C 语言实现面向对象编程
转载 https://blog.csdn.net/onlyshi/article/details/81672279
C 语言实现面向对象编程
1、引言
面向对象编程(OOP)并不是一种特定的语言或者工具,它只是一种设计方法、设计思想。它表现出来的三个最基本的特性就是封装、继承与多态。很多面向对象的编程语言已经包含这三个特性了,例如 Smalltalk、C++、Java。但是你也可以用几乎所有的编程语言来实现面向对象编程,例如 ANSI-C。要记住,面向对象是一种思想,一种方法,不要太拘泥于编程语言。
2、封装
封装就是把数据和方法打包到一个类里面。其实C语言编程者应该都已经接触过了,C 标准库
中的 fopen(), fclose(), fread(), fwrite()等函数的操作对象就是 FILE。数据内容就是 FILE,数据的读写操作就是 fread()、fwrite(),fopen() 类比于构造函数,fclose() 就是析构函数。这个看起来似乎很好理解,那下面我们实现一下基本的封装特性。
#ifndef SHAPE_H
#define SHAPE_H #include <stdint.h> // Shape 的属性
typedef struct {
int16_t x;
int16_t y;
} Shape; // Shape 的操作函数,接口函数
void Shape_ctor(Shape * const me, int16_t x, int16_t y);
void Shape_moveBy(Shape * const me, int16_t dx, int16_t dy);
int16_t Shape_getX(Shape const * const me);
int16_t Shape_getY(Shape const * const me); #endif /* SHAPE_H */
这是 Shape 类的声明,非常简单,很好理解。一般会把声明放到头文件里面 “Shape.h”。
来看下 Shape 类相关的定义,当然是在 “Shape.c” 里面。
#include "shape.h" // 构造函数
void Shape_ctor(Shape * const me, int16_t x, int16_t y)
{
me->x = x;
me->y = y;
} void Shape_moveBy(Shape * const me, int16_t dx, int16_t dy)
{
me->x += dx;
me->y += dy;
} // 获取属性值函数
int16_t Shape_getX(Shape const * const me)
{
return me->x;
}
int16_t Shape_getY(Shape const * const me)
{
return me->y;
}
再看下 main.c
#include "shape.h" /* Shape class interface */
#include <stdio.h> /* for printf() */ int main()
{
Shape s1, s2; /* multiple instances of Shape */ Shape_ctor(&s1, , );
Shape_ctor(&s2, -, ); printf("Shape s1(x=%d,y=%d)\n", Shape_getX(&s1), Shape_getY(&s1));
printf("Shape s2(x=%d,y=%d)\n", Shape_getX(&s2), Shape_getY(&s2)); Shape_moveBy(&s1, , -);
Shape_moveBy(&s2, , -); printf("Shape s1(x=%d,y=%d)\n", Shape_getX(&s1), Shape_getY(&s1));
printf("Shape s2(x=%d,y=%d)\n", Shape_getX(&s2), Shape_getY(&s2)); return ;
}
编译之后,看看执行结果:
Shape s1(x=0,y=1)
Shape s2(x=-1,y=2)
Shape s1(x=2,y=-3)
Shape s2(x=0,y=0)
整个例子,非常简单,非常好理解。以后写代码时候,要多去想想标准库的文件IO操作,这样也有意识的去培养面向对象编程的思维。
3、继承
继承就是基于现有的一个类去定义一个新类,这样有助于重用代码,更好的组织代码。在 C 语言里面,去实现单继承也非常简单,只要把基类放到继承类的第一个数据成员的位置就行了。
例如,我们现在要创建一个 Rectangle 类,我们只要继承 Shape 类已经存在的属性和操作,再添加不同于 Shape 的属性和操作到 Rectangle 中。
下面是 Rectangle 的声明与定义:
#ifndef RECT_H
#define RECT_H #include "shape.h" // 基类接口 // 矩形的属性
typedef struct {
Shape super; // 继承 Shape // 自己的属性
uint16_t width;
uint16_t height;
} Rectangle; // 构造函数
void Rectangle_ctor(Rectangle * const me, int16_t x, int16_t y,
uint16_t width, uint16_t height); #endif /* RECT_H */
#include "rect.h" // 构造函数
void Rectangle_ctor(Rectangle * const me, int16_t x, int16_t y,
uint16_t width, uint16_t height)
{
/* first call superclass’ ctor */
Shape_ctor(&me->super, x, y); /* next, you initialize the attributes added by this subclass... */
me->width = width;
me->height = height;
}
我们来看一下 Rectangle 的继承关系和内存布局

因为有这样的内存布局,所以你可以很安全的传一个指向 Rectangle 对象的指针到一个期望传入 Shape 对象的指针的函数中,就是一个函数的参数是 “Shape *”,你可以传入 “Rectangle *”,并且这是非常安全的。这样的话,基类的所有属性和方法都可以被继承类继承!
