Spring拓展接口之BeanPostProcessor,我们来看看它的底层实现
前言
开心一刻
小明:“妈,我被公司开除了”,妈:“啊,为什么呀?”, 小明:“我骂董事长是笨蛋,公司召开高层会议还要起诉我”,妈:“告你诽谤是吧?”,小明:“不是,他们说要告我泄露公司机密”

BeanPostProcessor定义
不管三七二十一,我们先来看看它的定义,看看spring是如何描述BeanPostProcessor的
/*
* Copyright 2002-2016 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.beans.factory.config; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable; /**
* 允许对新的bean示例进行自定义的修改,例如检查标志接口或进行代理封装
*
* spring上下文会在它的beng定义中自动检测BeanPostProcessor实例,并将它们应用于随后创建的每一个bean实例
*
* implement {@link #postProcessAfterInitialization}.
* 通常,通过实现BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法(配合标记接口,如@Autowired)来填充bean实例,
* 通过BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization方法进行bean实例的代理
*
*/
public interface BeanPostProcessor { /**
* 在bean实例的初始化方法(例如InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet或自定义的init-method)回调之前,
* spring会应用此方法到bean实例上。一般用于bean实例的属性值的填充
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>before</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
} /**
* 在bean实例的初始化方法(例如InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet或自定义的init-method)回调之后,
* spring会应用此方法到bean实例上。
* 在有FactoryBean时,此方法会在FactoryBean实例与FactoryBean的目标对象创建时各调用一次
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>after</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>In case of a FactoryBean, this callback will be invoked for both the FactoryBean
* instance and the objects created by the FactoryBean (as of Spring 2.0). The
* post-processor can decide whether to apply to either the FactoryBean or created
* objects or both through corresponding {@code bean instanceof FactoryBean} checks.
* <p>This callback will also be invoked after a short-circuiting triggered by a
* {@link InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation} method,
* in contrast to all other BeanPostProcessor callbacks.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
} }
简单点来理解,就是spring会自动从它的所有的bean定义中检测BeanPostProcessor类型的bean定义,然后实例化它们,再将它们应用于随后创建的每一个bean实例,在bean实例的初始化方法回调之前调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization的方法(进行bean实例属性的填充),在bean实例的初始化方法回调之后调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization的方法(可以进行bean实例的代理封装)
应用示例
我们先来看个简单的示例,注意:由于spring只是从spring容器中的bean定义中自动检测BeanPostProcessor类型的bean定义,所以我们自定义的BeanPostProcessor要通过某种方式注册到spring容器
MyBeanPostProcessor
@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { public MyBeanPostProcessor () {
System.out.println("MyBeanPostProcessor 实例化......");
} @Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("spring中bean实例:" + beanName + " 初始化之前处理......");
return bean;
} @Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("spring中bean实例:" + beanName + " 初始化之后处理......");
return bean;
}
}
AnimalConfig
@Configuration
public class AnimalConfig { public AnimalConfig() {
System.out.println("AnimalConfig 实例化");
} @Bean
public Dog dog() {
return new Dog();
} }
Dog
public class Dog {
private String name;
public Dog() {
System.out.println("Dog 实例化......");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
完整实例工程:spring-boot-BeanPostProcessor 我们来看看启动结果

有人可能会说了:“你是个逗比把,你举的这个例子有什么用? 实际上,根本就不会出现BeanPostProcessor的这样用法!” 有这样的疑问非常正常,示例中的BeanPostProcessor的两个方法:postProcessBeforeInitialization、postProcessAfterInitialization没做任何的处理,都只是直接返回bean,这不就是:脱了裤子放屁?
