Spring5.0源码学习系列之浅谈循环依赖问题
前言介绍
附录:Spring源码学习专栏
在上一章的学习中,我们对Bean的创建有了一个粗略的了解,接着本文浅谈Spring循环依赖问题,这是一个面试比较常见的问题
1、什么是循环依赖?
所谓的循环依赖就是两个以及两个以上的类互相调用依赖,形成闭环
// 类A依赖于B
class A{
public B b;
}
// 类B依赖了C
class B{
public C c;
}
// 类C依赖了A
class C{
public A a;
}

然后?看起来是很正常的,我们随便new一个类,循环依赖的类都是能正常调用的
A a = new A();
System.out.println(a);
为什么?因为这种情况,A.java->A.class,我们new就能获取到实例的对象,这个通过jvm支持的,jdk是能支持这种情况的,不过本文不详细说明,本文要讨论的Spring中的bean,循环依赖在Spring中就是一个问题了
为什么?首先回顾一下之前的知识点,首先在Spring框架中类的创建都是给Spring IOC容器创建的,如图:

然后?真的出现这种情况,会怎么样?

Spring框架检测到这种场景会抛 BeanCurrentlyInCreationException,提前暴露对象的方法,因为Spring创建bean的过程是一个很复杂的过程,首先是xml解析为document对象,document对象再转成BeanDefinition,然后进行bean的生命周期,才算得上是一个真正的spring bean,接着进行后置处理器加工,假如出现这种,设想一下会怎么样?spring容器就会一直循环调用,当然是在特定的条件,为什么说是特定情况?请看下文
2、实验环境准备
实验环境:
- SpringFramework版本
- Springframework5.0.x
- 开发环境
- JAR管理:gradle 4.9/ Maven3.+
- 开发IDE:IntelliJ IDEA 2018.2.5
- JDK:jdk1.8.0_31
- Git Server:Git fro window 2.8.3
- Git Client:SmartGit18.1.5(可选)
3、循环依赖问题
我们可以通过例子进行验证,创建类A:
package com.example.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* <pre>
* A class
* </pre>
*
* <pre>
* @author mazq
* 修改记录
* 修改后版本: 修改人: 修改日期: 2020/11/05 10:31 修改内容:
* </pre>
*/
@Component
public class A {
//@Autowired
B b;
public A() {
b = new B();
System.out.println("A class is create");
}
}
类B:
package com.example.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* <pre>
* B class
* </pre>
*
* <pre>
* @author mazq
* 修改记录
* 修改后版本: 修改人: 修改日期: 2020/11/16 14:03 修改内容:
* </pre>
*/
@Component
public class B {
//@Autowired
A a;
public B() {
a = new A();
System.out.println("B class is create");
}
}
注册类A、B
package com.example.config;
import com.example.bean.B;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import com.example.bean.A;
/**
* <pre>
* AppConfiguration
* </pre>
*
* <pre>
* @author mazq
* 修改记录
* 修改后版本: 修改人: 修改日期: 2020/11/05 10:26 修改内容:
* </pre>
*/
@Configuration
public class AppConfiguration {
@Bean
public A a(){
return new A();
}
@Bean
public B b() {
return new B();
}
}
package com.example;
import com.example.config.AppConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import com.example.bean.A;
/**
* <pre>
* TestController
* </pre>
*
* <pre>
* @author mazq
* 修改记录
* 修改后版本: 修改人: 修改日期: 2020/11/05 10:22 修改内容:
* </pre>
*/
public class TestApplication {
public static void testCircularReferences() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.register(AppConfiguration.class);
//context.setAllowCircularReferences(false);
context.refresh();
A bean = context.getBean(A.class);
System.out.println(bean);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试Sprin循环依赖
testCircularReferences();
}
}
经过测试,一直在循环调用:

4、循环依赖解决方法
对于这种情况,Spring有处理方法?答案是有的,方法就是通过@Autowired注解,当然bean要是单例的,多例的情况不支持,原因后面分析
@Component
public class A {
@Autowired
B b;
public A() {
System.out.println("A class is create");
}
}

补充:除了
@Autowired方法,我们还可以通过set方法处理循环依赖问题,当然也是仅支持单例bean,多例的情况不支持
5、关闭Spring循环依赖
有个疑问?Spring的循环依赖支持,默认情况是开启?是否有什么开关控制?通过源码学习,可以通过setAllowCircularReferences设置
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.register(AppConfiguration.class);
// 关闭Spring循环依赖支持
context.setAllowCircularReferences(false);
context.refresh();
通过测试,设置不开启这个属性的时候,即使加上@Autowired,代码还是抛异常了
6、prototype(多例)循环依赖
在多例的情况,Spring能支持循环依赖?加上@Scope("prototype"),将bean变成多例的

