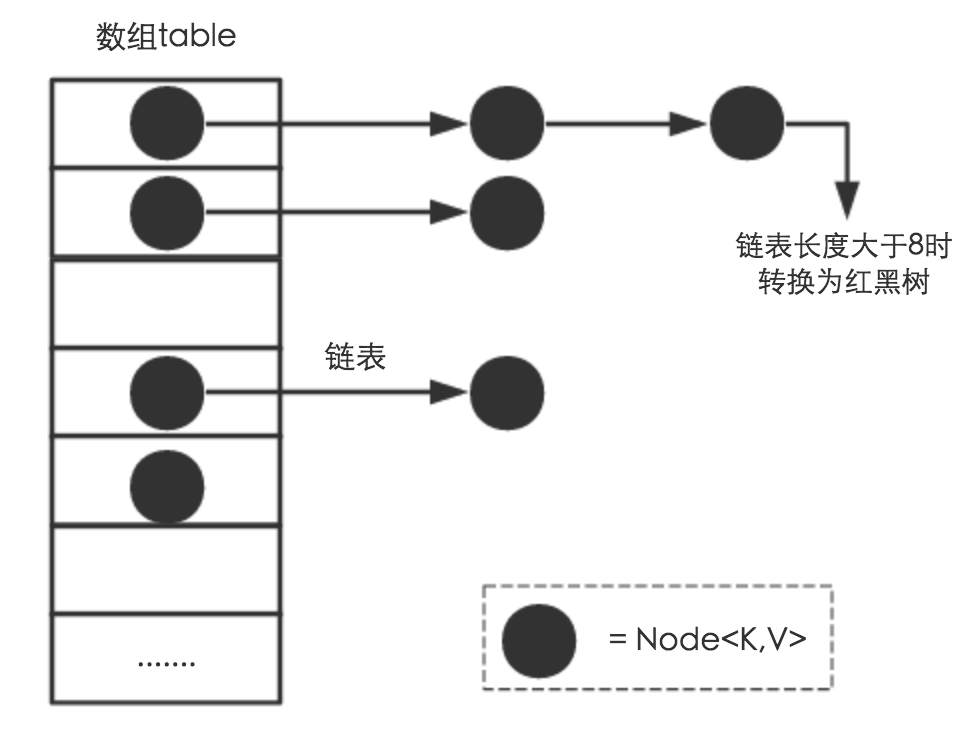
但是在jdk1.8之后,HashMap加入了红黑树机制,在一个单向链表的节点大于8的情况下,就把这个链表转换成红黑树。
同时让我们看看HashMap和Map之间的关系:
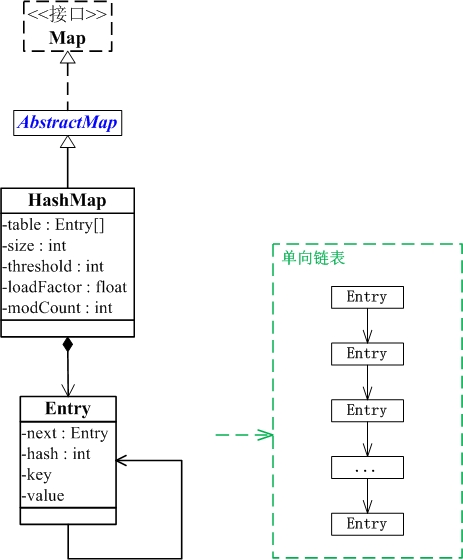
(1) HashMap继承于AbstractMap类,实现了Map接口。Map是"key-value键值对"接口,AbstractMap实现了"键值对"的通用函数接口。
(2) HashMap是通过"拉链法"实现的哈希表。它包括几个重要的成员变量:table, size, threshold, loadFactor, modCount。
table是一个Entry[]数组类型,而Entry实际上就是一个单向链表。哈希表的"key-value键值对"都是存储在Entry数组中的。
size是HashMap的大小,它是HashMap保存的键值对的数量。
threshold是HashMap的阈值,用于判断是否需要调整HashMap的容量。
threshold的值="容量*加载因子",当HashMap中存储数据的数量达到threshold时,就需要将HashMap的容量加倍。
loadFactor就是加载因子。
modCount是用来实现fail-fast机制的。java.util包下面的所有的集合类都是快速失败(fail-fast)的,
而java.util.concurrent包下面的所有的类都是安全失败(fail-safe)的。
快速失败的迭代器会抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常,而安全失败的迭代器永远不会抛出这样的异常。
当多个线程对同一个集合进行操作的时候,某线程访问集合的过程中,
该集合的内容被其他线程所改变(即其它线程通过add、remove、clear等方法,改变了modCount的值);
这时,就会抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常,产生fail-fast事件。
fail-fast机制,是一种错误检测机制。它只能被用来检测错误,因为JDK并不保证fail-fast机制一定会发生。
若在多线程环境下使用fail-fast机制的集合,建议使用“java.util.concurrent包下的类”去取代“java.util包下的类”。
下面我们看看在jdk1.8之中的HashMap源码实现方式:
/*
* Copyright (c) 1997, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*/ package java.util; import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InvalidObjectException;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.util.function.BiConsumer;
import java.util.function.BiFunction;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.function.Function; /**
* Hash table based implementation of the <tt>Map</tt> interface. This
* implementation provides all of the optional map operations, and permits
* <tt>null</tt> values and the <tt>null</tt> key. (The <tt>HashMap</tt>
* class is roughly equivalent to <tt>Hashtable</tt>, except that it is
* unsynchronized and permits nulls.) This class makes no guarantees as to
* the order of the map; in particular, it does not guarantee that the order
* will remain constant over time.
*
* <p>This implementation provides constant-time performance for the basic
* operations (<tt>get</tt> and <tt>put</tt>), assuming the hash function
* disperses the elements properly among the buckets. Iteration over
* collection views requires time proportional to the "capacity" of the
* <tt>HashMap</tt> instance (the number of buckets) plus its size (the number
* of key-value mappings). Thus, it's very important not to set the initial
* capacity too high (or the load factor too low) if iteration performance is
* important.
*
* <p>An instance of <tt>HashMap</tt> has two parameters that affect its
* performance: <i>initial capacity</i> and <i>load factor</i>. The
* <i>capacity</i> is the number of buckets in the hash table, and the initial
* capacity is simply the capacity at the time the hash table is created. The
* <i>load factor</i> is a measure of how full the hash table is allowed to
* get before its capacity is automatically increased. When the number of
* entries in the hash table exceeds the product of the load factor and the
* current capacity, the hash table is <i>rehashed</i> (that is, internal data
* structures are rebuilt) so that the hash table has approximately twice the
* number of buckets.
*
* <p>As a general rule, the default load factor (.75) offers a good
* tradeoff between time and space costs. Higher values decrease the
* space overhead but increase the lookup cost (reflected in most of
* the operations of the <tt>HashMap</tt> class, including
* <tt>get</tt> and <tt>put</tt>). The expected number of entries in
* the map and its load factor should be taken into account when
* setting its initial capacity, so as to minimize the number of
* rehash operations. If the initial capacity is greater than the
* maximum number of entries divided by the load factor, no rehash
* operations will ever occur.
*
* <p>If many mappings are to be stored in a <tt>HashMap</tt>
* instance, creating it with a sufficiently large capacity will allow
* the mappings to be stored more efficiently than letting it perform
* automatic rehashing as needed to grow the table. Note that using
* many keys with the same {@code hashCode()} is a sure way to slow
* down performance of any hash table. To ameliorate impact, when keys
* are {@link Comparable}, this class may use comparison order among
* keys to help break ties.
*
* <p><strong>Note that this implementation is not synchronized.</strong>
* If multiple threads access a hash map concurrently, and at least one of
* the threads modifies the map structurally, it <i>must</i> be
* synchronized externally. (A structural modification is any operation
* that adds or deletes one or more mappings; merely changing the value
* associated with a key that an instance already contains is not a
* structural modification.) This is typically accomplished by
* synchronizing on some object that naturally encapsulates the map.
*
* If no such object exists, the map should be "wrapped" using the
* {@link Collections#synchronizedMap Collections.synchronizedMap}
* method. This is best done at creation time, to prevent accidental
* unsynchronized access to the map:<pre>
* Map m = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap(...));</pre>
*
* <p>The iterators returned by all of this class's "collection view methods"
* are <i>fail-fast</i>: if the map is structurally modified at any time after
* the iterator is created, in any way except through the iterator's own
* <tt>remove</tt> method, the iterator will throw a
* {@link ConcurrentModificationException}. Thus, in the face of concurrent
* modification, the iterator fails quickly and cleanly, rather than risking
* arbitrary, non-deterministic behavior at an undetermined time in the
* future.
*
* <p>Note that the fail-fast behavior of an iterator cannot be guaranteed
* as it is, generally speaking, impossible to make any hard guarantees in the
* presence of unsynchronized concurrent modification. Fail-fast iterators
* throw <tt>ConcurrentModificationException</tt> on a best-effort basis.
* Therefore, it would be wrong to write a program that depended on this
* exception for its correctness: <i>the fail-fast behavior of iterators
* should be used only to detect bugs.</i>
*
* <p>This class is a member of the
* <a href="{@docRoot}/../technotes/guides/collections/index.html">
* Java Collections Framework</a>.
*
* @param <K> the type of keys maintained by this map
* @param <V> the type of mapped values
*
* @author Doug Lea
* @author Josh Bloch
* @author Arthur van Hoff
* @author Neal Gafter
* @see Object#hashCode()
* @see Collection
* @see Map
* @see TreeMap
* @see Hashtable
* @since 1.2
*/
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 362498820763181265L; /*
* Implementation notes.
*
* This map usually acts as a binned (bucketed) hash table, but
* when bins get too large, they are transformed into bins of
* TreeNodes, each structured similarly to those in
* java.util.TreeMap. Most methods try to use normal bins, but
* relay to TreeNode methods when applicable (simply by checking
* instanceof a node). Bins of TreeNodes may be traversed and
* used like any others, but additionally support faster lookup
* when overpopulated. However, since the vast majority of bins in
* normal use are not overpopulated, checking for existence of
* tree bins may be delayed in the course of table methods.
*
* Tree bins (i.e., bins whose elements are all TreeNodes) are
* ordered primarily by hashCode, but in the case of ties, if two
* elements are of the same "class C implements Comparable<C>",
* type then their compareTo method is used for ordering. (We
* conservatively check generic types via reflection to validate
* this -- see method comparableClassFor). The added complexity
* of tree bins is worthwhile in providing worst-case O(log n)
* operations when keys either have distinct hashes or are
* orderable, Thus, performance degrades gracefully under
* accidental or malicious usages in which hashCode() methods
* return values that are poorly distributed, as well as those in
* which many keys share a hashCode, so long as they are also
* Comparable. (If neither of these apply, we may waste about a
* factor of two in time and space compared to taking no
* precautions. But the only known cases stem from poor user
* programming practices that are already so slow that this makes
* little difference.)
*
* Because TreeNodes are about twice the size of regular nodes, we
* use them only when bins contain enough nodes to warrant use
* (see TREEIFY_THRESHOLD). And when they become too small (due to
* removal or resizing) they are converted back to plain bins. In
* usages with well-distributed user hashCodes, tree bins are
* rarely used. Ideally, under random hashCodes, the frequency of
* nodes in bins follows a Poisson distribution
* (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Poisson_distribution) with a
* parameter of about 0.5 on average for the default resizing
* threshold of 0.75, although with a large variance because of
* resizing granularity. Ignoring variance, the expected
* occurrences of list size k are (exp(-0.5) * pow(0.5, k) /
* factorial(k)). The first values are:
*
* 0: 0.60653066
* 1: 0.30326533
* 2: 0.07581633
* 3: 0.01263606
* 4: 0.00157952
* 5: 0.00015795
* 6: 0.00001316
* 7: 0.00000094
* 8: 0.00000006
* more: less than 1 in ten million
*
* The root of a tree bin is normally its first node. However,
* sometimes (currently only upon Iterator.remove), the root might
* be elsewhere, but can be recovered following parent links
* (method TreeNode.root()).
*
* All applicable internal methods accept a hash code as an
* argument (as normally supplied from a public method), allowing
* them to call each other without recomputing user hashCodes.
* Most internal methods also accept a "tab" argument, that is
* normally the current table, but may be a new or old one when
* resizing or converting.
*
* When bin lists are treeified, split, or untreeified, we keep
* them in the same relative access/traversal order (i.e., field
* Node.next) to better preserve locality, and to slightly
* simplify handling of splits and traversals that invoke
* iterator.remove. When using comparators on insertion, to keep a
* total ordering (or as close as is required here) across
* rebalancings, we compare classes and identityHashCodes as
* tie-breakers.
*
* The use and transitions among plain vs tree modes is
* complicated by the existence of subclass LinkedHashMap. See
* below for hook methods defined to be invoked upon insertion,
* removal and access that allow LinkedHashMap internals to
* otherwise remain independent of these mechanics. (This also
* requires that a map instance be passed to some utility methods
* that may create new nodes.)
*
* The concurrent-programming-like SSA-based coding style helps
* avoid aliasing errors amid all of the twisty pointer operations.
*/ /**
* The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two.
*/
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16 /**
* The maximum capacity, used if a higher value is implicitly specified
* by either of the constructors with arguments.
* MUST be a power of two <= 1<<30.
*/
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; /**
* The load factor used when none specified in constructor.
*/
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; /**
* The bin count threshold for using a tree rather than list for a
* bin. Bins are converted to trees when adding an element to a
* bin with at least this many nodes. The value must be greater
* than 2 and should be at least 8 to mesh with assumptions in
* tree removal about conversion back to plain bins upon
* shrinkage.
*/
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; /**
* The bin count threshold for untreeifying a (split) bin during a
* resize operation. Should be less than TREEIFY_THRESHOLD, and at
* most 6 to mesh with shrinkage detection under removal.
*/
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6; /**
* The smallest table capacity for which bins may be treeified.
* (Otherwise the table is resized if too many nodes in a bin.)
* Should be at least 4 * TREEIFY_THRESHOLD to avoid conflicts
* between resizing and treeification thresholds.
*/
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64; /**
* Basic hash bin node, used for most entries. (See below for
* TreeNode subclass, and in LinkedHashMap for its Entry subclass.)
*/
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next; Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
} public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; } public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
} public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
} public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
} /* ---------------- Static utilities -------------- */ /**
* Computes key.hashCode() and spreads (XORs) higher bits of hash
* to lower. Because the table uses power-of-two masking, sets of
* hashes that vary only in bits above the current mask will
* always collide. (Among known examples are sets of Float keys
* holding consecutive whole numbers in small tables.) So we
* apply a transform that spreads the impact of higher bits
* downward. There is a tradeoff between speed, utility, and
* quality of bit-spreading. Because many common sets of hashes
* are already reasonably distributed (so don't benefit from
* spreading), and because we use trees to handle large sets of
* collisions in bins, we just XOR some shifted bits in the
* cheapest possible way to reduce systematic lossage, as well as
* to incorporate impact of the highest bits that would otherwise
* never be used in index calculations because of table bounds.
*/
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
} /**
* Returns x's Class if it is of the form "class C implements
* Comparable<C>", else null.
*/
static Class<?> comparableClassFor(Object x) {
if (x instanceof Comparable) {
Class<?> c; Type[] ts, as; Type t; ParameterizedType p;
if ((c = x.getClass()) == String.class) // bypass checks
return c;
if ((ts = c.getGenericInterfaces()) != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < ts.length; ++i) {
if (((t = ts[i]) instanceof ParameterizedType) &&
((p = (ParameterizedType)t).getRawType() ==
Comparable.class) &&
(as = p.getActualTypeArguments()) != null &&
as.length == 1 && as[0] == c) // type arg is c
return c;
}
}
}
return null;
} /**
* Returns k.compareTo(x) if x matches kc (k's screened comparable
* class), else 0.
*/
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"}) // for cast to Comparable
static int compareComparables(Class<?> kc, Object k, Object x) {
return (x == null || x.getClass() != kc ? 0 :
((Comparable)k).compareTo(x));
} /**
* Returns a power of two size for the given target capacity.
*/
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
} /* ---------------- Fields -------------- */ /**
* The table, initialized on first use, and resized as
* necessary. When allocated, length is always a power of two.
* (We also tolerate length zero in some operations to allow
* bootstrapping mechanics that are currently not needed.)
*/
transient Node<K,V>[] table; /**
* Holds cached entrySet(). Note that AbstractMap fields are used
* for keySet() and values().
*/
transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet; /**
* The number of key-value mappings contained in this map.
*/
transient int size; /**
* The number of times this HashMap has been structurally modified
* Structural modifications are those that change the number of mappings in
* the HashMap or otherwise modify its internal structure (e.g.,
* rehash). This field is used to make iterators on Collection-views of
* the HashMap fail-fast. (See ConcurrentModificationException).
*/
transient int modCount; /**
* The next size value at which to resize (capacity * load factor).
*
* @serial
*/
// (The javadoc description is true upon serialization.
// Additionally, if the table array has not been allocated, this
// field holds the initial array capacity, or zero signifying
// DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY.)
int threshold; /**
* The load factor for the hash table.
*
* @serial
*/
final float loadFactor; /* ---------------- Public operations -------------- */ /**
* Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the specified initial
* capacity and load factor.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadFactor the load factor
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
} /**
* Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the specified initial
* capacity and the default load factor (0.75).
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative.
*/
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
} /**
* Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the default initial capacity
* (16) and the default load factor (0.75).
*/
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted
} /**
* Constructs a new <tt>HashMap</tt> with the same mappings as the
* specified <tt>Map</tt>. The <tt>HashMap</tt> is created with
* default load factor (0.75) and an initial capacity sufficient to
* hold the mappings in the specified <tt>Map</tt>.
*
* @param m the map whose mappings are to be placed in this map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null
*/
public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
putMapEntries(m, false);
} /**
* Implements Map.putAll and Map constructor
*
* @param m the map
* @param evict false when initially constructing this map, else
* true (relayed to method afterNodeInsertion).
*/
final void putMapEntries(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m, boolean evict) {
int s = m.size();
if (s > 0) {
if (table == null) { // pre-size
float ft = ((float)s / loadFactor) + 1.0F;
int t = ((ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : MAXIMUM_CAPACITY);
if (t > threshold)
threshold = tableSizeFor(t);
}
else if (s > threshold)
resize();
for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet()) {
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, evict);
}
}
} /**
* Returns the number of key-value mappings in this map.
*
* @return the number of key-value mappings in this map
*/
public int size() {
return size;
} /**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map contains no key-value mappings.
*
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this map contains no key-value mappings
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
} /**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code (key==null ? k==null :
* key.equals(k))}, then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise
* it returns {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
* <p>A return value of {@code null} does not <i>necessarily</i>
* indicate that the map contains no mapping for the key; it's also
* possible that the map explicitly maps the key to {@code null}.
* The {@link #containsKey containsKey} operation may be used to
* distinguish these two cases.
*
* @see #put(Object, Object)
*/
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
} /**
* Implements Map.get and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @return the node, or null if none
*/
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
} /**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map contains a mapping for the
* specified key.
*
* @param key The key whose presence in this map is to be tested
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this map contains a mapping for the specified
* key.
*/
public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
return getNode(hash(key), key) != null;
} /**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or
* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>.
* (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.)
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
} /**
* Implements Map.put and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to put
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
* @return previous value, or null if none
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
} /**
* Initializes or doubles table size. If null, allocates in
* accord with initial capacity target held in field threshold.
* Otherwise, because we are using power-of-two expansion, the
* elements from each bin must either stay at same index, or move
* with a power of two offset in the new table.
*
* @return the table
*/
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // preserve order
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
} /**
* Replaces all linked nodes in bin at index for given hash unless
* table is too small, in which case resizes instead.
*/
final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) {
int n, index; Node<K,V> e;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)
resize();
else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null;
do {
TreeNode<K,V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null);
if (tl == null)
hd = p;
else {
p.prev = tl;
tl.next = p;
}
tl = p;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
if ((tab[index] = hd) != null)
hd.treeify(tab);
}
} /**
* Copies all of the mappings from the specified map to this map.
* These mappings will replace any mappings that this map had for
* any of the keys currently in the specified map.
*
* @param m mappings to be stored in this map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null
*/
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
putMapEntries(m, true);
} /**
* Removes the mapping for the specified key from this map if present.
*
* @param key key whose mapping is to be removed from the map
* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or
* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>.
* (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.)
*/
public V remove(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ?
null : e.value;
} /**
* Implements Map.remove and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to match if matchValue, else ignored
* @param matchValue if true only remove if value is equal
* @param movable if false do not move other nodes while removing
* @return the node, or null if none
*/
final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value,
boolean matchValue, boolean movable) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
node = p;
else if ((e = p.next) != null) {
if (p instanceof TreeNode)
node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key);
else {
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key ||
(key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
node = e;
break;
}
p = e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value ||
(value != null && value.equals(v)))) {
if (node instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable);
else if (node == p)
tab[index] = node.next;
else
p.next = node.next;
++modCount;
--size;
afterNodeRemoval(node);
return node;
}
}
return null;
} /**
* Removes all of the mappings from this map.
* The map will be empty after this call returns.
*/
public void clear() {
Node<K,V>[] tab;
modCount++;
if ((tab = table) != null && size > 0) {
size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i)
tab[i] = null;
}
} /**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the
* specified value.
*
* @param value value whose presence in this map is to be tested
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the
* specified value
*/
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; V v;
if ((tab = table) != null && size > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) {
for (Node<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if ((v = e.value) == value ||
(value != null && value.equals(v)))
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
} /**
* Returns a {@link Set} view of the keys contained in this map.
* The set is backed by the map, so changes to the map are
* reflected in the set, and vice-versa. If the map is modified
* while an iteration over the set is in progress (except through
* the iterator's own <tt>remove</tt> operation), the results of
* the iteration are undefined. The set supports element removal,
* which removes the corresponding mapping from the map, via the
* <tt>Iterator.remove</tt>, <tt>Set.remove</tt>,
* <tt>removeAll</tt>, <tt>retainAll</tt>, and <tt>clear</tt>
* operations. It does not support the <tt>add</tt> or <tt>addAll</tt>
* operations.
*
* @return a set view of the keys contained in this map
*/
public Set<K> keySet() {
Set<K> ks;
return (ks = keySet) == null ? (keySet = new KeySet()) : ks;
} final class KeySet extends AbstractSet<K> {
public final int size() { return size; }
public final void clear() { HashMap.this.clear(); }
public final Iterator<K> iterator() { return new KeyIterator(); }
public final boolean contains(Object o) { return containsKey(o); }
public final boolean remove(Object key) {
return removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true) != null;
}
public final Spliterator<K> spliterator() {
return new KeySpliterator<>(HashMap.this, 0, -1, 0, 0);
}
public final void forEach(Consumer<? super K> action) {
Node<K,V>[] tab;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (size > 0 && (tab = table) != null) {
int mc = modCount;
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) {
for (Node<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next)
action.accept(e.key);
}
if (modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
} /**
* Returns a {@link Collection} view of the values contained in this map.