#include "rect.h"
#include <stdio.h> int main()
{
Rectangle r1, r2; // 实例化对象
Rectangle_ctor(&r1, , , , );
Rectangle_ctor(&r2, -, , , ); printf("Rect r1(x=%d,y=%d,width=%d,height=%d)\n",
Shape_getX(&r1.super), Shape_getY(&r1.super),
r1.width, r1.height);
printf("Rect r2(x=%d,y=%d,width=%d,height=%d)\n",
Shape_getX(&r2.super), Shape_getY(&r2.super),
r2.width, r2.height); // 注意,这里有两种方式,一是强转类型,二是直接使用成员地址
Shape_moveBy((Shape *)&r1, -, );
Shape_moveBy(&r2.super, , -); printf("Rect r1(x=%d,y=%d,width=%d,height=%d)\n",
Shape_getX(&r1.super), Shape_getY(&r1.super),
r1.width, r1.height);
printf("Rect r2(x=%d,y=%d,width=%d,height=%d)\n",
Shape_getX(&r2.super), Shape_getY(&r2.super),
r2.width, r2.height); return ;
}
输出结果:
Rect r1(x=0,y=2,width=10,height=15)
Rect r2(x=-1,y=3,width=5,height=8)
Rect r1(x=-2,y=5,width=10,height=15)
Rect r2(x=1,y=2,width=5,height=8)
4、多态
C++ 语言实现多态就是使用虚函数。在 C 语言里面,也可以实现多态。
现在,我们又要增加一个圆形,并且在 Shape 要扩展功能,我们要增加 area() 和 draw() 函数。但是 Shape 相当于抽象类,不知道怎么去计算自己的面积,更不知道怎么去画出来自己。而且,矩形和圆形的面积计算方式和几何图像也是不一样的。
下面让我们重新声明一下 Shape 类
#ifndef SHAPE_H
#define SHAPE_H #include <stdint.h> struct ShapeVtbl;
// Shape 的属性
typedef struct {
struct ShapeVtbl const *vptr;
int16_t x;
int16_t y;
} Shape; // Shape 的虚表
struct ShapeVtbl {
uint32_t (*area)(Shape const * const me);
void (*draw)(Shape const * const me);
}; // Shape 的操作函数,接口函数
void Shape_ctor(Shape * const me, int16_t x, int16_t y);
void Shape_moveBy(Shape * const me, int16_t dx, int16_t dy);
int16_t Shape_getX(Shape const * const me);
