用x种方式求第n项斐波那契数,99%的人只会第一种
大家好啊,我们又见面了。听说有人想学数据结构与算法却不知道从何下手?那你就认真看完本篇文章,或许能从中找到方法与技巧。
本期我们就从斐波那契数列的几种解法入手,感受算法的强大与奥妙吧。
原文链接:原文来自个人公众号:C you again,欢迎关注
斐波那契数列
斐波那契数列(Fibonacci sequence),又称黄金分割数列,因数学家莱昂纳多·斐波那契(Leonardoda Fibonacci)以兔子繁殖为例子而引入,故又称为“兔子数列”。
斐波那契数列指的是这样一个数列:
0、1、1、2、3、5、8、13、21、34......
有一组数列,它的第一项为1,第二项为1,从第三项开始,每一项为前两项之和。
斐波那契数列的第n项Fn可以通过如下的递归公式定义:
F(1)=1,F(2)=1,
F(n)=F(n-1)+F(n-2)(n ≥ 3,n ∈ N*)
通项公式
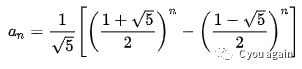
如上,又称为“比内公式”,是用无理数表示有理数的一个范例。
注:此时a1=1,a2=1,a(n)=a(n-1)+a(n-2),(n ≥ 3,n ∈ N*)
求第n项斐波那契数
现在写一个函数int fib(int n) 返回第n项Fn。例如,若n=0,则函数fib(0)应该返回0,若n=1, 则函数fib(1)应返回1,若 n > 1,返回 F(n-1)+F(n-2)。
若n = 9
输出:34
下面是返回斐波那契数列第n项Fn的不同方法:
方法1 (使用递归)
一个简捷的方法是直接使用递归定义关系式写出递归实现的代码,C/C++代码如下:
//Fibonacci Series using Recursion
#include<stdio.h>
int fib(int n) {
if (n <= 1)
return n;
return fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2);
}
int main() {
int n = 9;
printf("%d", fib(n));
return 0;
}
输出:34
时间复杂度:T(n) = T(n-1) + T(n-2),该时间复杂度是指数级别的
空间复杂度:如果考虑递归调用时栈的大小,则为O(n) ;如果不考虑调用栈的话,则为O(1)
通过观察,我们可以发现递归求解时做了很多重复的工作(见下面的递归调用树)。因此采用递归方式求解斐波那契数列的第n项Fn不是一种好的方法。

方法2 (使用动态规划Dynamic Programming:DP)
如果你还不了解动态规划,请看以下两篇文章:
在方法1中,在求解某项时,如果我们把计算结果存储起来,则后续的计算就可以使用前面的计算结果,从而可以避免很多重复的计算,C/C++代码如下:
//Fibonacci Series using Dynamic Programming
#include<stdio.h>
int fib(int n) {
/* Declare an array to store Fibonacci numbers. */
int f[n + 1];
int i;
/* 0th and 1st number of the series are 0 and 1*/
f[0] = 0;
f[1] = 1;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
/* Add the previous 2 numbers in the series
and store it */
f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i - 2];
}
return f[n];
}
int main() {
int n = 9;
printf("%d", fib(n));
return 0;
}
输出:34
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度: O(n)
方法3 (对方法2进行空间上的优化)
由于在计算某项时只需其前面相邻的两项,因此可以对方法2中的空间进行优化,C/C++代码如下:
// Fibonacci Series using Space Optimized Method
#include<stdio.h>
int fib(int n) {
int a = 0, b = 1, c, i;
if (n == 0)
return a;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return b;
}
int main() {
int n = 9;
printf("%d", fib(n));
return 0;
}
输出:34
时间复杂度: O(n)
空间复杂度: O(1)
当然,也可以使用滚动数组。滚动数组不是什么高大上的技术,我们在计算斐波那契数列的过程中,始终使用相邻的前两项,加上正在计算的项,总共就三项,因此可以定义一个长度只有3的数组,可以滚动地使用0、1、2这三个下标。代码如下:
//Fibonacci Series using Dynamic Programming
#include<stdio.h>
int fib(int n) {
/* Declare an array to store Fibonacci numbers. */
int f[3]; /* 只需定义一个长度为3的数组 */
int i;
/* 0th and 1st number of the series are 0 and 1*/
f[0] = 0;
f[1] = 1;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
/* Add the previous 2 numbers in the series
and store it:注意下标要对3取模 */
f[i % 3] = f[(i - 1) % 3] + f[(i - 2) % 3];
}
return f[n % 3]; /* 这里要注意下标对3取模 */
}
int main() {
int n = 9;
printf("%d", fib(n));
return 0;
}
方法4 (使用矩阵{{1,1},{1,0}}的幂)
另外一种复杂度为O(n)的方法是对矩阵M={{1,1},{1,0}}自乘n次(换句话说,就是计算矩阵M的n次幂:power(M,n)), 这样就可以在结果矩阵下标为(0, 0)的地方得到斐波那契数列的第(n+1)项,如下所示:
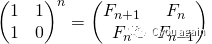
#include <stdio.h>
/* Helper function that multiplies 2 matrices F and M of size 2*2, and puts the multiplication result back to F[][] */
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]);
/* Helper function that calculates F[][] raise to the power n and puts the result in F[][]。Note that this function is designed only for fib() and won't work as general power function */
void power(int F[2][2], int n);
int fib(int n) {
int F[2][2] = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n - 1);
return F[0][0];
}
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]) {
int x = F[0][0] * M[0][0] + F[0][1] * M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0] * M[0][1] + F[0][1] * M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0] * M[0][0] + F[1][1] * M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0] * M[0][1] + F[1][1] * M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