* The collection is backed by the map, so changes to the map are
* reflected in the collection, and vice-versa. If the map is
* modified while an iteration over the collection is in progress
* (except through the iterator's own <tt>remove</tt> operation),
* the results of the iteration are undefined. The collection
* supports element removal, which removes the corresponding
* mapping from the map, via the <tt>Iterator.remove</tt>,
* <tt>Collection.remove</tt>, <tt>removeAll</tt>,
* <tt>retainAll</tt> and <tt>clear</tt> operations. It does not
* support the <tt>add</tt> or <tt>addAll</tt> operations.
*
* @return a view of the values contained in this map
*/
public Collection<V> values() {
Collection<V> vs;
return (vs = values) == null ? (values = new Values()) : vs;
} final class Values extends AbstractCollection<V> {
public final int size() { return size; }
public final void clear() { HashMap.this.clear(); }
public final Iterator<V> iterator() { return new ValueIterator(); }
public final boolean contains(Object o) { return containsValue(o); }
public final Spliterator<V> spliterator() {
return new ValueSpliterator<>(HashMap.this, 0, -1, 0, 0);
}
public final void forEach(Consumer<? super V> action) {
Node<K,V>[] tab;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (size > 0 && (tab = table) != null) {
int mc = modCount;
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) {
for (Node<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next)
action.accept(e.value);
}
if (modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
} /**
* Returns a {@link Set} view of the mappings contained in this map.
* The set is backed by the map, so changes to the map are
* reflected in the set, and vice-versa. If the map is modified
* while an iteration over the set is in progress (except through
* the iterator's own <tt>remove</tt> operation, or through the
* <tt>setValue</tt> operation on a map entry returned by the
* iterator) the results of the iteration are undefined. The set
* supports element removal, which removes the corresponding
* mapping from the map, via the <tt>Iterator.remove</tt>,
* <tt>Set.remove</tt>, <tt>removeAll</tt>, <tt>retainAll</tt> and
* <tt>clear</tt> operations. It does not support the
* <tt>add</tt> or <tt>addAll</tt> operations.
*
* @return a set view of the mappings contained in this map
*/
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> es;
return (es = entrySet) == null ? (entrySet = new EntrySet()) : es;
} final class EntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public final int size() { return size; }
public final void clear() { HashMap.this.clear(); }
public final Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
return new EntryIterator();
}
public final boolean contains(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>) o;
Object key = e.getKey();
Node<K,V> candidate = getNode(hash(key), key);
return candidate != null && candidate.equals(e);
}
public final boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>) o;
Object key = e.getKey();
Object value = e.getValue();
return removeNode(hash(key), key, value, true, true) != null;
}
return false;
}
public final Spliterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> spliterator() {
return new EntrySpliterator<>(HashMap.this, 0, -1, 0, 0);
}
public final void forEach(Consumer<? super Map.Entry<K,V>> action) {
Node<K,V>[] tab;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (size > 0 && (tab = table) != null) {
int mc = modCount;
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) {
for (Node<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next)
action.accept(e);
}
if (modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
} // Overrides of JDK8 Map extension methods @Override
public V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? defaultValue : e.value;
} @Override
public V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, true, true);
} @Override
public boolean remove(Object key, Object value) {
return removeNode(hash(key), key, value, true, true) != null;
} @Override
public boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {
Node<K,V> e; V v;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) != null &&
((v = e.value) == oldValue || (v != null && v.equals(oldValue)))) {
e.value = newValue;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return true;
}
return false;
} @Override
public V replace(K key, V value) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) != null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
return null;
} @Override
public V computeIfAbsent(K key,
Function<? super K, ? extends V> mappingFunction) {
if (mappingFunction == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = hash(key);
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first; int n, i;
int binCount = 0;
TreeNode<K,V> t = null;
Node<K,V> old = null;
if (size > threshold || (tab = table) == null ||
(n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((first = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
old = (t = (TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
else {
Node<K,V> e = first; K k;
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
old = e;
break;
}
++binCount;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
V oldValue;
if (old != null && (oldValue = old.value) != null) {
afterNodeAccess(old);
return oldValue;
}
}
V v = mappingFunction.apply(key);
if (v == null) {
return null;
} else if (old != null) {
old.value = v;
afterNodeAccess(old);
return v;
}
else if (t != null)
t.putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, v);
else {
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, v, first);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1)
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
}
++modCount;
++size;
afterNodeInsertion(true);
return v;
} public V computeIfPresent(K key,
BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {
if (remappingFunction == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
Node<K,V> e; V oldValue;
int hash = hash(key);
if ((e = getNode(hash, key)) != null &&
(oldValue = e.value) != null) {
V v = remappingFunction.apply(key, oldValue);
if (v != null) {
e.value = v;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return v;
}
else
removeNode(hash, key, null, false, true);
}
return null;
} @Override
public V compute(K key,
BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {
if (remappingFunction == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = hash(key);
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first; int n, i;
int binCount = 0;
TreeNode<K,V> t = null;
Node<K,V> old = null;
if (size > threshold || (tab = table) == null ||
(n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((first = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
old = (t = (TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
else {
Node<K,V> e = first; K k;
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
old = e;
break;
}
++binCount;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
V oldValue = (old == null) ? null : old.value;
V v = remappingFunction.apply(key, oldValue);
if (old != null) {
if (v != null) {
old.value = v;
afterNodeAccess(old);
}
else
removeNode(hash, key, null, false, true);
}
else if (v != null) {
if (t != null)
t.putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, v);
else {
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, v, first);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1)
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
}
++modCount;
++size;
afterNodeInsertion(true);
}
return v;
} @Override
public V merge(K key, V value,
BiFunction<? super V, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {
if (value == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (remappingFunction == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = hash(key);
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first; int n, i;
int binCount = 0;
TreeNode<K,V> t = null;
Node<K,V> old = null;
if (size > threshold || (tab = table) == null ||
(n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((first = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
old = (t = (TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
else {
Node<K,V> e = first; K k;
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
old = e;
break;
}
++binCount;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
if (old != null) {
V v;
if (old.value != null)
v = remappingFunction.apply(old.value, value);
else
v = value;
if (v != null) {
old.value = v;
afterNodeAccess(old);
}
else
removeNode(hash, key, null, false, true);
return v;
}
if (value != null) {
if (t != null)
t.putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, first);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1)
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
}
++modCount;
++size;
afterNodeInsertion(true);
}
return value;
} @Override
public void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) {
Node<K,V>[] tab;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (size > 0 && (tab = table) != null) {
int mc = modCount;
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) {
for (Node<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next)
action.accept(e.key, e.value);
}
if (modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
} @Override
public void replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> function) {
Node<K,V>[] tab;
if (function == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (size > 0 && (tab = table) != null) {
int mc = modCount;
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) {
for (Node<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
e.value = function.apply(e.key, e.value);
}
}
if (modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
} /* ------------------------------------------------------------ */
// Cloning and serialization /**
* Returns a shallow copy of this <tt>HashMap</tt> instance: the keys and
* values themselves are not cloned.
*
* @return a shallow copy of this map
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public Object clone() {
HashMap<K,V> result;
try {
result = (HashMap<K,V>)super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable
throw new InternalError(e);
}
result.reinitialize();
result.putMapEntries(this, false);
return result;
} // These methods are also used when serializing HashSets
final float loadFactor() { return loadFactor; }
final int capacity() {
return (table != null) ? table.length :
(threshold > 0) ? threshold :
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
} /**
* Save the state of the <tt>HashMap</tt> instance to a stream (i.e.,
* serialize it).
*
* @serialData The <i>capacity</i> of the HashMap (the length of the
* bucket array) is emitted (int), followed by the
* <i>size</i> (an int, the number of key-value
* mappings), followed by the key (Object) and value (Object)
* for each key-value mapping. The key-value mappings are
* emitted in no particular order.
*/
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws IOException {
int buckets = capacity();
// Write out the threshold, loadfactor, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultWriteObject();
s.writeInt(buckets);
s.writeInt(size);
internalWriteEntries(s);
} /**
* Reconstitute the {@code HashMap} instance from a stream (i.e.,
* deserialize it).
*/
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in the threshold (ignored), loadfactor, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultReadObject();
reinitialize();
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
s.readInt(); // Read and ignore number of buckets
int mappings = s.readInt(); // Read number of mappings (size)
if (mappings < 0)
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal mappings count: " +
mappings);
else if (mappings > 0) { // (if zero, use defaults)
// Size the table using given load factor only if within
// range of 0.25...4.0
float lf = Math.min(Math.max(0.25f, loadFactor), 4.0f);
float fc = (float)mappings / lf + 1.0f;
int cap = ((fc < DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) ?
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY :
(fc >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor((int)fc));
float ft = (float)cap * lf;
threshold = ((cap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] tab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[cap];
table = tab; // Read the keys and values, and put the mappings in the HashMap
for (int i = 0; i < mappings; i++) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K key = (K) s.readObject();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
V value = (V) s.readObject();
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, false);
}
}
} /* ------------------------------------------------------------ */
// iterators abstract class HashIterator {
Node<K,V> next; // next entry to return
Node<K,V> current; // current entry
int expectedModCount; // for fast-fail
int index; // current slot HashIterator() {
expectedModCount = modCount;
Node<K,V>[] t = table;
current = next = null;
index = 0;
if (t != null && size > 0) { // advance to first entry
do {} while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null);
}
} public final boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
} final Node<K,V> nextNode() {
Node<K,V>[] t;
Node<K,V> e = next;
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
if ((next = (current = e).next) == null && (t = table) != null) {
do {} while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null);
}
return e;
} public final void remove() {
Node<K,V> p = current;
if (p == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
current = null;
K key = p.key;
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, false);
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
} final class KeyIterator extends HashIterator
implements Iterator<K> {
public final K next() { return nextNode().key; }
} final class ValueIterator extends HashIterator
implements Iterator<V> {
public final V next() { return nextNode().value; }
} final class EntryIterator extends HashIterator
implements Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public final Map.Entry<K,V> next() { return nextNode(); }
} /* ------------------------------------------------------------ */
// spliterators static class HashMapSpliterator<K,V> {
final HashMap<K,V> map;
Node<K,V> current; // current node
int index; // current index, modified on advance/split
int fence; // one past last index
int est; // size estimate
int expectedModCount; // for comodification checks HashMapSpliterator(HashMap<K,V> m, int origin,
int fence, int est,
int expectedModCount) {
this.map = m;
this.index = origin;
this.fence = fence;
this.est = est;
this.expectedModCount = expectedModCount;
} final int getFence() { // initialize fence and size on first use
int hi;
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
HashMap<K,V> m = map;
est = m.size;
expectedModCount = m.modCount;
Node<K,V>[] tab = m.table;
hi = fence = (tab == null) ? 0 : tab.length;
}
return hi;
} public final long estimateSize() {
getFence(); // force init
return (long) est;
}
} static final class KeySpliterator<K,V>
extends HashMapSpliterator<K,V>
implements Spliterator<K> {
KeySpliterator(HashMap<K,V> m, int origin, int fence, int est,
int expectedModCount) {
super(m, origin, fence, est, expectedModCount);
} public KeySpliterator<K,V> trySplit() {
int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
return (lo >= mid || current != null) ? null :
new KeySpliterator<>(map, lo, index = mid, est >>>= 1,
expectedModCount);
} public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super K> action) {
int i, hi, mc;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
HashMap<K,V> m = map;
Node<K,V>[] tab = m.table;
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
mc = expectedModCount = m.modCount;
hi = fence = (tab == null) ? 0 : tab.length;
}
else
mc = expectedModCount;
if (tab != null && tab.length >= hi &&
(i = index) >= 0 && (i < (index = hi) || current != null)) {
Node<K,V> p = current;
current = null;
do {
if (p == null)
p = tab[i++];
else {
action.accept(p.key);
p = p.next;
}
} while (p != null || i < hi);
if (m.modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
} public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super K> action) {
int hi;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
Node<K,V>[] tab = map.table;
if (tab != null && tab.length >= (hi = getFence()) && index >= 0) {
while (current != null || index < hi) {
if (current == null)
current = tab[index++];
else {
K k = current.key;
current = current.next;
action.accept(k);
if (map.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
} public int characteristics() {
return (fence < 0 || est == map.size ? Spliterator.SIZED : 0) |
Spliterator.DISTINCT;
}
} static final class ValueSpliterator<K,V>
extends HashMapSpliterator<K,V>
implements Spliterator<V> {
ValueSpliterator(HashMap<K,V> m, int origin, int fence, int est,
int expectedModCount) {
super(m, origin, fence, est, expectedModCount);
} public ValueSpliterator<K,V> trySplit() {
int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
return (lo >= mid || current != null) ? null :
new ValueSpliterator<>(map, lo, index = mid, est >>>= 1,
expectedModCount);
} public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super V> action) {
int i, hi, mc;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
HashMap<K,V> m = map;
Node<K,V>[] tab = m.table;
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
mc = expectedModCount = m.modCount;
hi = fence = (tab == null) ? 0 : tab.length;
}
else
mc = expectedModCount;
if (tab != null && tab.length >= hi &&
(i = index) >= 0 && (i < (index = hi) || current != null)) {
Node<K,V> p = current;
current = null;
do {
if (p == null)
p = tab[i++];
else {
action.accept(p.value);
p = p.next;
}
} while (p != null || i < hi);
if (m.modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
} public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super V> action) {
int hi;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
Node<K,V>[] tab = map.table;
if (tab != null && tab.length >= (hi = getFence()) && index >= 0) {
while (current != null || index < hi) {
if (current == null)
current = tab[index++];
else {
V v = current.value;
current = current.next;
action.accept(v);
if (map.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
} public int characteristics() {
return (fence < 0 || est == map.size ? Spliterator.SIZED : 0);
}
} static final class EntrySpliterator<K,V>
extends HashMapSpliterator<K,V>
implements Spliterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
EntrySpliterator(HashMap<K,V> m, int origin, int fence, int est,
int expectedModCount) {
super(m, origin, fence, est, expectedModCount);
} public EntrySpliterator<K,V> trySplit() {
int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
return (lo >= mid || current != null) ? null :
new EntrySpliterator<>(map, lo, index = mid, est >>>= 1,
expectedModCount);
} public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super Map.Entry<K,V>> action) {
int i, hi, mc;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
HashMap<K,V> m = map;
Node<K,V>[] tab = m.table;
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
mc = expectedModCount = m.modCount;
hi = fence = (tab == null) ? 0 : tab.length;
}
else
mc = expectedModCount;
if (tab != null && tab.length >= hi &&
(i = index) >= 0 && (i < (index = hi) || current != null)) {
Node<K,V> p = current;
current = null;
do {
if (p == null)
p = tab[i++];
else {
action.accept(p);
p = p.next;
}
} while (p != null || i < hi);
if (m.modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
} public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super Map.Entry<K,V>> action) {
int hi;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
Node<K,V>[] tab = map.table;
if (tab != null && tab.length >= (hi = getFence()) && index >= 0) {
while (current != null || index < hi) {
if (current == null)
current = tab[index++];
else {
Node<K,V> e = current;
current = current.next;
action.accept(e);
if (map.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
} public int characteristics() {
return (fence < 0 || est == map.size ? Spliterator.SIZED : 0) |
Spliterator.DISTINCT;
}
} /* ------------------------------------------------------------ */
// LinkedHashMap support /*
* The following package-protected methods are designed to be
* overridden by LinkedHashMap, but not by any other subclass.
* Nearly all other internal methods are also package-protected
* but are declared final, so can be used by LinkedHashMap, view
* classes, and HashSet.
*/ // Create a regular (non-tree) node
Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
return new Node<>(hash, key, value, next);
} // For conversion from TreeNodes to plain nodes
Node<K,V> replacementNode(Node<K,V> p, Node<K,V> next) {
return new Node<>(p.hash, p.key, p.value, next);
} // Create a tree bin node
TreeNode<K,V> newTreeNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
return new TreeNode<>(hash, key, value, next);
} // For treeifyBin
TreeNode<K,V> replacementTreeNode(Node<K,V> p, Node<K,V> next) {
return new TreeNode<>(p.hash, p.key, p.value, next);
} /**
* Reset to initial default state. Called by clone and readObject.
*/
void reinitialize() {
table = null;
entrySet = null;
keySet = null;
values = null;
modCount = 0;
threshold = 0;
size = 0;
} // Callbacks to allow LinkedHashMap post-actions
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> p) { }
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { }
void afterNodeRemoval(Node<K,V> p) { } // Called only from writeObject, to ensure compatible ordering.
void internalWriteEntries(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) throws IOException {
Node<K,V>[] tab;
if (size > 0 && (tab = table) != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) {
for (Node<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
s.writeObject(e.key);
s.writeObject(e.value);
}
}
}
} /* ------------------------------------------------------------ */
// Tree bins /**
* Entry for Tree bins. Extends LinkedHashMap.Entry (which in turn
* extends Node) so can be used as extension of either regular or
* linked node.
*/
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> {
TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links
TreeNode<K,V> left;
TreeNode<K,V> right;
TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion
boolean red;
TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, val, next);
} /**
* Returns root of tree containing this node.
*/
final TreeNode<K,V> root() {
for (TreeNode<K,V> r = this, p;;) {
if ((p = r.parent) == null)
return r;
r = p;
}
} /**
* Ensures that the given root is the first node of its bin.
*/
static <K,V> void moveRootToFront(Node<K,V>[] tab, TreeNode<K,V> root) {
int n;
if (root != null && tab != null && (n = tab.length) > 0) {
int index = (n - 1) & root.hash;
TreeNode<K,V> first = (TreeNode<K,V>)tab[index];
if (root != first) {
Node<K,V> rn;
tab[index] = root;
TreeNode<K,V> rp = root.prev;
if ((rn = root.next) != null)
((TreeNode<K,V>)rn).prev = rp;
if (rp != null)
rp.next = rn;
if (first != null)
first.prev = root;
root.next = first;
root.prev = null;
}
assert checkInvariants(root);
}
} /**
* Finds the node starting at root p with the given hash and key.
* The kc argument caches comparableClassFor(key) upon first use
* comparing keys.
*/
final TreeNode<K,V> find(int h, Object k, Class<?> kc) {
TreeNode<K,V> p = this;
do {
int ph, dir; K pk;
TreeNode<K,V> pl = p.left, pr = p.right, q;
if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
p = pl;
else if (ph < h)
p = pr;
else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (k != null && k.equals(pk)))
return p;
else if (pl == null)
p = pr;
else if (pr == null)
p = pl;
else if ((kc != null ||
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) != null) &&
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) != 0)
p = (dir < 0) ? pl : pr;
else if ((q = pr.find(h, k, kc)) != null)
return q;
else
p = pl;
} while (p != null);
return null;
} /**
* Calls find for root node.
*/
final TreeNode<K,V> getTreeNode(int h, Object k) {
return ((parent != null) ? root() : this).find(h, k, null);
} /**
* Tie-breaking utility for ordering insertions when equal
* hashCodes and non-comparable. We don't require a total
* order, just a consistent insertion rule to maintain
* equivalence across rebalancings. Tie-breaking further than
* necessary simplifies testing a bit.
*/
static int tieBreakOrder(Object a, Object b) {
int d;
if (a == null || b == null ||
(d = a.getClass().getName().
compareTo(b.getClass().getName())) == 0)
d = (System.identityHashCode(a) <= System.identityHashCode(b) ?
-1 : 1);
return d;
} /**
* Forms tree of the nodes linked from this node.
* @return root of tree
*/
final void treeify(Node<K,V>[] tab) {
TreeNode<K,V> root = null;
for (TreeNode<K,V> x = this, next; x != null; x = next) {
next = (TreeNode<K,V>)x.next;
x.left = x.right = null;
if (root == null) {
x.parent = null;
x.red = false;
root = x;
}
else {
K k = x.key;
int h = x.hash;
Class<?> kc = null;
for (TreeNode<K,V> p = root;;) {
int dir, ph;
K pk = p.key;
if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
dir = -1;
else if (ph < h)
dir = 1;
else if ((kc == null &&
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0)
dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk); TreeNode<K,V> xp = p;
if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {
x.parent = xp;
if (dir <= 0)
xp.left = x;
else
xp.right = x;
root = balanceInsertion(root, x);
break;
}
}
}
}
moveRootToFront(tab, root);
} /**
* Returns a list of non-TreeNodes replacing those linked from
* this node.
*/
final Node<K,V> untreeify(HashMap<K,V> map) {
Node<K,V> hd = null, tl = null;
for (Node<K,V> q = this; q != null; q = q.next) {
Node<K,V> p = map.replacementNode(q, null);
if (tl == null)
hd = p;
else
tl.next = p;
tl = p;
}
return hd;
} /**
* Tree version of putVal.
*/
final TreeNode<K,V> putTreeVal(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab,
int h, K k, V v) {
Class<?> kc = null;
boolean searched = false;
TreeNode<K,V> root = (parent != null) ? root() : this;
for (TreeNode<K,V> p = root;;) {
int dir, ph; K pk;
if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
dir = -1;
else if (ph < h)
dir = 1;
else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (k != null && k.equals(pk)))
return p;
else if ((kc == null &&
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0) {
if (!searched) {
TreeNode<K,V> q, ch;
searched = true;
if (((ch = p.left) != null &&
(q = ch.find(h, k, kc)) != null) ||
((ch = p.right) != null &&
(q = ch.find(h, k, kc)) != null))
return q;
}
dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk);
} TreeNode<K,V> xp = p;
if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {
Node<K,V> xpn = xp.next;
TreeNode<K,V> x = map.newTreeNode(h, k, v, xpn);
if (dir <= 0)
xp.left = x;
else
xp.right = x;
xp.next = x;
x.parent = x.prev = xp;
if (xpn != null)
((TreeNode<K,V>)xpn).prev = x;
moveRootToFront(tab, balanceInsertion(root, x));
return null;
}
}
} /**
* Removes the given node, that must be present before this call.
* This is messier than typical red-black deletion code because we
* cannot swap the contents of an interior node with a leaf
* successor that is pinned by "next" pointers that are accessible
* independently during traversal. So instead we swap the tree
* linkages. If the current tree appears to have too few nodes,
* the bin is converted back to a plain bin. (The test triggers
* somewhere between 2 and 6 nodes, depending on tree structure).
