GeneralizedLinearAlgorithm in Spark MLLib
SparkMllib涉及到的算法
- Classification
- Linear Support Vector Machines (SVMs)
- Logistic regression
- Regression
- Linear least squares, Lasso, and ridge regression
- Streaming linear regression
GeneralizedLinearAlgorithm
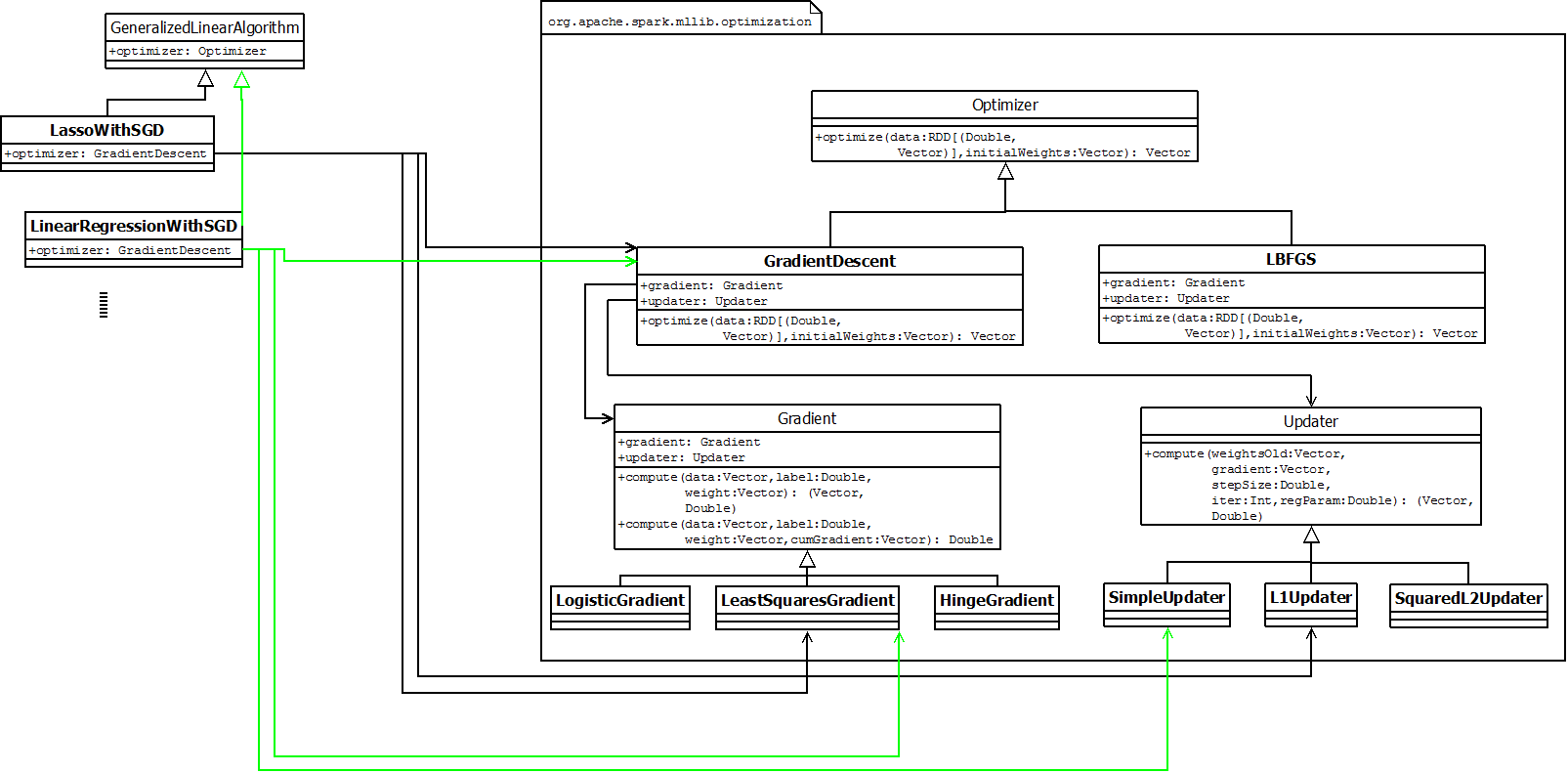
GLA,通用线性算法,作为通用回归算法(regression)和分类算法(classification)的抽象算法,run函数中实现了算法的流程,并最终产生通用线性模型。抽象算法流程主要包括:addIntercept, useFeatureScaling, 调用optimizer计算参数等。其中optimizer是抽象类,具体的线性算法需要指定具体的optimizer实现类。【模板模式——子类的训练大多调用了GLA中的run函数】
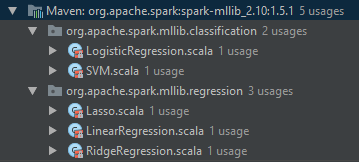
进一步地,optimizer是算法的核心,也是迭代算法的逻辑所在。具体类包括梯度下降等算法。这些优化算法又可以抽象并归纳出两个模块:梯度计算器(Gradient)和参数更新(Updater)。
综上,对于某一个具体的线性算法时主要一个优化器,而优化器是通过选择梯度计算器和参数更新器的组合来得到。【bridge pattern】
当前版本中GLA有多个子类,覆盖了多个分类和回归算法:
- LassoWithSGD (org.apache.spark.mllib.regression)
- LinearRegressionWithSGD (org.apache.spark.mllib.regression)
- RidgeRegressionWithSGD (org.apache.spark.mllib.regression)
- LogisticRegressionWithLBFGS (org.apache.spark.mllib.classification)
- LogisticRegressionWithSGD (org.apache.spark.mllib.classification)
- SVMWithSGD (org.apache.spark.mllib.classification)
例如,LinearRegressionWithSGD算法,对应的Optimizer是GradientDecent,对应的梯度计算器是LeaseSquareGradent,x位置的梯度$$\vec{\triangledown} = (\vec{x}^T\cdot\vec{w} - y)\cdot\vec{x}$$,对应的更新器为SimpleUpdater,更新算法是$$\vec{w} =: \vec{w} - \alpha / \sqrt{iter}\cdot\vec{\triangledown}/m$$
GeneralizedLinearModel
Algorithm will create a model by calling:
def createModel(...): M
**GeneralizedLinearModel **(GLM) represents a model trained using GeneralizedLinearAlgorithm. GLMs consist of a weight vector and an intercept.
Parameters:
- weights - Weights computed for every feature.
- intercept - Intercept computed for this model.
基本上每个线性算法都对应到一个线性模型: - LassoModel
- LinearRegressionModel
- LogisticRegressionModel
- RidgeRegressionModel
- SVMModel
GradientDecent梯度下降法
梯度下降法对convex函数必然能求解。
function [theta, J_history] = gradientDescent(X, y, theta, alpha, num_iters)
%GRADIENTDESCENT Performs gradient descent to learn theta
% theta = GRADIENTDESCENT(X, y, theta, alpha, num_iters) updates theta by
% taking num_iters gradient steps with learning rate alpha
% Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples
J_history = zeros(num_iters, 1);
for iter = 1:num_iters
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Perform a single gradient step on the parameter vector
% theta.
%
% Hint: While debugging, it can be useful to print out the values
% of the cost function (computeCost) and gradient here.