void power(int F[2][2], int n) {
int i;
int M[2][2] = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
// n - 1 times multiply the matrix to {{1,0},{0,1}}
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
int main() {
int n = 9;
printf("%d", fib(n));
return 0;
}
输出:34
时间复杂度: O(n)
空间复杂度: O(1)
方法 5 (对方法4进行优化 )
上面的方法4可以优化到)的时间复杂度。我们可以像计算x^n那样,采用递归的方式来计算power(M, n) ,C/C++代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]);
void power(int F[2][2], int n);
/* function that returns nth Fibonacci number */
int fib(int n) {
int F[2][2] = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n - 1);
return F[0][0];
}
/* Optimized version of power() in method 4 */
void power(int F[2][2], int n) {
if (n == 0 || n == 1)
return;
int M[2][2] = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
power(F, n / 2);
multiply(F, F);
if (n % 2 != 0)
multiply(F, M);
}
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]) {
int x = F[0][0] * M[0][0] + F[0][1] * M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0] * M[0][1] + F[0][1] * M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0] * M[0][0] + F[1][1] * M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0] * M[0][1] + F[1][1] * M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
int main() {
int n = 9;
printf("%d", fib(n));
return 0;
}
输出:34
时间复杂度: O(Logn)
空间复杂度: 如果考虑递归调用时栈的大小,则为O(n) ;如果不考虑调用栈的话,则为O(1)
方法 6 (O(Log n) 的时间复杂度)
下面是一个很有趣的计算斐波那契数列第n项的递归公式,该公式的时间复杂度为O(Log n)。
如果n是偶数, 则k=n/2,
F(n)=[2F(k-1)+F(k)]F(k)
如果n是奇数,则 k=(n+1)/2
F(n)=F(k)F(k)+F(k-1)F(k-1)
原文链接:原文来自个人公众号:C you again,欢迎关注
该公式是如何计算的?上面的公式可以从前面的矩阵幂推算出来:
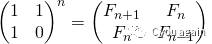

要证明上面的公式成立,只需做下面的工作即可:
如果n是偶数, 令 k = n/2
如果n是奇数, 令 k = (n+1)/2
下面是上述过程的C++ 实现:
// C++ Program to find n'th fibonacci Number in
// with O(Log n) arithmatic operations
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 1000;
// Create an array for memoization
int f[MAX] = { 0 };
// Returns n'th fuibonacci number using table f[]
int fib(int n) {
// Base cases
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n == 1 || n == 2)
return (f[n] = 1);
// If fib(n) is already computed
if (f[n])
return f[n];
int k = (n & 1) ? (n + 1) / 2 : n / 2;
// Applyting above formula [Note value n&1 is 1
// if n is odd, else 0.
f[n] = (n & 1) ?
(fib(k) * fib(k) + fib(k - 1) * fib(k - 1)) :
(2 * fib(k - 1) + fib(k)) * fib(k);
return f[n];
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
int main() {
int n = 9;
printf("%d ", fib(n));
return 0;
}
输出:34
时间复杂度为:O(Log n) ,因为每次递归调用时都将问题规模降了一半
方法 7 (使用Java提供的BigInteger类)
Java提供了BigInteger类,可以很轻易地算出当n很大时的斐波那契数。
// Java program to compute n-th Fibonacci number where n may be large.
import java.math.*;
public class Fibonacci {
// Returns n-th Fibonacci number
static BigInteger fib(int n) {
BigInteger a = BigInteger.valueOf(0);
BigInteger b = BigInteger.valueOf(1);
BigInteger c = BigInteger.valueOf(1);
for (int j = 2; j <= n; j++) {
c = a.add(b);
a = b;
b = c;
}
return (a);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 1000;
System.out.println("Fibonacci of " + n + "th term" + " " + "is" + " " + fib(n));
}
}
当n=1000时,输入结果如下:
原文链接:原文来自个人公众号:C you again,欢迎关注
公众号推荐(资源加油站)
了解更多资源请关注个人公众号:C you again,你将收获以下资源
1、PPT模板免费下载,简历模板免费下载
2、基于web的机票预订系统,基于web的图书管理系统
3、贪吃蛇小游戏源码
4、各类IT技术分享

文章推荐
推荐一:计算机网络中这些高频考题,你还在死记硬背吗?(一),讲述内容:IP地址及其分类,子网掩码的概念,网络号、主机号、直接广播地址计算方法等。
推荐二:计算机网络中这些高频考题,你还在死记硬背吗?(二),讲述内容:局域网接口配置、路由器的静态路由配置、OSPF动态路由协议配置和DHCP服务器配置。
以上就是本期的所有内容了,是否对你有帮助呢?了解更多算法请关注公众号“C you again”。
用x种方式求第n项斐波那契数,99%的人只会第一种的更多相关文章
- 非递归和递归分别实现求第n个斐波那契数。
菲波那切数列为:0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34... 规律:从第三个数字起后面的每一个数字都是前两个数字的和. 非递归算法: #include<stdio.h> int ma ...