*/
final void removeTreeNode(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab,
boolean movable) {
int n;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
return;
int index = (n - 1) & hash;
TreeNode<K,V> first = (TreeNode<K,V>)tab[index], root = first, rl;
TreeNode<K,V> succ = (TreeNode<K,V>)next, pred = prev;
if (pred == null)
tab[index] = first = succ;
else
pred.next = succ;
if (succ != null)
succ.prev = pred;
if (first == null)
return;
if (root.parent != null)
root = root.root();
if (root == null || root.right == null ||
(rl = root.left) == null || rl.left == null) {
tab[index] = first.untreeify(map); // too small
return;
}
TreeNode<K,V> p = this, pl = left, pr = right, replacement;
if (pl != null && pr != null) {
TreeNode<K,V> s = pr, sl;
while ((sl = s.left) != null) // find successor
s = sl;
boolean c = s.red; s.red = p.red; p.red = c; // swap colors
TreeNode<K,V> sr = s.right;
TreeNode<K,V> pp = p.parent;
if (s == pr) { // p was s's direct parent
p.parent = s;
s.right = p;
}
else {
TreeNode<K,V> sp = s.parent;
if ((p.parent = sp) != null) {
if (s == sp.left)
sp.left = p;
else
sp.right = p;
}
if ((s.right = pr) != null)
pr.parent = s;
}
p.left = null;
if ((p.right = sr) != null)
sr.parent = p;
if ((s.left = pl) != null)
pl.parent = s;
if ((s.parent = pp) == null)
root = s;
else if (p == pp.left)
pp.left = s;
else
pp.right = s;
if (sr != null)
replacement = sr;
else
replacement = p;
}
else if (pl != null)
replacement = pl;
else if (pr != null)
replacement = pr;
else
replacement = p;
if (replacement != p) {
TreeNode<K,V> pp = replacement.parent = p.parent;
if (pp == null)
root = replacement;
else if (p == pp.left)
pp.left = replacement;
else
pp.right = replacement;
p.left = p.right = p.parent = null;
} TreeNode<K,V> r = p.red ? root : balanceDeletion(root, replacement); if (replacement == p) { // detach
TreeNode<K,V> pp = p.parent;
p.parent = null;
if (pp != null) {
if (p == pp.left)
pp.left = null;
else if (p == pp.right)
pp.right = null;
}
}
if (movable)
moveRootToFront(tab, r);
} /**
* Splits nodes in a tree bin into lower and upper tree bins,
* or untreeifies if now too small. Called only from resize;
* see above discussion about split bits and indices.
*
* @param map the map
* @param tab the table for recording bin heads
* @param index the index of the table being split
* @param bit the bit of hash to split on
*/
final void split(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab, int index, int bit) {
TreeNode<K,V> b = this;
// Relink into lo and hi lists, preserving order
TreeNode<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
TreeNode<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
int lc = 0, hc = 0;
for (TreeNode<K,V> e = b, next; e != null; e = next) {
next = (TreeNode<K,V>)e.next;
e.next = null;
if ((e.hash & bit) == 0) {
if ((e.prev = loTail) == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
++lc;
}
else {
if ((e.prev = hiTail) == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
++hc;
}
} if (loHead != null) {
if (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
tab[index] = loHead.untreeify(map);
else {
tab[index] = loHead;
if (hiHead != null) // (else is already treeified)
loHead.treeify(tab);
}
}
if (hiHead != null) {
if (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
tab[index + bit] = hiHead.untreeify(map);
else {
tab[index + bit] = hiHead;
if (loHead != null)
hiHead.treeify(tab);
}
}
} /* ------------------------------------------------------------ */
// Red-black tree methods, all adapted from CLR static <K,V> TreeNode<K,V> rotateLeft(TreeNode<K,V> root,
TreeNode<K,V> p) {
TreeNode<K,V> r, pp, rl;
if (p != null && (r = p.right) != null) {
if ((rl = p.right = r.left) != null)
rl.parent = p;
if ((pp = r.parent = p.parent) == null)
(root = r).red = false;
else if (pp.left == p)
pp.left = r;
else
pp.right = r;
r.left = p;
p.parent = r;
}
return root;
} static <K,V> TreeNode<K,V> rotateRight(TreeNode<K,V> root,
TreeNode<K,V> p) {
TreeNode<K,V> l, pp, lr;
if (p != null && (l = p.left) != null) {
if ((lr = p.left = l.right) != null)
lr.parent = p;
if ((pp = l.parent = p.parent) == null)
(root = l).red = false;
else if (pp.right == p)
pp.right = l;
else
pp.left = l;
l.right = p;
p.parent = l;
}
return root;
} static <K,V> TreeNode<K,V> balanceInsertion(TreeNode<K,V> root,
TreeNode<K,V> x) {
x.red = true;
for (TreeNode<K,V> xp, xpp, xppl, xppr;;) {
if ((xp = x.parent) == null) {
x.red = false;
return x;
}
else if (!xp.red || (xpp = xp.parent) == null)
return root;
if (xp == (xppl = xpp.left)) {
if ((xppr = xpp.right) != null && xppr.red) {
xppr.red = false;
xp.red = false;
xpp.red = true;
x = xpp;
}
else {
if (x == xp.right) {
root = rotateLeft(root, x = xp);
xpp = (xp = x.parent) == null ? null : xp.parent;
}
if (xp != null) {
xp.red = false;
if (xpp != null) {
xpp.red = true;
root = rotateRight(root, xpp);
}
}
}
}
else {
if (xppl != null && xppl.red) {
xppl.red = false;
xp.red = false;
xpp.red = true;
x = xpp;
}
else {
if (x == xp.left) {
root = rotateRight(root, x = xp);
xpp = (xp = x.parent) == null ? null : xp.parent;
}
if (xp != null) {
xp.red = false;
if (xpp != null) {
xpp.red = true;
root = rotateLeft(root, xpp);
}
}
}
}
}
} static <K,V> TreeNode<K,V> balanceDeletion(TreeNode<K,V> root,
TreeNode<K,V> x) {
for (TreeNode<K,V> xp, xpl, xpr;;) {
if (x == null || x == root)
return root;
else if ((xp = x.parent) == null) {
x.red = false;
return x;
}
else if (x.red) {
x.red = false;
return root;
}
else if ((xpl = xp.left) == x) {
if ((xpr = xp.right) != null && xpr.red) {
xpr.red = false;
xp.red = true;
root = rotateLeft(root, xp);
xpr = (xp = x.parent) == null ? null : xp.right;
}
if (xpr == null)
x = xp;
else {
TreeNode<K,V> sl = xpr.left, sr = xpr.right;
if ((sr == null || !sr.red) &&
(sl == null || !sl.red)) {
xpr.red = true;
x = xp;
}
else {
if (sr == null || !sr.red) {
if (sl != null)
sl.red = false;
xpr.red = true;
root = rotateRight(root, xpr);
xpr = (xp = x.parent) == null ?
null : xp.right;
}
if (xpr != null) {
xpr.red = (xp == null) ? false : xp.red;
if ((sr = xpr.right) != null)
sr.red = false;
}
if (xp != null) {
xp.red = false;
root = rotateLeft(root, xp);
}
x = root;
}
}
}
else { // symmetric
if (xpl != null && xpl.red) {
xpl.red = false;
xp.red = true;
root = rotateRight(root, xp);
xpl = (xp = x.parent) == null ? null : xp.left;
}
if (xpl == null)
x = xp;
else {
TreeNode<K,V> sl = xpl.left, sr = xpl.right;
if ((sl == null || !sl.red) &&
(sr == null || !sr.red)) {
xpl.red = true;
x = xp;
}
else {
if (sl == null || !sl.red) {
if (sr != null)
sr.red = false;
xpl.red = true;
root = rotateLeft(root, xpl);
xpl = (xp = x.parent) == null ?
null : xp.left;
}
if (xpl != null) {
xpl.red = (xp == null) ? false : xp.red;
if ((sl = xpl.left) != null)
sl.red = false;
}
if (xp != null) {
xp.red = false;
root = rotateRight(root, xp);
}
x = root;
}
}
}
}
} /**
* Recursive invariant check
*/
static <K,V> boolean checkInvariants(TreeNode<K,V> t) {
TreeNode<K,V> tp = t.parent, tl = t.left, tr = t.right,
tb = t.prev, tn = (TreeNode<K,V>)t.next;
if (tb != null && tb.next != t)
return false;
if (tn != null && tn.prev != t)
return false;
if (tp != null && t != tp.left && t != tp.right)
return false;
if (tl != null && (tl.parent != t || tl.hash > t.hash))
return false;
if (tr != null && (tr.parent != t || tr.hash < t.hash))
return false;
if (t.red && tl != null && tl.red && tr != null && tr.red)
return false;
if (tl != null && !checkInvariants(tl))
return false;
if (tr != null && !checkInvariants(tr))
return false;
return true;
}
} }
jdk1.8中的HashMap源码
2.3、HashMap的基本思想
2.3.1、 确定哈希桶数组索引位置
不管增加、删除、查找键值对,定位到哈希桶数组的位置都是很关键的第一步。前面说过HashMap的数据结构是数组和链表(链地址法)的结合,所以我们当然希望这个HashMap里面的元素位置尽量分布均匀些,尽量使得每个位置上的元素数量只有一个,那么当我们用hash算法求得这个位置的时候,马上就可以知道对应位置的元素就是我们要的,不用遍历链表,大大优化了查询的效率。HashMap定位数组索引位置,直接决定了hash方法的离散性能。先看看源码的实现:
方法一:
static final int hash(Object key) { //jdk1.8 & jdk1.7
int h;
// h = key.hashCode() 为第一步 取hashCode值
// h ^ (h >>> 16) 为第二步 高位参与运算
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
方法二:
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
//jdk1.7的源码,jdk1.8没有这个方法,但是实现原理一样的
return h & (length-1); //第三步 取模运算
}
这里的Hash算法本质上就是三步:取key的hashCode值、高位运算、取模运算。
对于任意给定的对象,只要它的hashCode()返回值相同,那么程序调用方法一所计算得到的Hash码值总是相同的。我们首先想到的就是把hash值对数组长度取模运算,这样一来,元素的分布相对来说是比较均匀的。但是,模运算的消耗还是比较大的,在HashMap中是这样做的:调用方法二来计算该对象应该保存在table数组的哪个索引处。这个方法非常巧妙,它通过h & (table.length -1)来得到该对象的保存位,而HashMap底层数组的长度总是2的n次方,这是HashMap在速度上的优化。当length总是2的n次方时,h& (length-1)运算等价于对length取模,也就是h%length,但是&比%具有更高的效率。
在JDK1.8的实现中,优化了高位运算的算法,通过hashCode()的高16位异或低16位实现的:(h = k.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16),主要是从速度、功效、质量来考虑的,这么做可以在数组table的length比较小的时候,也能保证考虑到高低bit都参与到Hash的计算中,同时不会有太大的开销。
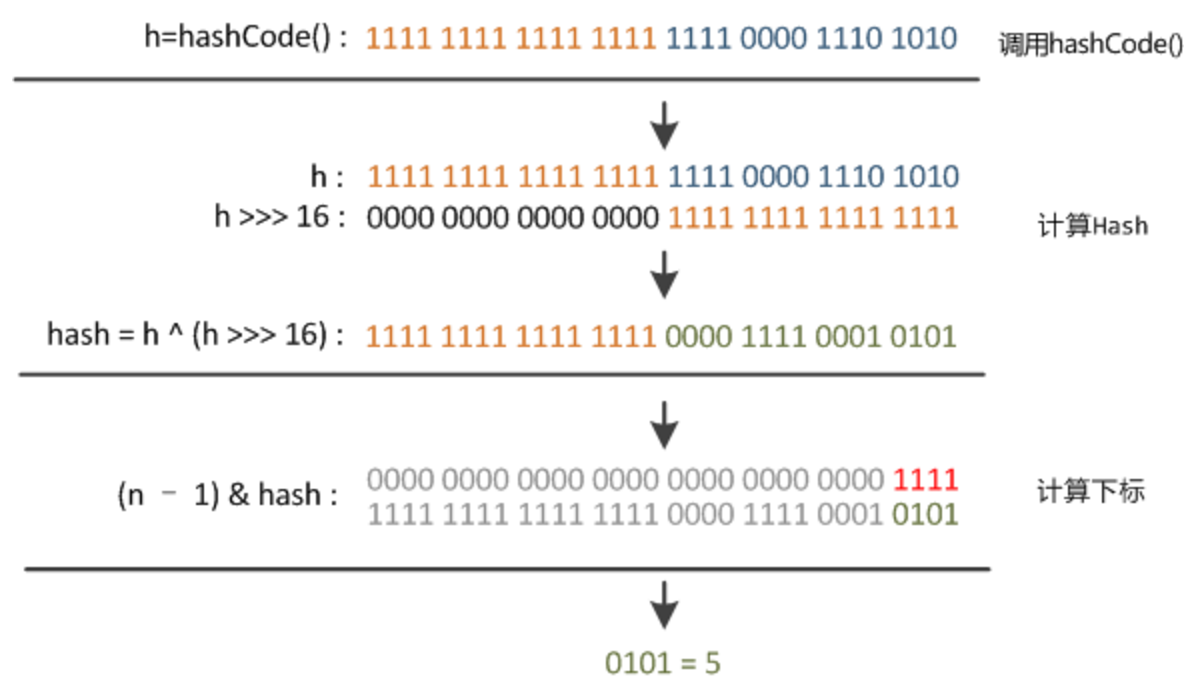
2.3.2、jdk1.8中的HashMap的put方法
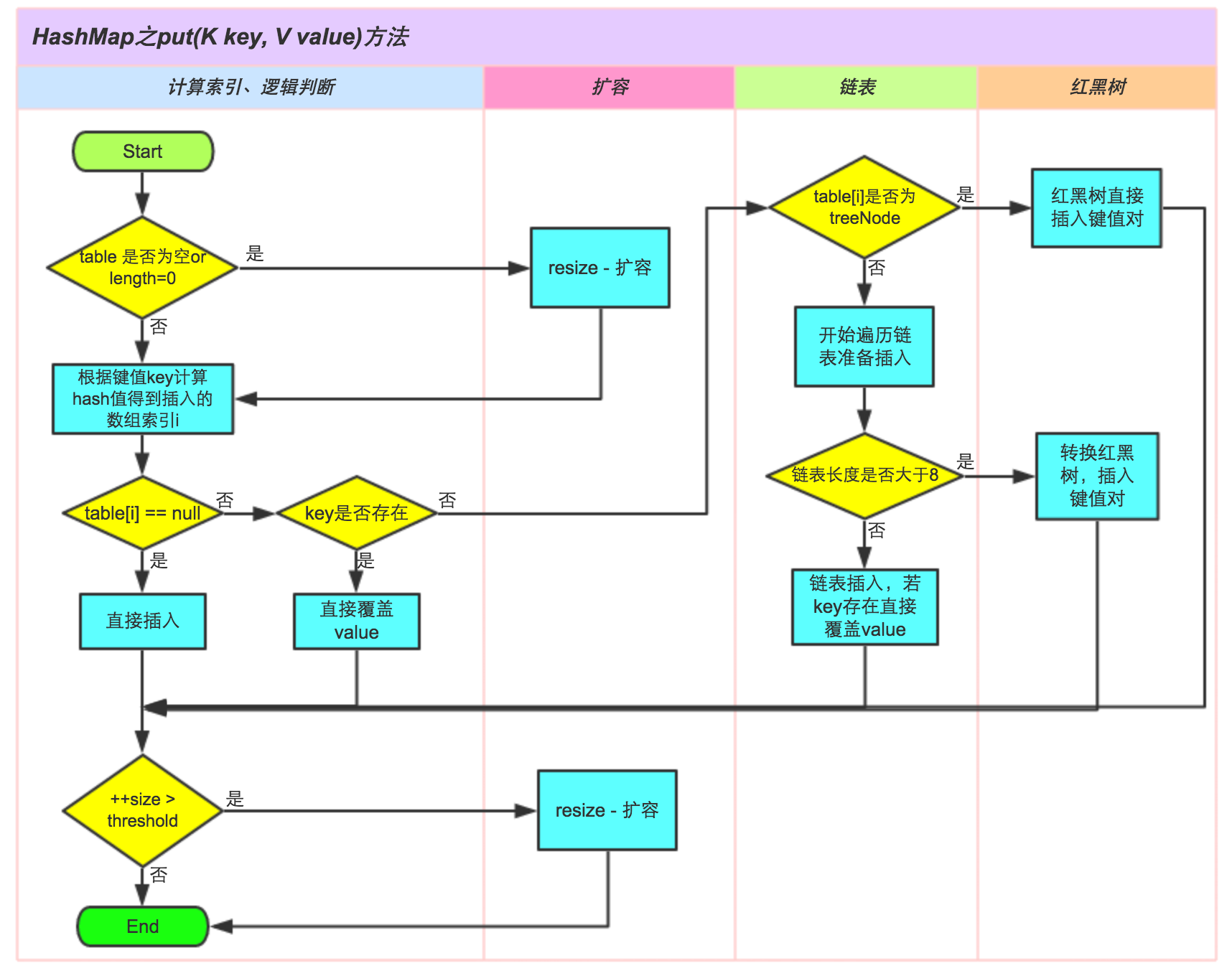
2.3.3、扩容机制
扩容(resize)就是重新计算容量,向HashMap对象里不停的添加元素,而HashMap对象内部的数组无法装载更多的元素时,对象就需要扩大数组的长度,以便能装入更多的元素。当然Java里的数组是无法自动扩容的,方法是使用一个新的数组代替已有的容量小的数组。
我们分析下resize的源码,鉴于JDK1.8融入了红黑树,较复杂,为了便于理解我们仍然使用JDK1.7的代码,好理解一些,本质上区别不大,具体区别后文再说。
void resize(int newCapacity) { //传入新的容量
Entry[] oldTable = table; //引用扩容前的Entry数组
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { //扩容前的数组大小如果已经达到最大(2^30)了
