【Hibernate】解析hibernate中的缓存
Hibernate中的缓存一共有三种,一级缓存、二级缓存、查询缓存。缓存除了使用Hibernate自带的缓存,还可以使用redis进行缓存,或是MongoDB进行缓存。
所使用的Demo:
User.java文件
- package cn.test.bean;
- import javax.persistence.Column;
- import javax.persistence.Entity;
- import javax.persistence.Id;
- import javax.persistence.Table;
- @Entity
- @Table(name="user")//表示对应的表名
- public class User {
- @Id
- @Column(name="uid")
- private int id;
- @Column(name="uname")
- private String name;
- @Column(name="upass")
- private String password;
- public int getId() {
- return id;
- }
- public void setId(int id) {
- this.id = id;
- }
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- public String getPassword() {
- return password;
- }
- public void setPassword(String password) {
- this.password = password;
- }
- }
User.java
hibernate.cfg.xml
- <?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
- <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
- "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
- "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
- <!-- Generated by MyEclipse Hibernate Tools. -->
- <hibernate-configuration>
- <session-factory>
- <property name="dialect">
- org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
- </property>
- <property name="connection.url">
- jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
- </property>
- <property name="connection.username">root</property>
- <property name="connection.password">517839</property>
- <property name="connection.driver_class">
- com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
- </property>
- <property name="show_sql">true</property>
- <property name="format_sql">true</property>
- <!-- 加载映射描述信息 -->
- <mapping class="cn.test.bean.User" />
- </session-factory>
- </hibernate-configuration>
hibernate.cfg.xml
其中:
- <property name="show_sql">true</property>
- <property name="format_sql">true</property>
表示开启打印底层执行的SQL日志。
下面这是图片反应了hibernate缓存的大致流程:
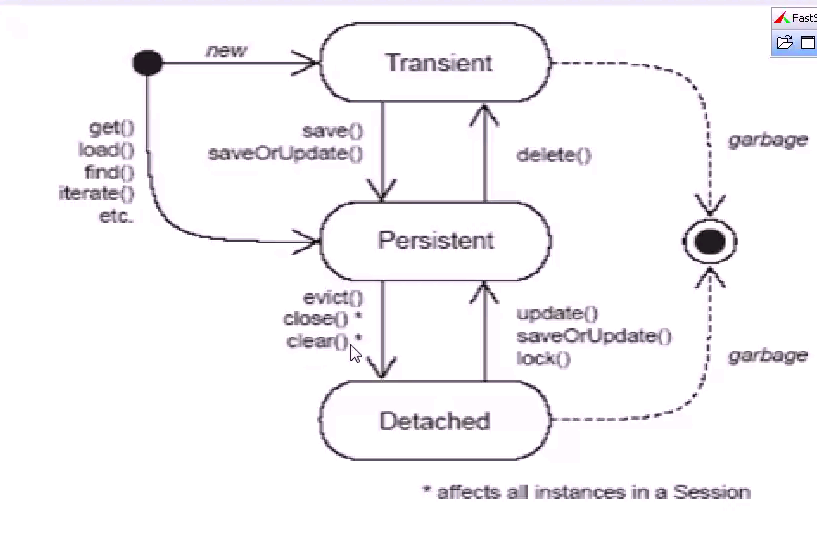
1,一级缓存
每个 Session 对象创建出来,就会分配一块缓存空间,可以存储 session 对象访问的对象信息。 session 关闭后会自动清除缓存,手动清除可以用session.clear() , session.evict(obj) 。 Session 一级缓存是独享。
load/get/save/update/saveorupdate 方法处理的对象都会放入缓存中
- Configuration conf = new Configuration();
- conf.configure("hibernate.cfg.xml");//读取连接参数和映射描述信息
- SessionFactory factory = conf.buildSessionFactory();
- Session session = factory.openSession();
- User user1 = (User)session.load(User.class,1);
- System.out.println(user1.getName());//honny,如果不调用用getName()方法,那么数据不会显示,因为load()默认使用的是一种延迟加载的机制,只有使用到数据的时候才会到数据库中查询
- //先从session缓存中查找,如果没找到再去数据库获取
- User user2 = (User)session.load(User.class,1);
- System.out.println(user2.getName());//honny
- System.out.println(user1==user2);//true,因为user1和user2使用的是同一个session
然后再来看一看控制台:

从控制台中,我们也可以看出上只执行了一次SQL查询。
一级查询的优缺点:
优点:可以减少查询数据库的次数,加快查询速度。
缺点:在批量操作中容易导致内存溢出问题。
2,二级缓存
二级缓存是SessionFactory 对象缓存,可以被创建出的多个 Session 对象共享。
下面是一张图片体现一级缓存和二级缓存的关系:
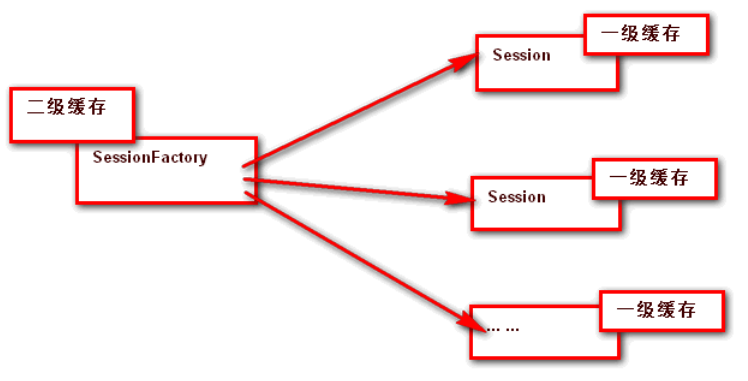
从这个我们就看出了二级缓存包含了一级缓存。
二级缓存默认是关闭的,如果要使用需要手动开启,下面是开启过程:
1.导入ehcache 工具包和 ehcache.xml 配置文件(配置文件放到src路径下)
echache工具包包括:ehcache-core-2.4.3.jar,hibernate-ehcache-4.2.21.Final.jar,slf4j-api-1.6.1.jar
ehcache.xml 文件
- <!--
- ~ Hibernate, Relational Persistence for Idiomatic Java
- ~
- ~ Copyright (c) 2007, Red Hat Middleware LLC or third-party contributors as
