skip list
概述
Skip list是平衡树的一种替代的数据结构,但是和红黑树不相同的是,跳表对于树的平衡的实现是基于一种随机化的算法的,这样也就是说跳表的插入和删除的工作是比较简单的。并且是Redis、LevelDB、nessDB、SkipDB等的底层结构,学习skip list为后面学习levelDB打下基础。
核心思想
如果是一个简单的链表,如图1,那么我们知道在链表中查找一个元素I的话,需要将整个链表遍历一次。
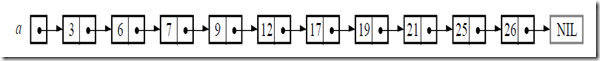
图 1
如果是说链表是排序的,并且节点中还存储了指向前面第二个节点的指针的话,如图2,那么在查找一个节点时,仅仅需要遍历N/2个节点即可。
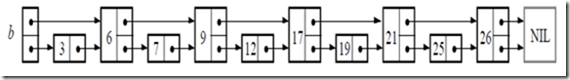
图 2
这基本上就是跳表的核心思想,其实也是一种通过“空间来换取时间”的一个算法,通过在每个节点中增加了向前的指针,从而提升查找的效率。
跳表数据存储模型
我们定义:
如果一个基点存在k个向前的指针的话,那么陈该节点是k层的节点。
一个跳表的层MaxLevel定义为跳表中所有节点中最大的层数。
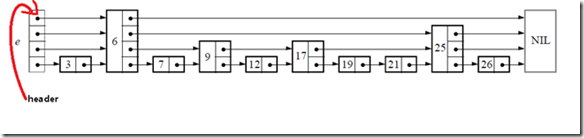
下面给出一个完整的跳表的图示:
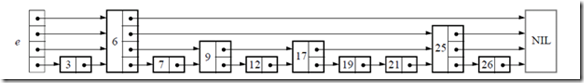
那么我们该如何将该数据结构使用二进制存储呢?通过上面的跳表的很容易设计这样的数据结构:
定义每个节点类型:
typedef struct NodeStructure *Node;
typedef struct NodeStructure
{
keyType key; // key值
valueType value; // value值
// 向前指针数组,根据该节点层数的不同指向不同大小的数组
NodeStructure *forward[1];
}NodeStructure;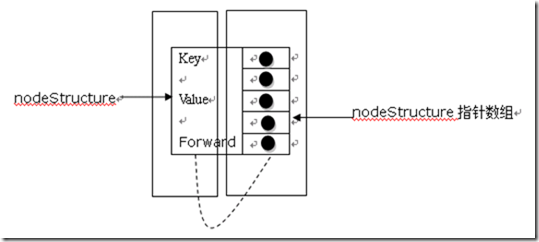
上面的每个结构体对应着图中的每个节点,如果一个节点是一层的节点的话(如7,12等节点),那么对应的forward将指向一个只含一个元素的数组,以此类推。
定义跳表数据类型:
// 定义跳表数据类型
typedef struct SkipList{
int level; /* Maximum level of the list
(1 more than the number of levels in the list) */
Node header; /* pointer to header */
} * SkipList;跳表数据类型中包含了维护跳表的必要信息,level表明跳表的层数,header如下所示:
定义辅助变量:
#define MAX_LEVEL 10
定义辅助方法:
创建节点
Node CreateNode(int level,int key,int value)
{
Node node=(NodeStructure *)malloc(sizeof(NodeStructure)+level*sizeof(NodeStructure*));
node->key=key;
node->value=value;
return node;
}
好的基本的数据结构定义已经完成,接下来来分析对于跳表的一个操作。
跳表代码实现
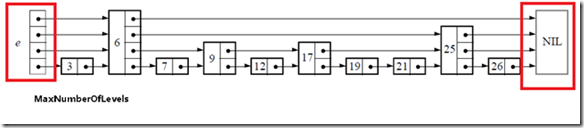
1 初始化
初始化的过程很简单,仅仅是生成下图中红线区域内的部分,也就是跳表的基础结构:
SkipList CreateSkiplist()
{
SkipList skiplist=(SkipList *)malloc(sizeof(struct SkipList));
skiplist->level=0;
skiplist->header=CreateNode(MAX_LEVEL-1,0,0);
for(int i=0;i<MAX_LEVEL;i++)
{
skiplist->header->forward[i]=NULL;
}
return skiplist;
}
2 查找
//搜索指定key的value
int Search(SkipList skiplist,int key)
{
Node pre,now=NULL;
pre=skiplist->header;
//从最高层开始搜
int k=skiplist->level;
for(int i=k-1; i >= 0; i--)
{
while((now=pre->forward[i])&&(now->key<=key))
{
if(now->key == key)
{
return now->value;
}
pre=now;
}
}
return NULL;
}
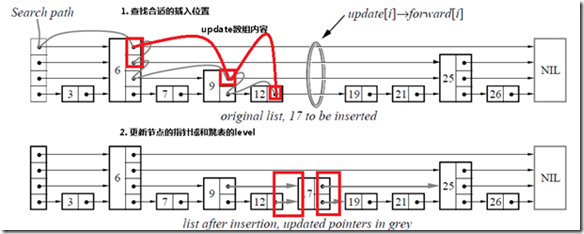
3 插入操作
由于跳表数据结构整体上是有序的,所以在插入时,需要首先查找到合适的位置,然后就是修改指针(和链表中操作类似),然后更新跳表的level变量。
//随机产生层数
int randomLevel()
{
int k=1;
while (rand()%2)
k++;
k=(k<MAX_LEVEL)?k:MAX_LEVEL;
return k;
}
//插入节点
bool Insert(SkipList *skiplist,int key,int value)
{
Node update[MAX_LEVEL];
Node p, q = NULL;
p=skiplist->header;
