A Beginner’s Guide to the OUTPUT Clause in SQL Server
原文 A Beginner’s Guide to the OUTPUT Clause in SQL Server
T-SQL supports the OUTPUT clause after the inception of SQL server 2005 and later editions. We can use the OUTPUT clause with DML statements (INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE) to return information from modified rows.
We primarily use the OUTPUT clause for auditing and archiving modified rows. In this tutorial, we will walk through the use of the OUTPUT clause with different DML statements and examples. First, we will create a table, dbo.Songs, and populate it with some data.
IF OBJECT_ID('dbo.Songs') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE dbo.Songs
GO
CREATE TABLE dbo.Songs
(
Id int CONSTRAINT PK_Songs_Id PRIMARY KEY,
Name varchar(200) NOT NULL,
Singer varchar(50) NOT NULL
)
GO
INSERT INTO dbo.Songs ( Id, Name, Singer)
VALUES (1, 'I hate everything about you', 'Adam Gontier');
INSERT INTO dbo.Songs ( Id, Name, Singer) VALUES (2, 'Dil se', 'A. R. Rahman');
INSERT INTO dbo.Songs ( Id, Name, Singer) VALUES
(3, 'My heart will go On', 'Celine Dion');
INSERT INTO dbo.Songs ( Id, Name, Singer) VALUES (4, 'Maeri', 'Euphoria');
GO
SELECT * from dbo.Songs
GO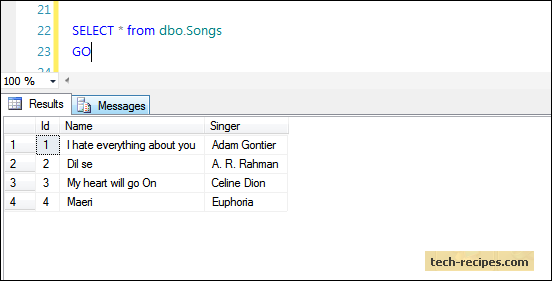
Inserted and Deleted Tables in an OUTPUT Clause
Inserted and Deleted tables are two memory-resident tables that reside within SQL server and are used with the OUTPUT clause.
Whenever any DML (INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE) statement is executed, these tables are populated.
The results of the INSERT statement are stored in the Inserted table, and the results of the Delete statement are stored in the Deleted table. Also, with an UPDATE statement, the deleted rows are stored in the Deleted table. The new inserted rows in the Inserted table as UPDATE are nothing but delete and insert operations combined together.
Note: You cannot directly query Inserted and Deleted tables to see what data they are currently holding, but you can use them with the OUTPUT clause as well as with Triggers.
The OUTPUT Clause with an Insert statement
When we do an Insert operation on a table, we get a message which reads, “(n row(s) affected),” but if we want to see what data rows were inserted into a table, we can use an OUTPUT clause and a memory resident inserted table to return the results back to the screen in the same way that a select statement does.
Let us insert a record, and use an OUTPUT clause to print the results on the screen.
INSERT INTO dbo.Songs ( Id, Name, Singer)
OUTPUT INSERTED.ID, INSERTED.name, INSERTED.Singer
VALUES (5, 'AINT no grave', 'Johnny Cash');
GOCheck the dbo.Songs table. A new row is inserted with id=5.
select * from dbo.Songs;
GO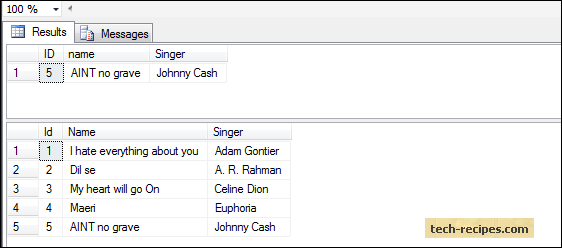
The OUTPUT Clause with a Delete Statement
The same goes with a delete operation. It shows only (n rows(s) affected). We can use an OUTPUT clause and a deleted table to see which rows were actually deleted from the table.
DELETE from dbo.Songs
OUTPUT DELETED.id, DELETED.name, DELETED.singer
WHERE ID=5;
GOQuery the dbo.Songs table row with id = 5 has been deleted.
select * from dbo.Songs;
GO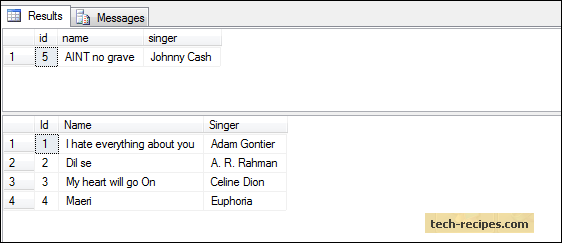
The OUTPUT Clause with an Update Statement
An Update statement does nothing but delete old data and insert new data, so with an Update statement, both memory resident tables are affected and are deleted as well as inserted.