%
theta = theta - alpha * X' * (X * theta - y) / m;
% ============================================================
% Save the cost J in every iteration
J_history(iter) = computeCost(X, y, theta);
end
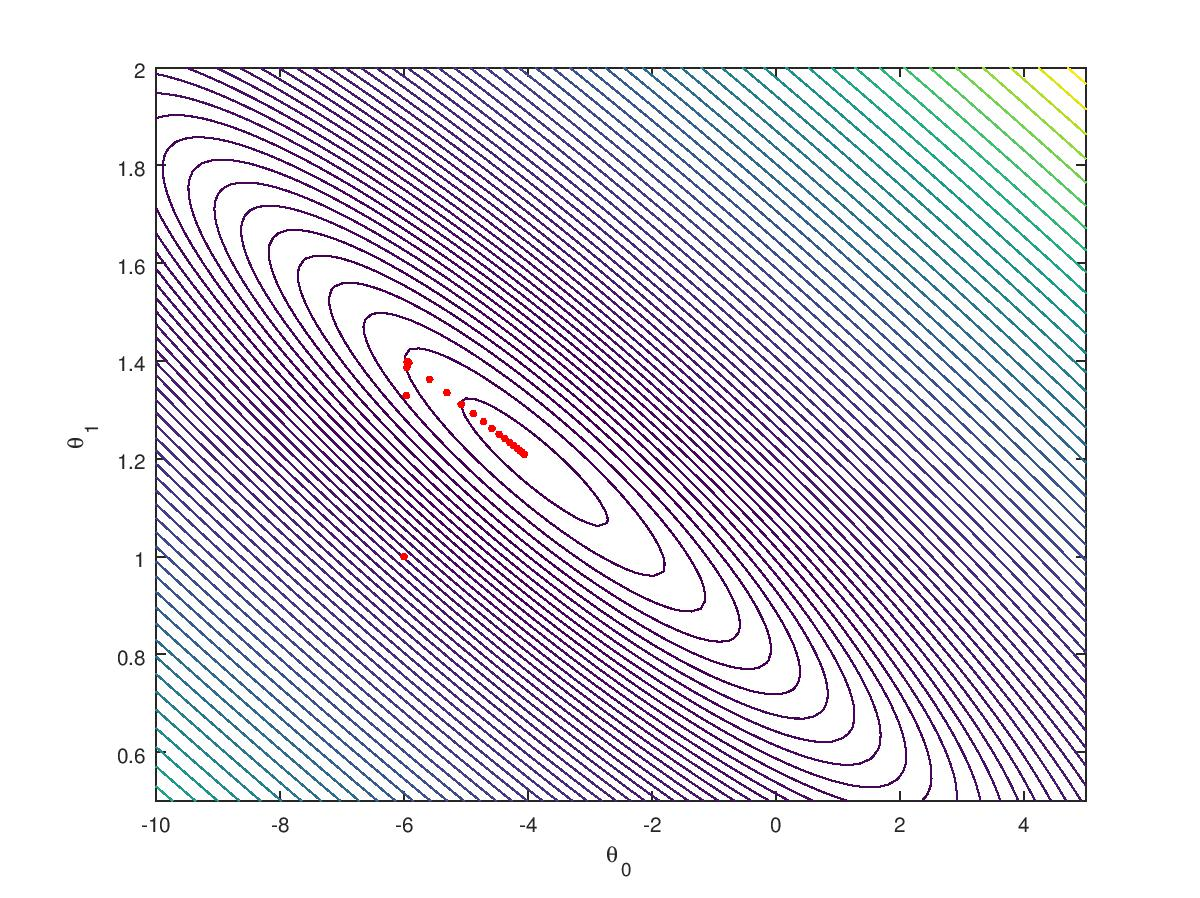
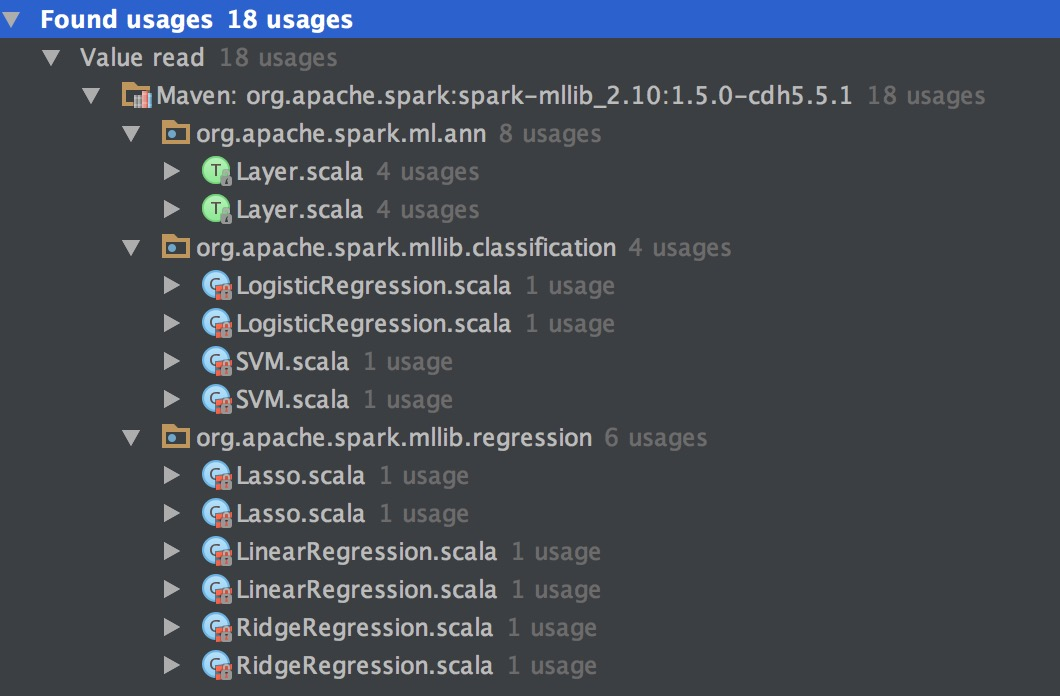
代码中可以发现多处使用了梯度下降法,包括ann,LR/SVM分类算法,Lasso/Linear/Ridge回归等算法。
主要构造函数:
class GradientDescent private[spark] (
private var gradient: Gradient,
private var updater: Updater)
extends Optimizer with Logging {
private var stepSize: Double = 1.0
private var numIterations: Int = 100
private var regParam: Double = 0.0
private var miniBatchFraction: Double = 1.0
private var convergenceTol: Double = 0.001
其中gradient为计算梯度的公式,updater为根据梯度的值去更新权重的公式。除了这两个参数之外,还有算法训练过程中的一些技术参数。
算法的基本参数设定之后便,再给定训练样本,便可以训练得到模型权重:
def optimize(
data: RDD[(Double, Vector)],
initialWeights: Vector): Vector = {
val (weights, _) = GradientDescent.runMiniBatchSGD(
data,
gradient,
updater,
stepSize,
numIterations,
regParam,
miniBatchFraction,
initialWeights,
convergenceTol)
weights
}
=> 调用迭代梯度下降法
def runMiniBatchSGD(data: RDD[(Double, Vector)],
gradient: Gradient,
updater: Updater,
stepSize: Double,
numIterations: Int,
regParam: Double,
miniBatchFraction: Double,
initialWeights: Vector,
convergenceTol: Double): (Vector, Array[Double])
Run stochastic gradient descent (SGD) in parallel using mini batches. In each iteration, we sample a subset (fraction miniBatchFraction) of the total data in order to compute a gradient estimate. Sampling, and averaging the subgradients over this subset is performed using one standard spark map-reduce in each iteration.
Parameters:
- data - Input data for SGD. RDD of the set of data examples, each of the form (label, [feature values]).
- gradient - Gradient object (used to compute the gradient of the loss function of one single data example)
- updater - Updater function to actually perform a gradient step in a given direction.
- stepSize - initial step size for the first step
- numIterations - number of iterations that SGD should be run.
- regParam - regularization parameter
- miniBatchFraction - fraction of the input data set that should be used for one iteration of SGD. Default value 1.0.