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; //修改阈值为int的最大值(2^31-1),这样以后就不会扩容了
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity]; //初始化一个新的Entry数组
transfer(newTable); //!!将数据转移到新的Entry数组里
table = newTable; //HashMap的table属性引用新的Entry数组
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);//修改阈值
}
这里就是使用一个容量更大的数组来代替已有的容量小的数组,transfer()方法将原有Entry数组的元素拷贝到新的Entry数组里。
void transfer(Entry[] newTable) {
Entry[] src = table; //src引用了旧的Entry数组
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (int j = 0; j < src.length; j++) { //遍历旧的Entry数组
Entry<K,V> e = src[j]; //取得旧Entry数组的每个元素
if (e != null) {
src[j] = null;//释放旧Entry数组的对象引用(for循环后,旧的Entry数组不再引用任何对象)
do {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity); //!!重新计算每个元素在数组中的位置
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e; //将元素放在数组上
e = next; //访问下一个Entry链上的元素
} while (e != null);
}
}
}
newTable[i]的引用赋给了e.next,也就是使用了单链表的头插入方式,同一位置上新元素总会被放在链表的头部位置;这样先放在一个索引上的元素终会被放到Entry链的尾部(如果发生了hash冲突的话),这一点和Jdk1.8有区别,下文详解。在旧数组中同一条Entry链上的元素,通过重新计算索引位置后,有可能被放到了新数组的不同位置上。
下面举个例子说明下扩容过程。假设了我们的hash算法就是简单的用key mod 一下表的大小(也就是数组的长度)。其中的哈希桶数组table的size=2, 所以key = 3、7、5,put顺序依次为 5、7、3。在mod 2以后都冲突在table[1]这里了。这里假设负载因子 loadFactor=1,即当键值对的实际大小size 大于 table的实际大小时进行扩容。接下来的三个步骤是哈希桶数组 resize成4,然后所有的Node重新rehash的过程。
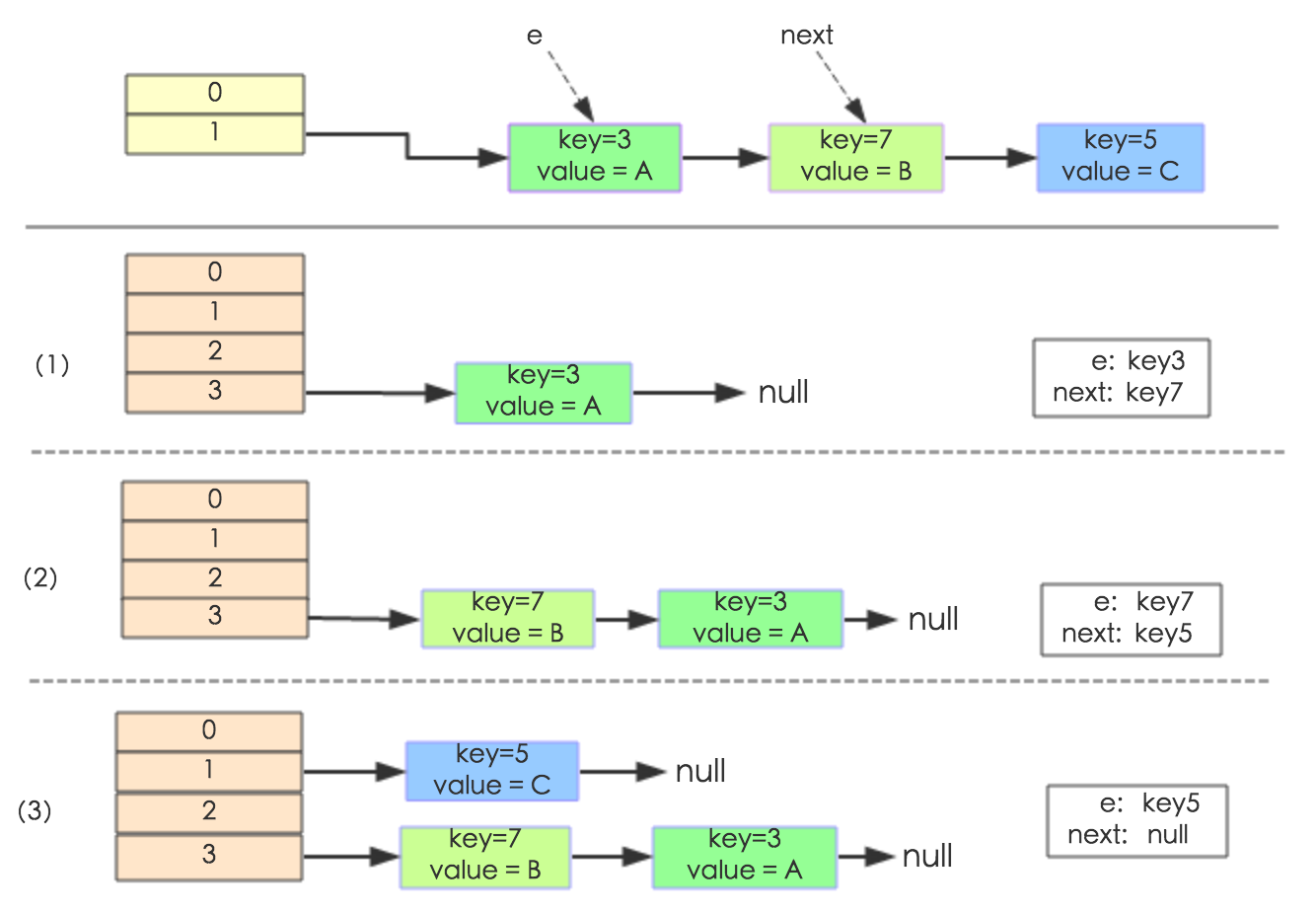
下面我们讲解下JDK1.8做的优化。经过观测可以发现,我们使用的是2次幂的扩展(指长度扩为原来2倍),所以,元素的位置要么是在原位置,要么是在原位置再移动2次幂的位置。下图n为table的长度,图(a)表示扩容前的key1和key2两种key确定索引位置的示例,图(b)表示扩容后key1和key2两种key确定索引位置的示例,其中hash1是key1对应的哈希与高位运算结果。
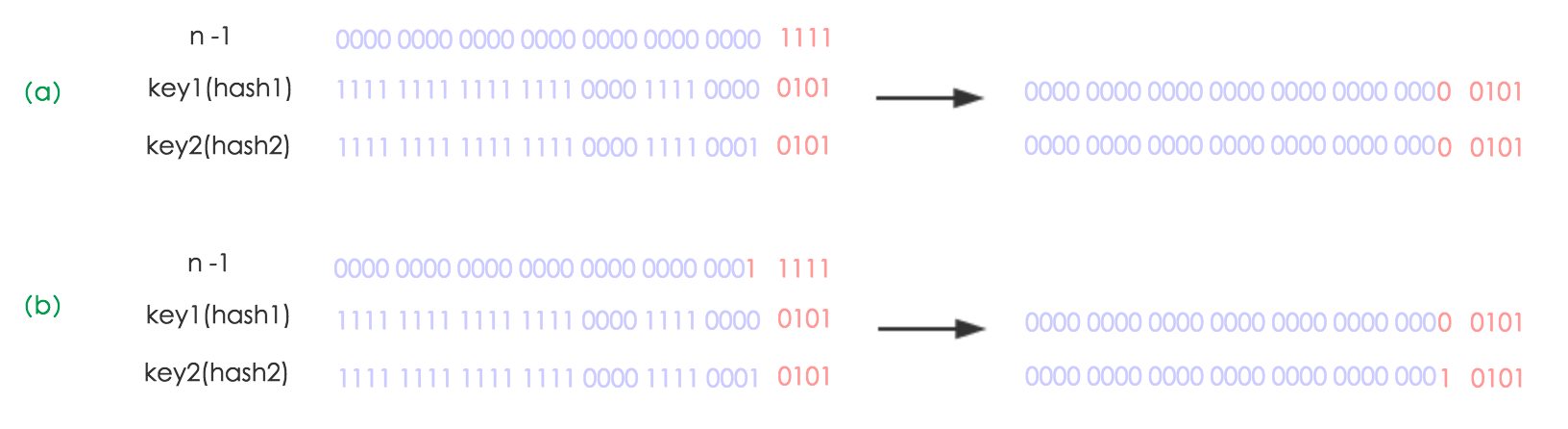
元素在重新计算hash之后,因为n变为2倍,那么n-1的mask范围在高位多1bit(红色),因此新的index就会发生这样的变化:
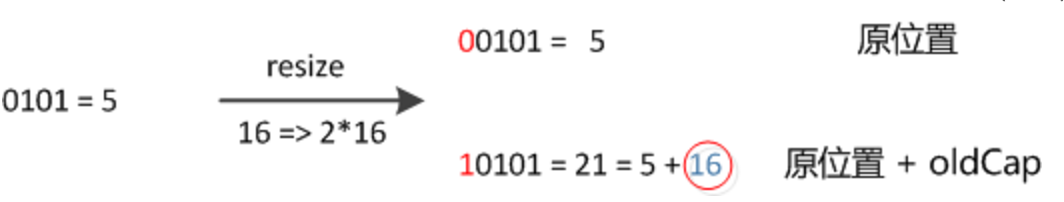
因此,我们在扩充HashMap的时候,不需要像JDK1.7的实现那样重新计算hash,只需要看看原来的hash值新增的那个bit是1还是0就好了,是0的话索引没变,是1的话索引变成“原索引+oldCap”,可以看看下图为16扩充为32的resize示意图:
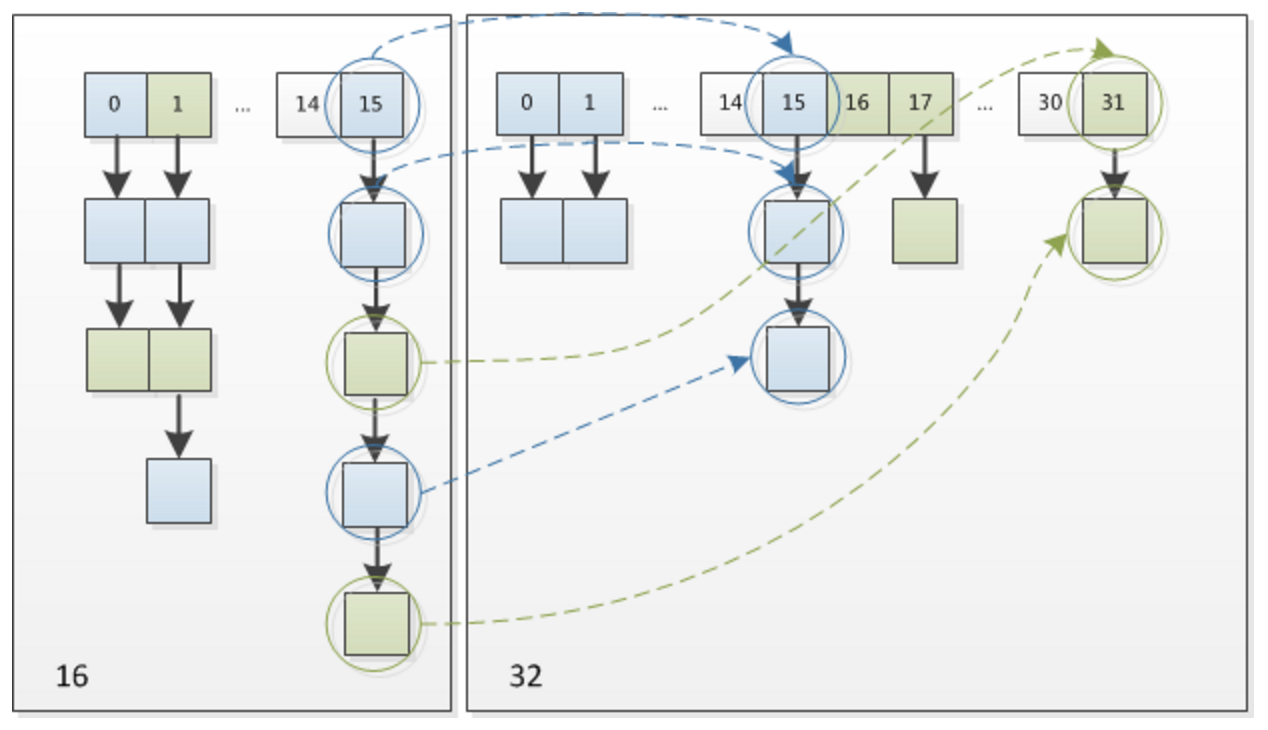
这个设计确实非常的巧妙,既省去了重新计算hash值的时间,而且同时,由于新增的1bit是0还是1可以认为是随机的,因此resize的过程,均匀的把之前的冲突的节点分散到新的bucket了。这一块就是JDK1.8新增的优化点。有一点注意区别,JDK1.7中rehash的时候,旧链表迁移新链表的时候,如果在新表的数组索引位置相同,则链表元素会倒置,但是JDK1.8不会倒置。
(1) 扩容是一个特别耗性能的操作,所以当程序员在使用HashMap的时候,估算map的大小,初始化的时候给一个大致的数值,避免map进行频繁的扩容。
(2) 负载因子是可以修改的,也可以大于1,但是建议不要轻易修改,除非情况非常特殊。
(3) HashMap是线程不安全的,不要在并发的环境中同时操作HashMap,建议使用ConcurrentHashMap。
(4) JDK1.8引入红黑树大程度优化了HashMap的性能。
三、ConcurrentHashMap的介绍
HashMap是非线程安全的,这意味着不应该在多个线程中对这些Map进行修改操作,轻则会产生数据不一致的问题,甚至还会因为并发插入元素而导致链表成环(插入会触发扩容,而扩容操作需要将原数组中的元素rehash到新数组,这时并发操作就有可能产生链表的循环引用从而成环),这样在查找时就会发生死循环,影响到整个应用程序。
Collections.synchronizedMap(Map<K,V> m)可以将一个Map转换成线程安全的实现,其实也就是通过一个包装类,然后把所有功能都委托给传入的Map实现,而且包装类是基于synchronized关键字来保证线程安全的(Hashtable也是基于synchronized关键字),底层使用的是互斥锁(同一时间内只能由持有锁的线程访问,其他竞争线程进入睡眠状态),性能与吞吐量比较低。
public static <K,V> Map<K,V> synchronizedMap(Map<K,V> m) {
return new SynchronizedMap<>(m);
}
private static class SynchronizedMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1978198479659022715L;
private final Map<K,V> m; // Backing Map
final Object mutex; // Object on which to synchronize
SynchronizedMap(Map<K,V> m) {
this.m = Objects.requireNonNull(m);
mutex = this;
}
SynchronizedMap(Map<K,V> m, Object mutex) {
this.m = m;
this.mutex = mutex;
}
public int size() {
synchronized (mutex) {return m.size();}
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
synchronized (mutex) {return m.isEmpty();}
}
............
}
然而ConcurrentHashMap的实现细节远没有这么简单,因此性能也要高上许多。它没有使用一个全局锁来锁住自己,而是采用了减少锁粒度的方法,尽量减少因为竞争锁而导致的阻塞与冲突,而且ConcurrentHashMap的检索操作是不需要锁的。
在Java 7中,ConcurrentHashMap把内部细分成了若干个小的HashMap,称之为段(Segment),默认被分为16个段。对于一个写操作而言,会先根据hash code进行寻址,得出该Entry应被存放在哪一个Segment,然后只要对该Segment加锁即可。理想情况下,一个默认的ConcurrentHashMap可以同时接受16个线程进行写操作(如果都是对不同Segment进行操作的话)。分段锁对于size()这样的全局操作来说就没有任何作用了,想要得出Entry的数量就需要遍历所有Segment,获得所有的锁,然后再统计总数。事实上,ConcurrentHashMap会先试图使用无锁的方式统计总数,这个尝试会进行3次,如果在相邻的2次计算中获得的Segment的modCount次数一致,代表这两次计算过程中都没有发生过修改操作,那么就可以当做最终结果返回,否则,就要获得所有Segment的锁,重新计算size。
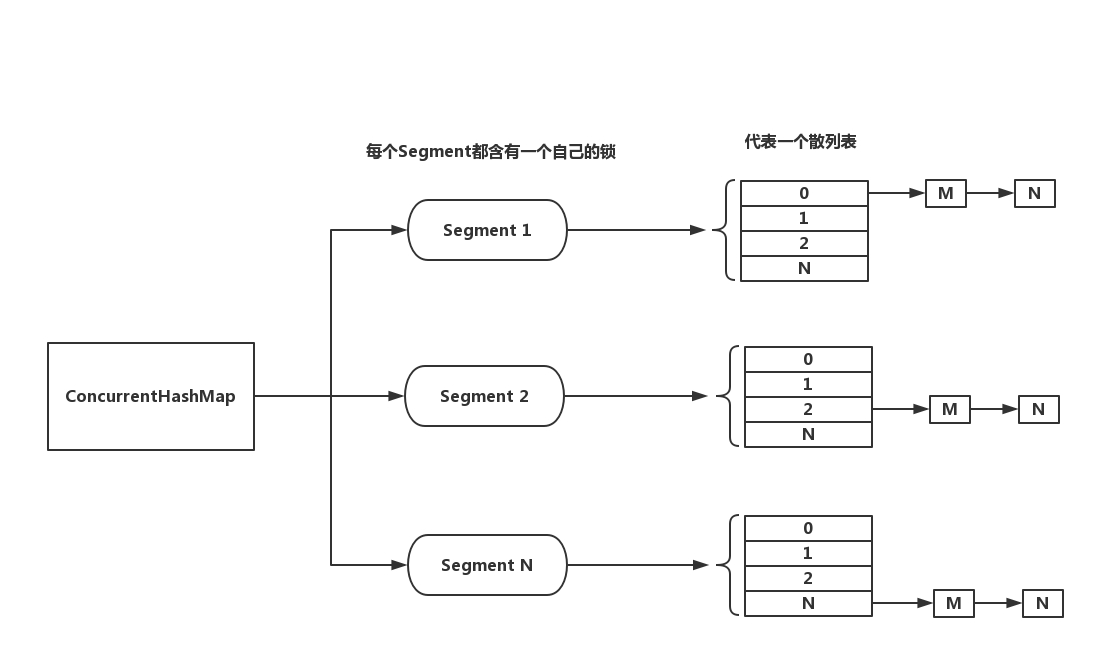
而Java 8的ConcurrentHashMap,它与Java 7的实现差别较大。完全放弃了段的设计,而是变回与HashMap相似的设计,使用buckets数组与分离链接法(同样会在超过阈值时树化,对于构造红黑树的逻辑与HashMap差别不大,只不过需要额外使用CAS来保证线程安全),锁的粒度也被细分到每个数组元素(因为HashMap在Java 8中也实现了不少优化,即使碰撞严重,也能保证一定的性能,而且Segment不仅臃肿还有弱一致性的问题存在),所以它的并发级别与数组长度相关(Java 7则是与段数相关)。
3.1、ConcurrentHashMap散列函数
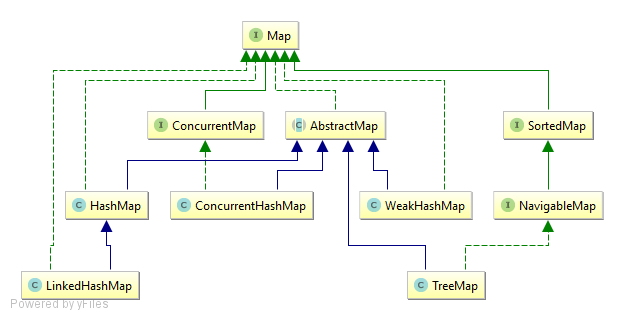
ConcurrentHashMap的散列函数与HashMap并没有什么区别,同样是把key的hash code的高16位与低16位进行异或运算(因为ConcurrentHashMap的buckets数组长度也永远是一个2的N次方),然后将扰乱后的hash code与数组的长度减一(实际可访问到的最大索引)进行与运算,得出的结果即是目标所在的位置。
// 2^31 - 1,int类型的最大值
// 该掩码表示节点hash的可用位,用来保证hash永远为一个正整数
static final int HASH_BITS = 0x7fffffff;
static final int spread(int h) {
return (h ^ (h >>> 16)) & HASH_BITS;
}
3.2、查找操作
下面是查找操作的源码:
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
int h = spread(key.hashCode());
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
// 先尝试判断链表头是否为目标,如果是就直接返回
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
}
else if (eh < 0)
// eh < 0代表这是一个特殊节点(TreeBin或ForwardingNode)
// 所以直接调用find()进行遍历查找
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
// 遍历链表
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}
一个普通的节点(链表节点)的hash不可能小于0(已经在spread()函数中修正过了),所以小于0的只可能是一个特殊节点,它不能用while循环中遍历链表的方式来进行遍历。TreeBin是红黑树的头部节点(红黑树的节点为TreeNode),它本身不含有key与value,而是指向一个TreeNode节点的链表与它们的根节点,同时使用CAS实现了一个读写锁,迫使Writer(持有这个锁)在树重构操作之前等待Reader完成。ForwardingNode是一个在数据转移过程(由扩容引起)中使用的临时节点,它会被插入到头部。它与TreeBin(和TreeNode)都是Node类的子类,为了判断出哪些是特殊节点,TreeBin和ForwardingNode的hash域都只是一个虚拟值:
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
volatile V val;
volatile Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
public final V setValue(V value) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
......
/**
* Virtualized support for map.get(); overridden in subclasses.
*/
Node<K,V> find(int h, Object k) {
Node<K,V> e = this;
if (k != null) {
do {
K ek;
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == k || (ek != null && k.equals(ek))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
return null;
}
}
/*
* Encodings for Node hash fields. See above for explanation.
*/
static final int MOVED = -1; // hash for forwarding nodes
static final int TREEBIN = -2; // hash for roots of trees
static final int RESERVED = -3; // hash for transient reservations
static final class TreeBin<K,V> extends Node<K,V> {
....
TreeBin(TreeNode<K,V> b) {
super(TREEBIN, null, null, null);
....
}
....
}
static final class ForwardingNode<K,V> extends Node<K,V> {
final Node<K,V>[] nextTable;
ForwardingNode(Node<K,V>[] tab) {
super(MOVED, null, null, null);
this.nextTable = tab;
}
.....
}
我们在get()函数中并没有发现任何与锁相关的代码,那么它是怎么保证线程安全的呢?一个操作ConcurrentHashMap.get("a"),它的步骤基本分为以下几步:
根据散列函数计算出的索引访问table。
从table中取出头节点。
遍历头节点直到找到目标节点。
从目标节点中取出value并返回。
所以只要保证访问table与节点的操作总是能够返回最新的数据就可以了。ConcurrentHashMap并没有采用锁的方式,而是通过volatile关键字来保证它们的可见性。在代码中可以发现,table、Node.val和Node.next都是被volatile关键字所修饰的。
volatile关键字保证了多线程环境下变量的可见性与有序性,底层实现基于内存屏障(Memory Barrier)。为了优化性能,现代CPU工作时的指令执行顺序与应用程序的代码顺序其实是不一致的(有些编译器也会进行这种优化),也就是所谓的乱序执行技术。乱序执行可以提高CPU流水线的工作效率,只要保证数据符合程序逻辑上的正确性即可(遵循happens-before原则)。不过如今是多核时代,如果随便乱序而不提供防护措施那是会出问题的。每一个cpu上都会进行乱序优化,单cpu所保证的逻辑次序可能会被其他cpu所破坏。内存屏障就是针对此情况的防护措施。可以认为它是一个同步点(但它本身也是一条cpu指令)。例如在IA32指令集架构中引入的SFENCE指令,在该指令之前的所有写操作必须全部完成,读操作仍可以乱序执行。LFENCE指令则保证之前的所有读操作必须全部完成,另外还有粒度更粗的MFENCE指令保证之前的所有读写操作都必须全部完成。内存屏障就像是一个保护指令顺序的栅栏,保护后面的指令不被前面的指令跨越。将内存屏障插入到写操作与读操作之间,就可以保证之后的读操作可以访问到最新的数据,因为屏障前的写操作已经把数据写回到内存(根据缓存一致性协议,不会直接写回到内存,而是改变该cpu私有缓存中的状态,然后通知给其他cpu这个缓存行已经被修改过了,之后另一个cpu在读操作时就可以发现该缓存行已经是无效的了,这时它会从其他cpu中读取最新的缓存行,然后之前的cpu才会更改状态并写回到内存)。
例如,读一个被volatile修饰的变量V总是能够从JMM(Java Memory Model)主内存中获得最新的数据。因为内存屏障的原因,每次在使用变量V(通过JVM指令use,后面说的也都是JVM中的指令而不是cpu)之前都必须先执行load指令(把从主内存中得到的数据放入到工作内存),根据JVM的规定,load指令必须发生在read指令(从主内存中读取数据)之后,所以每次访问变量V都会先从主内存中读取。相对的,写操作也因为内存屏障保证的指令顺序,每次都会直接写回到主内存。不过volatile关键字并不能保证操作的原子性,对该变量进行并发的连续操作是非线程安全的,所幸ConcurrentHashMap只是用来确保访问到的变量是最新的,所以也不会发生什么问题。
出于性能考虑,Doug Lea(java.util.concurrent包的作者)直接通过Unsafe类来对table进行操作。Java号称是安全的编程语言,而保证安全的代价就是牺牲程序员自由操控内存的能力。像在C/C++中可以通过操作指针变量达到操作内存的目的(其实操作的是虚拟地址),但这种灵活性在新手手中也经常会带来一些愚蠢的错误,比如内存访问越界。Unsafe从字面意思可以看出是不安全的,它包含了许多本地方法(在JVM平台上运行的其他语言编写的程序,主要为C/C++,由JNI实现),这些方法支持了对指针的操作,所以它才被称为是不安全的。虽然不安全,但毕竟是由C/C++实现的,像一些与操作系统交互的操作肯定是快过Java的,毕竟Java与操作系统之间还隔了一层抽象(JVM),不过代价就是失去了JVM所带来的多平台可移植性(本质上也只是一个c/cpp文件,如果换了平台那就要重新编译)。
对table进行操作的函数有以下三个,都使用到了Unsafe(在java.util.concurrent包随处可见):
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static final <K,V> Node<K,V> tabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i) {
// 从tab数组中获取一个引用,遵循Volatile语义
// 参数2是一个在tab中的偏移量,用来寻找目标对象
return (Node<K,V>)U.getObjectVolatile(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE);
}
static final <K,V> boolean casTabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i,
Node<K,V> c, Node<K,V> v) {
// 通过CAS操作将tab数组中位于参数2偏移量位置的值替换为v
// c是期望值,如果期望值与实际值不符,返回false
// 否则,v会成功地被设置到目标位置,返回true
return U.compareAndSwapObject(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE, c, v);
}
static final <K,V> void setTabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i, Node<K,V> v) {
// 设置tab数组中位于参数2偏移量位置的值,遵循Volatile语义
U.putObjectVolatile(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE, v);
}
初始化:ConcurrentHashMap与HashMap一样是Lazy的,buckets数组会在第一次访问put()函数时进行初始化,它的默认构造函数甚至是个空函数。
/**
* Creates a new, empty map with the default initial table size (16).
