Linux useful commands
#find the binary files
find . -type f | perl -lne 'print if -B'
another method is grepgrep -r -I -L -Z . | xargs -0 ls -l
-L : list the binary file
-r : rescusive
-Z :printf NULl byte after filename
xargs: run command, here is 'ls -l'
-0 : is the parameter of xargs #show directory size
du -h
du : disk usage
#history
histoy to list the histoy commands
#show the file path
find . -type f
other options can be : -type [bcdpflsD], d: is only directory
example:
./u-boot-imx_%.bbappend
./u-boot-imx/Kconfig.patch
./u-boot-imx/board/bosch/ulpanel/plugin.S
#list the file permission in number e.g. 666
stat -c "%a %n" *#compress a current date folder
DIR=$(date "+%Y%m%d")
tar -zcf $DIR.tar.gz $DIR
#change the real name of user
sudo chfn -f "FirstName LastName" *username*#backup file auto create sub folders
rsync -a -r ~/Documents/newsys/yocto/zeus/build/conf $DIR/
rsync -a -r ~/Documents/newsys/yocto/zeus/meta-ul_bsp $DIR/
#Putty
sudo apt-get install putty
after plug-in the imx6ullevk board to linux, the device is /dev/ttyUSB0
In my linux, I cannot open this device because I do not belong to ttyUSB0 groups (root dialout).
1)check the you belong. groups username
2)add to dialout group
>sudo usermod -a -G dialout zjb
or you can direct change the file : sudo vim /etc/group
3) you need restart or logout
#Quick copy the selected text as input in terminate
using middle button of mouse.
#Create a series of folder
install -d arch/arm/boot/dts
or mkdir -p arch/arm/boot/dts
tree .
.
└── arch
└── arm
└── boot
└── dts
#Info
Almost all the standard Linux programming tools (including ld, the linker; as, the assembler; and gprof, the profiler) come with useful Info pages.
e.g. info uname
#cat misc.
cat xxx | more
cat xxx | less
cat > xxx , create a file xxx
cat -n xxx | more with line number information.
cat aaa.txt >> bbb.txt, the aaa.txt will be appened to bbb.txt
#create a user belong to root group
>sudo su
>adduser yourname
>usermod -aG sudo username
>su - username
>sudo whoami
su : switch user
sudo : The sudo command allows you to run programs as another user, by default the root user. If you spend a lot of time on the command line, sudo is one of the commands that you will use quite frequently.
#get the user group
>groups
>id
#using awk to get the device major number
in a shell file, to get the device major number
major =$(awk '/scull/ print {$1}' /proc/devices)
#tail a file with auto update when file change
tail -f /var/log/syslog
#makefile with detail commands infomation
make V = 1 , which will show the detailed commands
#To switch root user
sudo su switch to root user
using exit to go back to login user
#To check which driver is mounting for CD-ROM
just typeing mount in terminate
/dev/sda2 on / type ext4 (rw,errors=remount-ro)
proc on /proc type proc (rw,noexec,nosuid,nodev)
sysfs on /sys type sysfs (rw,noexec,nosuid,nodev)
none on /sys/fs/cgroup type tmpfs (rw)
none on /sys/fs/fuse/connections type fusectl (rw)
none on /sys/kernel/debug type debugfs (rw)
none on /sys/kernel/security type securityfs (rw)
none on /sys/firmware/efi/efivars type efivarfs (rw)
udev on /dev type devtmpfs (rw,mode=)
devpts on /dev/pts type devpts (rw,noexec,nosuid,gid=,mode=)
tmpfs on /run type tmpfs (rw,noexec,nosuid,size=%,mode=)
none on /run/lock type tmpfs (rw,noexec,nosuid,nodev,size=)
none on /run/shm type tmpfs (rw,nosuid,nodev)
none on /run/user type tmpfs (rw,noexec,nosuid,nodev,size=,mode=)
none on /sys/fs/pstore type pstore (rw)
/dev/sda1 on /boot/efi type vfat (rw)
binfmt_misc on /proc/sys/fs/binfmt_misc type binfmt_misc (rw,noexec,nosuid,nodev)
systemd on /sys/fs/cgroup/systemd type cgroup (rw,noexec,nosuid,nodev,none,name=systemd)
gvfsd-fuse on /run/user//gvfs type fuse.gvfsd-fuse (rw,nosuid,nodev,user=zjb)
/dev/sr0 on /media/zjb/UDF Volume type udf (ro,nosuid,nodev,uid=1000,gid=1000,iocharset=utf8,umask=0077,uhelper=udisks2)
#To create ISO from CD-ROM
dd if=source of=destination
example, dd if=/dev/sr0 of=windows.iso
#To create ISO from folder
apt-get install genisoimage
genisoimage -o output_image.iso -J -R -l directory_name
-J -R -l is to keep the original filename
#To install .deb file
sudo dpkg -i /path/to/deb/file
sudo apt install ./name.deb
#source bash_file
source is a Unix command that evaluates the file following the command, as a list of commands, executed in the current context
#lz4c not found
apt-get install liblz4-tool
#mkfs.ubifs not found
apt-get install mtd-utils
#Installing the ncurses library which may used in make menuconfig
libncurses5-dev : Developer’s libraries for ncurses
libncursesw5-dev : Developer’s libraries for ncursesw
#tree list the folder/file in a tree way
tree -d directory only
tree -d -f full file.
