[js高手之路]打造通用的匀速运动框架
本文,是接着上文[js高手之路]匀速运动与实例实战(侧边栏,淡入淡出)继续的,在这篇文章的最后,我们做了2个小实例:侧边栏与改变透明度的淡入淡出效果,本文我们把上文的animate函数,继续改造,让他变得更加的通用和强大:
1,支持多个物体的运动
2,同时运动
3,顺序运动
这三种运动方式也是jquery中animate函数支持的
一、animate函数中怎么区分变化不同的样式?
上文中,侧边栏效果 用的animate函数 改变的是left值
function animate(obj, target, speed) {
clearInterval(timer);
timer = setInterval(function () {
if (obj.offsetLeft == target) {
clearInterval(timer);
} else {
obj.style.left = obj.offsetLeft + speed + 'px';
}
}, 30);
}
淡入淡出效果 用的animate函数 改变的是透明度
function animate(obj, target, speed) {
clearInterval(timer);
var cur = 0;
timer = setInterval(function () {
cur = css( obj, 'opacity') * 100;
if( cur == target ){
clearInterval( timer );
}else {
cur += speed;
obj.style.opacity = cur / 100;
obj.style.filter = "alpha(opacity:" + cur + ")";
}
}, 30);
}
而我们封装的函数,要变成通用的,首先面临的问题就是 这个函数要同时支持left值和透明度的变化,更通用的做法应该是要支持所有的样式变化,比如轮播功能,他有左右滑动,也有上下滑动。
我们可以在获取样式和改变样式的时候,做一下判断就可以了,判断分2类就能达到目的,因为其他样式( margin, left, top, right, font-size等等 )都是px,而透明度没有px单位
function animate(obj, attr, target, speed) {
clearInterval(timer);
var cur = 0;
timer = setInterval(function () {
if (attr == 'opacity') {
cur = css(obj, 'opacity') * 100;
} else {
cur = parseInt(css(obj, attr));
}
if (cur == target) {
clearInterval(timer);
} else {
if (attr == 'opacity') {
obj.style.opacity = ( cur + speed ) / 100;
obj.style.filter = "alpha(opacity:" + (cur + speed) + ")";
} else {
obj.style[attr] = cur + speed + "px";
}
}
}, 30);
}
合并之后的animate相比之前多了一个参数attr, 这个参数就是变化的样式,obj: 变化的对象, target: 样式需要变化到的目标值. speed: 样式每次变化的大小
如:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>合并的运动 - by ghostwu</title>
<style>
img {
border: none;
opacity: 0.3;
filter: alpha(opacity:30);
position: absolute;
left: 200px;
} #box {
width: 150px;
height: 300px;
background: red;
position: absolute;
left: -150px;
top: 50px;
} #box div {
width: 28px;
height: 100px;
position: absolute;
right: -28px;
top: 100px;
background: green;
}
</style>
<script>
window.onload = function () {
var oImg = document.getElementById("img"),
oBox = document.getElementById("box"),
timer = null; oImg.onmouseover = function () {
animate(this, 'opacity', 100, 10);
}
oImg.onmouseout = function () {
animate(this, 'opacity', 30, -10);
} oBox.onmouseover = function () {
animate(this, 'left', 0, 10);
} oBox.onmouseout = function () {
animate(this, 'left', -150, -10);
} function animate(obj, attr, target, speed) {
clearInterval(timer);
var cur = 0;
timer = setInterval(function () {
if (attr == 'opacity') {
cur = css(obj, 'opacity') * 100;
} else {
cur = parseInt(css(obj, attr));
} if (cur == target) {
clearInterval(timer);
} else {
if (attr == 'opacity') {
obj.style.opacity = ( cur + speed ) / 100;
obj.style.filter = "alpha(opacity:" + (cur + speed) + ")";
} else {
obj.style[attr] = cur + speed + "px";
}
}
}, 30);
} function css(obj, attr) {
if (obj.currentStyle) {
return obj.currentStyle[attr];
} else {
return getComputedStyle(obj, false)[attr];
}
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<div>分享到</div>
</div>
<img src="./img/h4.jpg" alt="" id="img"/>
</body>
</html>
上述就是完整的代码实例,请自行展开,点击run code预览效果
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
img {
border: none;
opacity: 0.3;
filter: alpha(opacity:30);
position: absolute;