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap() {
}
但是有一点需要注意,ConcurrentHashMap是工作在多线程并发环境下的,如果有多个线程同时调用了put()函数该怎么办?这会导致重复初始化,所以必须要有对应的防护措施。ConcurrentHashMap声明了一个用于控制table的初始化与扩容的实例变量sizeCtl,默认值为0。当它是一个负数的时候,代表table正处于初始化或者扩容的状态。-1表示table正在进行初始化,-N则表示当前有N-1个线程正在进行扩容。在其他情况下,如果table还未初始化(table == null),sizeCtl表示table进行初始化的数组大小(所以从构造函数传入的initialCapacity在经过计算后会被赋给它)。如果table已经初始化过了,则表示下次触发扩容操作的阈值,算法stzeCtl = n - (n >>> 2),也就是n的75%,与默认负载因子(0.75)的HashMap一致。
private transient volatile int sizeCtl;
初始化table的操作位于函数initTable(),源码如下:
/**
* Initializes table, using the size recorded in sizeCtl.
*/
private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() {
Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc;
while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
// sizeCtl小于0,这意味着已经有其他线程进行初始化了
// 所以当前线程让出CPU时间片
if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0)
Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spin
// 否则,通过CAS操作尝试修改sizeCtl
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
try {
if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
// 默认构造函数,sizeCtl = 0,使用默认容量(16)进行初始化
// 否则,会根据sizeCtl进行初始化
int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n];
table = tab = nt;
// 计算阈值,n的75%
sc = n - (n >>> 2);
}
} finally {
// 阈值赋给sizeCtl
sizeCtl = sc;
}
break;
}
}
return tab;
}
sizeCtl是一个volatile变量,只要有一个线程CAS操作成功,sizeCtl就会被暂时地修改为-1,这样其他线程就能够根据sizeCtl得知table是否已经处于初始化状态中,最后sizeCtl会被设置成阈值,用于触发扩容操作。
3.3、扩容
ConcurrentHashMap触发扩容的时机与HashMap类似,要么是在将链表转换成红黑树时判断table数组的长度是否小于阈值(64),如果小于就进行扩容而不是树化,要么就是在添加元素的时候,判断当前Entry数量是否超过阈值,如果超过就进行扩容。
private final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int index) {
Node<K,V> b; int n, sc;
if (tab != null) {
// 小于MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY,进行扩容
if ((n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)
tryPresize(n << 1);
else if ((b = tabAt(tab, index)) != null && b.hash >= 0) {
synchronized (b) {
// 将链表转换成红黑树...
}
}
}
}
...
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
...
addCount(1L, binCount); // 计数
return null;
}
private final void addCount(long x, int check) {
// 计数...
if (check >= 0) {
Node<K,V>[] tab, nt; int n, sc;
// s(元素个数)大于等于sizeCtl,触发扩容
while (s >= (long)(sc = sizeCtl) && (tab = table) != null &&
(n = tab.length) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
// 扩容标志位
int rs = resizeStamp(n);
// sizeCtl为负数,代表正有其他线程进行扩容
if (sc < 0) {
// 扩容已经结束,中断循环
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null ||
transferIndex <= 0)
break;
// 进行扩容,并设置sizeCtl,表示扩容线程 + 1
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1))
transfer(tab, nt);
}
// 触发扩容(第一个进行扩容的线程)
// 并设置sizeCtl告知其他线程
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,
(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))
transfer(tab, null);
// 统计个数,用于循环检测是否还需要扩容
s = sumCount();
}
}
}
扩容代码
可以看到有关sizeCtl的操作牵涉到了大量的位运算,我们先来理解这些位运算的意义。首先是resizeStamp(),该函数返回一个用于数据校验的标志位,意思是对长度为n的table进行扩容。它将n的前导零(最高有效位之前的零的数量)和1 << 15做或运算,这时低16位的最高位为1,其他都为n的前导零。
static final int resizeStamp(int n) {
// RESIZE_STAMP_BITS = 16
return Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(n) | (1 << (RESIZE_STAMP_BITS - 1));
}
初始化sizeCtl(扩容操作被第一个线程首次进行)的算法为(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2,首先RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT = 32 - RESIZE_STAMP_BITS = 16,那么rs << 16等于将这个标志位移动到了高16位,这时最高位为1,所以sizeCtl此时是个负数,然后加二(至于为什么是2,还记得有关sizeCtl的说明吗?1代表初始化状态,所以实际的线程个数是要减去1的)代表当前有一个线程正在进行扩容,这样sizeCtl就被分割成了两部分,高16位是一个对n的数据校验的标志位,低16位表示参与扩容操作的线程个数 + 1。可能会有读者有所疑惑,更新进行扩容的线程数量的操作为什么是sc + 1而不是sc - 1,这是因为对sizeCtl的操作都是基于位运算的,所以不会关心它本身的数值是多少,只关心它在二进制上的数值,而sc + 1会在低16位上加1。

tryPresize()函数跟addCount()的后半段逻辑类似,不断地根据sizeCtl判断当前的状态,然后选择对应的策略。
private final void tryPresize(int size) {
// 对size进行修正
int c = (size >= (MAXIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1)) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor(size + (size >>> 1) + 1);
int sc;
// sizeCtl是默认值或正整数
// 代表table还未初始化
// 或还没有其他线程正在进行扩容
while ((sc = sizeCtl) >= 0) {
Node<K,V>[] tab = table; int n;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) {
n = (sc > c) ? sc : c;
// 设置sizeCtl,告诉其他线程,table现在正处于初始化状态
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
try {
if (table == tab) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n];
table = nt;
// 计算下次触发扩容的阈值
sc = n - (n >>> 2);
}
} finally {
// 将阈值赋给sizeCtl
sizeCtl = sc;
}
}
}
// 没有超过阈值或者大于容量的上限,中断循环
else if (c <= sc || n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
break;
// 进行扩容,与addCount()后半段的逻辑一致
else if (tab == table) {
int rs = resizeStamp(n);
if (sc < 0) {
Node<K,V>[] nt;
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null ||
transferIndex <= 0)
break;
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1))
transfer(tab, nt);
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,
(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))
transfer(tab, null);
}
}
}
tryPresize
扩容操作的核心在于数据的转移,在单线程环境下数据的转移很简单,无非就是把旧数组中的数据迁移到新的数组。但是这在多线程环境下是行不通的,需要保证线程安全性,在扩容的时候其他线程也可能正在添加元素,这时又触发了扩容怎么办?有人可能会说,用一个互斥锁把数据转移操作的过程锁住不就好了?这确实是一种可行的解决方法,但同样也会带来极差的吞吐量。互斥锁会导致所有访问临界区的线程陷入阻塞状态,这会消耗额外的系统资源,内核需要保存这些线程的上下文并放到阻塞队列,持有锁的线程耗时越长,其他竞争线程就会一直被阻塞,因此吞吐量低下,导致响应时间缓慢。而且锁总是会伴随着死锁问题,一旦发生死锁,整个应用程序都会因此受到影响,所以加锁永远是最后的备选方案。Doug Lea没有选择直接加锁,而是基于CAS实现无锁的并发同步策略,令人佩服的是他不仅没有把其他线程拒之门外,甚至还邀请它们一起来协助工作。那么如何才能让多个线程协同工作呢?Doug Lea把整个table数组当做多个线程之间共享的任务队列,然后只需维护一个指针,当有一个线程开始进行数据转移,就会先移动指针,表示指针划过的这片bucket区域由该线程负责。这个指针被声明为一个volatile整型变量,它的初始位置位于table的尾部,即它等于table.length,很明显这个任务队列是逆向遍历的。
/**
* The next table index (plus one) to split while resizing.
*/
private transient volatile int transferIndex;
/**
* 一个线程需要负责的最小bucket数
*/
private static final int MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE = 16; /**
* The next table to use; non-null only while resizing.
*/
private transient volatile Node<K,V>[] nextTable;
一个已经迁移完毕的bucket会被替换成ForwardingNode节点,用来标记此bucket已经被其他线程迁移完毕了。ForwardingNode是一个特殊节点,可以通过hash域的虚拟值来识别它,它同样重写了find()函数,用来在新数组中查找目标。数据迁移的操作位于transfer()函数,多个线程之间依靠sizeCtl与transferIndex指针来协同工作,每个线程都有自己负责的区域,一个完成迁移的bucket会被设置为ForwardingNode,其他线程遇见这个特殊节点就跳过该bucket,处理下一个bucket。transfer()函数可以大致分为三部分,第一部分对后续需要使用的变量进行初始化:
/**
* Moves and/or copies the nodes in each bin to new table. See
* above for explanation.
*/
private final void transfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V>[] nextTab) {
int n = tab.length, stride;
// 根据当前机器的CPU数量来决定每个线程负责的bucket数
// 避免因为扩容线程过多,反而影响到性能
if ((stride = (NCPU > 1) ? (n >>> 3) / NCPU : n) < MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE)
stride = MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE; // subdivide range
// 初始化nextTab,容量为旧数组的一倍
if (nextTab == null) { // initiating
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n << 1];
nextTab = nt;
} catch (Throwable ex) { // try to cope with OOME
sizeCtl = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
nextTable = nextTab;
transferIndex = n; // 初始化指针
}
int nextn = nextTab.length;
ForwardingNode<K,V> fwd = new ForwardingNode<K,V>(nextTab);
boolean advance = true;
boolean finishing = false; // to ensure sweep before committing nextTab
第二部分为当前线程分配任务和控制当前线程的任务进度,这部分是transfer()的核心逻辑,描述了如何与其他线程协同工作:
// i指向当前bucket,bound表示当前线程所负责的bucket区域的边界
for (int i = 0, bound = 0;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int fh;
// 这个循环使用CAS不断尝试为当前线程分配任务
// 直到分配成功或任务队列已经被全部分配完毕
// 如果当前线程已经被分配过bucket区域
// 那么会通过--i指向下一个待处理bucket然后退出该循环
while (advance) {
int nextIndex, nextBound;
// --i表示将i指向下一个待处理的bucket
// 如果--i >= bound,代表当前线程已经分配过bucket区域
// 并且还留有未处理的bucket
if (--i >= bound || finishing)
advance = false;
// transferIndex指针 <= 0 表示所有bucket已经被分配完毕
else if ((nextIndex = transferIndex) <= 0) {
i = -1;
advance = false;
}
// 移动transferIndex指针
// 为当前线程设置所负责的bucket区域的范围
// i指向该范围的第一个bucket,注意i是逆向遍历的
// 这个范围为(bound, i),i是该区域最后一个bucket,遍历顺序是逆向的
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt
(this, TRANSFERINDEX, nextIndex,
nextBound = (nextIndex > stride ?
nextIndex - stride : 0))) {
bound = nextBound;
i = nextIndex - 1;
advance = false;
}
}
// 当前线程已经处理完了所负责的所有bucket
if (i < 0 || i >= n || i + n >= nextn) {
int sc;
// 如果任务队列已经全部完成
if (finishing) {
nextTable = null;
table = nextTab;
// 设置新的阈值
sizeCtl = (n << 1) - (n >>> 1);
return;
}
// 工作中的扩容线程数量减1
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc = sizeCtl, sc - 1)) {
// (resizeStamp << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2代表当前有一个扩容线程
// 相对的,(sc - 2) != resizeStamp << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT
// 表示当前还有其他线程正在进行扩容,所以直接返回
if ((sc - 2) != resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT)
return;
// 否则,当前线程就是最后一个进行扩容的线程
// 设置finishing标识
finishing = advance = true;
i = n; // recheck before commit
}
}
// 如果待处理bucket是空的
// 那么插入ForwardingNode,以通知其他线程
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i)) == null)
advance = casTabAt(tab, i, null, fwd);
// 如果待处理bucket的头节点是ForwardingNode
// 说明此bucket已经被处理过了,跳过该bucket
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
advance = true; // already processed
最后一部分是具体的迁移过程(对当前指向的bucket),这部分的逻辑与HashMap类似,拿旧数组的容量当做一个掩码,然后与节点的hash进行与操作,可以得出该节点的新增有效位,如果新增有效位为0就放入一个链表A,如果为1就放入另一个链表B,链表A在新数组中的位置不变(跟在旧数组的索引一致),链表B在新数组中的位置为原索引加上旧数组容量。这个方法减少了rehash的计算量,而且还能达到均匀分布的目的。
else {
// 对于节点的操作还是要加上锁的
// 不过这个锁的粒度很小,只锁住了bucket的头节点
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
Node<K,V> ln, hn;
// hash code不为负,代表这是条链表
if (fh >= 0) {
// fh & n 获得hash code的新增有效位,用于将链表分离成两类
// 要么是0要么是1,关于这个位运算的更多细节
// 请看本文中有关HashMap扩容操作的解释
int runBit = fh & n;
Node<K,V> lastRun = f;
// 这个循环用于记录最后一段连续的同一类节点
// 这个类别是通过fh & n来区分的
// 这段连续的同类节点直接被复用,不会产生额外的复制
for (Node<K,V> p = f.next; p != null; p = p.next) {
int b = p.hash & n;
if (b != runBit) {
runBit = b;
lastRun = p;
}
}
// 0被放入ln链表,1被放入hn链表
// lastRun是连续同类节点的起始节点
if (runBit == 0) {
ln = lastRun;
hn = null;
}
else {
hn = lastRun;
ln = null;
}
// 将最后一段的连续同类节点之前的节点按类别复制到ln或hn
// 链表的插入方向是往头部插入的,Node构造函数的第四个参数是next
// 所以就算遇到类别与lastRun一致的节点也只会被插入到头部
for (Node<K,V> p = f; p != lastRun; p = p.next) {
int ph = p.hash; K pk = p.key; V pv = p.val;
if ((ph & n) == 0)
ln = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, ln);
else
hn = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, hn);
}
// ln链表被放入到原索引位置,hn放入到原索引 + 旧数组容量
// 这一点与HashMap一致,如果看不懂请去参考本文对HashMap扩容的讲解
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd); // 标记该bucket已被处理
advance = true;
}
// 对红黑树的操作,逻辑与链表一样,按新增有效位进行分类
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
TreeBin<K,V> t = (TreeBin<K,V>)f;
TreeNode<K,V> lo = null, loTail = null;
TreeNode<K,V> hi = null, hiTail = null;
int lc = 0, hc = 0;
for (Node<K,V> e = t.first; e != null; e = e.next) {
int h = e.hash;
TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V>
(h, e.key, e.val, null, null);
if ((h & n) == 0) {
if ((p.prev = loTail) == null)
lo = p;
else
loTail.next = p;
loTail = p;
++lc;
}
else {
if ((p.prev = hiTail) == null)
hi = p;
else
hiTail.next = p;
hiTail = p;
++hc;
}
}
// 元素数量没有超过UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD,退化成链表
ln = (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(lo) :
(hc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(lo) : t;
hn = (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(hi) :
(lc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(hi) : t;
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
advance = true;
}
3.4、计数
在Java 7中ConcurrentHashMap对每个Segment单独计数,想要得到总数就需要获得所有Segment的锁,然后进行统计。由于Java 8抛弃了Segment,显然是不能再这样做了,而且这种方法虽然简单准确但也舍弃了性能。Java 8声明了一个volatile变量baseCount用于记录元素的个数,对这个变量的修改操作是基于CAS的,每当插入元素或删除元素时都会调用addCount()函数进行计数。
private transient volatile long baseCount;
private final void addCount(long x, int check) {
CounterCell[] as; long b, s;
// 尝试使用CAS更新baseCount失败
// 转用CounterCells进行更新
if ((as = counterCells) != null ||
!U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, b = baseCount, s = b + x)) {
CounterCell a; long v; int m;
boolean uncontended = true;
// 在CounterCells未初始化
// 或尝试通过CAS更新当前线程的CounterCell失败时
// 调用fullAddCount(),该函数负责初始化CounterCells和更新计数
if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
(a = as[ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m]) == null ||
!(uncontended =
U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))) {
fullAddCount(x, uncontended);
return;
}
if (check <= 1)
return;
// 统计总数
s = sumCount();
}
if (check >= 0) {
// 判断是否需要扩容,在上文中已经讲过了
}
}
counterCells是一个元素为CounterCell的数组,该数组的大小与当前机器的CPU数量有关,并且它不会被主动初始化,只有在调用fullAddCount()函数时才会进行初始化。CounterCell是一个简单的内部静态类,每个CounterCell都是一个用于记录数量的单元:
/**
* Table of counter cells. When non-null, size is a power of 2.
*/
private transient volatile CounterCell[] counterCells;
/**
* A padded cell for distributing counts. Adapted from LongAdder
* and Striped64. See their internal docs for explanation.