int16_t Shape_getY(Shape const * const me); static inline uint32_t Shape_area(Shape const * const me)
{
return (*me->vptr->area)(me);
} static inline void Shape_draw(Shape const * const me)
{
(*me->vptr->draw)(me);
} Shape const *largestShape(Shape const *shapes[], uint32_t nShapes);
void drawAllShapes(Shape const *shapes[], uint32_t nShapes); #endif /* SHAPE_H */
看下加上虚函数之后的类关系图
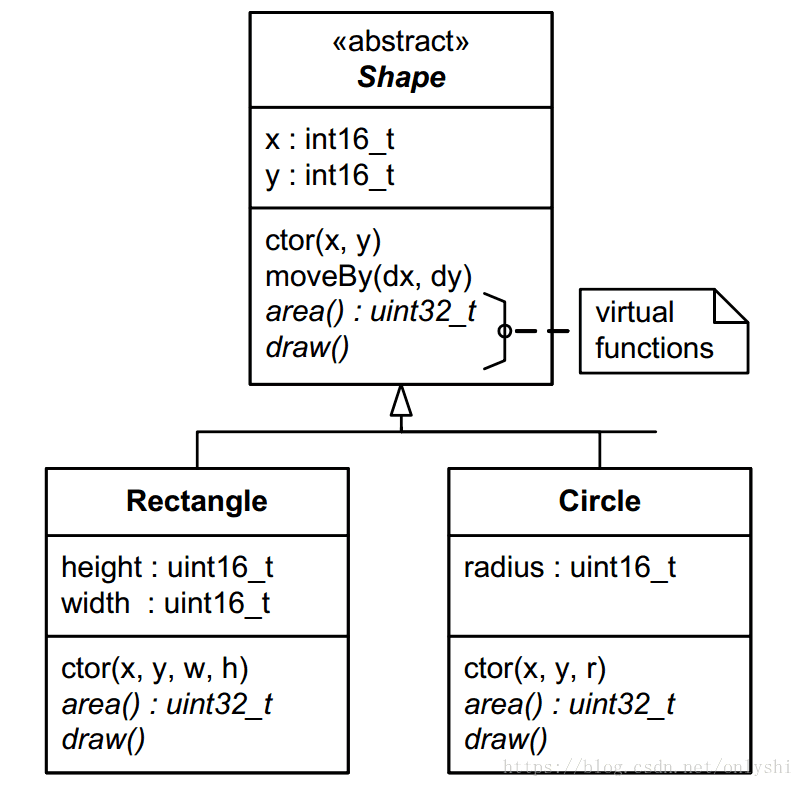
4.1 虚表和虚指针
虚表(Virtual Table)是这个类所有虚函数的函数指针的集合。
虚指针(Virtual Pointer)是一个指向虚表的指针。这个虚指针必须存在于每个对象实例中,会被所有子类继承。
在《Inside The C++ Object Model》的第一章内容中,有这些介绍。
4.2 在构造函数中设置vptr
在每一个对象实例中,vptr 必须被初始化指向其 vtbl。最好的初始化位置就是在类的构造函数中。事实上,在构造函数中,C++ 编译器隐式的创建了一个初始化的vptr。在 C 语言里面, 我们必须显示的初始化vptr。
下面就展示一下,在 Shape 的构造函数里面,如何去初始化这个 vptr。 #include "shape.h"
#include <assert.h> // Shape 的虚函数
static uint32_t Shape_area_(Shape const * const me);
static void Shape_draw_(Shape const * const me); // 构造函数
void Shape_ctor(Shape * const me, int16_t x, int16_t y)
{
// Shape 类的虚表
static struct ShapeVtbl const vtbl =
{
&Shape_area_,
&Shape_draw_
};
me->vptr = &vtbl;
me->x = x;
me->y = y;
} void Shape_moveBy(Shape * const me, int16_t dx, int16_t dy)
{
me->x += dx;
me->y += dy;
} int16_t Shape_getX(Shape const * const me)
{
return me->x;
}
int16_t Shape_getY(Shape const * const me)
{
return me->y;
} // Shape 类的虚函数实现
static uint32_t Shape_area_(Shape const * const me)
{
assert(); // 类似纯虚函数
return 0U; // 避免警告
} static void Shape_draw_(Shape const * const me)
{
assert(); // 纯虚函数不能被调用