Here we are updating the name of a singer, who has sung ‘Dil se’ song, with ID equal to two.
UPDATE dbo.Songs
SET Singer = 'Rahman'
OUTPUT DELETED.Singer, INSERTED.Singer
WHERE ID = 2;
GOYou can see the old singer’s name along with the new singer’s name.
select * from dbo.Songs;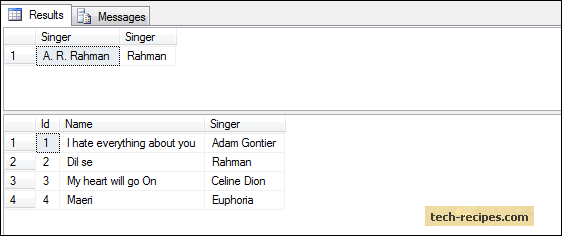
The three examples above show how to use an OUTPUT clause for auditing purposes. Now, we will see how to use it for archiving.
Before, we were just printing the results of a DML statement on the screen, which was temporary, but with the OUTPUT clause, you can store the results of a DML statement in a table, too.
Store Results of an OUTPUT Clause into a Table
Inserting the data return from an OUTPUT clause into a table can be done using an OUTPUT INTO clause. Keep in mind that you first need to create the target table which must have the same number of columns and data types that match the source table.
IF OBJECT_ID('dbo.Songs_Inserted') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE dbo.Songs_Inserted
GO
CREATE TABLE dbo.Songs_Inserted
(
Id int CONSTRAINT PK_Songs__Inserted_Id PRIMARY KEY,
Name varchar(200) NOT NULL,
Singer varchar(50) NOT NULL
)
GO
INSERT INTO dbo.Songs ( Id, Name, Singer)
OUTPUT Inserted.* INTO dbo.Songs_Inserted
VALUES (5, 'Duniya', 'Piyush Mishra');
GO
-- Result of Songs_Inserted table and base table.
select * from dbo.Songs_Inserted;
select * from dbo.Songs;
GO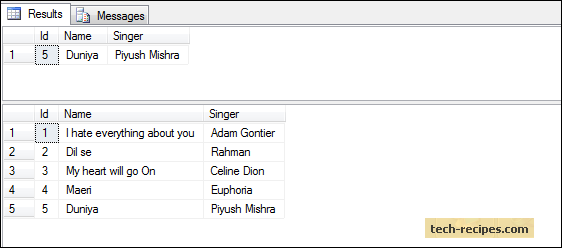
As the results above show, data is inserted into both the tables.
Store Results of an OUTPUT Clause into a Temporary Table
The same goes with a temporary table. Create a temporary table first, and then using an OUTPUT INTO clause, insert the data returned by the OUTPUT clause into a temporary table.
IF OBJECT_ID('tempdb..#Songs_Deleted') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE dbo.#Songs_Deleted
GO
CREATE TABLE dbo.#Songs_Deleted
(
Id int,
Name varchar(200) NOT NULL,
Singer varchar(50) NOT NULL
)
GO
DELETE from dbo.Songs
OUTPUT deleted.* INTO dbo.#Songs_Deleted
WHERE ID IN (4,5);
GO
-- Result of temporary table and base table.
SELECT * from dbo.#Songs_Deleted;
Select * from dbo.Songs;
Store Results of an OUTPUT Clause into a Table Variable
Nothing changes for table variables as well. Declare a table variable structure the same as a source table. Do not forget to run the entire script at once so that you can see the output inserted into a table variable.
Declare @Songs_Deleted TABLE
(
Id int,
Name varchar(200) NOT NULL,
Singer varchar(50) NOT NULL
)
DELETE from dbo.Songs
OUTPUT deleted.* INTO @Songs_Deleted
WHERE ID IN (1,2);
-- Result of table variable
SELECT * from @Songs_Deleted;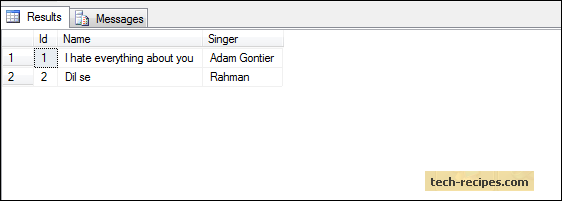
Browse through our SQL server archive articles for more useful information.