*/
@sun.misc.Contended static final class CounterCell {
volatile long value;
CounterCell(long x) { value = x; }
}
注解@sun.misc.Contended用于解决伪共享问题。所谓伪共享,即是在同一缓存行(CPU缓存的基本单位)中存储了多个变量,当其中一个变量被修改时,就会影响到同一缓存行内的其他变量,导致它们也要跟着被标记为失效,其他变量的缓存命中率将会受到影响。解决伪共享问题的方法一般是对该变量填充一些无意义的占位数据,从而使它独享一个缓存行。
ConcurrentHashMap的计数设计与LongAdder类似。在一个低并发的情况下,就只是简单地使用CAS操作来对baseCount进行更新,但只要这个CAS操作失败一次,就代表有多个线程正在竞争,那么就转而使用CounterCell数组进行计数,数组内的每个ConuterCell都是一个独立的计数单元。每个线程都会通过ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m寻址找到属于它的CounterCell,然后进行计数。ThreadLocalRandom是一个线程私有的伪随机数生成器,每个线程的probe都是不同的(这点基于ThreadLocalRandom的内部实现,它在内部维护了一个probeGenerator,这是一个类型为AtomicInteger的静态常量,每当初始化一个ThreadLocalRandom时probeGenerator都会先自增一个常量然后返回的整数即为当前线程的probe,probe变量被维护在Thread对象中),可以认为每个线程的probe就是它在CounterCell数组中的hash code。这种方法将竞争数据按照线程的粒度进行分离,相比所有竞争线程对一个共享变量使用CAS不断尝试在性能上要效率好多了,这也是为什么在高并发环境下LongAdder要优于AtomicInteger的原因。
fullAddCount()函数根据当前线程的probe寻找对应的CounterCell进行计数,如果CounterCell数组未被初始化,则初始化CounterCell数组和CounterCell。该函数的实现与Striped64类(LongAdder的父类)的longAccumulate()函数是一样的,把CounterCell数组当成一个散列表,每个线程的probe就是hash code,散列函数也仅仅是简单的(n - 1) & probe。CounterCell数组的大小永远是一个2的n次方,初始容量为2,每次扩容的新容量都是之前容量乘以二,处于性能考虑,它的最大容量上限是机器的CPU数量。所以说CounterCell数组的碰撞冲突是很严重的,因为它的bucket基数太小了。而发生碰撞就代表着一个CounterCell会被多个线程竞争,为了解决这个问题,Doug Lea使用无限循环加上CAS来模拟出一个自旋锁来保证线程安全,自旋锁的实现基于一个被volatile修饰的整数变量,该变量只会有两种状态:0和1,当它被设置为0时表示没有加锁,当它被设置为1时表示已被其他线程加锁。这个自旋锁用于保护初始化CounterCell、初始化CounterCell数组以及对CounterCell数组进行扩容时的安全。CounterCell更新计数是依赖于CAS的,每次循环都会尝试通过CAS进行更新,如果成功就退出无限循环,否则就调用ThreadLocalRandom.advanceProbe()函数为当前线程更新probe,然后重新开始循环,以期望下一次寻址到的CounterCell没有被其他线程竞争。如果连着两次CAS更新都没有成功,那么会对CounterCell数组进行一次扩容,这个扩容操作只会在当前循环中触发一次,而且只能在容量小于上限时触发。
fullAddCount()函数的主要流程如下:
首先检查当前线程有没有初始化过ThreadLocalRandom,如果没有则进行初始化。ThreadLocalRandom负责更新线程的probe,而probe又是在数组中进行寻址的关键。
检查CounterCell数组是否已经初始化,如果已初始化,那么就根据probe找到对应的CounterCell。
如果这个CounterCell等于null,需要先初始化CounterCell,通过把计数增量传入构造函数,所以初始化只要成功就说明更新计数已经完成了。初始化的过程需要获取自旋锁。
如果不为null,就按上文所说的逻辑对CounterCell实施更新计数。
CounterCell数组未被初始化,尝试获取自旋锁,进行初始化。数组初始化的过程会附带初始化一个CounterCell来记录计数增量,所以只要初始化成功就表示更新计数完成。
如果自旋锁被其他线程占用,无法进行数组的初始化,只好通过CAS更新baseCount。
private final void fullAddCount(long x, boolean wasUncontended) {
int h;
// 当前线程的probe等于0,证明该线程的ThreadLocalRandom还未被初始化
// 以及当前线程是第一次进入该函数
if ((h = ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe()) == 0) {
// 初始化ThreadLocalRandom,当前线程会被设置一个probe
ThreadLocalRandom.localInit(); // force initialization
// probe用于在CounterCell数组中寻址
h = ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe();
// 未竞争标志
wasUncontended = true;
}
// 冲突标志
boolean collide = false; // True if last slot nonempty
for (;;) {
CounterCell[] as; CounterCell a; int n; long v;
// CounterCell数组已初始化
if ((as = counterCells) != null && (n = as.length) > 0) {
// 如果寻址到的Cell为空,那么创建一个新的Cell
if ((a = as[(n - 1) & h]) == null) {
// cellsBusy是一个只有0和1两个状态的volatile整数
// 它被当做一个自旋锁,0代表无锁,1代表加锁
if (cellsBusy == 0) { // Try to attach new Cell
// 将传入的x作为初始值创建一个新的CounterCell
CounterCell r = new CounterCell(x); // Optimistic create
// 通过CAS尝试对自旋锁加锁
if (cellsBusy == 0 &&
U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
// 加锁成功,声明Cell是否创建成功的标志
boolean created = false;
try { // Recheck under lock
CounterCell[] rs; int m, j;
// 再次检查CounterCell数组是否不为空
// 并且寻址到的Cell为空
if ((rs = counterCells) != null &&
(m = rs.length) > 0 &&
rs[j = (m - 1) & h] == null) {
// 将之前创建的新Cell放入数组
rs[j] = r;
created = true;
}
} finally {
// 释放锁
cellsBusy = 0;
}
// 如果已经创建成功,中断循环
// 因为新Cell的初始值就是传入的增量,所以计数已经完毕了
if (created)
break;
// 如果未成功
// 代表as[(n - 1) & h]这个位置的Cell已经被其他线程设置
// 那么就从循环头重新开始
continue; // Slot is now non-empty
}
}
collide = false;
}
// as[(n - 1) & h]非空
// 在addCount()函数中通过CAS更新当前线程的Cell进行计数失败
// 会传入wasUncontended = false,代表已经有其他线程进行竞争
else if (!wasUncontended) // CAS already known to fail
// 设置未竞争标志,之后会重新计算probe,然后重新执行循环
wasUncontended = true; // Continue after rehash
// 尝试进行计数,如果成功,那么就退出循环
else if (U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))
break;
// 尝试更新失败,检查counterCell数组是否已经扩容
// 或者容量达到最大值(CPU的数量)
else if (counterCells != as || n >= NCPU)
// 设置冲突标志,防止跳入下面的扩容分支
// 之后会重新计算probe
collide = false; // At max size or stale
// 设置冲突标志,重新执行循环
// 如果下次循环执行到该分支,并且冲突标志仍然为true
// 那么会跳过该分支,到下一个分支进行扩容
else if (!collide)
collide = true;
// 尝试加锁,然后对counterCells数组进行扩容
else if (cellsBusy == 0 &&
U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
try {
// 检查是否已被扩容
if (counterCells == as) {// Expand table unless stale
// 新数组容量为之前的1倍
CounterCell[] rs = new CounterCell[n << 1];
// 迁移数据到新数组
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
rs[i] = as[i];
counterCells = rs;
}
} finally {
// 释放锁
cellsBusy = 0;
}
collide = false;
// 重新执行循环
continue; // Retry with expanded table
}
// 为当前线程重新计算probe
h = ThreadLocalRandom.advanceProbe(h);
}
// CounterCell数组未初始化,尝试获取自旋锁,然后进行初始化
else if (cellsBusy == 0 && counterCells == as &&
U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
boolean init = false;
try { // Initialize table
if (counterCells == as) {
// 初始化CounterCell数组,初始容量为2
CounterCell[] rs = new CounterCell[2];
// 初始化CounterCell
rs[h & 1] = new CounterCell(x);
counterCells = rs;
init = true;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
// 初始化CounterCell数组成功,退出循环
if (init)
break;
}
// 如果自旋锁被占用,则只好尝试更新baseCount
else if (U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, v = baseCount, v + x))
break; // Fall back on using base
}
}
对于统计总数,只要能够理解CounterCell的思想,就很简单了。仔细想一想,每次计数的更新都会被分摊在baseCount和CounterCell数组中的某一CounterCell,想要获得总数,把它们统计相加就是了。
public int size() {
long n = sumCount();
return ((n < 0L) ? 0 :
(n > (long)Integer.MAX_VALUE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE :
(int)n);
}
final long sumCount() {
CounterCell[] as = counterCells; CounterCell a;
long sum = baseCount;
if (as != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < as.length; ++i) {
if ((a = as[i]) != null)
sum += a.value;
}
}
return sum;
}
其实size()函数返回的总数可能并不是百分百精确的,试想如果前一个遍历过的CounterCell又进行了更新会怎么样?尽管只是一个估算值,但在大多数场景下都还能接受,而且性能上是要比Java 7好上太多了。
3.5、其他操作
添加元素的主要逻辑与HashMap没什么区别,所以整体来说putVal()函数还是比较简单的,可能唯一需要注意的就是在对节点进行操作的时候需要通过互斥锁保证线程安全,这个互斥锁的粒度很小,只对需要操作的这个bucket加锁。
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
/** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0; // 节点计数器,用于判断是否需要树化
// 无限循环+CAS,无锁的标准套路
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
// 初始化table
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
// bucket为null,通过CAS创建头节点,如果成功就结束循环
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
// bucket为ForwardingNode
// 当前线程前去协助进行扩容
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
// 节点是链表
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
// 找到目标,设置value
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
// 未找到节点,插入新节点到链表尾部
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
// 节点是红黑树
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
// 根据bucket中的节点数决定是否树化
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
// oldVal不等于null,说明没有新节点
// 所以直接返回,不进行计数
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
// 计数
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
至于删除元素的操作位于函数replaceNode(Object key, V value, Object cv),当table[key].val等于期望值cv时(或cv等于null),更新节点的值为value,如果value等于null,那么删除该节点。
remove()函数通过调用replaceNode(key, null, null)来达成删除目标节点的目的,replaceNode()的具体实现与putVal()没什么差别,只不过对链表的操作有所不同而已。
四、Hashtable介绍
和HashMap一样,Hashtable 也是一个散列表,它存储的内容是键值对(key-value)映射。
Hashtable 继承于Dictionary,实现了Map、Cloneable、java.io.Serializable接口。
Hashtable 的函数都是同步的,这意味着它是线程安全的。它的key、value都不可以为null。
此外,Hashtable中的映射不是有序的。
Hashtable的实例有两个参数影响其性能:初始容量和加载因子。容量是哈希表中桶 的数量,初始容量就是哈希表创建时的容量。注意,哈希表的状态为 open:在发生“哈希冲突”的情况下,单个桶会存储多个条目,这些条目必须按顺序搜索。加载因子是对哈希表在其容量自动增加之前可以达到多满的一个尺度。初始容量和加载因子这两个参数只是对该实现的提示。关于何时以及是否调用 rehash 方法的具体细节则依赖于该实现。通常,默认加载因子是 0.75, 这是在时间和空间成本上寻求一种折衷。
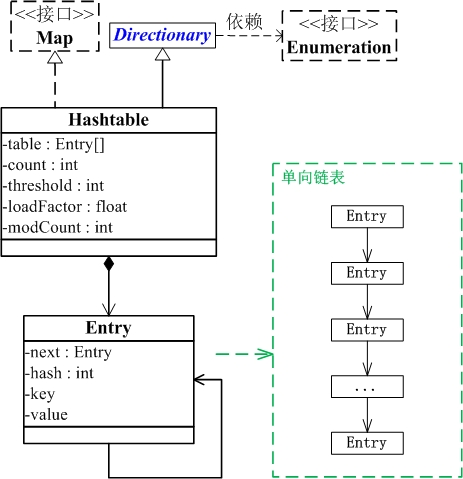
package java.util;
import java.io.*; public class Hashtable<K,V>
extends Dictionary<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { // Hashtable保存key-value的数组。
// Hashtable是采用拉链法实现的,每一个Entry本质上是一个单向链表
private transient Entry[] table; // Hashtable中元素的实际数量
private transient int count; // 阈值,用于判断是否需要调整Hashtable的容量(threshold = 容量*加载因子)
private int threshold; // 加载因子
private float loadFactor; // Hashtable被改变的次数
private transient int modCount = 0; // 序列版本号
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1421746759512286392L; // 指定“容量大小”和“加载因子”的构造函数
public Hashtable(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Load: "+loadFactor); if (initialCapacity==0)
initialCapacity = 1;
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
table = new Entry[initialCapacity];
threshold = (int)(initialCapacity * loadFactor);
} // 指定“容量大小”的构造函数
public Hashtable(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0.75f);
} // 默认构造函数。
public Hashtable() {
// 默认构造函数,指定的容量大小是11;加载因子是0.75
this(11, 0.75f);
} // 包含“子Map”的构造函数
public Hashtable(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> t) {
this(Math.max(2*t.size(), 11), 0.75f);
// 将“子Map”的全部元素都添加到Hashtable中
putAll(t);
} public synchronized int size() {
return count;
} public synchronized boolean isEmpty() {
return count == 0;
} // 返回“所有key”的枚举对象
public synchronized Enumeration<K> keys() {
return this.<K>getEnumeration(KEYS);
} // 返回“所有value”的枚举对象
public synchronized Enumeration<V> elements() {
return this.<V>getEnumeration(VALUES);
} // 判断Hashtable是否包含“值(value)”
public synchronized boolean contains(Object value) {
// Hashtable中“键值对”的value不能是null,
// 若是null的话,抛出异常!
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
} // 从后向前遍历table数组中的元素(Entry)
// 对于每个Entry(单向链表),逐个遍历,判断节点的值是否等于value
Entry tab[] = table;
for (int i = tab.length ; i-- > 0 ;) {
for (Entry<K,V> e = tab[i] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if (e.value.equals(value)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
} public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
return contains(value);
} // 判断Hashtable是否包含key
public synchronized boolean containsKey(Object key) {
Entry tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
// 计算索引值,
// % tab.length 的目的是防止数据越界
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
// 找到“key对应的Entry(链表)”,然后在链表中找出“哈希值”和“键值”与key都相等的元素
for (Entry<K,V> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
} // 返回key对应的value,没有的话返回null
public synchronized V get(Object key) {
Entry tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
// 计算索引值,
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
// 找到“key对应的Entry(链表)”,然后在链表中找出“哈希值”和“键值”与key都相等的元素
for (Entry<K,V> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
return e.value;
}
}
return null;
} // 调整Hashtable的长度,将长度变成原来的(2倍+1)
// (01) 将“旧的Entry数组”赋值给一个临时变量。
// (02) 创建一个“新的Entry数组”,并赋值给“旧的Entry数组”
// (03) 将“Hashtable”中的全部元素依次添加到“新的Entry数组”中
protected void rehash() {
int oldCapacity = table.length;
Entry[] oldMap = table; int newCapacity = oldCapacity * 2 + 1;
Entry[] newMap = new Entry[newCapacity]; modCount++;
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);
table = newMap; for (int i = oldCapacity ; i-- > 0 ;) {
for (Entry<K,V> old = oldMap[i] ; old != null ; ) {
Entry<K,V> e = old;
old = old.next; int index = (e.hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % newCapacity;
e.next = newMap[index];
newMap[index] = e;
}
}
} // 将“key-value”添加到Hashtable中
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// Hashtable中不能插入value为null的元素!!!
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
} // 若“Hashtable中已存在键为key的键值对”,
// 则用“新的value”替换“旧的value”
Entry tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
for (Entry<K,V> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
V old = e.value;
e.value = value;
return old;
}
} // 若“Hashtable中不存在键为key的键值对”,
// (01) 将“修改统计数”+1
modCount++;
// (02) 若“Hashtable实际容量” > “阈值”(阈值=总的容量 * 加载因子)
// 则调整Hashtable的大小
if (count >= threshold) {
// Rehash the table if the threshold is exceeded
rehash(); tab = table;
index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
} // (03) 将“Hashtable中index”位置的Entry(链表)保存到e中
Entry<K,V> e = tab[index];
// (04) 创建“新的Entry节点”,并将“新的Entry”插入“Hashtable的index位置”,并设置e为“新的Entry”的下一个元素(即“新Entry”为链表表头)。
tab[index] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
// (05) 将“Hashtable的实际容量”+1
count++;
return null;
} // 删除Hashtable中键为key的元素
public synchronized V remove(Object key) {
Entry tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
// 找到“key对应的Entry(链表)”
// 然后在链表中找出要删除的节点,并删除该节点。
for (Entry<K,V> e = tab[index], prev = null ; e != null ; prev = e, e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
modCount++;
if (prev != null) {
prev.next = e.next;
} else {
tab[index] = e.next;
}
count--;
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = null;
return oldValue;
}
}
return null;
} // 将“Map(t)”的中全部元素逐一添加到Hashtable中
public synchronized void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> t) {
for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : t.entrySet())
put(e.getKey(), e.getValue());
} // 清空Hashtable
// 将Hashtable的table数组的值全部设为null
public synchronized void clear() {
Entry tab[] = table;
modCount++;
for (int index = tab.length; --index >= 0; )
tab[index] = null;
count = 0;
} // 克隆一个Hashtable,并以Object的形式返回。
public synchronized Object clone() {
try {
Hashtable<K,V> t = (Hashtable<K,V>) super.clone();
t.table = new Entry[table.length];
for (int i = table.length ; i-- > 0 ; ) {
t.table[i] = (table[i] != null)
? (Entry<K,V>) table[i].clone() : null;
}
t.keySet = null;
t.entrySet = null;
t.values = null;
t.modCount = 0;
return t;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable
throw new InternalError();
}
} public synchronized String toString() {
int max = size() - 1;
if (max == -1)
return "{}"; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> it = entrySet().iterator(); sb.append('{');
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
Map.Entry<K,V> e = it.next();
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
sb.append(key == this ? "(this Map)" : key.toString());
sb.append('=');
sb.append(value == this ? "(this Map)" : value.toString()); if (i == max)
return sb.append('}').toString();
sb.append(", ");
}
} // 获取Hashtable的枚举类对象
// 若Hashtable的实际大小为0,则返回“空枚举类”对象;
// 否则,返回正常的Enumerator的对象。(Enumerator实现了迭代器和枚举两个接口)
private <T> Enumeration<T> getEnumeration(int type) {
if (count == 0) {
return (Enumeration<T>)emptyEnumerator;
} else {
return new Enumerator<T>(type, false);
}
} // 获取Hashtable的迭代器
// 若Hashtable的实际大小为0,则返回“空迭代器”对象;
// 否则,返回正常的Enumerator的对象。(Enumerator实现了迭代器和枚举两个接口)
private <T> Iterator<T> getIterator(int type) {
if (count == 0) {
return (Iterator<T>) emptyIterator;
} else {
return new Enumerator<T>(type, true);
}
} // Hashtable的“key的集合”。它是一个Set,意味着没有重复元素
private transient volatile Set<K> keySet = null;
// Hashtable的“key-value的集合”。它是一个Set,意味着没有重复元素
private transient volatile Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet = null;
// Hashtable的“key-value的集合”。它是一个Collection,意味着可以有重复元素
private transient volatile Collection<V> values = null; // 返回一个被synchronizedSet封装后的KeySet对象
// synchronizedSet封装的目的是对KeySet的所有方法都添加synchronized,实现多线程同步
public Set<K> keySet() {
if (keySet == null)
keySet = Collections.synchronizedSet(new KeySet(), this);
return keySet;
} // Hashtable的Key的Set集合。
// KeySet继承于AbstractSet,所以,KeySet中的元素没有重复的。
private class KeySet extends AbstractSet<K> {
public Iterator<K> iterator() {
return getIterator(KEYS);
}
public int size() {
return count;
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return containsKey(o);
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return Hashtable.this.remove(o) != null;
}
public void clear() {
Hashtable.this.clear();
}
} // 返回一个被synchronizedSet封装后的EntrySet对象
// synchronizedSet封装的目的是对EntrySet的所有方法都添加synchronized,实现多线程同步
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
if (entrySet==null)
entrySet = Collections.synchronizedSet(new EntrySet(), this);
return entrySet;
} // Hashtable的Entry的Set集合。
// EntrySet继承于AbstractSet,所以,EntrySet中的元素没有重复的。
private class EntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
return getIterator(ENTRIES);
} public boolean add(Map.Entry<K,V> o) {
return super.add(o);
} // 查找EntrySet中是否包含Object(0)
// 首先,在table中找到o对应的Entry(Entry是一个单向链表)
// 然后,查找Entry链表中是否存在Object
public boolean contains(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)o;
Object key = entry.getKey();
Entry[] tab = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length; for (Entry e = tab[index]; e != null; e = e.next)
if (e.hash==hash && e.equals(entry))
return true;
return false;
} // 删除元素Object(0)
// 首先,在table中找到o对应的Entry(Entry是一个单向链表)
// 然后,删除链表中的元素Object
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<K,V> entry = (Map.Entry<K,V>) o;
K key = entry.getKey();
Entry[] tab = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length; for (Entry<K,V> e = tab[index], prev = null; e != null;
prev = e, e = e.next) {
if (e.hash==hash && e.equals(entry)) {
modCount++;
if (prev != null)
prev.next = e.next;
else
tab[index] = e.next; count--;
e.value = null;
return true;
}
}
return false;
} public int size() {
return count;
} public void clear() {
Hashtable.this.clear();
}
} // 返回一个被synchronizedCollection封装后的ValueCollection对象
// synchronizedCollection封装的目的是对ValueCollection的所有方法都添加synchronized,实现多线程同步
public Collection<V> values() {
if (values==null)
values = Collections.synchronizedCollection(new ValueCollection(),
this);
return values;
} // Hashtable的value的Collection集合。
// ValueCollection继承于AbstractCollection,所以,ValueCollection中的元素可以重复的。
private class ValueCollection extends AbstractCollection<V> {
public Iterator<V> iterator() {
return getIterator(VALUES);
}
public int size() {
return count;
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return containsValue(o);
}
public void clear() {
Hashtable.this.clear();
}
} // 重新equals()函数
// 若两个Hashtable的所有key-value键值对都相等,则判断它们两个相等
public synchronized boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true; if (!(o instanceof Map))
return false;
Map<K,V> t = (Map<K,V>) o;
if (t.size() != size())
return false; try {
// 通过迭代器依次取出当前Hashtable的key-value键值对
// 并判断该键值对,存在于Hashtable(o)中。
// 若不存在,则立即返回false;否则,遍历完“当前Hashtable”并返回true。
Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<K,V> e = i.next();
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
if (value == null) {
if (!(t.get(key)==null && t.containsKey(key)))
return false;
} else {
if (!value.equals(t.get(key)))
return false;
}
}
} catch (ClassCastException unused) {
return false;
} catch (NullPointerException unused) {
return false;
} return true;
} // 计算Hashtable的哈希值
// 若 Hashtable的实际大小为0 或者 加载因子<0,则返回0。
// 否则,返回“Hashtable中的每个Entry的key和value的异或值 的总和”。
public synchronized int hashCode() {
int h = 0;
if (count == 0 || loadFactor < 0)
return h; // Returns zero loadFactor = -loadFactor; // Mark hashCode computation in progress
Entry[] tab = table;
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; i++)
for (Entry e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next)
h += e.key.hashCode() ^ e.value.hashCode();
loadFactor = -loadFactor; // Mark hashCode computation complete return h;
} // java.io.Serializable的写入函数
// 将Hashtable的“总的容量,实际容量,所有的Entry”都写入到输出流中
private synchronized void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws IOException
{
// Write out the length, threshold, loadfactor
s.defaultWriteObject(); // Write out length, count of elements and then the key/value objects
s.writeInt(table.length);
s.writeInt(count);
for (int index = table.length-1; index >= 0; index--) {
Entry entry = table[index]; while (entry != null) {
s.writeObject(entry.key);
s.writeObject(entry.value);
entry = entry.next;
}
}
} // java.io.Serializable的读取函数:根据写入方式读出
// 将Hashtable的“总的容量,实际容量,所有的Entry”依次读出
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
{
// Read in the length, threshold, and loadfactor
s.defaultReadObject(); // Read the original length of the array and number of elements
int origlength = s.readInt();
int elements = s.readInt(); // Compute new size with a bit of room 5% to grow but
// no larger than the original size. Make the length
// odd if it's large enough, this helps distribute the entries.
// Guard against the length ending up zero, that's not valid.
int length = (int)(elements * loadFactor) + (elements / 20) + 3;
if (length > elements && (length & 1) == 0)
length--;
if (origlength > 0 && length > origlength)
length = origlength; Entry[] table = new Entry[length];
count = 0; // Read the number of elements and then all the key/value objects
for (; elements > 0; elements--) {
K key = (K)s.readObject();
V value = (V)s.readObject();
// synch could be eliminated for performance
reconstitutionPut(table, key, value);
}
this.table = table;
} private void reconstitutionPut(Entry[] tab, K key, V value)
throws StreamCorruptedException
{
if (value == null) {
throw new java.io.StreamCorruptedException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
// This should not happen in deserialized version.
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
for (Entry<K,V> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
throw new java.io.StreamCorruptedException();
}
}
// Creates the new entry.
Entry<K,V> e = tab[index];
tab[index] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
count++;
} // Hashtable的Entry节点,它本质上是一个单向链表。
// 也因此,我们才能推断出Hashtable是由拉链法实现的散列表
private static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
// 哈希值
int hash;
K key;
V value;
// 指向的下一个Entry,即链表的下一个节点
Entry<K,V> next; // 构造函数
protected Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Entry<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
} protected Object clone() {
return new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value,
(next==null ? null : (Entry<K,V>) next.clone()));
} public K getKey() {
return key;
} public V getValue() {
return value;
} // 设置value。若value是null,则抛出异常。
public V setValue(V value) {
if (value == null)
throw new NullPointerException(); V oldValue = this.value;
this.value = value;
return oldValue;
} // 覆盖equals()方法,判断两个Entry是否相等。
// 若两个Entry的key和value都相等,则认为它们相等。
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o; return (key==null ? e.getKey()==null : key.equals(e.getKey())) &&
(value==null ? e.getValue()==null : value.equals(e.getValue()));
} public int hashCode() {
return hash ^ (value==null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
} public String toString() {
return key.toString()+"="+value.toString();
}
} private static final int KEYS = 0;
private static final int VALUES = 1;
private static final int ENTRIES = 2; // Enumerator的作用是提供了“通过elements()遍历Hashtable的接口” 和 “通过entrySet()遍历Hashtable的接口”。因为,它同时实现了 “Enumerator接口”和“Iterator接口”。
private class Enumerator<T> implements Enumeration<T>, Iterator<T> {
// 指向Hashtable的table
Entry[] table = Hashtable.this.table;
// Hashtable的总的大小
int index = table.length;
Entry<K,V> entry = null;
Entry<K,V> lastReturned = null;
int type; // Enumerator是 “迭代器(Iterator)” 还是 “枚举类(Enumeration)”的标志
// iterator为true,表示它是迭代器;否则,是枚举类。
boolean iterator; // 在将Enumerator当作迭代器使用时会用到,用来实现fail-fast机制。
protected int expectedModCount = modCount; Enumerator(int type, boolean iterator) {
this.type = type;
this.iterator = iterator;
} // 从遍历table的数组的末尾向前查找,直到找到不为null的Entry。
public boolean hasMoreElements() {
Entry<K,V> e = entry;
int i = index;
Entry[] t = table;
/* Use locals for faster loop iteration */
while (e == null && i > 0) {
e = t[--i];
}
entry = e;
index = i;
return e != null;
} // 获取下一个元素
// 注意:从hasMoreElements() 和nextElement() 可以看出“Hashtable的elements()遍历方式”
// 首先,从后向前的遍历table数组。table数组的每个节点都是一个单向链表(Entry)。
// 然后,依次向后遍历单向链表Entry。
public T nextElement() {
Entry<K,V> et = entry;
int i = index;
Entry[] t = table;
/* Use locals for faster loop iteration */
while (et == null && i > 0) {
et = t[--i];
}
entry = et;
index = i;
if (et != null) {
Entry<K,V> e = lastReturned = entry;
entry = e.next;
return type == KEYS ? (T)e.key : (type == VALUES ? (T)e.value : (T)e);
}
throw new NoSuchElementException("Hashtable Enumerator");
} // 迭代器Iterator的判断是否存在下一个元素
// 实际上,它是调用的hasMoreElements()
public boolean hasNext() {
return hasMoreElements();
} // 迭代器获取下一个元素
// 实际上,它是调用的nextElement()
public T next() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return nextElement();
} // 迭代器的remove()接口。
// 首先,它在table数组中找出要删除元素所在的Entry,
// 然后,删除单向链表Entry中的元素。
public void remove() {
if (!iterator)
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Hashtable Enumerator");
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); synchronized(Hashtable.this) {
Entry[] tab = Hashtable.this.table;
int index = (lastReturned.hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length; for (Entry<K,V> e = tab[index], prev = null; e != null;
prev = e, e = e.next) {
if (e == lastReturned) {
modCount++;
expectedModCount++;
if (prev == null)
tab[index] = e.next;
else
prev.next = e.next;
count--;
lastReturned = null;
return;
}
}
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
} private static Enumeration emptyEnumerator = new EmptyEnumerator();
private static Iterator emptyIterator = new EmptyIterator(); // 空枚举类
// 当Hashtable的实际大小为0;此时,又要通过Enumeration遍历Hashtable时,返回的是“空枚举类”的对象。
private static class EmptyEnumerator implements Enumeration<Object> { EmptyEnumerator() {
} // 空枚举类的hasMoreElements() 始终返回false
public boolean hasMoreElements() {
return false;
} // 空枚举类的nextElement() 抛出异常
public Object nextElement() {
throw new NoSuchElementException("Hashtable Enumerator");
}
} // 空迭代器
// 当Hashtable的实际大小为0;此时,又要通过迭代器遍历Hashtable时,返回的是“空迭代器”的对象。
private static class EmptyIterator implements Iterator<Object> { EmptyIterator() {
} public boolean hasNext() {
return false;
} public Object next() {
throw new NoSuchElementException("Hashtable Iterator");
} public void remove() {
throw new IllegalStateException("Hashtable Iterator");
} }
}
jdk1.6的Hashtable源码解析
/*
* Copyright (c) 1994, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*/ package java.util; import java.io.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadLocalRandom;
import java.util.function.BiConsumer;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.function.BiFunction; /**
* This class implements a hash table, which maps keys to values. Any
* non-<code>null</code> object can be used as a key or as a value. <p>
*
* To successfully store and retrieve objects from a hashtable, the
* objects used as keys must implement the <code>hashCode</code>
* method and the <code>equals</code> method. <p>
*
* An instance of <code>Hashtable</code> has two parameters that affect its
* performance: <i>initial capacity</i> and <i>load factor</i>. The
* <i>capacity</i> is the number of <i>buckets</i> in the hash table, and the
* <i>initial capacity</i> is simply the capacity at the time the hash table
* is created. Note that the hash table is <i>open</i>: in the case of a "hash
* collision", a single bucket stores multiple entries, which must be searched
* sequentially. The <i>load factor</i> is a measure of how full the hash
* table is allowed to get before its capacity is automatically increased.
