linux 将进程或者线程绑定到指定的cpu上
基本概念
cpu亲和性(affinity)
CPU的亲和性, 就是进程要在指定的 CPU 上尽量长时间地运行而不被迁移到其他处理器,也称为CPU关联性;再简单的点的描述就将指定的进程或线程绑定到相应的cpu上;在多核运行的机器上,每个CPU本身自己会有缓存,缓存着进程使用的信息,而进程可能会被OS调度到其他CPU上,如此,CPU cache命中率就低了,当绑定CPU后,程序就会一直在指定的cpu跑,不会由操作系统调度到其他CPU上,性能有一定的提高。
软亲和性(affinity)
就是进程要在指定的 CPU 上尽量长时间地运行而不被迁移到其他处理器,Linux 内核进程调度器天生就具有被称为 软 CPU 亲和性(affinity) 的特性,这意味着进程通常不会在处理器之间频繁迁移。这种状态正是我们希望的,因为进程迁移的频率小就意味着产生的负载小。
硬亲和性(affinity)
简单来说就是利用linux内核提供给用户的API,强行将进程或者线程绑定到某一个指定的cpu核运行。
相关函数
void CPU_ZERO (cpu_set_t *set) /*这个宏对 CPU 集 set 进行初始化,将其设置为空集。*/
void CPU_SET (int cpu, cpu_set_t *set) /*这个宏将 指定的 cpu 加入 CPU 集 set 中*/
void CPU_CLR (int cpu, cpu_set_t *set) /*这个宏将 指定的 cpu 从 CPU 集 set 中删除。*/
int CPU_ISSET (int cpu, const cpu_set_t *set) /*如果 cpu 是 CPU 集 set 的一员,这个宏就返回一个非零值(true),否则就返回零(false)。*/
进程与cpu的绑定
#include <sched.h>
int sched_setaffinity(pid_t pid, size_t cpusetsize, const cpu_set_t *mask);
int sched_getaffinity(pid_t pid, size_t cpusetsize, const cpu_set_t *mask);
代码示例:
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <sched.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
/* sysconf( _SC_NPROCESSORS_CONF ) 查看cpu的个数;打印用%ld长整。
* sysconf( _SC_NPROCESSORS_ONLN ) 查看在使用的cpu个数;打印用%ld长整 */
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int cpus = 0;
int i = 0;
cpu_set_t mask;
cpu_set_t get;
cpus = sysconf(_SC_NPROCESSORS_CONF);
printf("cpus: %d\n", cpus);
CPU_ZERO(&mask); /* 初始化set集,将set置为空*/
CPU_SET(0, &mask); /* 依次将0、1、2、3号cpu加入到集合,前提是你的机器是多核处理器*/
CPU_SET(1, &mask);
CPU_SET(2, &mask);
CPU_SET(3, &mask);
/*设置cpu 亲和性(affinity)*/
if (sched_setaffinity(0, sizeof(mask), &mask) == -1) {
printf("Set CPU affinity failue, ERROR:%s\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
usleep(1000); /* 让当前的设置有足够时间生效*/
/*查看当前进程的cpu 亲和性*/
CPU_ZERO(&get);
if (sched_getaffinity(0, sizeof(get), &get) == -1) {
printf("get CPU affinity failue, ERROR:%s\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
/*查看运行在当前进程的cpu*/
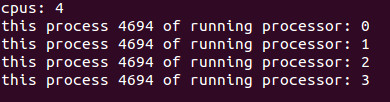
for(i = 0; i < cpus; i++) {
if (CPU_ISSET(i, &get)) { /*查看cpu i 是否在get 集合当中*/
printf("this process %d of running processor: %d\n", getpid(), i);
}
}
sleep(10); //让程序停在这儿,方便top命令查看
return 0;
}
结果:
线程与cpu的绑定
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_setaffinity_np(pthread_t thread, size_t cpusetsize, const cpu_set_t *cpuset);
int pthread_getaffinity_np(pthread_t thread, size_t cpusetsize, const cpu_set_t *cpuset);
代码示例:
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sched.h>
void *testfunc(void *arg)
{
int i, cpus = 0;
cpu_set_t mask;
cpu_set_t get;
cpus = sysconf(_SC_NPROCESSORS_CONF);
printf("this system has %d processor(s)\n", cpus);
CPU_ZERO(&mask);
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) { /*将0、1、2、3添加到集合中*/
CPU_SET(i, &mask);
}
/* 设置cpu 亲和性(affinity)*/
if (pthread_setaffinity_np(pthread_self(), sizeof(mask), &mask) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "set thread affinity failed\n");
}
/* 查看cpu 亲和性(affinity)*/
CPU_ZERO(&get);
if (pthread_getaffinity_np(pthread_self(), sizeof(get), &get) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "get thread affinity failed\n");
}
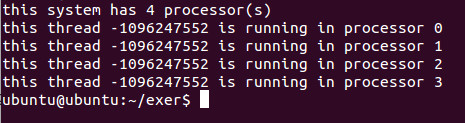
/* 查看当前线程所运行的所有cpu*/
for (i = 0; i < cpus; i++) {
if (CPU_ISSET(i, &get)) {
printf("this thread %d is running in processor %d\n", (int)pthread_self(), i);
}
}
sleep(3); //查看
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid;
if (pthread_create(&tid, NULL, (void *)testfunc, NULL) != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "thread create failed\n");
return -1;
}
pthread_join(tid, NULL);
return 0;
}
结果:
指定在哪个CPU上运行:
void *threadfunc(void *arg)
{
cpu_set_t mask;
cpu_set_t mask;
int cpuid = 1;
CPU_ZERO(&mask);
CPU_SET(cpuid, &mask);
/* 设置cpu 亲和性(affinity)*/
if (pthread_setaffinity_np(pthread_self(), sizeof(mask), &mask) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "set thread affinity failed\n");
}
}
linux 将进程或者线程绑定到指定的cpu上的更多相关文章
- Linux进程或线程绑定到CPU
Linux进程或线程绑定到CPU 为了让程序拥有更好的性能,有时候需要将进程或线程绑定到特定的CPU,这样可以减少调度的开销和保护关键进程或线程. 进程绑定到CPU Linux提供一个接口,可以将进程 ...