A Beginner’s Guide to the OUTPUT Clause in SQL Server的更多相关文章
- Guide to Database Migration from Microsoft SQL Server using MySQL Workbench
http://mysqlworkbench.org/2012/07/migrating-from-ms-sql-server-to-mysql-using-workbench-migration-wi ...
- A Beginner's Guide To Understanding Convolutional Neural Networks(转)
A Beginner's Guide To Understanding Convolutional Neural Networks Introduction Convolutional neural ...
- (转)A Beginner's Guide To Understanding Convolutional Neural Networks Part 2
Adit Deshpande CS Undergrad at UCLA ('19) Blog About A Beginner's Guide To Understanding Convolution ...
- (转)A Beginner's Guide To Understanding Convolutional Neural Networks
Adit Deshpande CS Undergrad at UCLA ('19) Blog About A Beginner's Guide To Understanding Convolution ...
- A Beginner’s Guide to Eigenvectors, PCA, Covariance and Entropy
A Beginner’s Guide to Eigenvectors, PCA, Covariance and Entropy Content: Linear Transformations Prin ...
- A Beginner's Guide to Paxos
Google Drive: A Beginner's Guide to Paxos The code ideas of Paxos protocol: 1) Optimistic concurrenc ...
- Beginner's Guide to Python-新手指导
Refer English Version: http://wiki.python.org/moin/BeginnersGuide New to programming? Python is free ...
- 新手教程之:循环网络和LSTM指南 (A Beginner’s Guide to Recurrent Networks and LSTMs)
新手教程之:循环网络和LSTM指南 (A Beginner’s Guide to Recurrent Networks and LSTMs) 本文翻译自:http://deeplearning4j.o ...
- Photography theory: a beginner's guide(telegraph.co.uk)
By Diane Smyth, Tim Clark, Rachel Segal Hamilton and Lewis Bush 11:00AM BST 09 Jun 2014 Have you r ...
随机推荐
- Python3基本语法
#编码 ''' 默认情况下,Python 3 源码文件以 UTF-8 编码,所有字符串都是 unicode 字符串. 当然你也可以为源码文件指定不同的编码: # -*- coding: cp-1252 ...
- 团队Alpha版本(九)
目录 组员情况 组员1(组长):胡绪佩 组员2:胡青元 组员3:庄卉 组员4:家灿 组员5:凯琳 组员6:翟丹丹 组员7:何家伟 组员8:政演 组员9:黄鸿杰 组员10:刘一好 组员11:何宇恒 展示 ...
- restorator 运行后其他所有EXE文件都无法运行的解决方案
昨天要反编译一个EXE,用RESTORATOR来查看资源罗列情况,倒霉的事情发生了,所有EXE文件点右键后‘打开’都没有了,刚开始以为中度了,进安全模式看,发现文件都没有异常,并且在安全模式下问题照样 ...
- 201621123034 《Java程序设计》第11周学习总结
作业11-多线程 1. 本周学习总结 1.1 以你喜欢的方式(思维导图或其他)归纳总结多线程相关内容. 2. 书面作业 本次PTA作业题集多线程 1. 源代码阅读:多线程程序BounceThread ...
- Codeforces - 220B Little Elephant and Array(莫队模板题)
题意: m次查询.每次查询范围[L,R]中出现次数等于该数字的数字个数. 题解: 由于分块,在每次询问中,同一块时l至多移动根号n,从一块到另一块也是最多2倍根号n.对于r,每个块中因为同一块是按y排 ...
- ndk开发-ffmpeg编译
进入模拟器shell: D:\Users\zhouhaitao\AppData\Local\Android\sdk\platform-tools\adb shell ndk编译链接静态库: LOCAL ...
- 让JS帮你决定午餐吃什么吧
最愁就是每天中午吃什么了,有空就做了个 JavaScript 轮播随机选择.会轮播预先自定义的菜单中,然后点选定的时候确定一款.代码可以查看本页源代码获得,你可以自定义修改菜单数组. 效果演示 准备选 ...
- Linux下find命令参数及用法详解
由于find具有强大的功能,所以它的选项也很多,其中大部分选项都值得我们花时间来了解一下.即使系统中含有网络文件系统( NFS),find命令在该文件系统中同样有效,只你具有相应的权限.在运行一个非常 ...
- jdk,tomcat,mvn,android,php,linux等的初始化配置
jdk配置:系统变量->新建->变量名:JAVA_HOME 变量值:c:\jdk1.6.0_21(jdk安装目录:C:\Program Files (x86)\Java\jdk1.7.0_ ...
- Sql Server 事务/回滚
,'test1','test1') commit tran t1 ---提交事务 功能:实现begin tran 和commit tran之间的语句,任一如果出现错误,所有都不执 事务不是有错就回滚 ...