int k=skiplist->level;
//从最高层往下查找需要插入的位置
//填充update
for(int i=k-1; i >= 0; i--)
{
//q!=NULL
while((q=p->forward[i])&&(q->key<key))
{
p=q;
}
update[i]=p;
}
// 这里已经查找到了合适的位置,并且update数组已经
// 填充好了元素
//不能插入相同的key
if(q&&q->key==key)
{
return false;
}
//产生一个随机层数K
//新建一个待插入节点q
//一层一层插入
k=randomLevel();
// 如果新生成的层数比跳表的层数大的话
// 增加整个跳表的层数
if(k>(skiplist->level))
{
for(int i=skiplist->level; i < k; i++)
{
// 在update数组中将新添加的层指向skiplist->header
update[i] = skiplist->header;
}
skiplist->level=k;
}
q=CreateNode(k,key,value);
//逐层更新节点的指针,和普通列表插入一样
for(int i=0;i<k;i++)
{
q->forward[i]=update[i]->forward[i];
update[i]->forward[i]=q;
}
return true;
}
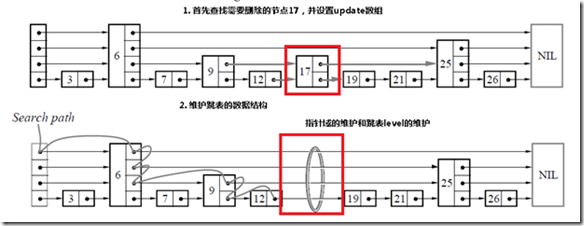
4 删除某个节点
和插入是相同的,首先查找需要删除的节点,如果找到了该节点的话,那么只需要更新指针域,如果跳表的level需要更新的话,进行更新。
//删除指定的key
bool Delete(SkipList skiplist,int key)
{
Node update[MAX_LEVEL];
Node p,q=NULL;
p=skiplist->header;
//从最高层开始搜
int k=skiplist->level;
for(int i=k-1; i >= 0; i--)
{
while((q=p->forward[i])&&(q->key<key))
{
p=q;
}
update[i]=p;
}
if(q&&q->key==key)
{
//逐层删除,和普通列表删除一样
for(int i=0; i<skiplist->level; i++)
{
if(update[i]->forward[i]==q)
{
update[i]->forward[i]=q->forward[i];
}
}
free(q);
//如果删除的是最大层的节点,那么需要重新维护跳表的
for(int i=skiplist->level - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
if(skiplist->header->forward[i]==NULL)
{
skiplist->level--;
}
}
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
5 参考文献
ftp://ftp.cs.umd.edu/pub/skipLists/skiplists.pdf
#define MAX_LEVEL 10
typedef struct NodeStructure *Node; typedef struct NodeStructure
{
keyType key; // key值
valueType value; // value值
// 向前指针数组,根据该节点层数的不同指向不同大小的数组
NodeStructure *forward[1];
}NodeStructure; typedef struct SkipList{
int level; /* Maximum level of the list
(1 more than the number of levels in the list) */
Node header; /* pointer to header */
} * SkipList; Node CreateNode(int level,int key,int value)
{
Node node=(NodeStructure *)malloc(sizeof(NodeStructure)+level*sizeof(NodeStructure*));
node->key=key;
node->value=value;
return node;
} SkipList CreateSkiplist()
{
SkipList skiplist=(SkipList *)malloc(sizeof(struct SkipList));
skiplist->level=0;
skiplist->header=CreateNode(MAX_LEVEL-1,0,0); for(int i=0;i<MAX_LEVEL;i++)
{
skiplist->header->forward[i]=NULL;
}
return skiplist;
} //搜索指定key的value
int Search(SkipList skiplist,int key)
{
Node pre,now=NULL;
pre=skiplist->header;
//从最高层开始搜
int k=skiplist->level;
for(int i=k-1; i >= 0; i--)
{
while((now=pre->forward[i])&&(now->key<=key))
