Netty Associated -- ChannelPipeline
A list of ChannelHandlers which handles or intercepts inbound events and outbound operations of a Channel. ChannelPipeline implements an advanced form of the Intercepting Filter pattern to give a user full control over how an event is handled and how the ChannelHandlers in a pipeline interact with each other.
ChannelPipeline是一个ChannelHandlers的列表, 它用来处理或拦截Channel的进站(inbound)事件或出站(outbound)操作. ChannelPipeline实现了Intercepting Filter 模式, 他使用户可以对事件处理和pipeline中的ChannelHandler之间的交互.
Creation of a pipeline
创建一个管道
Each channel has its own pipeline and it is created automatically when a new channel is created.
每个channel都有自己的pipeline, 并且在channel创建的时候会自动创建一个新的pipeline
How an event flows in a pipeline
管道中的事件是如何流动的
The following diagram describes how I/O events are processed by ChannelHandlers in a ChannelPipeline typically. An I/O event is handled by either a ChannelInboundHandler or a ChannelOutboundHandler and be forwarded to its closest handler by calling the event propagation methods defined in ChannelHandlerContext, such as ChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelRead(Object) and ChannelHandlerContext.write(Object).
下表描述了一个典型的I/O事件在ChannelPipeline中是如何被ChannelHandlers处理的. 一个I/O时间不是被一个ChannelInboundHandler处理就是被一个ChannelOutboundHandler处理, 并且通过调用ChannelHandlerContext中定义的事件传播方法, 它会被转发给它最近的一个handler, 例如ChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelRead(Object) 和 ChannelHandlerContext.write(Object)
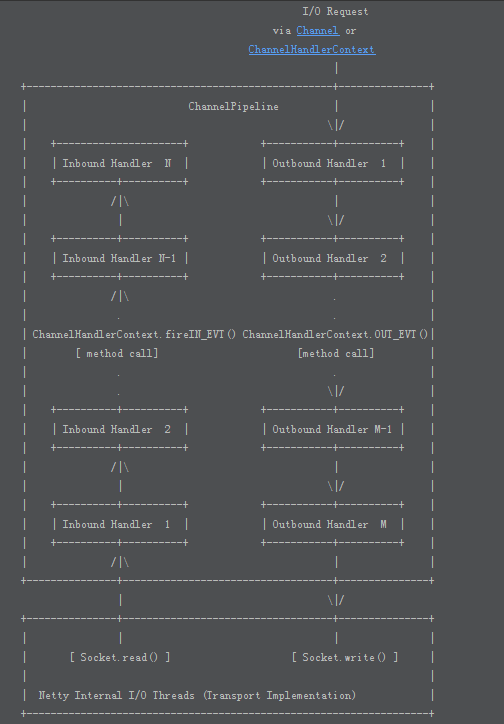
附注: 顺序是 request --> Socket.read() --> Inbound Handlers --> Context.wirte() --> Outbound Handlers --> Socket.write() --> Response
An inbound event is handled by the inbound handlers in the bottom-up direction as shown on the left side of the diagram. An inbound handler usually handles the inbound data generated by the I/O thread on the bottom of the diagram. The inbound data is often read from a remote peer via the actual input operation such as SocketChannel.read(ByteBuffer). If an inbound event goes beyond the top inbound handler, it is discarded silently, or logged if it needs your attention.
一个 inbound 事件是被 inbound handlers 自底向上处理, 就像上图左边画的那样. 一个 inbound handler 通常是处理图表底部被 I/O 线程生成的入站数据. 入站数据通常是从一个远程端通过真正的input操作读取到的, 例如 SocketChannel.read(ByteBuffer). 如果一个inbound事件流动超过了最顶端的inbound处理器, 他会被丢弃, 或者在需要引起你注意的时候打log
An outbound event is handled by the outbound handler in the top-down direction as shown on the right side of the diagram. An outbound handler usually generates or transforms the outbound traffic such as write requests. If an outbound event goes beyond the bottom outbound handler, it is handled by an I/O thread associated with the Channel. The I/O thread often performs the actual output operation such as SocketChannel.write(ByteBuffer).
一个 outbound 事件是会被 outbound handlers 自顶向下处理的, 就像上图的右边那样. 一个 outbound handler通常生成或转换诸如写请求(write requests)的出站流量.假如一个出站事件流动超出了最底层的outbound处理器, 他将会被一个和Channel相关的I/O线程处理. 这个 I/O 一般表现为真实的输出操作, 例如 SocketChannel.write(ByteBuffer)
For example, let us assume that we created the following pipeline:
例如, 假设我们创建了如下的管道:
ChannelPipeline p = ...;
p.addLast("1", new InboundHandlerA());
p.addLast("2", new InboundHandlerB());
p.addLast("3", new OutboundHandlerA());
p.addLast("4", new OutboundHandlerB());
p.addLast("5", new InboundOutboundHandlerX());
In the example above, the class whose name starts with Inbound means it is an inbound handler. The class whose name starts with Outbound means it is a outbound handler.