- ~ indicated by the @author tags or express copyright attribution
- ~ statements applied by the authors. All third-party contributions are
- ~ distributed under license by Red Hat Middleware LLC.
- ~
- ~ This copyrighted material is made available to anyone wishing to use, modify,
- ~ copy, or redistribute it subject to the terms and conditions of the GNU
- ~ Lesser General Public License, as published by the Free Software Foundation.
- ~
- ~ This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
- ~ but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY
- ~ or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
- ~ for more details.
- ~
- ~ You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
- ~ along with this distribution; if not, write to:
- ~ Free Software Foundation, Inc.
- ~ 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor
- ~ Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA
- -->
- <ehcache>
- <!-- Sets the path to the directory where cache .data files are created.
- If the path is a Java System Property it is replaced by
- its value in the running VM.
- The following properties are translated:
- user.home - User's home directory
- user.dir - User's current working directory
- java.io.tmpdir - Default temp file path -->
- <diskStore path="./target/tmp"/>
- <!--Default Cache configuration. These will applied to caches programmatically created through
- the CacheManager.
- The following attributes are required for defaultCache:
- maxInMemory - Sets the maximum number of objects that will be created in memory
- eternal - Sets whether elements are eternal. If eternal, timeouts are ignored and the element
- is never expired.
- timeToIdleSeconds - Sets the time to idle for an element before it expires. Is only used
- if the element is not eternal. Idle time is now - last accessed time
- timeToLiveSeconds - Sets the time to live for an element before it expires. Is only used
- if the element is not eternal. TTL is now - creation time
- overflowToDisk - Sets whether elements can overflow to disk when the in-memory cache
- has reached the maxInMemory limit.
- -->
- <defaultCache
- maxElementsInMemory="10000"
- eternal="false"
- timeToIdleSeconds="120"
- timeToLiveSeconds="120"
- overflowToDisk="true"
- />
- <!--Predefined caches. Add your cache configuration settings here.
- If you do not have a configuration for your cache a WARNING will be issued when the
- CacheManager starts
- The following attributes are required for defaultCache:
- name - Sets the name of the cache. This is used to identify the cache. It must be unique.
- maxInMemory - Sets the maximum number of objects that will be created in memory
- eternal - Sets whether elements are eternal. If eternal, timeouts are ignored and the element
- is never expired.
- timeToIdleSeconds - Sets the time to idle for an element before it expires. Is only used
- if the element is not eternal. Idle time is now - last accessed time
- timeToLiveSeconds - Sets the time to live for an element before it expires. Is only used
- if the element is not eternal. TTL is now - creation time
- overflowToDisk - Sets whether elements can overflow to disk when the in-memory cache
- has reached the maxInMemory limit.