{
if(now->key == key)
{
return now->value;
}
pre=now;
}
}
return NULL;
} //随机产生层数
int randomLevel()
{
int k=1;
while (rand()%2)
k++;
k=(k<MAX_LEVEL)?k:MAX_LEVEL;
return k;
} //插入节点
bool Insert(SkipList skiplist,int key,int value)
{
Node update[MAX_LEVEL];
Node p, q = NULL;
p=skiplist->header;
int k=skiplist->level;
//从最高层往下查找需要插入的位置
//填充update
for(int i=k-1; i >= 0; i--)
{
//q!=NULL
while((q=p->forward[i])&&(q->key<key))
{
p=q;
}
update[i]=p;
}
// 这里已经查找到了合适的位置,并且update数组已经
// 填充好了元素
//不能插入相同的key
if(q&&q->key==key)
{
return false;
} //产生一个随机层数K
//新建一个待插入节点q
//一层一层插入
k=randomLevel();
// 如果新生成的层数比跳表的层数大的话
// 增加整个跳表的层数
if(k>(skiplist->level))
{
for(int i=skiplist->level; i < k; i++)
{
// 在update数组中将新添加的层指向skiplist->header
update[i] = skiplist->header;
}
skiplist->level=k;
} q=CreateNode(k,key,value);
//逐层更新节点的指针,和普通列表插入一样
for(int i=0;i<k;i++)
{
q->forward[i]=update[i]->forward[i];
update[i]->forward[i]=q;
}
return true;
} //删除指定的key
bool Delete(SkipList skiplist,int key)
{
Node update[MAX_LEVEL];
Node p,q=NULL;
p=skiplist->header;
//从最高层开始搜
int k=skiplist->level;
for(int i=k-1; i >= 0; i--)
{
while((q=p->forward[i])&&(q->key<key))
{
p=q;
}
update[i]=p;
}
if(q&&q->key==key)
{
//逐层删除,和普通列表删除一样
for(int i=0; i<skiplist->level; i++)
{
if(update[i]->forward[i]==q)
{
update[i]->forward[i]=q->forward[i];
}
}
free(q);
//如果删除的是最大层的节点,那么需要重新维护跳表的
for(int i=skiplist->level - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
if(skiplist->header->forward[i]==NULL)
{
skiplist->level--;
}
}
return true;
}
else
return false;
} void Print(SkipList skiplist)
{
//从最高层开始打印
nodeStructure *p,*q=NULL; //从最高层开始搜
int k=skiplist->level;
for(int i=k-1; i >= 0; i--)
{
p=skiplist->header;
while(q=p->forward[i])
{
printf("%d -> ",p->value);
p=q;
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
} int main()
{
SkipList skiplist=CreateSkiplist();
for(int i=1;i<=19;i++)
{
Insert(skiplist,i,i*2);
}
Print(skiplist);
//搜索
int i=Search(skiplist,4);
printf("i=%d\n",i);
//删除
bool b=Delete(skiplist,4);
if(b)
printf("删除成功\n");
Print(skiplist);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
skip list的更多相关文章
- LINQ系列:LINQ to SQL Take/Skip
1. Take var expr = context.Products .Take(); var expr = (from p in context.Products select p) .Take( ...
- EntityFramework 7 OrderBy Skip Take-计算排序分页 SQL 翻译
先解释一下这个标题的意思,OrderBy 在 Linq 语句中,我们经常使用,比如 OrderBy(b => b.BlogId) 就是对 BlogId 字段进行升序排序,这是针对一个字段的排序, ...