经过测试:多例的情况会抛出异常,即使加上了@Autowired,原因请看下文
7、Spring循环依赖特征
ok,经过前面例子的验证,到这来,可以对Spring的循环依赖特点进行归纳:
- Spring中的循环依赖场景
- 构造器的循环依赖,通过构造函数
- Field属性的循环依赖,通过set方法
- Spring的循环依赖是默认开启的(setAllowCircularReferences)
- Spring对单例和多例Bean的支持
- 单例Bean(singleton) :只能通过
@Autowired和set方法支持 - 多例Bean(prototype):默认不支持,直接抛异常
BeanCurrentlyInCreationException
- 单例Bean(singleton) :只能通过
8、Spring循环依赖原理
我们通过实验进行了验证,也归纳出了Spring循环依赖的特点,然后具体原因是什么?我们只能通过源码学习得到答案
在上一章的学习中,我们对Bean的创建有了一个粗略的了解,所以,顺着这条路线,跟下源码:
在前面的学习,我们知道了{@link org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#doGetBean}这个方法就是Spring Bean创建的真正执行方法
protected <T> T doGetBean(
String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)
throws BeansException {
// 处理BeanName,前面说的FactoryBean带‘&’符号,要在这里进行转换
String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean;
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
// 从map(singletonObjects)里获取单例bean,确定是否已经存在对应实例
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
logger.debug("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName +
"' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference");
}
else {
logger.debug("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
// 两种情况:普通的bean,直接从singletonObjects返回sharedInstance
//如果是FactoryBean,返回其创建的对象实例
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
}
else {
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
// 校验是否是多例(Prototype)的Bean,多例的bean是不支持循环依赖的
// 为了避免循环依赖,遇到这种情况,直接抛出异常
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
// Check if bean definition exists in this factory.
// 检查BeanFactory是否存在这个BeanDefinition
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// Not found -> check parent.
// 当前容器找不到BeanDefinition,去parent容器查询
String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name);
if (parentBeanFactory instanceof AbstractBeanFactory) {
return ((AbstractBeanFactory) parentBeanFactory).doGetBean(
nameToLookup, requiredType, args, typeCheckOnly);
}
else if (args != null) {
// Delegation to parent with explicit args.
// 返回parent容器的查询结果
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);
}
else {
// No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);
}
}
if (!typeCheckOnly) {
//typeCheckOnly为false的情况,将beanName放在一个alreadyCreated的集合
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
}
try {
RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
// Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
// 校验是否配置了 depends-on
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
// 存在循环引用的情况,要抛出异常
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'");
}
// 正常情况,注册依赖关系
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
try {
// 初始化被依赖项
getBean(dep);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"'" + beanName + "' depends on missing bean '" + dep + "'", ex);
}
}
}
// Create bean instance.
// 单例的Bean
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
// 创建单例bean
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
// 多例的Bean,scope = protoType
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
// 多例的情况,创建bean之前添加标记(用于循环依赖校验)
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
// 执行多例Bean创建
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
// 创建原型(多例)bean之后擦除标记
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
// 如果不是单例bean也不是多例的bean,委托给对应的实现类
else {
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(scopeName)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No scope name defined for bean ´" + beanName + "'");
}
Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
// 执行bean创建
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " +
"defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton",
ex);
}
}
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
// Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance.
// 检查一下类型是否正确,不正确抛出异常,正确返回实例
if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) {
try {
T convertedBean = getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);
if (convertedBean == null) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
return convertedBean;
}
catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" +
ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex);
}
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
}
return (T) bean;
}
- 源码比较复杂,所以可以带着疑问来跟,首先以单例Bean的情况:#doGetBean.getSingleton
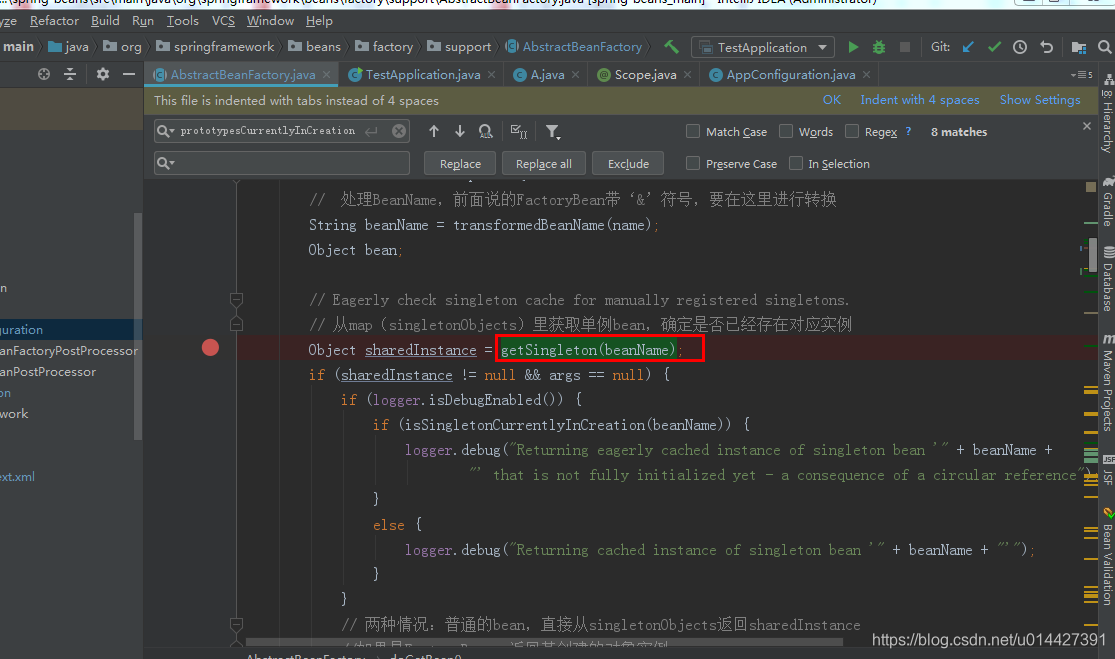

protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
// 一级缓存:singletonObjects (单例池)
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// 二级缓存:earlySingletonObjects(BeanDefinition还没进行属性填充)
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
// 三级缓存:singletonFactories
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
在某些情况,循环依赖会造成循环调用,所以需要怎么解决?

Spring框架的方法是使用了三级缓存,其实最关键的是earlySingletonObjects
- 一级缓存:singletonObjects,这是Spring BeanDefinition的单例池,首先只保存单例Bean的BeanDefinition,而且这个Bean是一个真正的bean,也就是进行过属性填充的
- 二级缓存:earlySingletonObjects,early从单词意思来说,这个缓存是在singletonObjects之前的,也就是BeanDefinition还没进行属性填充等等操作,Spring引入这个缓存的目的就是为了处理单例bean的循环依赖问题
- 三级缓存:singletonFactories,缓存的是ObjectFactory,表示对象工厂,为什么要加上这个缓存?原因比较复杂,涉及到AOP等等原因,因为我还没理解清楚,所以本文不说明
加上了earlySingletonObjects缓存之后,Spring就能支持单例bean的循环依赖,参考语雀某大佬的笔记,画图表示:

- 带着疑问来跟一下多例Bean的情况:
Spring框架是不支持多例bean的循环依赖的,原因跟下代码:#doGetBean
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
// 校验是否是多例(Prototype)的Bean,多例的bean是不支持循环依赖的
// 为了避免循环依赖,遇到这种情况,直接抛出异常
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
多例的情况:看代码是通过prototypesCurrentlyInCreation里的数据校验的,prototypesCurrentlyInCreation是一个ThreadLocal对象
protected boolean isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(String beanName) {
Object curVal = this.prototypesCurrentlyInCreation.get();
return (curVal != null &&
(curVal.equals(beanName) || (curVal instanceof Set && ((Set<?>) curVal).contains(beanName))));
}
继续找代码,找到beforePrototypeCreation:
protected void beforePrototypeCreation(String beanName) {
Object curVal = this.prototypesCurrentlyInCreation.get();
if (curVal == null) {
this.prototypesCurrentlyInCreation.set(beanName);
}
else if (curVal instanceof String) {
Set<String> beanNameSet = new HashSet<>(2);
beanNameSet.add((String) curVal);
beanNameSet.add(beanName);
this.prototypesCurrentlyInCreation.set(beanNameSet);
}
else {
Set<String> beanNameSet = (Set<String>) curVal;
beanNameSet.add(beanName);
}
}
Ctrl+Alt+H,查看这个方法的调用栈:其实就是在#doGetBean就调用了,也就是bean创建之前