我们细看下,会发现postProcessBeforeInitialization、postProcessAfterInitialization中各多了一行打印( ),其实示例只是验证下Spring对BeanPostProcessor的支持、BeanPostProcessor的两个方法的执行时机,是否如BeanPostProcessor 的注释所说的那样,实际应用中肯定不会这么用的。那问题来了:BeanPostProcessor能用来干什么? 回答这个问题之前,我们先来看看spring对BeanPostProcessor的底层支持
),其实示例只是验证下Spring对BeanPostProcessor的支持、BeanPostProcessor的两个方法的执行时机,是否如BeanPostProcessor 的注释所说的那样,实际应用中肯定不会这么用的。那问题来了:BeanPostProcessor能用来干什么? 回答这个问题之前,我们先来看看spring对BeanPostProcessor的底层支持
源码解析
BeanPostProcessor的实例化与注册
很明显,我们从spring的启动过程的refresh方法开始,如下图
此时spring容器中所有的BeanPostProcessor都进行了实例化,并注册到了beanFactory的beanPostProcessors属性中
registerBeanPostProcessors
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) { String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false); // Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
// a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
// a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount)); // Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
// 将所有BeanPostProcessor bean定义分三类:实现了PriorityOrdered、实现了Ordered,以及剩下的常规BeanPostProcessor
List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
// 实例化实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
} // First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
// 注册实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanPostProcessor到beanFactory的beanPostProcessors属性中
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors); // Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
// 实例化实现了Ordered接口的BeanPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
// 注册实现了Ordered接口的BeanPostProcessor到beanFactory的beanPostProcessors属性中
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors); // Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors.
List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
// 实例化剩下的所有的常规的BeanPostProcessors
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors); // Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors.
// 注册所有常规的的BeanPostProcessor到beanFactory的beanPostProcessors属性中
sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors); // Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners,
// moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc).
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext));
}
BeanPostProcessor的生效时机
前面我们已经知道,spring会应用BeanPostProcessor于随后创建的每一个bean实例,具体spring是如何做到的了,我们仔细来看看
finishBeanFactoryInitialization方法实例化所有剩余的、非延迟初始化的单例(默认情况下spring的bean都是非延迟初始化单例),具体如下

BeanPostProcessor应用场景
其实只要我们弄清楚了BeanPostProcessor的执行时机:在bean实例化之后、初始化前后被执行,允许我们对bean实例进行自定义的修改;只要我们明白了这个时机点,我们就能分辨出BeanPostProcessor适用于哪些需求场景,哪些需求场景可以用BeanPostProcessor来实现
spring中有很多BeanPostProcessor的实现,我们接触的比较多的自动装配:AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor也是BeanPostProcessor的实现之一,关于自动装配我会在下篇博文中与大家一起探索
总结
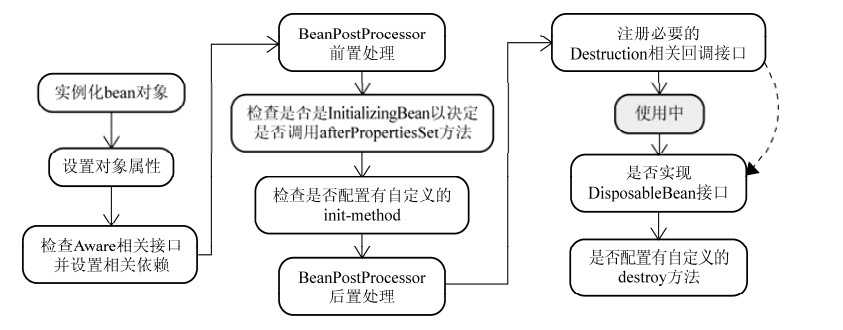
spring中bean的生命周期如下图
引用自:Spring实战系列(三)-BeanPostProcessor的妙用
Spring拓展接口之BeanPostProcessor,我们来看看它的底层实现的更多相关文章
- spring源码分析系列 (3) spring拓展接口InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
更多文章点击--spring源码分析系列 主要分析内容: 一.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor简述与demo示例 二.InstantiationAwareBean ...
- spring源码分析系列 (2) spring拓展接口BeanPostProcessor
Spring更多分析--spring源码分析系列 主要分析内容: 一.BeanPostProcessor简述与demo示例 二.BeanPostProcessor源码分析:注册时机和触发点 (源码基于 ...