- 【记录】AutoMapper Project To OrderBy Skip Take 正确写法
AutoMapper:Queryable Extensions 示例代码: using (var context = new orderEntities()) { return context.Ord ...
- Xcode插件安装 错选了Skip Bundle解决办法
1.首先找到Xcode的UUID,在终端运行defaults read /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Info DVTPlugInCompatibilityUUID ...
- ASP.NET泛型List的各种用法Skip、Take等
List在.NET里面使用得非常频繁,但有好多人不了解它各种小用法.我就一直记不大住... asp.net中List的简单用法,例如: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 List<int> li ...
- mongodb-$type、limit、skip、sort方法、索引、聚合
一.$type操作符 $type操作符是基于BSON类型来检索集合中匹配的数据类型,并返回结果. MongoDB 中可以使用的类型如下表所示: 类型 数字 备注 Double 1 String 2 ...
- Xcode安装插件,错误选择了Skip Bundles,重新出现Load Bundles方法
Xcode安装插件经常会遇到这样的问题,出现提示性选择,还是英文提示,所以没仔细看就习惯性的选择了右侧的按钮 点击了Skip Bundle,结果悲剧的发现,发现插件完全失效了,以后不管怎么打开Xcod ...
- [Android Pro] InputStream.skip方法的思考
参考 : http://blog.csdn.net/gsyzhu/article/details/8102286 在java.io.InputStream类中定义了skip这个方法.在API中的描述如 ...
- 跳跃表Skip List的原理和实现
>>二分查找和AVL树查找 二分查找要求元素可以随机访问,所以决定了需要把元素存储在连续内存.这样查找确实很快,但是插入和删除元素的时候,为了保证元素的有序性,就需要大量的移动元素了.如果 ...
- 转MongoDB 使用Skip和limit分页
关于MongoDB 数据分页和排序 limit,skip用户的一些基础语句,介绍MongoDB 数据分页和排序实例方法. 使用Skip和limit可以如下做数据分页: Code: page1 = db ...
随机推荐
- ExtJS FormPanel不执行校验
经检查问题原因在于使用了 validator 属性. 使用validator属性,必须添加返回值.不添加返回值,就会出现FormPanel不执行校验的问题.
- git创建分支并提交项目
git 创建分支, 切换分支, 合并分支, 删除分支及提交[commit提交到本地仓库push名利提交到远程服务器], 检出[pull], 冲突修改, 本地仓库同步远程服务器[pul和push命令l] ...
- LNMP系列网站零基础开发记录(一)
[目录] 扯淡吹逼之开发前奏 Django 开发环境搭建及配置 web 页面开发 Django app开发 Django 站点管理 Python 简易爬虫开发 Nginx&uWSGI 服务器配 ...
- 不会JS中的OOP,你也太菜了吧!(第一篇)
一.你必须知道的 1) 字面量 2) 原型 3) 原型链 4) 构造函数 5) 稳妥对象(没有公共属性,而且其方法也不引用this的对象.稳妥对象适合用在安全的环境中和防止数据被其它程序改变的时候) ...
- storm集成kafka
kafkautil: import java.util.Properties; import kafka.javaapi.producer.Producer; import kafka.produce ...
- 【Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II 】cpp
题目: Given a binary tree, return the bottom-up level order traversal of its nodes' values. (ie, from ...
- 文件和文件夹同步工具AFiles 1.0 发布
文件和文件夹同步工具AFiles 1.0 正式发布了! 本软件支持按文件日期或长度的各种比较方式来同步文件或者文件夹. 支持双向同步功能. 支持深层文件夹功能. 可以自动产生比较和同步的记录情况. ...
- Geo-Fence
转自:http://blog.jobbole.com/86633/ 地理围栏(Geo-fencing)是LBS的一种应用,就是用一个虚拟的栅栏围出一个虚拟地理边界,当手机进入.离开某个特定地理区域,或 ...
- ansii、unicode、utf8 区别和关系
本地化过程中涉及到源文件和目标文件的传输问题,这时候编码就显得很重要.中文的网页和操作系统中通常采用ANSI编码,这也是微软OS的一个字符标准.对于ANSI,不同的国家和地区制定了不同的标准,由此产生 ...
- c++ dirname() basename()
http://linux.about.com/library/cmd/blcmdl3_dirname.htm #include <iostream> #include <libgen ...