left: 200px;
}
#box {
width: 150px;
height: 300px;
background: red;
position: absolute;
left: -150px;
top: 50px;
}
#box div {
width: 28px;
height: 100px;
position: absolute;
right: -28px;
top: 100px;
background: green;
}
</style>
<script>
window.onload = function () {
var oImg = document.getElementById("img"),
oBox = document.getElementById("box"),
timer = null;
oImg.onmouseover = function () {
animate(this, 'opacity', 100, 10);
}
oImg.onmouseout = function () {
animate(this, 'opacity', 30, -10);
}
oBox.onmouseover = function () {
animate(this, 'left', 0, 10);
}
oBox.onmouseout = function () {
animate(this, 'left', -150, -10);
}
function animate(obj, attr, target, speed) {
clearInterval(timer);
var cur = 0;
timer = setInterval(function () {
if (attr == 'opacity') {
cur = css(obj, 'opacity') * 100;
} else {
cur = parseInt(css(obj, attr));
}
if (cur == target) {
clearInterval(timer);
} else {
if (attr == 'opacity') {
obj.style.opacity = ( cur + speed ) / 100;
obj.style.filter = "alpha(opacity:" + (cur + speed) + ")";
} else {
obj.style[attr] = cur + speed + "px";
}
}
}, 30);
}
function css(obj, attr) {
if (obj.currentStyle) {
return obj.currentStyle[attr];
} else {
return getComputedStyle(obj, false)[attr];
}
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<div>分享到</div>
</div>
<img src="http://images2017.cnblogs.com/blog/253192/201710/253192-20171015095909480-1867777993.png" alt="" id="img"/>
</body>
</html>
run code
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
img {
border: none;
opacity: 0.3;
filter: alpha(opacity:30);
position: absolute;
left: 200px;
} #box {
width: 150px;
height: 300px;
background: red;
position: absolute;
left: -150px;
top: 50px;
} #box div {
width: 28px;
height: 100px;
position: absolute;
right: -28px;
top: 100px;
background: green;
}
</style>
<script>
window.onload = function () {
var oImg = document.getElementById("img"),
oBox = document.getElementById("box"); oImg.onmouseover = function () {
animate(this, 'opacity', 100, 10);
}
oImg.onmouseout = function () {
animate(this, 'opacity', 30, -10);
} oBox.onmouseover = function () {
animate(this, 'left', 0, 10);
} oBox.onmouseout = function () {
animate(this, 'left', -150, -10);
} function animate(obj, attr, target, speed) {
clearInterval(obj.timer);
var cur = 0;
obj.timer = setInterval(function () {
if (attr == 'opacity') {
cur = css(obj, 'opacity') * 100;
} else {
cur = parseInt(css(obj, attr));
} if (cur == target) {
clearInterval(obj.timer);
} else {
if (attr == 'opacity') {
obj.style.opacity = ( cur + speed ) / 100;
obj.style.filter = "alpha(opacity:" + (cur + speed) + ")";
} else {
obj.style[attr] = cur + speed + "px";
}
}
}, 30);
} function css(obj, attr) {
if (obj.currentStyle) {
return obj.currentStyle[attr];
} else {
return getComputedStyle(obj, false)[attr];
}
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<div>分享到</div>
</div>
<img src="./img/h4.jpg" alt="" id="img"/>
</body>
</html>
至此,我们就完成了多物体运动与不同样式的修改
二、让animate函数支持多个样式同时改变
比如:
oBox.onmouseover = function(){
animate( this, { "width" : 500, "height" : 400 }, 10 );
}
oBox是一个div元素,animate各参数的意思:
this: 当前div元素
{width : 500, "height" : 400 } : 把宽度变成500, 高度变成400,这两个样式要在同一时间完成,
10: 样式每次在原来的基础上变化10(如width初始值200--> 210, 220, 230.....)