#.bashrc
.bashrc文件主要保存个人的一些个性化设置,如命令别名、路径等。
.bash_profile'只在会话开始时被读取一次,而'.bashrc'则每次打开新的终端时,都要被读取。
要定义一个全局变量,使在以后打开的终端中生效,您需要将局部变量输出(export),可以用"export"命令:
export PATH=$PATH:/some/directory
#get the inserted disk or sd card
sudo fdisk -l
or using
lsblk
so you can find the usb device is on media/xxxx, you can visit by cd media/xxx
#generate the patch file
e.g. diff -Nupr --no-dereference xyssl-0.8/ xyssl-0.8-dll/ >xyssl.patch
#find a file
find . -name xxx.file
#grep a word
grep [options] pattern [files]
grep yocto readme.txt, search yocto in readme.txt file
grep 'yocto\|org' readme.txt , search yocto or org in readme.txt file
ps -aux | grep timer, only list the timer process in ps output
example below..
grep -rnw '/path/to/somewhere/' -e 'pattern'-ror-Ris recursive,-nis line number, and-wstands for match the whole word.-l(lower-case L) can be added to just give the file name of matching files.
Along with these, --exclude, --include, --exclude-dir flags could be used for efficient searching:
This will only search through those files which have .c or .h extensions:
grep --include=\*.{c,h} -rnw '/path/to/somewhere/' -e "pattern"
This will exclude searching all the files ending with .o extension:
grep --exclude=*.o -rnw '/path/to/somewhere/' -e "pattern"
For directories it's possible to exclude a particular directory(ies) through
--exclude-dirparameter. For example, this will exclude the dirs dir1/, dir2/ and all of them matching *.dst/:grep --exclude-dir={dir1,dir2,*.dst} -rnw '/path/to/somewhere/' -e "pattern"
This works very well for me, to achieve almost the same purpose like yours.
For more options check man grep.
#Linux 下计算代码行数的工具
cloc
#source and .
you can replace the first . as source, example . ./oe-init-build-env, you can run as : source ./oe-init-build-env,
source is a shell built-in command which is used to read and execute the content of a file(generally set of commands), passed as an argument in the current shell script. It has a synonym in .
#using samba to visit network driver
1) Install cifs tool:
sudo apt-get install cifs-utils
2) Create the local folder for mount (I would recommend you not to create these folder directly under your home directory, because it cause it slowly to every time you open your home directory)
~$ mkdir ~/RND-tool
3) create the credentials
~$ gedit ~/.smbcredentials
4) Add the following content to it (not include ‘[‘&’]’):
username=[ user name]
password=[password]
Save the file
1) Change the permission:
~$ chmod 600 ~/.smbcredentials
2) Edit /etc/fstab
~$ sudo gedit /etc/fstab
3) add the following content: network disk folder
//10.54.128.19/folder$ /home/[your ubuntu user name]/RND-tool cifs uid=[your ubuntu user id],gid=[your ubuntu user group id],credentials=/home/[your ubuntu user name]/.smbcredentials,iocharset=utf8,sec=ntlm,noserverino 0 0
Save the file and,
**** in unbutun 18.04.
//10.54.128.19/folder$ /home/[your ubuntu user name]/RND-tool cifs uid=[your ubuntu user id],gid=[your ubuntu user group id],credentials=/home/[your ubuntu user name]/.smbcredentials ,iocharset=utf8 0 0
Restart Ubuntu to test R disk if works.
4) ~$ sudo mount –a
If the last step is failed, don’t worry, just reboot system, and then it will works if previous operations are correct. Now you can access network disk.
Note: mount -a is to mount all stuff from /etc/fstab
This command can be tested in terminal before fstab.
sudo mount //10.54.128.19/folder$ /home/[your ubuntu user name]/RND-tool -t cifs -o uid=[your ubuntu user id],gid=[your ubuntu user group id],credentials=/home/[your ubuntu user name]/.smbcredentials ,iocharset=utf8
sudo umount RND-tool
#Shell file Error
Syntax error: end of file unexpected (expecting "then")
The problem is the shell file is windows format, so cover to unix format.
#Find the location of program
which xxx
dpkg -listfiles xxx
#type to know the command
type -a xx
examples:
type -a ls
type -a cd
cd is a shell buildin
#Show system information
uname -a, will show all information of system
#file redirection
">" is the output redirection in linux command
e.g. ls -l >abc.txt, the ls output will be in abc.txt, the abc.txt will be overried.
e.g. ls -l >>abc.txt same as before but the abc.txt will not be overrided.
e.g. ls -l >abc.txt 2>&1, here 2 is stderr, redirect the stderr to abc.txt
also "<" is input redirection.
#get the last command return value
echo $?
#ipcs/ipcrm
ipcs lists the system interprocess communication, incl. share memory, queue, semphore.
ipcrm remove a IPC e.g. share memory .