} Shape const *largestShape(Shape const *shapes[], uint32_t nShapes)
{
Shape const *s = (Shape *);
uint32_t max = 0U;
uint32_t i;
for (i = 0U; i < nShapes; ++i)
{
uint32_t area = Shape_area(shapes[i]);// 虚函数调用
if (area > max)
{
max = area;
s = shapes[i];
}
}
return s;
} void drawAllShapes(Shape const *shapes[], uint32_t nShapes)
{
uint32_t i;
for (i = 0U; i < nShapes; ++i)
{
Shape_draw(shapes[i]); // 虚函数调用
}
}
注释比较清晰,这里不再多做解释。
4.3 继承 vtbl 和 重载 vptr
上面已经提到过,基类包含 vptr,子类会自动继承。但是,vptr 需要被子类的虚表重新赋值。并且,这也必须发生在子类的构造函数中。下面是 Rectangle 的构造函数。
#include "rect.h"
#include <stdio.h> // Rectangle 虚函数
static uint32_t Rectangle_area_(Shape const * const me);
static void Rectangle_draw_(Shape const * const me); // 构造函数
void Rectangle_ctor(Rectangle * const me, int16_t x, int16_t y,
uint16_t width, uint16_t height)
{
static struct ShapeVtbl const vtbl =
{
&Rectangle_area_,
&Rectangle_draw_
};
Shape_ctor(&me->super, x, y); // 调用基类的构造函数
me->super.vptr = &vtbl; // 重载 vptr
me->width = width;
me->height = height;
} // Rectangle's 虚函数实现
static uint32_t Rectangle_area_(Shape const * const me)
{
Rectangle const * const me_ = (Rectangle const *)me; //显示的转换
return (uint32_t)me_->width * (uint32_t)me_->height;
} static void Rectangle_draw_(Shape const * const me)
{
Rectangle const * const me_ = (Rectangle const *)me; //显示的转换
printf("Rectangle_draw_(x=%d,y=%d,width=%d,height=%d)\n",
Shape_getX(me), Shape_getY(me), me_->width, me_->height);
}
4.4 虚函数调用
有了前面虚表(Virtual Tables)和虚指针(Virtual Pointers)的基础实现,虚拟调用(后期绑定)就可以用下面代码实现了。