- 【C++】【斐波那契】求第几个斐波那契数字。
首先在头文件 whichfibonaccinumber.h 中写了一个使用加法的解法.没有验证输入数字是否小于0. #ifndef WHICHFIBONACCINUMBER_H_ #define WH ...
- POJ 3070(求斐波那契数 矩阵快速幂)
题意就是求第 n 个斐波那契数. 由于时间和内存限制,显然不能直接暴力解或者打表,想到用矩阵快速幂的做法. 代码如下: #include <cstdio> using namespace ...
- 数学算法(一):快速求斐波那契数第n项通过黄金分割率公式
有一个固定的数学公式= =,不知道的话显然没法应用 首先黄金分割率接近于这个公式, (以下为黄金分割率与斐波那契的关系,可跳过) 通过斐波那契数列公式 两边同时除以 得: (1) 注意后一项比前一项接 ...
- C++求斐波那契数
题目内容:斐波那契数定义为:f(0)=0,f(1)=1,f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2)(n>1且n为整数) 如果写出菲氏数列,则应该是: 0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 …… ...
- python递归方式和普通方式实现输出和查询斐波那契数列
●斐波那契数列 斐波那契数列(Fibonacci sequence),是从1,1开始,后面每一项等于前面两项之和. 如果为了方便可以用递归实现,要是为了性能更好就用循环. ◆递归方式实现生成前30个斐 ...
- hdu1568&&hdu3117 求斐波那契数前四位和后四位
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1568 题意:如标题所示,求斐波那契数前四位,不足四位直接输出答案 斐波那契数列通式: 当n<=2 ...
- HDU 1568 Fibonacci【求斐波那契数的前4位/递推式】
Fibonacci Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) Proble ...
- Java算法求最大最小值,冒泡排序,斐波纳契数列一些经典算法<不断更新中>
清明在家,无聊,把一些经典的算法总结了一下. 一.求最大,最小值 Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); int[] a={21,31,4,2,766,345,2, ...
随机推荐
- JAVA 字节流 与 字符流 的区别
字节流与和字符流的使用非常相似,两者除了操作代码上的不同之外,是否还有其他的不同呢? 字节流 在操作时本身不会用到缓冲区(内存),是文件本身直接操作的 字符流 在操作时使用了缓冲区,通过缓冲区再操作文 ...
- Python3-随笔目录
Python3-面向对象 标准库模块 Python3-collections模块-容器数据类型 Python3-datetime模块-日期与时间 Python3-re模块-正则表达式 Python ...
- 计算机网络之tcp四次挥手
TCP的四次挥手(Four-Way Wavehand)1.前言对于"三次握手"我们耳熟能详,因为其相对的简单.但是,我们却不常听见“四次挥手”,就算听过也未必能详细地说明白它的具体 ...
- vueX基础知识点笔记
vuex是专门用来管理vue.js应用程序中状态的一个插件.他的作用是将应用中的所有状态都放在一起, 集中式来管理.需要声明的是,这里所说的状态指的是vue组件中data里面的属性.简单的来说, 它就 ...
- ceph rbd块存储挂载及文件存储建立
一.rbd块存储挂载 1 创建一个OSD pool # ceph osd pool create rbd1 128 查询存储空间使用 # ceph df GLOBAL: SIZE AVAIL RAW ...
- css设置边框阴影;box-shadow的使用
html代码: <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <t ...
- 讲讲 Promise
一.什么是 Promise 1.1 Promise 的前世今生 Promise 最早出现在 1988 年,由 Barbara Liskov.Liuba Shrira 首创(论文:Promises: L ...
- CSS五种方式实现 Footer 置底
页脚置底(Sticky footer)就是让网页的footer部分始终在浏览器窗口的底部.当网页内容足够长以至超出浏览器可视高度时,页脚会随着内容被推到网页底部:但如果网页内容不够长,置底的页脚就会保 ...
- ICPC 2018 亚洲横滨赛 C Emergency Evacuation(暴力,贪心)
ICPC 2018 亚洲横滨赛 C Emergency Evacuation 题目大意 你一个车厢和一些人,这些人都坐在座位上,求这些人全部出去的时间最小值 Solution 题目咋说就咋做 直接模拟 ...
- PE文件格式详解(八)
0x00 前言 前面了解了PE文件的输入和输出,今天来看看另一个重要的结构——资源.资源结构是很典型的树形结构,层层查找,最终找到资源位置. 0x01 资源结构介绍 Windows程序的各种界面成为资 ...
