ARM64 Linux kernel virtual address space
墙外通道:http://thinkiii.blogspot.com/2014/02/arm64-linux-kernel-virtual-address-space.html
Now let's talk about the Linux kernel virtual address space on 64-bit ARM CPU. You can find information about ARMv8 in ARM official website. http://www.arm.com/products/processors/armv8-architecture.php
Actually 2^64 is too large, so in the Linux kernel implementation, only part of 64 bits are used (42 bits for CONFIG_ARM64_64K_PAGES, 39 bit for 4K page). This article is assuming 4K page is used (VA_BITS = 39 case)
#ifdef CONFIG_ARM64_64K_PAGES
#define VA_BITS (42)
#else
#define VA_BITS (39)
#endif
All user virtual addresses have 25 leading zeros and kernel addresses have 25 leading ones. Address between user space and kernel space are not used and they are used to trap illegal accesses.
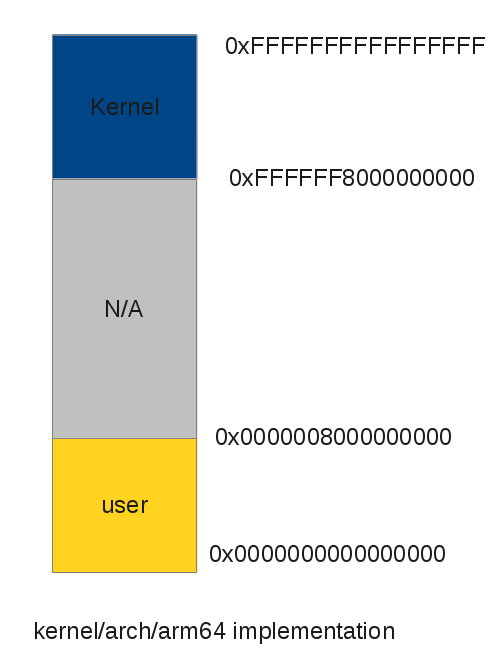
ARM64 Linux virtual address space layout
kernel:
Although we have no ARM64 environment now, we can analysis the kernel virtual address space by reading the source code and observing a running AMD64 Linux box.
In arch/arm64/include/asm/memory.h, we can see the some differences: we have no lowmem zone, since the virtual address is so big that we can treat all memory of lowmem and do not have to worry about virtual address. (Yes, there is still a limit of kernel virtual address). Second, the order of different kernel virtual address changes:
#ifdef CONFIG_ARM64_64K_PAGES
#define VA_BITS (42)
#else
#define VA_BITS (39)
#endif
#define PAGE_OFFSET (UL(0xffffffffffffffff) << (VA_BITS - 1))
#define MODULES_END (PAGE_OFFSET)
#define MODULES_VADDR (MODULES_END - SZ_64M)
#define EARLYCON_IOBASE (MODULES_VADDR - SZ_4M)
pr_notice("Virtual kernel memory layout:\n"
" vmalloc : 0x%16lx - 0x%16lx (%6ld MB)\n"
#ifdef CONFIG_SPARSEMEM_VMEMMAP
" vmemmap : 0x%16lx - 0x%16lx (%6ld MB)\n"
#endif
" modules : 0x%16lx - 0x%16lx (%6ld MB)\n"
" memory : 0x%16lx - 0x%16lx (%6ld MB)\n"
" .init : 0x%p" " - 0x%p" " (%6ld kB)\n"
" .text : 0x%p" " - 0x%p" " (%6ld kB)\n"
" .data : 0x%p" " - 0x%p" " (%6ld kB)\n",
MLM(VMALLOC_START, VMALLOC_END),
#ifdef CONFIG_SPARSEMEM_VMEMMAP
MLM((unsigned long)virt_to_page(PAGE_OFFSET),
(unsigned long)virt_to_page(high_memory)),
#endif
MLM(MODULES_VADDR, MODULES_END),
MLM(PAGE_OFFSET, (unsigned long)high_memory),
MLK_ROUNDUP(__init_begin, __init_end),
MLK_ROUNDUP(_text, _etext),
MLK_ROUNDUP(_sdata, _edata));
see also:
arch/arm64/mm/init.c
arch/arm64/include/asm/pgtable.h
You can see that there is no pkmap or fixmap, it's because the kernel is assuming every memory has a valid kernel virtual address and there's no need to create pkmap/fixmap.