- -->
- <!-- Sample cache named sampleCache1
- This cache contains a maximum in memory of 10000 elements, and will expire
- an element if it is idle for more than 5 minutes and lives for more than
- 10 minutes.
- If there are more than 10000 elements it will overflow to the
- disk cache, which in this configuration will go to wherever java.io.tmp is
- defined on your system. On a standard Linux system this will be /tmp"
- -->
- <cache name="sampleCache1"
- maxElementsInMemory="10000"
- eternal="false"
- timeToIdleSeconds="300"
- timeToLiveSeconds="600"
- overflowToDisk="true"
- />
- <!-- Sample cache named sampleCache2
- This cache contains 1000 elements. Elements will always be held in memory.
- They are not expired. -->
- <cache name="sampleCache2"
- maxElementsInMemory="1000"
- eternal="true"
- timeToIdleSeconds="0"
- timeToLiveSeconds="0"
- overflowToDisk="false"
- /> -->
- <!-- Place configuration for your caches following -->
- </ehcache>
ehcache.xml
2.在 hibernate.cfg.xml 中配置参数开启二级缓存,启用 ehcache
- <property name="hibernate.cache.use_sencond_level_cache">true</property>
- <property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class">
- org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.EhCacheRegionFactory
- </property>
3.在要缓存的对象类型中,指定 @Cache 注解标记
- @Entity
- @Table(name="user")//表示对应的表名
- @Cache(usage=CacheConcurrencyStrategy.READ_WRITE)
- public class User {
- //........
- }
到这里hibernate的二级缓存配置就配好了,下面来测试一下:
- Configuration conf = new Configuration();
- conf.configure("hibernate.cfg.xml");//读取连接参数和映射描述信息
- SessionFactory factory = conf.buildSessionFactory();
- Session session1 = factory.openSession();
- User user1=(User)session1.load(User.class, 1);
- System.out.println(user1.getName());//honny
- Session session2 = factory.openSession();
- //先从缓存中查找,如果没有查到再去数据库中取
- User user2=(User)session2.load(User.class, 1);
- System.out.println(user2.getName());//honny
下面是控制台打印的打印:

我们可以看出,用同一个SessionFactory的两个不同session对象查询相同的数据,只从数据库中取了一次。
3,查询缓存
一级和二级缓存,只能缓存单个对象,如果需要缓存一个结果集,必须使用查询缓存。
查询缓存默认也是关闭的,如需使用需要手动开启,下面是开启过程:
1.针对的对象必需已经开启了二级缓存
2.在 hibernate.cfg.xml 中添加开启查询缓存的配置
- <property name="hibernate.cache.use_query_cache">true</property>
3.在查询执行前,调用 query.setCacheable(true);
下面看一看测试:
- String hql="from User";
- Configuration conf=new Configuration();
- conf.configure("hibernate.cfg.xml");
- SessionFactory factory=conf.buildSessionFactory();
- Session session1 = factory.openSession();
- Query query1 = session1.createQuery(hql);
- query1.setCacheable(true);//设置开启缓存
- List list1 = query1.list();
- for(Object user:list1){
- System.out.println(((User)user).getName());
- }
- System.out.println("------------------------");
- Session session2 = factory.openSession();
- Query query2 = session2.createQuery(hql);
- query2.setCacheable(true);
- List list2 =query2.list();
- for(Object user:list2){
- System.out.println(((User)user).getName());
- }
然后来看一看控制台:

从控制台中,我们可以看出,底层查询的数据库的过程也只执行了一次。
上面就是hibernate的三种缓存。最后总结一下,并不是所有的方法都会产生缓存效果,只有“load/get/save/update/saveorupdate”才会产生缓存效果。三种缓存中一级缓存是默认开启的,二级缓存和三级缓存默认是关闭的。
【Hibernate】解析hibernate中的缓存的更多相关文章
- 分享知识-快乐自己:论Hibernate中的缓存机制
Hibernate缓存 缓存: 是计算机领域的概念,它介于应用程序和永久性数据存储源之间. 缓存: 一般人的理解是在内存中的一块空间,可以将二级缓存配置到硬盘.用白话来说,就是一个存储数据的容器.我们 ...
- Hibernate中一级缓存和二级缓存使用详解
一.一级缓存二级缓存的概念解释 (1)一级缓存就是Session级别的缓存,一个Session做了一个查询操作,它会把这个操作的结果放在一级缓存中,如果短时间内这个 session(一定要同一个ses ...