uint32_t Shape_area(Shape const * const me)
{
return (*me->vptr->area)(me);
}
这个函数可以放到.c文件里面,但是会带来一个缺点就是每个虚拟调用都有额外的调用开销。为了避免这个缺点,如果编译器支持内联函数(C99)。我们可以把定义放到头文件里面,类似下面:
static inline uint32_t Shape_area(Shape const * const me)
{
return (*me->vptr->area)(me);
}
如果是老一点的编译器(C89),我们可以用宏函数来实现,类似下面这样:
#define Shape_area(me_) ((*(me_)->vptr->area)((me_)))
1
看一下例子中的调用机制:
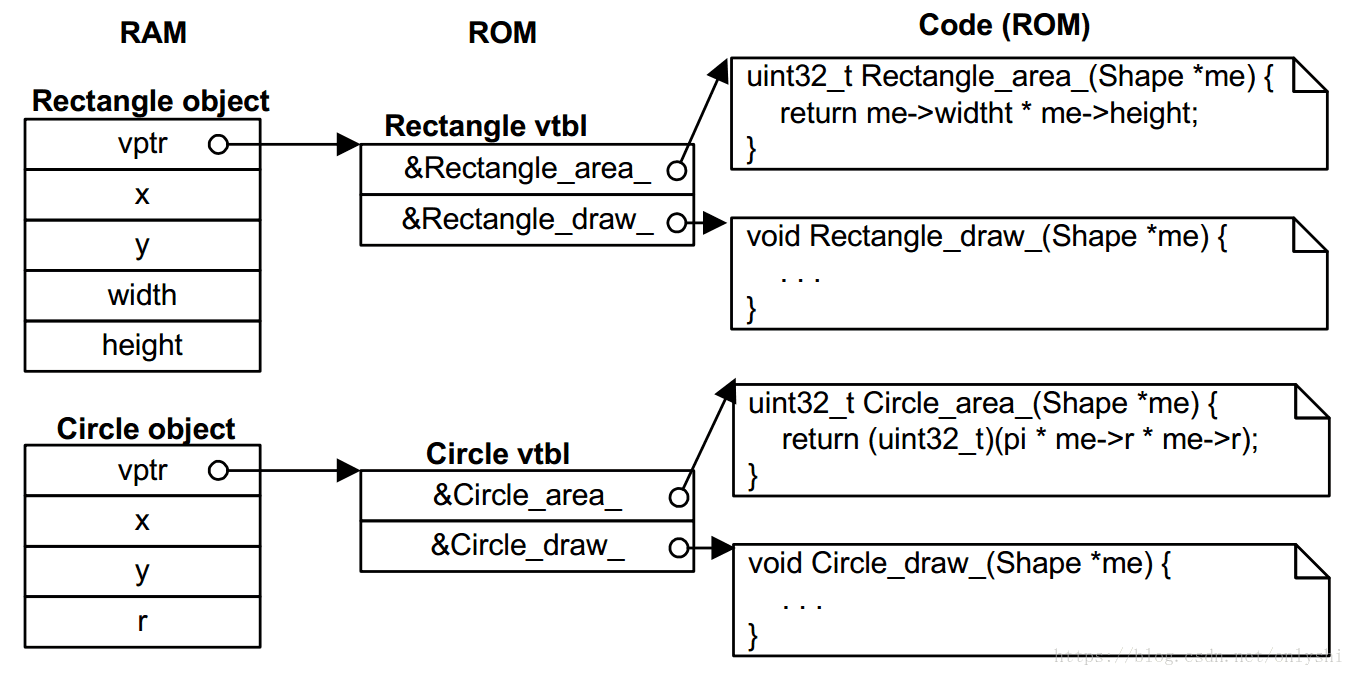
4.5 main.c
#include "rect.h"
#include "circle.h"
#include <stdio.h> int main()
{
Rectangle r1, r2;
Circle c1, c2;
Shape const *shapes[] =
{
&c1.super,
&r2.super,
&c2.super,
&r1.super
};
Shape const *s; // 实例化矩形对象
Rectangle_ctor(&r1, , , , );
Rectangle_ctor(&r2, -, , , ); // 实例化圆形对象
Circle_ctor(&c1, , -, );
Circle_ctor(&c2, , -, ); s = largestShape(shapes, sizeof(shapes)/sizeof(shapes[]));
printf("largetsShape s(x=%d,y=%d)\n", Shape_getX(s), Shape_getY(s)); drawAllShapes(shapes, sizeof(shapes)/sizeof(shapes[])); return ;
}
输出结果:
largetsShape s(x=1,y=-2)
Circle_draw_(x=1,y=-2,rad=12)
Rectangle_draw_(x=-1,y=3,width=5,height=8)
Circle_draw_(x=1,y=-3,rad=6)
Rectangle_draw_(x=0,y=2,width=10,height=15)
5、总结
还是那句话,面向对象编程是一种方法,并不局限于某一种编程语言。用 C 语言实现封装、单继承,理解和实现起来比较简单,多态反而会稍微复杂一点,如果打算广泛的使用多态,还是推荐转到 C++ 语言上,毕竟这层复杂性被这个语言给封装了,你只需要简单的使用就行了。但并不代表,C 语言实现不了多态这个特性。
C 语言实现面向对象编程的更多相关文章
- 基于C语言的面向对象编程
嵌入式软件开发中,虽然很多的开发工具已经支持C++的开发,但是因为有时考虑运行效率和编程习惯,还是有很多人喜欢用C来开发嵌入式软件.Miro Samek说:"我在开发现场发现,很多嵌入式软件 ...
- 一步步分析:C语言如何面向对象编程
这是道哥的第009篇原创 一.前言 在嵌入式开发中,C/C++语言是使用最普及的,在C++11版本之前,它们的语法是比较相似的,只不过C++提供了面向对象的编程方式. 虽然C++语言是从C语言发展而来 ...