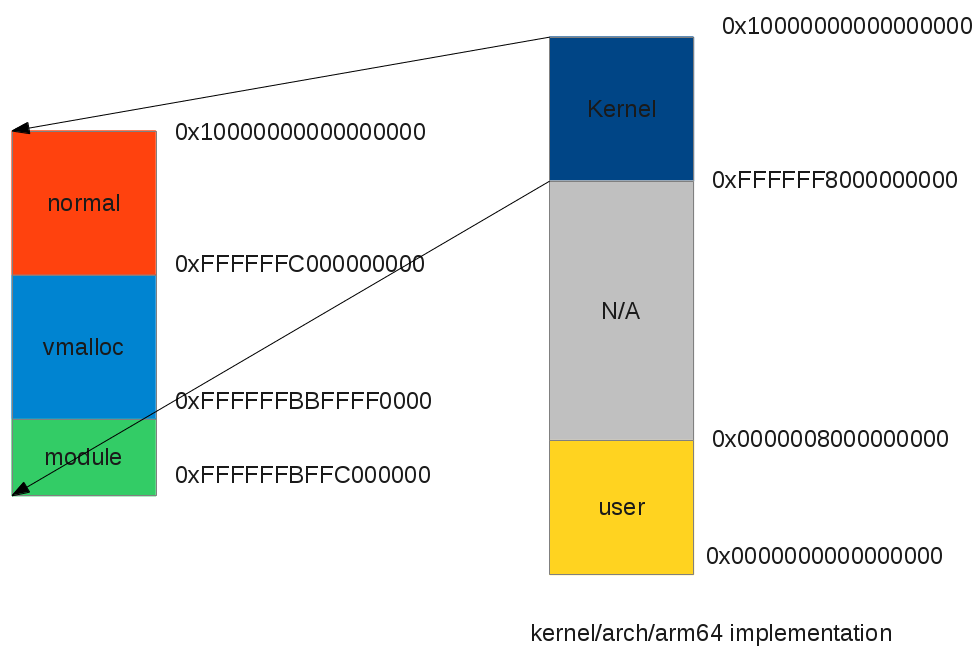
ARM64 kernel virtual address space layout
One interesting topic is that ARM claims the ARMv8 is compatible with ARM 32-bit applications, all 32-bit applications can run on ARMv8 without modification.How does the 32-bit application virtual memory layout look like on a 64-bit kernel?
Actually, all process on 64-bit kernel is a 64-bit process. To run ARM 32-bit applications, Linux kernel still create a process from a 64-bit init process, but limit the user address space to 4GB. In this way, we can have both 32-bit and 64-bit application on a 64-bit Linux kernel.
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
#define TASK_SIZE_32 UL(0x100000000)
#define TASK_SIZE (test_thread_flag(TIF_32BIT) ? \
TASK_SIZE_32 : TASK_SIZE_64)
#else
#define TASK_SIZE TASK_SIZE_64
#endif /* CONFIG_COMPAT */
64-bit ARM applications on 64-bit Linux kernel

ARM64 64-bit user space program virtual address space layout
32-bit ARM applications on 64-bit Linux kernel
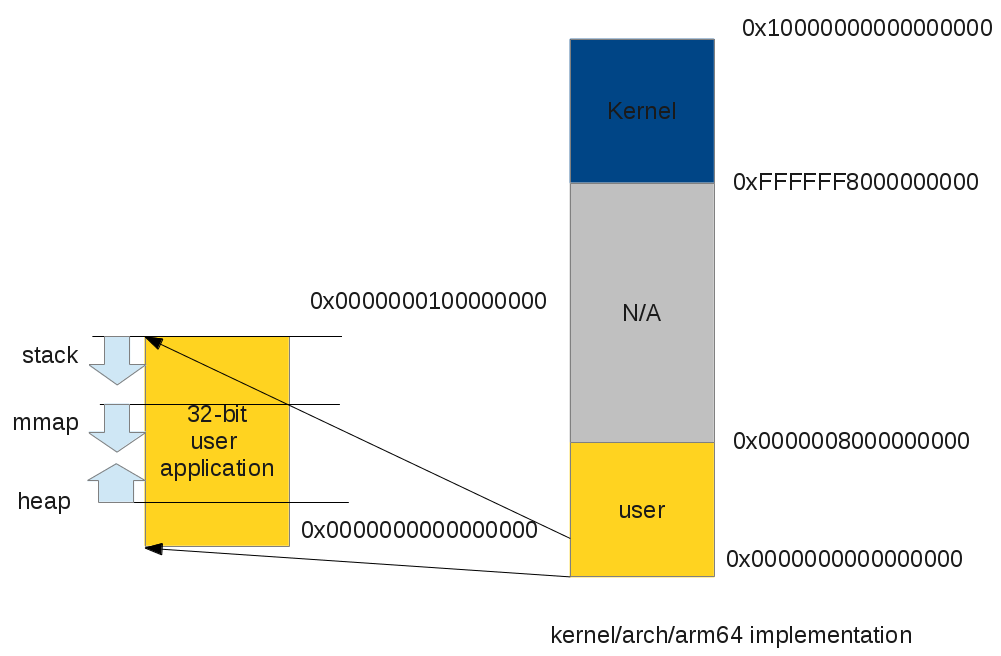
ARM64 32-bit user space program virtual address space layout
Note that the 32-bit application still have a 512GB kernel virtual address space and do not share it's own 4GB of virtual address space with kernel, the user applications have a complete 4GB of virtual address. On the other hand, 32-bit applications on 32-bit kernel have only 3GB of virtual address space.