- initialWeights - initial weights for model training.
- convergenceTol - Minibatch iteration will end before numIterations if the relative difference between the current weight and the previous weight is less than this value. In measuring convergence, L2 norm is calculated. Default value 0.001. Must be between 0.0 and 1.0 inclusively.
Returns:
A tuple containing two elements. The first element is a column matrix containing weights for every feature, and the second element is an array containing the stochastic loss computed for every iteration.
迭代梯度下降法 (SGD)
上述分析可以发现梯度下降法采用的实现法法是SGD,该算法对模型进行迭代更新,非常适合分布式计算,算法流程:
- Sample a subset of data or just use all the data;
- [MAPPER] for each entry, calculate gradient and model loss by
Gradient$$(g^{(i)}, l^{(i)}) := \cal{Gradient}(x^{(i)}, y^{(i)}, \theta)$$; - [AGGREGATION] sum of gradient = $$\sum_ig^{(i)}$$, sum of loss = $$\sum_i l^{(i)}$$, counter = $$\sum_i 1$$;
Updater$$\theta' := \cal{Update}(\theta, \sum_ig^{(i)} / \sum_i 1, \alpha, ...)$$;- if $$||\theta'-\theta||_2 / ||\theta'||_2 < convergenceTol$$ finish, else $$\theta := \theta'$$, repeat from step 1.
各线性算法的G/U组合
| Algorithm | optimizer | Gradient | updater |
|---|---|---|---|
| LinearRegressionWithSGD | GradientDescent | LeastSquares | Simple |
| LassoWithSGD | GradientDescent | LeastSquares | L1Updater |
| RidgeRegressionWithSGD | GradientDescent | LeastSquares | SquaredL2 |
| LogisticRegressionWithSGD | GradientDescent | Logistic | SquaredL2 |