在上面的例子中, 名字以Inbound开始的类表示一个inbound处理器. 名字已Outbound开始的类表示一个outbound处理器
In the given example configuration, the handler evaluation order is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 when an event goes inbound. When an event goes outbound, the order is 5, 4, 3, 2, 1. On top of this principle, ChannelPipeline skips the evaluation of certain handlers to shorten the stack depth:
在上面给出的例子中, 在时间进站的时候,handler的计算顺序是 1 2 3 4 5. 当时间出站的时候, 顺序是 5 4 3 2 1. 在此原则之上, ChannelPipeline会跳过某一处理器的计算来缩短栈深:
- 3 and 4 don't implement ChannelInboundHandler, and therefore the actual evaluation order of an inbound event will be: 1, 2, and 5.
- 3和4没有实现ChannelInboundHandler, 因此实际的入站事件计算顺序是 1 2 5
- 1 and 2 don't implement ChannelOutboundHandler, and therefore the actual evaluation order of a outbound event will be: 5, 4, and 3.
- 1和2没有实现ChannelOutboundHandler, 因此实际的出站事件计算顺序是 5 4 3
- If 5 implements both ChannelInboundHandler and ChannelOutboundHandler, the evaluation order of an inbound and a outbound event could be 125 and 543 respectively.
- 假如 5 实现了 ChannelInboundHandler , 又实现了 ChannelOutboundHandler, 那么入站顺序和出站顺序将会是 125 和 543
Forwarding an event to the next handler
将事件转发给下一个处理器
As you might noticed in the diagram shows, a handler has to invoke the event propagation methods in ChannelHandlerContext to forward an event to its next handler. Those methods include:
如你在图表中所见, 一个处理器必须调用ChannelHandlerContext的传播方法来将事件转发给下一个处理器, 这些方法包括:
- Inbound event propagation methods:
- 入站事件传播方法:
ChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelRegistered()
ChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelActive()
ChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelRead(Object)
ChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelReadComplete()
ChannelHandlerContext.fireExceptionCaught(Throwable)
ChannelHandlerContext.fireUserEventTriggered(Object)
ChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelWritabilityChanged()
ChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelInactive()
ChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelUnregistered()
- Outbound event propagation methods:
- 出站事件传播方法:
ChannelHandlerContext.bind(SocketAddress, ChannelPromise)
ChannelHandlerContext.connect(SocketAddress, SocketAddress, ChannelPromise)
ChannelHandlerContext.write(Object, ChannelPromise)
ChannelHandlerContext.flush()
ChannelHandlerContext.read()
ChannelHandlerContext.disconnect(ChannelPromise)
ChannelHandlerContext.close(ChannelPromise)
ChannelHandlerContext.deregister(ChannelPromise)
and the following example shows how the event propagation is usually done:
下面的例子展示了时间传播是怎么完成的:
public class MyInboundHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
System.out.println("Connected!");
ctx.fireChannelActive();
}
}
public class MyOutboundHandler extends ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void close(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ChannelPromise promise) {
System.out.println("Closing ..");
ctx.close(promise);
}
}
Building a pipeline
创建一个管道
A user is supposed to have one or more ChannelHandlers in a pipeline to receive I/O events (e.g. read) and to request I/O operations (e.g. write and close). For example, a typical server will have the following handlers in each channel's pipeline, but your mileage may vary depending on the complexity and characteristics of the protocol and business logic:
一个用户应该在管道中设置一个或多个ChannelHandlers来接收I/O时间(例如read)和请求 I/O 操作(例如write和close).例如, 一个典型的服务器在每个channel的pipeline有如下handlers, 但你的里程可能会根据复杂程度, 协议特征以及业务逻辑有所改变:
1. Protocol Decoder - translates binary data (e.g. ByteBuf) into a Java object.
协议解码器 - 将二进制数据(例如 ByteBuf) 转化为 Java对象
2. Protocol Encoder - translates a Java object into binary data.
协议编码器 - 将Java对象转化为二进制数据
3. Business Logic Handler - performs the actual business logic (e.g. database access).
业务逻辑处理器 - 执行实际业务逻辑(例如数据库访问)
and it could be represented as shown in the following example:
下面是一个代表例子:
static final EventExecutorGroup group = new DefaultEventExecutorGroup(16);
... ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast("decoder", new MyProtocolDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new MyProtocolEncoder()); // Tell the pipeline to run MyBusinessLogicHandler's event handler methods
// in a different thread than an I/O thread so that the I/O thread is not blocked by
// a time-consuming task.
// If your business logic is fully asynchronous or finished very quickly, you don't
// need to specify a group.
pipeline.addLast(group, "handler", new MyBusinessLogicHandler());
Thread safety
线程安全
A ChannelHandler can be added or removed at any time because a ChannelPipeline is thread safe. For example, you can insert an encryption handler when sensitive information is about to be exchanged, and remove it after the exchange.