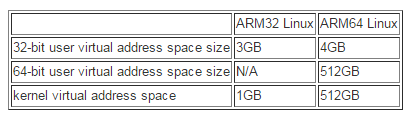
ARM64 Linux kernel virtual address space的更多相关文章
- ARM32 Linux kernel virtual address space
http://thinkiii.blogspot.jp/2014/02/arm32-linux-kernel-virtual-address-space.html The 32-bit ARM C ...
- Memory Layout (Virtual address space of a C process)
Memory Layout (Virtual address space of a C process) 分类: C语言基础2012-12-06 23:16 2174人阅读 评论(0) 收藏 举报 f ...
- linux内核可以接受的参数 | Linux kernel启动参数 | 通过grub给内核传递参数
在Linux中,给kernel传递参数以控制其行为总共有三种方法: 1.build kernel之时的各个configuration选项. 2.当kernel启动之时,可以参数在kernel被GRUB ...
- Linux kernel学习-内存管理【转】
转自:https://zohead.com/archives/linux-kernel-learning-memory-management/ 本文同步自(如浏览不正常请点击跳转):https://z ...
- Linux kernel Programming - Allocating Memory
kmalloc #include <linux/slab.h> void *kmalloc(size_t size,int flags); void kfree(void *addr); ...
- Linux kernel学习-内存管理
转自:https://zohead.com/archives/linux-kernel-learning-memory-management/ 本文同步自(如浏览不正常请点击跳转):https://z ...
- Android linux kernel privilege escalation vulnerability and exploit (CVE-2014-4322)
In this blog post we'll go over a Linux kernel privilege escalation vulnerability I discovered which ...
- Linux Kernel - Debug Guide (Linux内核调试指南 )
http://blog.csdn.net/blizmax6/article/details/6747601 linux内核调试指南 一些前言 作者前言 知识从哪里来 为什么撰写本文档 为什么需要汇编级 ...
- Linux kernel memory-faq.txt
## Linux kernel memory-faq.txt What is some existing documentation on Linux memory management? Ulric ...
随机推荐
- SSRF绕过filter_var(),preg_match()和parse_url()
1.利用curl的变量解释符$ php版本 利用代码 /*ssrf.php*/<?php echo ]."n"; // check if argument is a vali ...
- HTML中的table导出为Excel文件
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- docker-compose安装redis-sentinel集群(1主+2副+2哨兵)
前提:本试验环境已经提前安装了docker和docker-compose 说明:本次部署是单机伪集群,想要部署真正的集群,需要将秒个主件拆分到各个机器上去部署,只修改ip地址 1.下载redis的相关 ...
- Shell脚本学习-数组
跟着RUNOOB网站的教程学习的笔记 Shell数组 数组中可以存放多个值,Bash Shell只支持一维数组(不支持多维数组),初始化时不需要定义数组大小(与PHP类似). 与大部分编程语言类似,数 ...
- 可遇不可求的Question之skip-name-resolve模式篇
mysql启用skip-name-resolve模式时出现Warning的处理办法 在优化MYSQL配置时,加入 skip-name-resolve ,在重新启动MYSQL时检查启动日志,发现有警告信 ...
- org.apache.subversion.javahl.ClientException: Previous operation has not finished
1.问题 eclipse使用SVN出现异常: org.apache.subversion.javahl.ClientException: Previous operation has not fini ...
- Altera 在线资源使用
Altera 在线资源使用 Altera 在线资源使用 1 1.Altera中文版 2 2.建立myaltera账户 获取官网信息与支持 2 3系统化的设计资源 2 3.1.设计实例 2 3.2.参考 ...
- hdu 4911 Inversion and poj2299 [树状数组+离散化]
题目 题意: 给你一串数字,然后给你最多进行k次交换(只能交换相邻的)问交换后的最小逆序对个数是多少. 给你一个序列,每次只能交换相邻的位置,把他交换成一个递增序列所需要的最少步数 等于 整个序列的 ...
- 如何将已有的本地Git 库推送到远端仓库?
以Github 为例 step 1. 在Github建立一个空的仓库 Step 2. 建立远端仓库的别名 >$ git remote add origin https://github.com/ ...
- redis之一初识redis
本文主要围绕以下几点进行阐述: 1.什么是redis? 2.为什么要使用redis呢? 3.redis的一些基本配置 4.redis的缺点? 正文: 1.什么是redis? Redis是一款内存高速缓 ...