完整的同时运动变化 代码:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: red;
}
</style>
<script>
window.onload = function () {
var oBox = document.getElementById("box");
oBox.onmouseover = function(){
// animate( this, { "width" : 500, "height" : 500 }, 10 );
animate( this, { "width" : 500, "height" : 400 }, 10 );
} function animate(obj, attr, speed) {
clearInterval(obj.timer);
var cur = 0;
obj.timer = setInterval(function () {
for ( var key in attr ) {
if (key == 'opacity') {
cur = css(obj, 'opacity') * 100;
} else {
cur = parseInt(css(obj, key));
}
var target = attr[key];
if (cur == target) {
clearInterval(obj.timer);
} else {
if (key == 'opacity') {
obj.style.opacity = ( cur + speed ) / 100;
obj.style.filter = "alpha(opacity:" + (cur + speed) + ")";
} else {
obj.style[key] = cur + speed + "px";
}
}
}
}, 30);
} function css(obj, attr) {
if (obj.currentStyle) {
return obj.currentStyle[attr];
} else {
return getComputedStyle(obj, false)[attr];
}
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box"></div>
</body>
</html>
请自行展开这段代码,这段代码能够同时运动,但是有一个问题:
div的初始宽度与高度( width : 200, height : 200)
变化步长一样( 10 )
变化时间一样( 每30毫秒变化一次 )
目标( width: 500, height : 400 )
你能想到什么问题吗?( 两个人在同一起跑线上,速度一样, 时间一样,但是要同时到达不同的目标,一个500, 一个400 )
答案是很明显的,肯定是目标近的( height : 400 )那个先到达,然后把对象上的定时器关了,另一个目标更远的( width: 500 )肯定到达不了
你可以在这句代码下面,输出当前的值和目标值:
输出来的结果是:
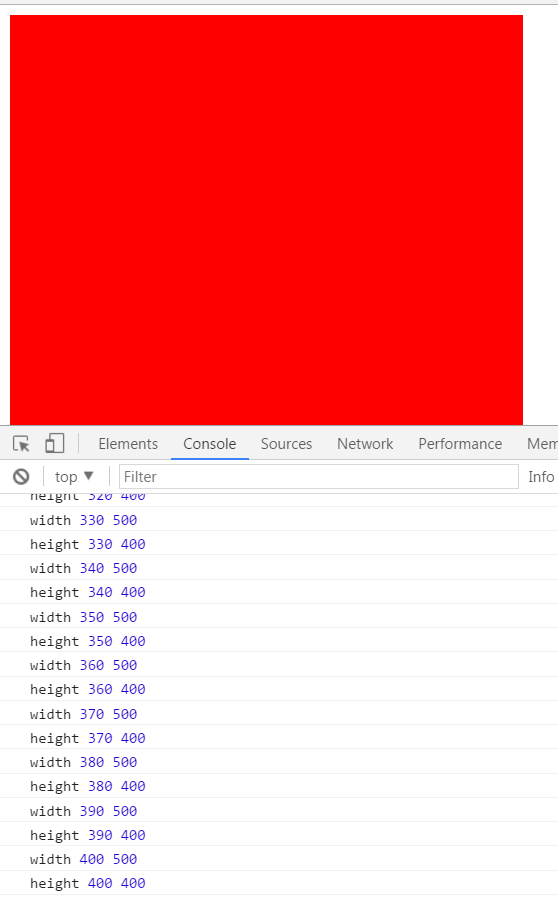
从上图可以看出,height已经达到了400px,但是width停在了410px,为什么不是400px ? 因为width = 400的时候, 就是( cur == 500 ) 相当于( 400 == 500 ) 不成立,所以执行了else语句,width = cur + 10 = 400 + 10 = 410,然后height到达400px停止了定时器,所以width停在了410px.
那么我们怎么解决这个问题呢?
其实也好办,就是height = 400的时候 不要把定时器关了,应该等width = 500的时候再关闭定时器,不就在同一时间,完成了同时到达目标的效果吗?