因为一个ChannelPipeline是线程安全的, 所以ChannelHandler可以在任意时间被添加或者删除. 例如, 你可以在需要交换敏感信息的时候插入一个加密处理器, 并在交换完成后移除它.
Netty Associated -- ChannelPipeline的更多相关文章
- Netty 源码解析(四): Netty 的 ChannelPipeline
今天是猿灯塔“365篇原创计划”第四篇. 接下来的时间灯塔君持续更新Netty系列一共九篇 Netty 源码解析(一): 开始 Netty 源码解析(二): Netty 的 Channel Netty ...
- Netty 源码解析: Netty 的 ChannelPipeline
ChannelPipeline和Inbound.Outbound 我想很多读者应该或多或少都有 Netty 中 pipeline 的概念.前面我们说了,使用 Netty 的时候,我们通 ...
- Netty源代码学习——ChannelPipeline模型分析
參考Netty API io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline A list of ChannelHandlers which handles or intercepts i ...
- netty源码解解析(4.0)-8 ChannelPipeline的设计
io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline 设计原理 上图中,为了更直观地展示事件处理顺序, 故意有规律地放置两种handler的顺序,实际上ChannelInboundHa ...
- 责任链模式的使用-Netty ChannelPipeline和Mina IoFilterChain分析
本文来自网易云社区 作者:乔安然 1. Chain of Responsiblity 定义: 使多个对象都有机会处理请求,从而避免请求的发送者和接受者之间的耦合关系.将这个对象连成一条链,并沿着这条链 ...
- Netty源码分析之ChannelPipeline(一)—ChannelPipeline的构造与初始化
Netty中ChannelPipeline实际上类似与一条数据管道,负责传递Channel中读取的消息,它本质上是基于责任链模式的设计与实现,无论是IO事件的拦截器,还是用户自定义的ChannelHa ...
- Netty源码分析之ChannelPipeline(二)—ChannelHandler的添加与删除
上篇文章中,我们对Netty中ChannelPipeline的构造与初始化进行了分析与总结,本篇文章我们将对ChannelHandler的添加与删除操作进行具体的的代码分析: 一.ChannelHan ...
- 自顶向下深入分析Netty(七)--ChannelPipeline和ChannelHandler总述
自顶向下深入分析Netty(七)--ChannelPipeline和ChannelHandler总述 自顶向下深入分析Netty(七)--ChannelPipeline源码实现 自顶向下深入分析Net ...
- 谈谈如何使用Netty开发实现高性能的RPC服务器
RPC(Remote Procedure Call Protocol)远程过程调用协议,它是一种通过网络,从远程计算机程序上请求服务,而不必了解底层网络技术的协议.说的再直白一点,就是客户端在不必知道 ...
随机推荐
- [java] DOS编译 .java 文件得到 .class 文件 并执行 以及使用外部 .jar包 时的命令
当写一个java文件后,在DOS中进行编译与执行时,如果没有引入外来的包,那情况很简单 例如: public class hello_world { public static void main(S ...
- mysql varchar 转 decimal
在我们写代码的实际业务中,有时候实体类用的是String,数据库中自然是VARCHAR类型,但是如果这个实体的属性值放的是数字类型,你查询的时候又需要对它进行排序.sql怎么写呢. 别担心MySQL提 ...
- PC端meta标签
下面介绍meta标签的几个属性,charset,content,http-equiv,name. 一.charset 此特性声明当前文档所使用的字符编码,但该声明可以被任何一个元素的lang特性的值覆 ...
- curl dns缓存设置
CURLOPT_DNS_USE_GLOBAL_CACHE 启用时会启用一个全局的DNS缓存,此项为线程安全的,并且默认启用.CURLOPT_DNS_CACHE_TIMEOUT 设置在内存中保存DNS信 ...
- bzoj 2809 可并堆维护子树信息
对于每个节点,要在其子树中选尽量多的节点,并且节点的权值和小于一个定值. 建立大根堆,每个节点从儿子节点合并,并弹出最大值直到和满足要求. /***************************** ...
- 【BZOJ-2063】我爸是李刚 数位dp 好题
2063: 我爸是李刚 Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 64 MBSubmit: 139 Solved: 72[Submit][Status][Discuss] ...
- Intel Code Challenge Final Round (Div. 1 + Div. 2, Combined) D. Dense Subsequence 暴力
D. Dense Subsequence 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/724/problem/D Description You are given a s ...
- Codeforces Round #281 (Div. 2) A. Vasya and Football 模拟
A. Vasya and Football 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/493/problem/A Description Vasya has starte ...
- OpenVPN推送默认路由表
根据官方Server配置文件:https://github.com/OpenVPN/openvpn/blob/master/sample/sample-config-files/server.conf ...
- word删除空白行
情况一:如果粘贴后,word页面既有表格又有文字(有时网页中选定时看不到表格,粘贴后却有表格),还有许多空行! 硬回车: “编辑--替换” -查找内容为“^p^p”,替换成“^p”--然后全部替换! ...