try {
// 多例的情况,创建bean之前添加标记(用于循环依赖校验)
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
// 执行多例Bean创建
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
// 创建原型(多例)bean之后擦除标记
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
知识点归纳
- Spring中的循环依赖场景
- 构造器的循环依赖,通过构造函数
- Field属性的循环依赖,通过set方法
- Spring的循环依赖是默认开启的(setAllowCircularReferences)
- Spring对单例和多例Bean的支持
- 单例Bean(singleton) :只能通过
@Autowired和set方法支持 - 多例Bean(prototype):默认不支持,直接抛异常
BeanCurrentlyInCreationException
- 单例Bean(singleton) :只能通过
- Spring支持单例bean的循环依赖原因:使用了三级缓存
Spring5.0源码学习系列之浅谈循环依赖问题的更多相关文章
- Spring5.0源码学习系列之浅谈BeanFactory创建
Spring5.0源码学习系列之浅谈BeanFactory创建过程 系列文章目录 提示:Spring源码学习专栏链接 @ 目录 系列文章目录 博客前言介绍 一.获取BeanFactory主流程 二.r ...
- Spring5.0源码学习系列之浅谈懒加载机制原理
前言介绍 附录:Spring源码学习专栏 在上一章的学习中,我们对Bean的创建有了一个粗略的了解,接着本文挑一个比较重要的知识点Bean的懒加载进行学习 1.什么是懒加载? 懒加载(Lazy-ini ...
- Spring5.0源码学习系列之事务管理概述
Spring5.0源码学习系列之事务管理概述(十一),在学习事务管理的源码之前,需要对事务的基本理论比较熟悉,所以本章节会对事务管理的基本理论进行描述 1.什么是事务? 事务就是一组原子性的SQL操作 ...
- Spring5.0源码学习系列之Spring AOP简述
前言介绍 附录:Spring源码学习专栏 在前面章节的学习中,我们对Spring框架的IOC实现源码有了一定的了解,接着本文继续学习Springframework一个核心的技术点AOP技术. 在学习S ...
- JDK源码学习系列05----LinkedList
JDK源码学习系列05----LinkedList 1.LinkedList简介 LinkedList是基于双向链表实 ...
- JDK源码学习系列04----ArrayList
JDK源码学习系列04----ArrayList 1. ...
- JDK源码学习系列03----StringBuffer+StringBuilder
JDK源码学习系列03----StringBuffer+StringBuilder 由于前面学习了StringBuffer和StringBuilder的父类A ...
- JDK源码学习系列02----AbstractStringBuilder
JDK源码学习系列02----AbstractStringBuilder 因为看StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder 的源码时发现两者都继承了AbstractStringBuil ...
- JDK源码学习系列01----String
JDK源码学习系列01----String 写在最前面: 这是我JDK源码学习系列的第一篇博文,我知道 ...
随机推荐
- [转载]volitale关键字详解
来看这个代码: int fun(int& a) { int b = a; int c = a; return a+b+c; } int main() { int a=1; //........ ...
- c++程序设计实践——银行系统
银行系统 本科大二程序设计实践的作业,算是一个比较简单的项目吧,主要使用的编程范式有面向对象编程 其中引入<multimap><map>头文件实现多映射输出存取记录 引入< ...
- 【转载】动态规划—各种 DP 优化
原博客地址 关于氵博客:其实主要是防止我找不到这篇文了
- linux(centos8):使用zip/unzip压缩和解压缩文件
一,查看zip命令所属的rpm包 1,zip [root@kubemaster ~]# whereis zip zip: /usr/bin/zip /usr/share/man/man1/zip.1. ...
- scrapy Request方法
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import scrapy class TestSpider(scrapy.Spider): name = 'test' allowed_domains ...
- gti 常用命令
git add 文件 : 追踪指定文件git add . :追踪所有的文件git commit -m "注释" : 提交报本地仓库git push : 推送远程仓库git pull ...
- WebSocket的理解
Websocket相对于无状态的HTTp协议,是在一次成功连接之后,在关闭请求之前,服务器和客户端能顺利进行信息传输.而不用像HTTP那样每一次都要告诉服务器这个请求者是谁(身份鉴别信息). 在HTT ...
- 56.Qt-滚动字幕之无间隙滚动(原创)
1.描述 最近要实现一个滚动条字幕,但是搜到的系列文章都是利用定时器QTimer,在固定的时间截取文本并显示,这样滚动的时候其实是断断续续的,因为实际上是一个个字符位移实现的,不过实现方便. 所以只有 ...
- [斯坦福大学2014机器学习教程笔记]第六章-代价函数(Cost function)
在这节中主要讲的是如何更好地拟合逻辑回归模型的参数θ.具体来说,要定义用来拟合参数的优化目标或者叫代价函数,这便是监督学习问题中的逻辑回归模型的拟合问题. 我们有一个训练集,训练集中有m个训练样本:{ ...
- Java网关服务-AIO(二)
Java网关服务-AIO(二) 概述 AIO的特点就是用户程序注册一个事件后就可以做其他事情,当事件被内核执行并得到结果后,我们的CompletionHandler会在I/O回调线程中被自动调用,有点 ...