修改后的代码如下:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: red;
}
</style>
<script>
window.onload = function () {
var oBox = document.getElementById("box");
oBox.onmouseover = function(){
animate( this, { "width" : 500, "height" : 400 }, 10 );
} function animate(obj, attr, speed) {
clearInterval(obj.timer);
var cur = 0;
obj.timer = setInterval(function () {
var bFlag = true;
for ( var key in attr ) {
if (key == 'opacity') {
cur = css(obj, 'opacity') * 100;
} else {
cur = parseInt(css(obj, key));
}
var target = attr[key];
if (cur != target) {
bFlag = false;
if (key == 'opacity') {
obj.style.opacity = ( cur + speed ) / 100;
obj.style.filter = "alpha(opacity:" + (cur + speed) + ")";
} else {
obj.style[key] = cur + speed + "px";
}
}
}
if ( bFlag ) {
clearInterval( obj.timer );
}
}, 30);
} function css(obj, attr) {
if (obj.currentStyle) {
return obj.currentStyle[attr];
} else {
return getComputedStyle(obj, false)[attr];
}
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box"></div>
</body>
</html>
声明一个变量,每次变化完一次( width, height )样式 把bFlag = true, 只要在for循环中有一个没有到达目标,bFlag的值都是false,这样就不会关闭定时器。当两个都到达目标,才关闭定时器.
三、顺序运动
如样式变化,按顺序来,不是同时变化, 如:
oBox.onmouseover = function(){
//回调函数: 把函数当做参数传递给另一个函数
animate( this, { 'width' : 500 }, 10, function(){
animate( this, { 'height' : 500 }, 10 );
} );
}
当把width变成500px的时候,如果传递了回调函数, 再接着执行回调函数里面的运动
修改后的完整代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head lang="en">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>通用的匀速运动框架 - by ghostwu</title>
<style>
div {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: red;
}
</style>
<script>
window.onload = function () {
var oBox = document.getElementById("box");
oBox.onmouseover = function(){
//回调函数: 把函数当做参数传递给另一个函数
animate( this, { 'width' : 500 }, 10, function(){
animate( this, { 'height' : 500 }, 10 );
} );
} function animate(obj, attr, speed, fn ) { clearInterval(obj.timer);
var cur = 0;
obj.timer = setInterval(function () {
var bFlag = true;
for (var key in attr) {
if (key == 'opacity') {
cur = css(obj, 'opacity') * 100;
} else {
cur = parseInt(css(obj, key));
}
var target = attr[key];
if (cur != target) {
bFlag = false;
if (key == 'opacity') {
obj.style.opacity = ( cur + speed ) / 100;
obj.style.filter = "alpha(opacity:" + (cur + speed) + ")";
} else {
obj.style[key] = cur + speed + "px";
}
}
} if (bFlag) {
clearInterval(obj.timer);
fn && fn.call( obj );
}
}, 30);
} function css(obj, attr) {
if (obj.currentStyle) {
return obj.currentStyle[attr];
} else {
return getComputedStyle(obj, false)[attr];
}
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box"></div>
</body>
</html>
[js高手之路]打造通用的匀速运动框架的更多相关文章
- [js高手之路] 我的开源javascript框架gdom - 选择器用法
gdom框架是我开发的一款dom和字符串处理框架,目前版本是1.0.0. 使用方法跟jquery是差不多的, 会用jquery就会用gdom,目前 1.0.0版本的选择器完全支持CSS3选择器.没有做 ...
- [js高手之路]面向对象版本匀速运动框架
这篇文章的效果,需要看过以下3篇文章: [js插件开发教程]一步步开发一个可以定制配置的隔行变色小插件 [js高手之路]匀速运动与实例实战(侧边栏,淡入淡出) [js高手之路]打造通用的匀速运动框架 ...
- [js高手之路]封装运动框架实战左右与上下滑动的焦点轮播图
在这篇文章[js高手之路]打造通用的匀速运动框架中,封装了一个匀速运动框架,我们在这个框架的基础之上,加上缓冲运动效果,然后用运动框架来做幻灯片(上下,左右),效果如下: 1 2 3 4 5 // 0 ...