| LogisticRegressionWithLBFGS | LBFGS | Logistic | SquaredL2 |
| SVMWithSGD | GradientDescent | Hinge | SquaredL2 |
GradientDecent以及SGD算法的流程在上面已经描述,接下来具体分析各种梯度计算和权重更新算法:
LeaseSquareGradent
lost function:
\]
\]
SimpleUpdater
A simple updater for gradient descent without any regularization.
更新算法是$$\vec{w} := \vec{w} - \alpha / \sqrt{iter}\cdot\vec{\triangledown}$$,
其中$$ \vec{\triangledown} = \sum_i{\vec{\triangledown_i} / \sum_i {i}}$$
算法迭代过程中整体的步长会随着迭代次数而逐渐减小,
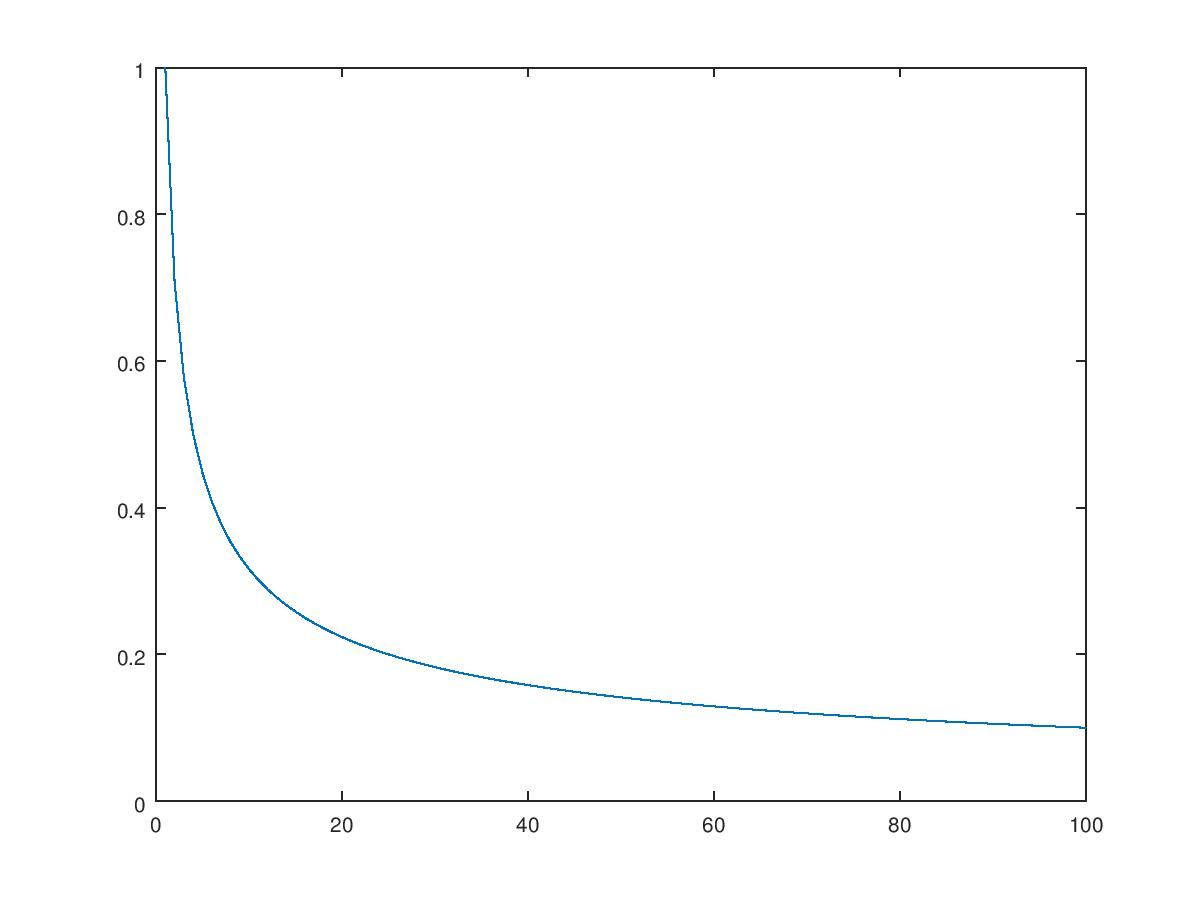
SquaredL2Updater
L2 regularized problems:
L = 1/n ||X \cdot w - y||^2 + R(w),\\
\text{then:} \frac{dL}{dw}=\vec{\triangledown} + \lambda w\\
w:=w' - \alpha \cdot \frac{dL}{dw}\\
\ \ \ = (1-\alpha \lambda)\vec{w} - \alpha / \sqrt{iter}\cdot\vec{\triangledown}\]
与LinearRegressionWithSGD比较,RidgeRegressionWithSGD的优化器依然是LeastSquaresGradient,训练样本计算Gradient额算法也相同,不通点是在给定Gradient结果基础上更新权重时,old权重需要额外乘以一个系数。
GeneralizedLinearAlgorithm in Spark MLLib的更多相关文章
- Spark MLlib之线性回归源代码分析
1.理论基础 线性回归(Linear Regression)问题属于监督学习(Supervised Learning)范畴,又称分类(Classification)或归纳学习(Inductive Le ...
- Spark MLlib - LFW
val path = "/usr/data/lfw-a/*" val rdd = sc.wholeTextFiles(path) val first = rdd.first pri ...
- 《Spark MLlib机器学习实践》内容简介、目录
http://product.dangdang.com/23829918.html Spark作为新兴的.应用范围最为广泛的大数据处理开源框架引起了广泛的关注,它吸引了大量程序设计和开发人员进行相 ...
- Spark MLlib 之 Basic Statistics
Spark MLlib提供了一些基本的统计学的算法,下面主要说明一下: 1.Summary statistics 对于RDD[Vector]类型,Spark MLlib提供了colStats的统计方法 ...