- 真的可以啊,用C语言实现面向对象编程O O P!C语言真的无所不能~
解释区分一下C语言和OOP 我们经常说C语言是面向过程的,而C++是面向对象的,然而何为面向对象,什么又是面向过程呢?不管怎么样,我们最原始的目标只有一个就是实现我们所需要的功能,从这一点说它们是殊途 ...
- Python源代码 -- C语言实现面向对象编程(基类&派生类&多态)
背景 python是面向对象的解释性语言.然而python是通过C语言实现的,C语言怎么跟面向对象扯上了关系? C语言能够实现面向对象的性质? 原文链接:http://blog.csdn.net/or ...
- 真的可以,用C语言实现面向对象编程OOP
ID:技术让梦想更伟大 作者:李肖遥 解释区分一下C语言和OOP 我们经常说C语言是面向过程的,而C++是面向对象的,然而何为面向对象,什么又是面向过程呢?不管怎么样,我们最原始的目标只有一个就是实现 ...
- Objective-C语言介绍 、 Objc与C语言 、 面向对象编程 、 类和对象 、 属性和方法 、 属性和实例变量
1 第一个OC控制台程序 1.1 问题 Xcode是苹果公司向开发人员提供的集成开发环境(非开源),用于开发Mac OS X,iOS的应用程序.其运行于苹果公司的Mac操作系统下. 本案例要求使用集成 ...
- C语言进行面向对象编程
http://blog.csdn.net/dadalan/article/details/3983888 http://blog.163.com/zhqh43@126/blog/static/4043 ...
- c语言实现面向对象编程
1.通用校验器接口(validator.h) #ifndef VALIDATOR_H_INCLUDED #define VALIDATOR_H_INCLUDED #include<stdbool ...
- 云风:我所偏爱的C语言面向对象编程范式
面向对象编程不是银弹.大部分场合,我对面向对象的使用非常谨慎,能不用则不用.相关的讨论就不展开了. 但是,某些场合下,采用面向对象的确是比较好的方案.比如 UI 框架,又比如 3d 渲染引擎中的场景管 ...
随机推荐
- css实现梯形样式(含有border)
类似本文热门评论 效果 .hot-comment-title{ float:right; position:absolute; right: -8px; top: -30px; padding: 0; ...
- 《NVM-Express-1_4-2019.06.10-Ratified》学习笔记(5.23)-- Format NVM command
5.23 Format NVM command - NVM Command Set Specific Format NVM命令用于低级格式化NVM媒介.这个命令被host主机使用,来变更LBA数据大小 ...
- 微信小程序中如何上传图片
本篇文章给大家带来的内容是关于微信小程序中如何上传图片(代码示例),有一定的参考价值,有需要的朋友可以参考一下,希望对你有所帮助. 一.wxml文件 <text>上传图片</text ...
- C#调用WSDL接口
http://www.cnblogs.com/wlming/p/8032782.html
- How to read a paper efficiently - by prof. Pete carr
DON'T DO THAT: read the article from the beginning to end; it's a waste of time! READ A PAPER IN TWO ...
- Java连载84-Collection的常用方法、迭代器
一.Collections的常用方法介绍 1.承接上次连载,先介绍几个简单的常用方法 package com.bjpowernode.java_learning; import java.util.* ...
- pandas处理csv,分组统计
需求: /tmp/demo/data下有10个csv文件,按col0和col1分组分别统计col2和col3总和并计算col2和col3的商 # encoding:utf-8 import panda ...
- 简单的Spring1.0小配置
开始Spring AOP的小理解 拿一个小例子来说吧! 老师上课 这样的例子! 老师上课--就是一个核心的业务! 那么上课之前需要点名,天气太热,需要开空调! 这个时候,一个老 ...
- 算法竞赛入门经典第二版 蛇形填数 P40
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define maxn 20 int a[maxn][maxn]; int main(){ ; ...
- LED Craft Light - How To Solve: Home Decoration Lighting
Home décor usually comes with a certain period of theme or a specific style of furniture, which will ...