- spring源码分析系列 (1) spring拓展接口BeanFactoryPostProcessor、BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
更多文章点击--spring源码分析系列 主要分析内容: 一.BeanFactoryPostProcessor.BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor简述与demo示例 ...
- Spring拓展接口之BeanFactoryPostProcessor,占位符与敏感信息解密原理
前言 开心一刻 一只被二哈带偏了的柴犬,我只想弄死隔壁的二哈 what:是什么 BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口很简单,只包含一个方法 /** * 通过BeanFactoryPos ...
- Spring拓展接口之FactoryBean,我们来看看其源码实现
前言 开心一刻 那年去相亲,地点在饭店里,威特先上了两杯水,男方绅士的喝了一口,咧嘴咋舌轻放桌面,手抚额头闭眼一脸陶醉,白水硬是喝出了82年拉菲的感觉.如此有生活情调的幽默男人,果断拿下,相处后却发现 ...
- Spring点滴十一:Spring中BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor区别
Spring中BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor都是Spring初始化bean时对外暴露的扩展点.两个接口从名字看起来很相似,但是作用及使用场景却不同 ...
- Java拓展接口-default关键词
Java接口在使用过程中有两点规定: 1.接口中只能有定义方法名.方法返回类型,不能有方法的实现. 2.实现接口的类,必须实现接口中所有的方法. 例如下面的例子: //定义接口 public inte ...
- Spring InitializingBean 接口以及Aware接口实现的原理
关于Spring InitializingBean 接口以及Aware接口实现的其实都在 第11步中: finishBeanFactoryInitialization() 方法中完成了3部分的内容: ...
- WebService—CXF整合Spring实现接口发布和调用过程
一.CXF整合Spring实现接口发布 发布过程如下: 1.引入jar包(基于maven管理) <!-- cxf --> <dependency> <groupId> ...
随机推荐
- SpringBoot | 问题 | 注解方式下无法发现Bean
在排除注解的问题后,考虑扫描类的位置, [SpringBoot项目的Bean装配默认规则是根据Application类所在的包位置从上往下扫描! “Application类”是指SpringBoot项 ...
- JAVA平台的理解
主题: JAVA是解释执行还是编译执行? 我的答案 : 混合模式 闲谈 : 1. JAVA(write once,run anywhere): 2. GC(Garbagae Collection), ...
- C#方法拓展
作用: “扩展方法使您能够向现有类型“添加”方法,而无需创建新的派生类型.重新编译或以其他方式修改原始类型.” 要求: 1.拓展方法必须是在一个非嵌套.非泛型的静态类中定义.2.他至少有一个参数.3. ...
- 基于webmagic的爬虫小应用
以前没有写过爬虫程序,最近两天就研究了一下java的爬虫框架webmagic.然后写了一个demo 写爬虫的基本思想: 1.抓取目标连接 2.根据页面中标签,抓捕你需要的内容 3.保存结果集 以下是实 ...
- UVA6531Go up the ultras
链接 这题意甚是难懂..当且峰值为h 如果他能为ultras 需要满足条件 d>=15W d满足它到任意一个比它高的点须经过h-d这个点 通俗一点来说,如果这个点满足条件 就找离他最近的一个&l ...
- java学习第二章
- python实战之爬取喜玛拉雅专辑信息
import urllib.request import json from lxml import etree url='http://www.ximalaya.com/dq/8.ajax' hea ...
- Spring Boot学到的内容
Hello World:了解程序入口(创建启动类) Web程序:写Controller类(@RestController),写Controller方法(@GetMapping),maven依赖spri ...
- 如何创建你的第一个手机APP?
本文使用helloworld来作为android的入门项目,通过这个最简单的项目来帮助大家了解android程序开发包含哪些部分,以及如何运行android程序,本次开发android程序的工具是ec ...
- 在Android上使用酷狗歌词API
参考自http://blog.csdn.net/u010752082/article/details/50810190 代码先贴出来: public void searchLyric(){ final ...