- [js高手之路]深入浅出webpack教程系列4-插件使用之html-webpack-plugin配置(上)
还记得我们上文中的index.html文件吗? 那里面的script标签还是写死的index.bundle.js文件,那么怎么把他们变成动态的index.html文件,这个动态生成的index.htm ...
- [js高手之路]Node.js实现简易的爬虫-抓取博客文章列表信息
抓取目标:就是我自己的博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/ghostwu/ 需要实现的功能: 抓取文章标题,超链接,文章摘要,发布时间 需要用到的库: node.js自带的http库 ...
- [js高手之路]html5 canvas动画教程 - 边界判断与小球粒子模拟喷泉,散弹效果
备注:本文后面的代码,如果加载了ball.js,那么请使用这篇文章[js高手之路] html5 canvas动画教程 - 匀速运动的ball.js代码. 本文,我们要做点有意思的效果,首先,来一个简单 ...
- [js高手之路]html5 canvas动画教程 - 边界判断与反弹
备注:本文后面的代码,如果加载了ball.js,那么请使用这篇文章[js高手之路] html5 canvas动画教程 - 匀速运动的ball.js代码. 边界反弹: 当小球碰到canvas的四个方向的 ...
- [js高手之路]Node.js实现简易的爬虫-抓取博客所有文章列表信息
抓取目标:就是我自己的博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/ghostwu/ 需要实现的功能: 抓取博客所有的文章标题,超链接,文章摘要,发布时间 需要用到的库: node.js自带的h ...
- [js高手之路] es6系列教程 - 对象功能扩展详解
第一:字面量对象的方法,支持缩写形式 //es6之前,这么写 var User = { name : 'ghostwu', showName : function(){ return this.nam ...
随机推荐
- easyUI创建人员树
最近做了一个树状的下拉列表,在这里记录一下,以后可以直接使用 项目中的树状下拉列表是用来选择人员用的,具体实现展示如下: 先说一说功能,左边的人员数是提供选人的,当点击中间的按钮,选中的人员会直接移到 ...
- FormData 上传多种格式的文件
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/ ...
- 201521123067 《Java程序设计》第8周学习总结
201521123067 <Java程序设计>第8周学习总结 1. 本周学习总结 1.1 以你喜欢的方式(思维导图或其他)归纳总结集合与泛型相关内容. 2. 书面作业 Q1.List中指定 ...
- JS运动缓冲的封装函数
之前经常写运动函数,要写好多好多,后来想办法封装起来.(运动缓冲). /* 物体多属性同时运动的函数 obj:运动的物体 oTarget:对象,属性名为运动的样式名,属性值为样式运动的终点值 rati ...
- 安装wampserve之前需要安装vc++2012.
本人是64位系统下载了wampserver3.0.6之后安装好,启动报错缺少msvcr110.dll. 于是从网上下载了msvcr110.dll放到了windows的syswow64文件夹下,甚至还重 ...
- Python爬虫总结
Python爬虫的原理:1通过URLopen()来获取到url页面, 这个过程可以加代理 2这个页面上都是字符串,所以我们而通过字符串查找的方法来获取到目标字符串,用到了正则来匹配目标re.finda ...
- JavaScript总体的介绍【JavaScript介绍、定义函数方式、对象类型、变量类型】
什么是JavaScript? 我们可以从几个方面去说JavaScript是什么: 基于对象 javaScript中内置了许多对象供我们使用[String.Date.Array]等等 javaScrip ...
- OSGi-开发环境的建立和HelloWorld(04)
1 OSGi开发环境的建立 1.1 Equinox是什么 从代码角度来看,Equinox其实就是OSGi核心标准的完整实现,并且还在这个基础上增加了一些额外的功能(比如为框架增加了命令行和程序执行的入 ...
- 编译Linux-4.9.9内核流程记录
本文部分资料出自: http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaocen/p/3717993.html 首先下载代码: https://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/ker ...
- PuTsangTo-单撸游戏开发02 测试场景与单轴移动
且不说立项与设计阶段的工作量,一个完整的游戏在开发阶段设计的职责范围也是很广,还有个大问题就是PuTsangTo项目也是本人在边学边做,截止目前还是满满的无从下手的感觉,一方面是技能与经验不足,另一方 ...