#mount
mount [-t vfstype] [-o options] device directory
e.g. mount -t ext4 /dev/mmcblk0p1 /mnt
#chmod
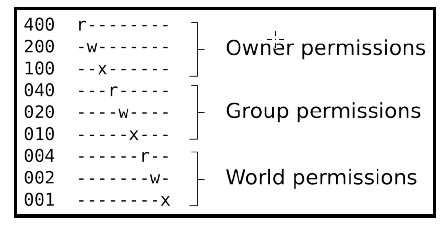
e.g. chmod 777 abc 7 = 4+2+1
#Change password
- Open the terminal application by pressing Ctrl + Alt + T
- To change a password for user named tom in Ubuntu, type:
- sudo passwd tom
- To change a password for root user on Ubuntu Linux, run:
- sudo passwd root
- And to change your own password for Ubuntu, execute:
- passwd
Linux useful commands的更多相关文章
- linux basic commands
1. man - an interface to the on-line reference manuals $man man 2. apt - advanced package tool SEE A ...
- Linux Basis --- commands of vi
EDIT mode to GENERAL mode: press ESC general mode: CLOSE FILE :q! :force to close the file but no ...
- Linux Network Commands
https://www.tecmint.com/linux-network-configuration-and-troubleshooting-commands/ http://www.tldp.or ...
- Linux YUM (Yellowdog Updater, Modified) Commands for Package Management
Linux YUM (Yellowdog Updater, Modified) Commands for Package Management In this article, we will lea ...
- 13 Basic Cat Command Examples in Linux(转) Linux中cat命令的13中基本用法
Cat (串联) 命令是Linux/Unix开源系统中比较常用的一个命令.我们可以通过Cat命令创建一个或多个文件,查看文件内容,串联文件并将内容输出到终端设备或新的文件当中,这篇文章我们将会以实例的 ...
- Linux 各类设置、配置、使用技巧参考,Linux使用集锦
========== 参考格式 (新增记录时,复制粘贴在下)============= [日期]: <标题> 参考链接ref1: 参考链接ref2: 正文: ========== 参考格式 ...
- 系统管理员需知:25个Linux服务器安全技巧(转)
来源:51CTO 作者:51CTO 大家都认为 Linux 默认是安全的,我大体是认可的 (这是个有争议的话题).Linux默认确实有内置的安全模型.你需要打开它并且对其进行定制,这样才能 ...
- 13 Basic Cat Command Examples in Linux
FROM: http://www.tecmint.com/13-basic-cat-command-examples-in-linux/ The cat (short for “concatenate ...
- java使用Runtime.exec()运行windwos dos或linux shell命令
使用Runtime.exec()运行windwos dos或linux shell命令,按实际情况具体测试 实例代码: package com.bookoo.test.command; imp ...
随机推荐
- 调研IOS的开发环境的发展演变
一. 关于IOS的开发发展历史: 百度一下,关于这方面的详细资料有很多,在这里就不复制粘贴占用篇幅了. 二. 关于个人搭建IOS开发环境的体验: 本人用的是华硕电脑,window7的操作系统,本来为了 ...
- 使用Docker方式创建3节点的Etcd集群
一.简要说明 二.运行容器 三.验证集群 四.运行截图 五.参考链接 一.简要说明 参考etcd官网文档, 在node1.node2.node3三个节点上,分别运行etcd容器,创建etcd集 ...
- Android View 阴影的总结
关于 Android 阴影,大家肯定不陌生的.但是Android 中到底有多少种方式可以实现阴影效果以及各种方式之间有什么区别和优缺点,这就是我想总结的.下面我们一个一个来说: 一.各种实现阴影的方式 ...
- 9foundation
注意点 1NSDate时间,时间字符串, 时间戳,格式器,四者的的关系 <1NSDate拥有属性时间戳 <2format格式器,可以直接把NSDate读取为时间字符串,把时间字符串读取为N ...
- LeetCode--018--四数之和(java)
给定一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums 和一个目标值 target,判断 nums 中是否存在四个元素 a,b,c 和 d ,使得 a + b + c + d 的值与 target 相等?找出所有满 ...
- axios和promise
什么是axios axios is a promise based HTTP client for the browser and node.js Features: Make XMLHttpRequ ...
- 手机端页面可以左右轻微拖动的bug
在做项目的时候,必须要适应各种屏幕,移动端是必须的. 但是在移动端中,网站是左右可以动,怎么办呢? 这是只要在样式表中写入 html,body{overfow-x:hidden;} bug产生在H5的 ...
- 页面检测网络外网连接- 网页基础模块(JavaScript)
方法一 html 添加图片标签 加载外站图片 <img id="connect-test" style="display:none;" onload=&q ...
- QANet
Reading Comprehension(RC) 阅读理解对于机器来说, 是一项非常艰巨的任务.google提出QANet, 目前(2018 0505)一直是SQuAD的No. 1. 今天简单地与大 ...
- [poj P2411] Mondriaan's Dream
[poj P2411] Mondriaan's Dream Time Limit: 3000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 18023 A ...