- Linux 进程、线程运行在指定CPU核上
/******************************************************************************** * Linux 进程.线程运行在指定 ...
- linux下将不同线程绑定到不同core和cpu上——pthread_setaffinity_np
=============================================================== linux下的单进程多线程的程序,要实现每个线程平均分配到多核cpu,主 ...
- Windows10 临时将线程绑定至指定CPU的方法
本文首发:https://www.somata.work/2019/WindowsThreadBind.html 将线程绑定至指定CPU,这个应该时很多管理员需要了解认知的操作了吧,这样可以在一定程度 ...
- 理解Linux的进程,线程,PID,LWP,TID,TGID
在Linux的top和ps命令中,默认看到最多的是pid (process ID),也许你也能看到lwp (thread ID)和tgid (thread group ID for the threa ...
- linux 下 进程和线程的区别
1.进程与线程 进程是程序执行时的一个实例,即它是程序已经执行到课中程度的数据结构的汇集.从内核的观点看,进程的目的就是担当分配系统资源(CPU时间.内存等)的基本单位. 线程是进程的一个执行流,是C ...
- 深入理解 Linux的进程,线程,PID,LWP,TID,TGID
转载:https://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2019-03/157819.htm 在Linux的top和ps命令中,默认看到最多的是pid (process ID),也许你也能 ...
- [转载]了解Linux的进程与线程
本文转自Tim Yang的博客http://timyang.net/linux/linux-process/ .对于理解Linux的进程与线程非常有帮助.支持原创.尊重原创,分享知识! 上周碰到部署在 ...
- [转] linux 下 进程和线程的区别
1.进程与线程 进程是程序执行时的一个实例,即它是程序已经执行到课中程度的数据结构的汇集.从内核的观点看,进程的目的就是担当分配系统资源(CPU时间.内存等)的基本单位. 线程是进程的一个执行流,是C ...
随机推荐
- C语言源字符集与执行字符集
参考: http://blog.csdn.net/yucan1001/article/details/7188267 http://blog.csdn.net/dbzhang800/article ...
- Java 设计模式系列(十四)命令模式(Command)
Java 设计模式系列(十四)命令模式(Command) 命令模式把一个请求或者操作封装到一个对象中.命令模式允许系统使用不同的请求把客户端参数化,对请求排队或者记录请求日志,可以提供命令的撤销和恢复 ...
- matplotlib安装错误依赖问题解决
When install "matplotlib" with "pip", if you get the following error, it means t ...
- 不要怂,就是GAN (生成式对抗网络) (二):数据读取和操作
前面我们了解了 GAN 的原理,下面我们就来用 TensorFlow 搭建 GAN(严格说来是 DCGAN,如无特别说明,本系列文章所说的 GAN 均指 DCGAN),如前面所说,GAN 分为有约束条 ...
- 使用VMWare12.0安装Ubuntu系统
使用VMWare12.0安装Ubuntu系统 Vmware12的虚拟机的文档说明: http://pubs.vmware.com/workstation-12/index.jsp#com.vmware ...
- CYUSB3014固件部分低版本工程在Eclipse中编译得到img文件时无效的解决方案
最近在做基于我们AC6102开发板的UVC图像视频方案,下载了官方的an75779应用工程,但是倒入到FX3—SDK自带的Eclipse中后,却无法编译生成img文件,经过比对后确认是生成该文件的命令 ...
- handsontable-developer guide-load and save
不过handsontable不能用jquery取对象 var $$ = function(id) { return document.getElementById(id); }, container ...
- threadpoolExecutor----自动执行任务
使用threadpoolExecutor,主要是任务的提交的执行和获取结果. 提交任务的方法有: 1.submit 2.execute 3.queue的add 其中1和2的使用必须是threadpoo ...
- Tempdb--Row version
Trigger:在SQL SERVER 2005之前,触发器需要使用日志来获取DELETED AND INSERTED的数据,因此会打乱日志顺序写的模式,造成磁盘压力,在SQL Server2005 ...
- 微信小程序web-view之wx.miniProgram.redirectTo
17年微信小程序官方提供了web-view组件. 官方描述:web-view组件是一个可以用来承载网页的容器,会自动铺满整个小程序页面.个人类型与海外类型的小程序暂不支持使用. 这段时间研究了一下小程 ...