- Spark MLlib Data Type
MLlib 支持存放在单机上的本地向量和矩阵,也支持通过多个RDD实现的分布式矩阵.因此MLlib的数据类型主要分为两大类:一个是本地单机向量:另一个是分布式矩阵.下面分别介绍一下这两大类都有哪些类型 ...
- Spark MLlib - Decision Tree源码分析
http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/mllib-decision-tree.html 以决策树作为开始,因为简单,而且也比较容易用到,当前的boosting或ran ...
- Spark入门实战系列--8.Spark MLlib(上)--机器学习及SparkMLlib简介
[注]该系列文章以及使用到安装包/测试数据 可以在<倾情大奉送--Spark入门实战系列>获取 .机器学习概念 1.1 机器学习的定义 在维基百科上对机器学习提出以下几种定义: l“机器学 ...
- Spark入门实战系列--8.Spark MLlib(下)--机器学习库SparkMLlib实战
[注]该系列文章以及使用到安装包/测试数据 可以在<倾情大奉送--Spark入门实战系列>获取 .MLlib实例 1.1 聚类实例 1.1.1 算法说明 聚类(Cluster analys ...
- spark mllib配置pom.xml错误 Multiple markers at this line Could not transfer artifact net.sf.opencsv:opencsv:jar:2.3 from/to central (https://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2): repo.maven.apache.org
刚刚spark mllib,在maven repository网站http://mvnrepository.com/中查询mllib后得到相关库的最新dependence为: <dependen ...
随机推荐
- [Spark]Spark章1 Spark架构浅析
Spark架构 Spark架构采用了分布式计算中的Master-Slave模型.集群中运行Master进程的节点称为Master,同样,集群中含有Worker进程的节点为Slave.Master负责控 ...
- word2vec_训练模型
from gensim.models import Word2Vecfrom gensim.models.word2vec import LineSentence # 原始的训练语料转化成一个sent ...
- linux-ubuntu 下R无法安装HH包的原因及解决方案
错误信息: configure: error: GNU MP not found, or not 4.1.4 or up, see http://gmplib.org ERROR: configura ...
- Visual code 搭建Vue项目
使用VS Code搭建Vue项目 1.安装 VScode 2..安装最新node.JS 2.安装cnpm镜像 淘宝镜像(node自带安装了npm,故不再安装) npm install -g cnpm ...
- cocos js 3.8.1 clippingNode 不能被 ccui.ScrollView 或者ccui.Layout裁剪的bug
clippingNode不能被ccui.ScrollView.ccui.ListView.ccui.Layout裁剪问题,只需要 设置scrollView ...的裁剪类型 scrollView.se ...
- 基于centos6.5 hadoop 集群搭建
1.修改Linux主机名2.修改IP3.修改主机名和IP的映射关系 ######注意######如果你们公司是租用的服务器或是使用的云主机(如华为用主机.阿里云主机等) /etc/hosts里面要配置 ...
- docker 加速器配置目录
centos 7 : /lib/systemd/system/docker.service
- Python开课复习9-28
一.什么是迭代器#迭代器即迭代的工具,那什么是迭代呢?#迭代是一个重复的过程,每次重复即一次迭代,并且每次迭代的结果都是下一次迭代的初始值 举例: l=[1,2,3] count=0 while co ...
- php-fpm 的 pm.start_servers 参数调整
大家注意一下 在 php-fpm 的配置文件中, pm.start_servers 必须是介于 pm.min_spare_servers 和 pm.max_spare_servers 这个值之间 ...
- 2018.10.25 洛谷P4187 [USACO18JAN]Stamp Painting(计数dp)
传送门 其实本来想做组合数学的2333. 谁知道是道dpdpdp. 唉只能顺手做了 还是用真难则反的思想. 这题我们倒着考虑,只需要求出不合法方案数就行了. 这个显然是随便dpdpdp的. f[i]f ...