* The initial capacity and load factor parameters are merely hints to
* the implementation. The exact details as to when and whether the rehash
* method is invoked are implementation-dependent.<p>
*
* Generally, the default load factor (.75) offers a good tradeoff between
* time and space costs. Higher values decrease the space overhead but
* increase the time cost to look up an entry (which is reflected in most
* <tt>Hashtable</tt> operations, including <tt>get</tt> and <tt>put</tt>).<p>
*
* The initial capacity controls a tradeoff between wasted space and the
* need for <code>rehash</code> operations, which are time-consuming.
* No <code>rehash</code> operations will <i>ever</i> occur if the initial
* capacity is greater than the maximum number of entries the
* <tt>Hashtable</tt> will contain divided by its load factor. However,
* setting the initial capacity too high can waste space.<p>
*
* If many entries are to be made into a <code>Hashtable</code>,
* creating it with a sufficiently large capacity may allow the
* entries to be inserted more efficiently than letting it perform
* automatic rehashing as needed to grow the table. <p>
*
* This example creates a hashtable of numbers. It uses the names of
* the numbers as keys:
* <pre> {@code
* Hashtable<String, Integer> numbers
* = new Hashtable<String, Integer>();
* numbers.put("one", 1);
* numbers.put("two", 2);
* numbers.put("three", 3);}</pre>
*
* <p>To retrieve a number, use the following code:
* <pre> {@code
* Integer n = numbers.get("two");
* if (n != null) {
* System.out.println("two = " + n);
* }}</pre>
*
* <p>The iterators returned by the <tt>iterator</tt> method of the collections
* returned by all of this class's "collection view methods" are
* <em>fail-fast</em>: if the Hashtable is structurally modified at any time
* after the iterator is created, in any way except through the iterator's own
* <tt>remove</tt> method, the iterator will throw a {@link
* ConcurrentModificationException}. Thus, in the face of concurrent
* modification, the iterator fails quickly and cleanly, rather than risking
* arbitrary, non-deterministic behavior at an undetermined time in the future.
* The Enumerations returned by Hashtable's keys and elements methods are
* <em>not</em> fail-fast.
*
* <p>Note that the fail-fast behavior of an iterator cannot be guaranteed
* as it is, generally speaking, impossible to make any hard guarantees in the
* presence of unsynchronized concurrent modification. Fail-fast iterators
* throw <tt>ConcurrentModificationException</tt> on a best-effort basis.
* Therefore, it would be wrong to write a program that depended on this
* exception for its correctness: <i>the fail-fast behavior of iterators
* should be used only to detect bugs.</i>
*
* <p>As of the Java 2 platform v1.2, this class was retrofitted to
* implement the {@link Map} interface, making it a member of the
* <a href="{@docRoot}/../technotes/guides/collections/index.html">
*
* Java Collections Framework</a>. Unlike the new collection
* implementations, {@code Hashtable} is synchronized. If a
* thread-safe implementation is not needed, it is recommended to use
* {@link HashMap} in place of {@code Hashtable}. If a thread-safe
* highly-concurrent implementation is desired, then it is recommended
* to use {@link java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap} in place of
* {@code Hashtable}.
*
* @author Arthur van Hoff
* @author Josh Bloch
* @author Neal Gafter
* @see Object#equals(java.lang.Object)
* @see Object#hashCode()
* @see Hashtable#rehash()
* @see Collection
* @see Map
* @see HashMap
* @see TreeMap
* @since JDK1.0
*/
public class Hashtable<K,V>
extends Dictionary<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { /**
* The hash table data.
*/
private transient Entry<?,?>[] table; /**
* The total number of entries in the hash table.
*/
private transient int count; /**
* The table is rehashed when its size exceeds this threshold. (The
* value of this field is (int)(capacity * loadFactor).)
*
* @serial
*/
private int threshold; /**
* The load factor for the hashtable.
*
* @serial
*/
private float loadFactor; /**
* The number of times this Hashtable has been structurally modified
* Structural modifications are those that change the number of entries in
* the Hashtable or otherwise modify its internal structure (e.g.,
* rehash). This field is used to make iterators on Collection-views of
* the Hashtable fail-fast. (See ConcurrentModificationException).
*/
private transient int modCount = 0; /** use serialVersionUID from JDK 1.0.2 for interoperability */
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1421746759512286392L; /**
* Constructs a new, empty hashtable with the specified initial
* capacity and the specified load factor.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the hashtable.
* @param loadFactor the load factor of the hashtable.
* @exception IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is less
* than zero, or if the load factor is nonpositive.
*/
public Hashtable(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Load: "+loadFactor); if (initialCapacity==0)
initialCapacity = 1;
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
table = new Entry<?,?>[initialCapacity];
threshold = (int)Math.min(initialCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
} /**
* Constructs a new, empty hashtable with the specified initial capacity
* and default load factor (0.75).
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the hashtable.
* @exception IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is less
* than zero.
*/
public Hashtable(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0.75f);
} /**
* Constructs a new, empty hashtable with a default initial capacity (11)
* and load factor (0.75).
*/
public Hashtable() {
this(11, 0.75f);
} /**
* Constructs a new hashtable with the same mappings as the given
* Map. The hashtable is created with an initial capacity sufficient to
* hold the mappings in the given Map and a default load factor (0.75).
*
* @param t the map whose mappings are to be placed in this map.
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null.
* @since 1.2
*/
public Hashtable(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> t) {
this(Math.max(2*t.size(), 11), 0.75f);
putAll(t);
} /**
* Returns the number of keys in this hashtable.
*
* @return the number of keys in this hashtable.
*/
public synchronized int size() {
return count;
} /**
* Tests if this hashtable maps no keys to values.
*
* @return <code>true</code> if this hashtable maps no keys to values;
* <code>false</code> otherwise.
*/
public synchronized boolean isEmpty() {
return count == 0;
} /**
* Returns an enumeration of the keys in this hashtable.
*
* @return an enumeration of the keys in this hashtable.
* @see Enumeration
* @see #elements()
* @see #keySet()
* @see Map
*/
public synchronized Enumeration<K> keys() {
return this.<K>getEnumeration(KEYS);
} /**
* Returns an enumeration of the values in this hashtable.
* Use the Enumeration methods on the returned object to fetch the elements
* sequentially.
*
* @return an enumeration of the values in this hashtable.
* @see java.util.Enumeration
* @see #keys()
* @see #values()
* @see Map
*/
public synchronized Enumeration<V> elements() {
return this.<V>getEnumeration(VALUES);
} /**
* Tests if some key maps into the specified value in this hashtable.
* This operation is more expensive than the {@link #containsKey
* containsKey} method.
*
* <p>Note that this method is identical in functionality to
* {@link #containsValue containsValue}, (which is part of the
* {@link Map} interface in the collections framework).
*
* @param value a value to search for
* @return <code>true</code> if and only if some key maps to the
* <code>value</code> argument in this hashtable as
* determined by the <tt>equals</tt> method;
* <code>false</code> otherwise.
* @exception NullPointerException if the value is <code>null</code>
*/
public synchronized boolean contains(Object value) {
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
} Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
for (int i = tab.length ; i-- > 0 ;) {
for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[i] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if (e.value.equals(value)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
} /**
* Returns true if this hashtable maps one or more keys to this value.
*
* <p>Note that this method is identical in functionality to {@link
* #contains contains} (which predates the {@link Map} interface).
*
* @param value value whose presence in this hashtable is to be tested
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the
* specified value
* @throws NullPointerException if the value is <code>null</code>
* @since 1.2
*/
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
return contains(value);
} /**
* Tests if the specified object is a key in this hashtable.
*
* @param key possible key
* @return <code>true</code> if and only if the specified object
* is a key in this hashtable, as determined by the
* <tt>equals</tt> method; <code>false</code> otherwise.
* @throws NullPointerException if the key is <code>null</code>
* @see #contains(Object)
*/
public synchronized boolean containsKey(Object key) {
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
} /**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code (key.equals(k))},
* then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise it returns
* {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
* @param key the key whose associated value is to be returned
* @return the value to which the specified key is mapped, or
* {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
* @see #put(Object, Object)
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public synchronized V get(Object key) {
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
return (V)e.value;
}
}
return null;
} /**
* The maximum size of array to allocate.
* Some VMs reserve some header words in an array.
* Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in
* OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit
*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; /**
* Increases the capacity of and internally reorganizes this
* hashtable, in order to accommodate and access its entries more
* efficiently. This method is called automatically when the
* number of keys in the hashtable exceeds this hashtable's capacity
* and load factor.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected void rehash() {
int oldCapacity = table.length;
Entry<?,?>[] oldMap = table; // overflow-conscious code
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity << 1) + 1;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) {
if (oldCapacity == MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)
// Keep running with MAX_ARRAY_SIZE buckets
return;
newCapacity = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
Entry<?,?>[] newMap = new Entry<?,?>[newCapacity]; modCount++;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
table = newMap; for (int i = oldCapacity ; i-- > 0 ;) {
for (Entry<K,V> old = (Entry<K,V>)oldMap[i] ; old != null ; ) {
Entry<K,V> e = old;
old = old.next; int index = (e.hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % newCapacity;
e.next = (Entry<K,V>)newMap[index];
newMap[index] = e;
}
}
} private void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int index) {
modCount++; Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
if (count >= threshold) {
// Rehash the table if the threshold is exceeded
rehash(); tab = table;
hash = key.hashCode();
index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
} // Creates the new entry.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>) tab[index];
tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
count++;
} /**
* Maps the specified <code>key</code> to the specified
* <code>value</code> in this hashtable. Neither the key nor the
* value can be <code>null</code>. <p>
*
* The value can be retrieved by calling the <code>get</code> method
* with a key that is equal to the original key.
*
* @param key the hashtable key
* @param value the value
* @return the previous value of the specified key in this hashtable,
* or <code>null</code> if it did not have one
* @exception NullPointerException if the key or value is
* <code>null</code>
* @see Object#equals(Object)
* @see #get(Object)
*/
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// Make sure the value is not null
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
} // Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return old;
}
} addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
return null;
} /**
* Removes the key (and its corresponding value) from this
* hashtable. This method does nothing if the key is not in the hashtable.
*
* @param key the key that needs to be removed
* @return the value to which the key had been mapped in this hashtable,
* or <code>null</code> if the key did not have a mapping
* @throws NullPointerException if the key is <code>null</code>
*/
public synchronized V remove(Object key) {
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for(Entry<K,V> prev = null ; e != null ; prev = e, e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
modCount++;
if (prev != null) {
prev.next = e.next;
} else {
tab[index] = e.next;
}
count--;
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = null;
return oldValue;
}
}
return null;
} /**
* Copies all of the mappings from the specified map to this hashtable.
* These mappings will replace any mappings that this hashtable had for any
* of the keys currently in the specified map.
*
* @param t mappings to be stored in this map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null
* @since 1.2
*/
public synchronized void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> t) {
for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : t.entrySet())
put(e.getKey(), e.getValue());
} /**
* Clears this hashtable so that it contains no keys.
*/
public synchronized void clear() {
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
modCount++;
for (int index = tab.length; --index >= 0; )
tab[index] = null;
count = 0;
} /**
* Creates a shallow copy of this hashtable. All the structure of the
* hashtable itself is copied, but the keys and values are not cloned.
* This is a relatively expensive operation.
*
* @return a clone of the hashtable
*/
public synchronized Object clone() {
try {
Hashtable<?,?> t = (Hashtable<?,?>)super.clone();
t.table = new Entry<?,?>[table.length];
for (int i = table.length ; i-- > 0 ; ) {
t.table[i] = (table[i] != null)
? (Entry<?,?>) table[i].clone() : null;
}
t.keySet = null;
t.entrySet = null;
t.values = null;
t.modCount = 0;
return t;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable
throw new InternalError(e);
}
} /**
* Returns a string representation of this <tt>Hashtable</tt> object
* in the form of a set of entries, enclosed in braces and separated
* by the ASCII characters "<tt>, </tt>" (comma and space). Each
* entry is rendered as the key, an equals sign <tt>=</tt>, and the
* associated element, where the <tt>toString</tt> method is used to
* convert the key and element to strings.
*
* @return a string representation of this hashtable
*/
public synchronized String toString() {
int max = size() - 1;
if (max == -1)
return "{}"; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> it = entrySet().iterator(); sb.append('{');
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
Map.Entry<K,V> e = it.next();
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
sb.append(key == this ? "(this Map)" : key.toString());
sb.append('=');
sb.append(value == this ? "(this Map)" : value.toString()); if (i == max)
return sb.append('}').toString();
sb.append(", ");
}
} private <T> Enumeration<T> getEnumeration(int type) {
if (count == 0) {
return Collections.emptyEnumeration();
} else {
return new Enumerator<>(type, false);
}
} private <T> Iterator<T> getIterator(int type) {
if (count == 0) {
return Collections.emptyIterator();
} else {
return new Enumerator<>(type, true);
}
} // Views /**
* Each of these fields are initialized to contain an instance of the
* appropriate view the first time this view is requested. The views are
* stateless, so there's no reason to create more than one of each.
*/
private transient volatile Set<K> keySet;
private transient volatile Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;
private transient volatile Collection<V> values; /**
* Returns a {@link Set} view of the keys contained in this map.
* The set is backed by the map, so changes to the map are
* reflected in the set, and vice-versa. If the map is modified
* while an iteration over the set is in progress (except through
* the iterator's own <tt>remove</tt> operation), the results of
* the iteration are undefined. The set supports element removal,
* which removes the corresponding mapping from the map, via the
* <tt>Iterator.remove</tt>, <tt>Set.remove</tt>,
* <tt>removeAll</tt>, <tt>retainAll</tt>, and <tt>clear</tt>
* operations. It does not support the <tt>add</tt> or <tt>addAll</tt>
* operations.
*
* @since 1.2
*/
public Set<K> keySet() {
if (keySet == null)
keySet = Collections.synchronizedSet(new KeySet(), this);
return keySet;
} private class KeySet extends AbstractSet<K> {
public Iterator<K> iterator() {
return getIterator(KEYS);
}
public int size() {
return count;
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return containsKey(o);
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return Hashtable.this.remove(o) != null;
}
public void clear() {
Hashtable.this.clear();
}
} /**
* Returns a {@link Set} view of the mappings contained in this map.
* The set is backed by the map, so changes to the map are
* reflected in the set, and vice-versa. If the map is modified
* while an iteration over the set is in progress (except through
* the iterator's own <tt>remove</tt> operation, or through the
* <tt>setValue</tt> operation on a map entry returned by the
* iterator) the results of the iteration are undefined. The set
* supports element removal, which removes the corresponding
* mapping from the map, via the <tt>Iterator.remove</tt>,
* <tt>Set.remove</tt>, <tt>removeAll</tt>, <tt>retainAll</tt> and
* <tt>clear</tt> operations. It does not support the
* <tt>add</tt> or <tt>addAll</tt> operations.
*
* @since 1.2
*/
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
if (entrySet==null)
entrySet = Collections.synchronizedSet(new EntrySet(), this);
return entrySet;
} private class EntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
return getIterator(ENTRIES);
} public boolean add(Map.Entry<K,V> o) {
return super.add(o);
} public boolean contains(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<?,?> entry = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
Object key = entry.getKey();
Entry<?,?>[] tab = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length; for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index]; e != null; e = e.next)
if (e.hash==hash && e.equals(entry))
return true;
return false;
} public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<?,?> entry = (Map.Entry<?,?>) o;
Object key = entry.getKey();
Entry<?,?>[] tab = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for(Entry<K,V> prev = null; e != null; prev = e, e = e.next) {
if (e.hash==hash && e.equals(entry)) {
modCount++;
if (prev != null)
prev.next = e.next;
else
tab[index] = e.next; count--;
e.value = null;
return true;
}
}
return false;
} public int size() {
return count;
} public void clear() {
Hashtable.this.clear();
}
} /**
* Returns a {@link Collection} view of the values contained in this map.
* The collection is backed by the map, so changes to the map are
* reflected in the collection, and vice-versa. If the map is
* modified while an iteration over the collection is in progress
* (except through the iterator's own <tt>remove</tt> operation),
* the results of the iteration are undefined. The collection
* supports element removal, which removes the corresponding
* mapping from the map, via the <tt>Iterator.remove</tt>,
* <tt>Collection.remove</tt>, <tt>removeAll</tt>,
* <tt>retainAll</tt> and <tt>clear</tt> operations. It does not
* support the <tt>add</tt> or <tt>addAll</tt> operations.
*
* @since 1.2
*/
public Collection<V> values() {
if (values==null)
values = Collections.synchronizedCollection(new ValueCollection(),
this);
return values;
} private class ValueCollection extends AbstractCollection<V> {
public Iterator<V> iterator() {
return getIterator(VALUES);
}
public int size() {
return count;
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return containsValue(o);
}
public void clear() {
Hashtable.this.clear();
}
} // Comparison and hashing /**
* Compares the specified Object with this Map for equality,
* as per the definition in the Map interface.
*
* @param o object to be compared for equality with this hashtable
* @return true if the specified Object is equal to this Map
* @see Map#equals(Object)
* @since 1.2
*/
public synchronized boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true; if (!(o instanceof Map))
return false;
Map<?,?> t = (Map<?,?>) o;
if (t.size() != size())
return false; try {
Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<K,V> e = i.next();
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
if (value == null) {
if (!(t.get(key)==null && t.containsKey(key)))
return false;
} else {
if (!value.equals(t.get(key)))
return false;
}
}
} catch (ClassCastException unused) {
return false;
} catch (NullPointerException unused) {
return false;
} return true;
} /**
* Returns the hash code value for this Map as per the definition in the
* Map interface.
*
* @see Map#hashCode()
* @since 1.2
*/
public synchronized int hashCode() {
/*
* This code detects the recursion caused by computing the hash code
* of a self-referential hash table and prevents the stack overflow
* that would otherwise result. This allows certain 1.1-era
* applets with self-referential hash tables to work. This code
* abuses the loadFactor field to do double-duty as a hashCode
* in progress flag, so as not to worsen the space performance.
* A negative load factor indicates that hash code computation is
* in progress.