- [原理][源代码解析]spring中@Transactional,Propagation.SUPPORTS,以及 Hibernate Session,以及jdbc Connection关系---转载
问题: 一. 1. Spring 如何处理propagation=Propagation.SUPPORTS? 2. Spring 何时生成HibernateSession ? 3. propagati ...
- hibernate中的缓存机制
一.为什么要用Hibernate缓存? Hibernate是一个持久层框架,经常访问物理数据库. 为了降低应用程序对物理数据源访问的频次,从而提高应用程序的运行性能. 缓存内的数据是对物理数据源中的数 ...
- hibernate中的缓存问题与快照机制
1. 什么是缓存 数据存储到数据库里面,数据库本身是一个文件系统,使用流方式操作文件(效率不高) 改进方式:把数据存到内存中,不需要使用流方式,可以直接读取内存中的数据 缓存:内存中的临时数据,当内 ...
- Hibernate中一级缓存和二级缓存
缓存是介于应用程序和物理数据源之间,其作用是为了降低应用程序对物理数据源访问的频次,从而提高了应用的运行性能.缓存内的数据是对物理数据源中的数据的复制,应用程序在运行时从缓存读写数据,在特定的时刻或事 ...
- Hibernate 中一级缓存和快照区的理解
刚刚开始的时候觉得这个快照区很难理解,在网上看了很多博客之后,开始明白了.我是结合 ADO.NET 理解的,在ADO.NET 中有一个类, 叫 SqlCommandBuilder,在我看来,他就是 A ...
- Hibernate中"二级缓存"配置
实体类 : package cn.happy.entity; public class Emp { private Integer empNo; private String empName; pub ...
- Hibernate中二级缓存指的是什么?
一.一级缓存.二级缓存的概念解释 (1)一级缓存就是Session级别的缓存,一个Session做了一个查询操作,它会把这个操作的结果放在一级缓存中,如果短时间内这个 session(一定要同一个se ...
随机推荐
- docker service ps打印出来的错误信息被截断了怎么办?
[解决方法] 用Format属性: 这个其实解决不了截断的问题,不过可以显示更少的列,看起来更清楚. Formatting The formatting options (--format) pr ...
- HighCharts设置图表背景透明
其实就一句话: backgroundColor: 'rgba(0,0,0,0)' 完整示例: $(function () { $('#container').highcharts({ chart: { ...
- DISQLite3在XE4中的安装
时隔这么久,因为工作中需要将一些图片序列文件进行分析,然后将结果进行分组统计,而分组统计用SQL语法很容易实现,但是要求程序运行的环境中安装有庞大的数据库系统,经过网上的寻找,终于发现了SQLite. ...
- Direct2D教程IV——笔刷(Brush)对象
目前博客园中成系列的Direct2D的教程有 1.万一的 Direct2D 系列,用的是Delphi 2009 2.zdd的 Direct2D 系列,用的是VS中的C++ 3.本文所在的 Direct ...
- maven 下载源码downloadsources
mvn eclipse:eclipse -Ddownloadsources=true -Ddownloadjavadocs=true
- Spring Boot中Starter是什么
比如我们要在Spring Boot中引入Web MVC的支持时,我们通常会引入这个模块spring-boot-starter-web,而这个模块如果解压包出来会发现里面什么都没有,只定义了一些POM依 ...
- 【Ubuntu】Ubuntu网络配置DNS失效问题处理
安装了Ubuntu Server版本,配置了静态IP地址,并配置了DNS.但重启之后,发现连接外网时候,还是存在问题. 找了一下,是DNS的问题. 可以这样处理: lifeccp@ubuntu:~/w ...
- 微软BI 之SSRS 系列 - 使用 LookupSet 和 Adjacent Group 等高级技巧在报表中跨 Dataset 分组查询
SSRS 报表中有一些高级的技巧,平常很少用到,下面我通过这个案例来展现一下如何在实际开发中使用它们,并且如何解决一些实际的需求. 这张报表分别统计了不同的 Product 产品在不同的月份的 Ord ...
- 学习 Linux,302(混合环境): Samba 角色
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/l-lpic3-310-2/ 概述 在本文中,了解下列概念: Samba 安全模式 核心 Samba 守护程序的角 ...
- Python+OpenCV实现FasterRcnn样本查看器
一.上代码 import cv2 import os def get_samples(dir): datasets = [] files = os.listdir(dir) for file in f ...