*/
int h = 0;
if (count == 0 || loadFactor < 0)
return h; // Returns zero loadFactor = -loadFactor; // Mark hashCode computation in progress
Entry<?,?>[] tab = table;
for (Entry<?,?> entry : tab) {
while (entry != null) {
h += entry.hashCode();
entry = entry.next;
}
} loadFactor = -loadFactor; // Mark hashCode computation complete return h;
} @Override
public synchronized V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) {
V result = get(key);
return (null == result) ? defaultValue : result;
} @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public synchronized void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action); // explicit check required in case
// table is empty.
final int expectedModCount = modCount; Entry<?, ?>[] tab = table;
for (Entry<?, ?> entry : tab) {
while (entry != null) {
action.accept((K)entry.key, (V)entry.value);
entry = entry.next; if (expectedModCount != modCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
} @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public synchronized void replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> function) {
Objects.requireNonNull(function); // explicit check required in case
// table is empty.
final int expectedModCount = modCount; Entry<K, V>[] tab = (Entry<K, V>[])table;
for (Entry<K, V> entry : tab) {
while (entry != null) {
entry.value = Objects.requireNonNull(
function.apply(entry.key, entry.value));
entry = entry.next; if (expectedModCount != modCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
} @Override
public synchronized V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) {
Objects.requireNonNull(value); // Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for (; entry != null; entry = entry.next) {
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
V old = entry.value;
if (old == null) {
entry.value = value;
}
return old;
}
} addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
return null;
} @Override
public synchronized boolean remove(Object key, Object value) {
Objects.requireNonNull(value); Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for (Entry<K,V> prev = null; e != null; prev = e, e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key) && e.value.equals(value)) {
modCount++;
if (prev != null) {
prev.next = e.next;
} else {
tab[index] = e.next;
}
count--;
e.value = null;
return true;
}
}
return false;
} @Override
public synchronized boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {
Objects.requireNonNull(oldValue);
Objects.requireNonNull(newValue);
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for (; e != null; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
if (e.value.equals(oldValue)) {
e.value = newValue;
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
return false;
} @Override
public synchronized V replace(K key, V value) {
Objects.requireNonNull(value);
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for (; e != null; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
}
return null;
} @Override
public synchronized V computeIfAbsent(K key, Function<? super K, ? extends V> mappingFunction) {
Objects.requireNonNull(mappingFunction); Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for (; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.hash == hash && e.key.equals(key)) {
// Hashtable not accept null value
return e.value;
}
} V newValue = mappingFunction.apply(key);
if (newValue != null) {
addEntry(hash, key, newValue, index);
} return newValue;
} @Override
public synchronized V computeIfPresent(K key, BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {
Objects.requireNonNull(remappingFunction); Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for (Entry<K,V> prev = null; e != null; prev = e, e = e.next) {
if (e.hash == hash && e.key.equals(key)) {
V newValue = remappingFunction.apply(key, e.value);
if (newValue == null) {
modCount++;
if (prev != null) {
prev.next = e.next;
} else {
tab[index] = e.next;
}
count--;
} else {
e.value = newValue;
}
return newValue;
}
}
return null;
} @Override
public synchronized V compute(K key, BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {
Objects.requireNonNull(remappingFunction); Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for (Entry<K,V> prev = null; e != null; prev = e, e = e.next) {
if (e.hash == hash && Objects.equals(e.key, key)) {
V newValue = remappingFunction.apply(key, e.value);
if (newValue == null) {
modCount++;
if (prev != null) {
prev.next = e.next;
} else {
tab[index] = e.next;
}
count--;
} else {
e.value = newValue;
}
return newValue;
}
} V newValue = remappingFunction.apply(key, null);
if (newValue != null) {
addEntry(hash, key, newValue, index);
} return newValue;
} @Override
public synchronized V merge(K key, V value, BiFunction<? super V, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {
Objects.requireNonNull(remappingFunction); Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for (Entry<K,V> prev = null; e != null; prev = e, e = e.next) {
if (e.hash == hash && e.key.equals(key)) {
V newValue = remappingFunction.apply(e.value, value);
if (newValue == null) {
modCount++;
if (prev != null) {
prev.next = e.next;
} else {
tab[index] = e.next;
}
count--;
} else {
e.value = newValue;
}
return newValue;
}
} if (value != null) {
addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
} return value;
} /**
* Save the state of the Hashtable to a stream (i.e., serialize it).
*
* @serialData The <i>capacity</i> of the Hashtable (the length of the
* bucket array) is emitted (int), followed by the
* <i>size</i> of the Hashtable (the number of key-value
* mappings), followed by the key (Object) and value (Object)
* for each key-value mapping represented by the Hashtable
* The key-value mappings are emitted in no particular order.
*/
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws IOException {
Entry<Object, Object> entryStack = null; synchronized (this) {
// Write out the length, threshold, loadfactor
s.defaultWriteObject(); // Write out length, count of elements
s.writeInt(table.length);
s.writeInt(count); // Stack copies of the entries in the table
for (int index = 0; index < table.length; index++) {
Entry<?,?> entry = table[index]; while (entry != null) {
entryStack =
new Entry<>(0, entry.key, entry.value, entryStack);
entry = entry.next;
}
}
} // Write out the key/value objects from the stacked entries
while (entryStack != null) {
s.writeObject(entryStack.key);
s.writeObject(entryStack.value);
entryStack = entryStack.next;
}
} /**
* Reconstitute the Hashtable from a stream (i.e., deserialize it).
*/
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
{
// Read in the length, threshold, and loadfactor
s.defaultReadObject(); // Read the original length of the array and number of elements
int origlength = s.readInt();
int elements = s.readInt(); // Compute new size with a bit of room 5% to grow but
// no larger than the original size. Make the length
// odd if it's large enough, this helps distribute the entries.
// Guard against the length ending up zero, that's not valid.
int length = (int)(elements * loadFactor) + (elements / 20) + 3;
if (length > elements && (length & 1) == 0)
length--;
if (origlength > 0 && length > origlength)
length = origlength;
table = new Entry<?,?>[length];
threshold = (int)Math.min(length * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
count = 0; // Read the number of elements and then all the key/value objects
for (; elements > 0; elements--) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K key = (K)s.readObject();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
V value = (V)s.readObject();
// synch could be eliminated for performance
reconstitutionPut(table, key, value);
}
} /**
* The put method used by readObject. This is provided because put
* is overridable and should not be called in readObject since the
* subclass will not yet be initialized.
*
* <p>This differs from the regular put method in several ways. No
* checking for rehashing is necessary since the number of elements
* initially in the table is known. The modCount is not incremented
* because we are creating a new instance. Also, no return value
* is needed.
*/
private void reconstitutionPut(Entry<?,?>[] tab, K key, V value)
throws StreamCorruptedException
{
if (value == null) {
throw new java.io.StreamCorruptedException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
// This should not happen in deserialized version.
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
throw new java.io.StreamCorruptedException();
}
}
// Creates the new entry.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
count++;
} /**
* Hashtable bucket collision list entry
*/
private static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next; protected Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Entry<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
} @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected Object clone() {
return new Entry<>(hash, key, value,
(next==null ? null : (Entry<K,V>) next.clone()));
} // Map.Entry Ops public K getKey() {
return key;
} public V getValue() {
return value;
} public V setValue(V value) {
if (value == null)
throw new NullPointerException(); V oldValue = this.value;
this.value = value;
return oldValue;
} public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o; return (key==null ? e.getKey()==null : key.equals(e.getKey())) &&
(value==null ? e.getValue()==null : value.equals(e.getValue()));
} public int hashCode() {
return hash ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
} public String toString() {
return key.toString()+"="+value.toString();
}
} // Types of Enumerations/Iterations
private static final int KEYS = 0;
private static final int VALUES = 1;
private static final int ENTRIES = 2; /**
* A hashtable enumerator class. This class implements both the
* Enumeration and Iterator interfaces, but individual instances
* can be created with the Iterator methods disabled. This is necessary
* to avoid unintentionally increasing the capabilities granted a user
* by passing an Enumeration.
*/
private class Enumerator<T> implements Enumeration<T>, Iterator<T> {
Entry<?,?>[] table = Hashtable.this.table;
int index = table.length;
Entry<?,?> entry;
Entry<?,?> lastReturned;
int type; /**
* Indicates whether this Enumerator is serving as an Iterator
* or an Enumeration. (true -> Iterator).
*/
boolean iterator; /**
* The modCount value that the iterator believes that the backing
* Hashtable should have. If this expectation is violated, the iterator
* has detected concurrent modification.
*/
protected int expectedModCount = modCount; Enumerator(int type, boolean iterator) {
this.type = type;
this.iterator = iterator;
} public boolean hasMoreElements() {
Entry<?,?> e = entry;
int i = index;
Entry<?,?>[] t = table;
/* Use locals for faster loop iteration */
while (e == null && i > 0) {
e = t[--i];
}
entry = e;
index = i;
return e != null;
} @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T nextElement() {
Entry<?,?> et = entry;
int i = index;
Entry<?,?>[] t = table;
/* Use locals for faster loop iteration */
while (et == null && i > 0) {
et = t[--i];
}
entry = et;
index = i;
if (et != null) {
Entry<?,?> e = lastReturned = entry;
entry = e.next;
return type == KEYS ? (T)e.key : (type == VALUES ? (T)e.value : (T)e);
}
throw new NoSuchElementException("Hashtable Enumerator");
} // Iterator methods
public boolean hasNext() {
return hasMoreElements();
} public T next() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return nextElement();
} public void remove() {
if (!iterator)
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Hashtable Enumerator");
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); synchronized(Hashtable.this) {
Entry<?,?>[] tab = Hashtable.this.table;
int index = (lastReturned.hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for(Entry<K,V> prev = null; e != null; prev = e, e = e.next) {
if (e == lastReturned) {
modCount++;
expectedModCount++;
if (prev == null)
tab[index] = e.next;
else
prev.next = e.next;
count--;
lastReturned = null;
return;
}
}
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
}
jdk1.8的Hashtable
测试程序:
package com.hash.hashmaptest;
import java.util.*; public class HashtableTest { public static void main(String[] args) {
testHashtableAPIs();
} private static void testHashtableAPIs() {
// 初始化随机种子
Random r = new Random();
// 新建Hashtable
Hashtable table = new Hashtable();
// 添加操作
table.put("one", new Integer(r.nextInt(10)));
table.put("two", new Integer(r.nextInt(10)));
table.put("three", new Integer(r.nextInt(10))); // 打印出table
System.out.println("table:"+table ); // 通过Iterator遍历key-value
Iterator iter = table.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iter.next();
System.out.println("next : "+ entry.getKey() +" - "+entry.getValue());
} // Hashtable的键值对个数
System.out.println("size:"+table.size()); // containsKey(Object key) :是否包含键key
System.out.println("contains key two : "+table.containsKey("two"));
System.out.println("contains key five : "+table.containsKey("five")); // containsValue(Object value) :是否包含值value
System.out.println("contains value 0 : "+table.containsValue(new Integer(0))); // remove(Object key) : 删除键key对应的键值对
table.remove("three"); System.out.println("table:"+table ); // clear() : 清空Hashtable
table.clear(); // isEmpty() : Hashtable是否为空
System.out.println((table.isEmpty()?"table is empty":"table is not empty") );
}
}

五、HashMap和Hashtable的对比
5.1、产生的时间和作者
HashTable产生于JDK 1.1,而HashMap产生于JDK 1.2。从时间的维度上来看,HashMap要比HashTable出现得晚一些。
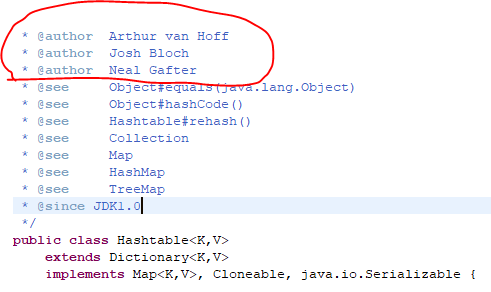
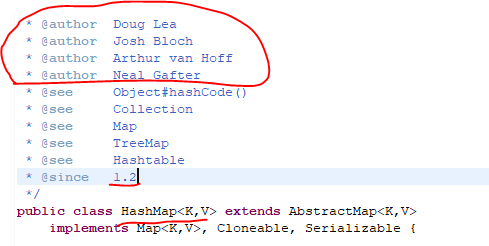
5.2、从方法层面分析

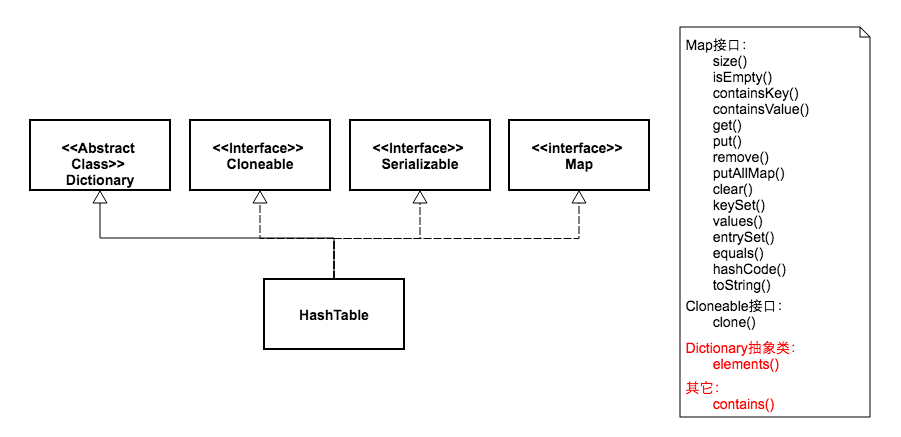
两个类的继承体系有些不同,虽然都实现了Map、Cloneable、Serializable三个接口。但是HashMap继承自抽象类AbstractMap,而HashTable继承自抽象类Dictionary。其中Dictionary类是一个已经被废弃的类。
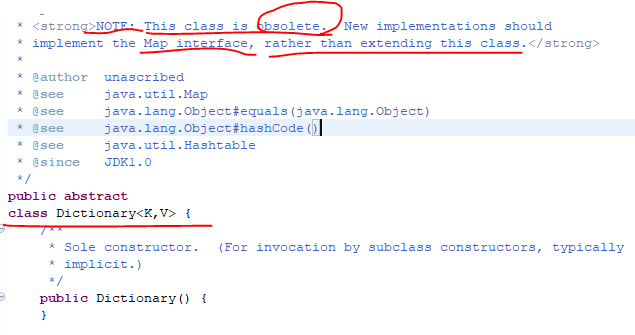
同时Hashtable比HashMap多了两个公开方法。一个是elements,这来自于抽象类Dictionary,鉴于该类已经废弃,所以这个方法也就没什么用处了。另一个多出来的方法是contains,这个多出来的方法也没什么用,因为它跟containsValue方法功能是一样的。
此外HashMap是支持null键和null值的,而Hashtable在遇到null时,会抛出NullPointerException异常。这并不是因为HashTable有什么特殊的实现层面的原因导致不能支持null键和null值,这仅仅是因为HashMap在实现时对null做了特殊处理,将null的hashCode值定为了0,从而将其存放在哈希表的第0个bucket中。
5.3、从算法层面上分析
初始容量大小和每次扩充容量大小的不同。
以下代码及注释来自java.util.HashTable
// 哈希表默认初始大小为11
public Hashtable() {
this(11, 0.75f);
}
protected void rehash() {
int oldCapacity = table.length;
Entry<K,V>[] oldMap = table; // 每次扩容为原来的2n+1
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity << 1) + 1;
// ...
}
以下代码及注释来自java.util.HashMap
// 哈希表默认初始大小为2^4=16
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
// 每次扩充为原来的2n
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
resize(2 * table.length);
}
可以看到Hashtable默认的初始大小为11,之后每次扩充为原来的2n+1。HashMap默认的初始化大小为16,之后每次扩充为原来的2倍。如果在创建时给定了初始化大小,那么Hashtable会直接使用你给定的大小,而HashMap会将其扩充为2的幂次方大小。也就是说Hashtable会尽量使用素数、奇数。而HashMap则总是使用2的幂作为哈希表的大小。我们知道当哈希表的大小为素数时,简单的取模哈希的结果会更加均匀,所以单从这一点上看,Hashtable的哈希表大小选择,似乎更高明些。但另一方面我们又知道,在取模计算时,如果模数是2的幂,那么我们可以直接使用位运算来得到结果,效率要大大高于做除法。所以从hash计算的效率上,又是HashMap更胜一筹。所以,事实就是HashMap为了加快hash的速度,将哈希表的大小固定为了2的幂。当然这引入了哈希分布不均匀的问题,所以HashMap为解决这问题,又对hash算法做了一些改动。具体我们来看看,在获取了key对象的hashCode之后,Hashtable和HashMap分别是怎样将它们hash到确定的哈希桶(Entry数组位置)中的。
HashMap由于使用了2的幂次方,所以在取模运算时不需要做除法,只需要位的与运算就可以了。但是由于引入的hash冲突加剧问题,HashMap在调用了对象的hashCode方法之后,又做了一些位运算在打散数据。
以下代码及注释来自java.util.Hashtable // hash 不能超过Integer.MAX_VALUE 所以要取其最小的31个bit
int hash = hash(key);
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length; // 直接计算key.hashCode()
private int hash(Object k) {
// hashSeed will be zero if alternative hashing is disabled.
return hashSeed ^ k.hashCode();
}
以下代码及注释来自java.util.HashMap
int hash = hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); // 在计算了key.hashCode()之后,做了一些位运算来减少哈希冲突
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = hashSeed;
if (0 != h && k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
} h ^= k.hashCode(); // This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
} // 取模不再需要做除法
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
// assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2";
return h & (length-1);
}
HashMap和HashTable在计算hash时都用到了一个叫hashSeed的变量。这是因为映射到同一个hash桶内的Entry对象,是以链表的形式存在的,而链表的查询效率比较低,所以HashMap/Hashtable的效率对哈希冲突非常敏感,所以可以额外开启一个可选hash(hashSeed),从而减少哈希冲突。事实上,这个优化在JDK 1.8中已经去掉了,因为JDK 1.8中,映射到同一个哈希桶(数组位置)的Entry对象,使用了红黑树来存储,从而大大加速了其查找效率。
5.4、线程安全
HashTable是同步的,HashMap不是,也就是说HashTable在多线程使用的情况下,不需要做额外的同步,而HashMap则不行。但是使用了synchronized描述符降低了效率。
5.5、代码风格
HashMap的代码要比Hashtable整洁很多。
5.6、使用情况
Hashtable已经被淘汰了,不要在代码中再使用它。简单来说就是,如果不需要线程安全,那么使用HashMap,如果需要线程安全,那么使用ConcurrentHashMap。
5.7、持续优化
虽然HashMap和Hashtable的公开接口应该不会改变,或者说改变不频繁。但每一版本的JDK,都会对HashMap和Hashtable的内部实现做优化,比如JDK 1.8的红黑树优化。所以,尽可能的使用新版本的JDK,除了那些炫酷的新功能,普通的API也会有性能上有提升。为什么HashTable已经淘汰了,还要优化它?因为有老的代码还在使用它,所以优化了它之后,这些老的代码也能获得性能提升。
六、总结
本文中我们深入探讨了三种Map结构,对于其中的实现原理,初始化,增删改查,扩容,提升查找效率等等方面进行了分析和探讨,对我们以后的使用非常有帮助。
参考文献: https://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3310835.html
http://www.importnew.com/20386.html
http://www.importnew.com/29832.html
http://www.importnew.com/24822.html
沉淀再出发:java中的HashMap、ConcurrentHashMap和Hashtable的认识的更多相关文章
- 沉淀再出发:java中的equals()辨析
沉淀再出发:java中的equals()辨析 一.前言 关于java中的equals,我们可能非常奇怪,在Object中定义了这个函数,其他的很多类中都重载了它,导致了我们对于辨析其中的内涵有了混淆, ...
- 沉淀再出发:java中注解的本质和使用
沉淀再出发:java中注解的本质和使用 一.前言 以前XML是各大框架的青睐者,它以松耦合的方式完成了框架中几乎所有的配置,但是随着项目越来越庞大,XML的内容也越来越复杂,维护成本变高.于是就有人提 ...
- 沉淀再出发:java中线程池解析
沉淀再出发:java中线程池解析 一.前言 在多线程执行的环境之中,如果线程执行的时间短但是启动的线程又非常多,线程运转的时间基本上浪费在了创建和销毁上面,因此有没有一种方式能够让一个线程执行完自己的 ...
- 沉淀再出发:如何在eclipse中查看java的核心代码
沉淀再出发:如何在eclipse中查看java的核心代码 一.前言 很多时候我们在eclipse中按F3键打算查看某一个系统类的定义的时候,总是弹出找不到类这样的界面,这里我们把核心对应的代码加进 ...
- 沉淀再出发:关于java中的AQS理解
沉淀再出发:关于java中的AQS理解 一.前言 在java中有很多锁结构都继承自AQS(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer)这个抽象类如果我们仔细了解可以发现AQS的作用是非常大的 ...
- 沉淀再出发:java中的CAS和ABA问题整理
沉淀再出发:java中的CAS和ABA问题整理 一.前言 在多并发程序设计之中,我们不得不面对并发.互斥.竞争.死锁.资源抢占等等问题,归根到底就是读写的问题,有了读写才有了增删改查,才有了所有的一切 ...
- 沉淀再出发:java的文件读写
沉淀再出发:java的文件读写 一.前言 对于java的文件读写是我们必须使用的一项基本技能,因此了解其中的原理,字节流和字符流的本质有着重要的意义. 二.java中的I/O操作 2.1.文件读写的本 ...
- 沉淀再出发:再谈java的多线程机制
沉淀再出发:再谈java的多线程机制 一.前言 自从我们学习了操作系统之后,对于其中的线程和进程就有了非常深刻的理解,但是,我们可能在C,C++语言之中尝试过这些机制,并且做过相应的实验,但是对于ja ...
- 沉淀再出发:在python3中导入自定义的包
沉淀再出发:在python3中导入自定义的包 一.前言 在python中如果要使用自己的定义的包,还是有一些需要注意的事项的,这里简单记录一下. 二.在python3中导入自定义的包 2.1.什么是模 ...
随机推荐
- WPF中使用RenderTransformOrigin来控制动画的起点
Render :渲染:Transform:动画:Origin:起点 RenderTransformOrigin:渲染动画的起点 取值为一个坐标的形式 取值范围: 0,0 到 1,1 0,0:表示左上 ...
- [中英对照]INTEL与AT&T汇编语法对比
本文首先对文章Intel and AT&T Syntax做一个中英文对照翻译,然后给出一个简单的例子,再用gdb反汇编后,对INTEL与AT&T的汇编语法进行对照从而加深理解. Int ...
- easyform表单校验插件改版源码
改动特性: 1.支持回调,可用于ajax提交 2.提示框样式修改,原版太丑,修改成bootstrap的popover 样式 原版还存在缺陷:被校验的表单元素设置不灵活,还得加上id.name 什么的 ...
- JavaScript ES6 promiss的理解。
本着互联网的分享精神,我将我对promise的理解分享给大家. JavaScript ES6的promise方法主要应用在处理异步函数返回的结果,注意他不是将异步函数转换为同步函数,而是等异步函数有结 ...
- PictureBox控件
PictureBox控件可以显示来自位图.图标或者元文件,以及来自增强的元文件.JPEG.GIF文件的图形,如果控件不足以显示整幅图像,则裁剪图像以适应控件的大小. Sizemode 图片的大小方式 ...
- 二、spark SQL交互scala操作示例
一.安装spark spark SQL是spark的一个功能模块,所以我们事先要安装配置spark,参考: https://www.cnblogs.com/lay2017/p/10006935.htm ...
- js 判断浏览器是否64位
js判断是否64位 浏览器 navigator.userAgent.match(/x64/i);
- C++ STL:stack和queue
http://blog.csdn.net/wallwind/article/details/6858634 http://blog.csdn.net/chao_xun/article/details/ ...
- angular开发中的两大问题
一.在我们的angular开发中,会请求数据但轮播图等...在请求过数据后他的事件和方法将不再执行: 看我们的解决方案一: app.controller("text",functi ...
- log4net.dll添加报错
描述: 新建项目Log4Net类库项目,添加log4net.dll,封装Log类对日志进行操作 新建webForm项目添加Log4Net类库生成的dll生成日志,页面报错,未能加载文件或程序集log4 ...
