27个Jupyter Notebook使用技巧及快捷键(翻译版)
Jupyter Notebook
Jupyter Notebook 以前被称为IPython notebook。Jupyter Notebook是一款能集各种分析包括代码、图片、注释、公式及自己画的图一体的灵活工具。
Jupyter 具有可扩展性。它支持多种语言,能容易的部署到自己的计算机或远程服务器上。用户只要通过ssh或http就能访问远程的Jupyter。更赞的是Jupyter完全免费。

Jupyter接口
1 快捷键
正如大神所知,使用快捷键能省很多时间。在菜单Help→Keyboard Shortcuts中向用户展示很多快捷键。每次升级Jupyter时都需要看下该菜单,因为升级的同时会增加很多快捷键。
访问并快速学习快捷键的另一种方式是使用命令面板:Cmd+Shift+P或Ctrl+Shift+P,后者在Linux和Windows系统都适用。在不知道某个动作的快捷键或该动作没有快捷键时,你可以使用这个对话框通过名称来运行任何命令。
该功能类似在Mac上的Spotlight搜索。一旦开始使用就会停不下来。
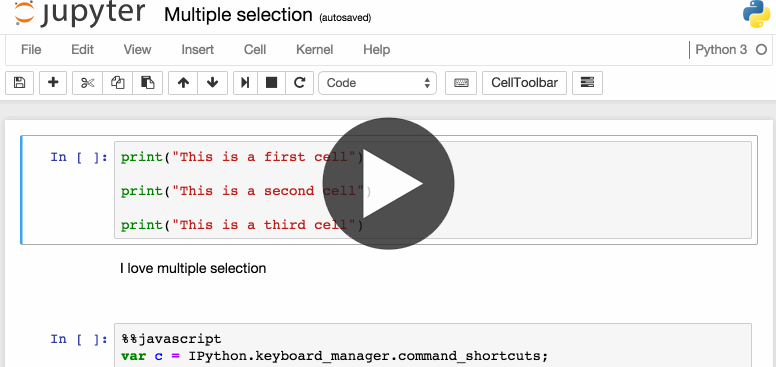
命令面板
作者喜欢的快捷键:
- Esc+F:查找并替换代码但不包括输出内容。
- Esc+0:切换输出单元。
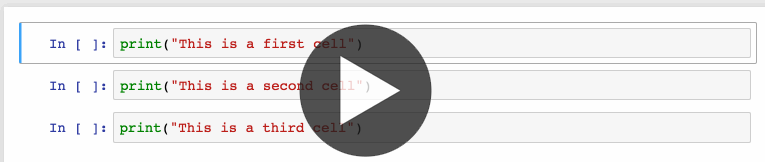
- 选择多个单元:
- Shift+J 或Shift+Down:向下选择单元格。
- Shift+K或Shift+Up:向上选择单元格
- 选定单元格之后,可以同时删除、复制、剪切、粘贴及运行这些单元格。在需要移动notebook中部分内容时,该功能很有用。
- Shit+M:合并多个单元格。
2 优雅的展示变量信息
第一部分内容很多人都知道。当一个Jupyter以一个变量的名字结束或未分配输出语句时,Jupyter会自动展示变量的内容而无需使用print 语句。当使用Pandas的DataFrames时,该功能很有用。因为Jupyter会把结果以表格形式输出。
知道的人不是很多的是可以通过修改kernel选项ast_note_interactivity的值使Jupyter自动展示变量及语句的输出。这样你就可以很方便的查看多条语句的输出内容。
In [1]:
- from IPython.core.interactiveshell import InteractiveShell
- InteractiveShell.ast_node_interactivity = "all"
In [2]:
- from pydataset import data
- quakes = data('quakes')
- quakes.head()
- quakes.tail()
Out[2]:
|
|
lat |
long |
depth |
mag |
stations |
|
1 |
-20.42 |
181.62 |
562 |
4.8 |
41 |
|
2 |
-20.62 |
181.03 |
650 |
4.2 |
15 |
|
3 |
-26.00 |
184.10 |
42 |
5.4 |
43 |
|
4 |
-17.97 |
181.66 |
626 |
4.1 |
19 |
|
5 |
-20.42 |
181.96 |
649 |
4.0 |
11 |
Out[2]:
|
|
lat |
long |
depth |
mag |
stations |
|
996 |
-25.93 |
179.54 |
470 |
4.4 |
22 |
|
997 |
-12.28 |
167.06 |
248 |
4.7 |
35 |
|
998 |
-20.13 |
184.20 |
244 |
4.5 |
34 |
|
999 |
-17.40 |
187.80 |
40 |
4.5 |
14 |
|
1000 |
-21.59 |
170.56 |
165 |
6.0 |
119 |
如果你想让所有Jupyter的工具(Notebook 和Console)都有该功能,可以创建一个文件:~/.ipython/profile_default/ipython_config.py,文件的内容如下:
- c = get_config()
- #Run all nodes interactively
- c.InteractiveShell.ast_node_interactivity = "all"
3 轻松连接到帮助文档
点击help菜单,你会轻松地找到NumPython,Pandas,Scipy和Matplotlib的oneline document链接。
不要忘记库、方法和变量是以’?’什么开头的。你可以通过Docstring来快速访问相关语法.
- In [3]:
- ?str.replace()
- Docstring:
- S.replace(old, new[, count]) -> str
- Return a copy of S with all occurrences of substring
- old replaced by new. If the optional argument count is
- given, only the first count occurrences are replaced.
- Type: method_descriptor
4 在notebooks中画图
有很多包都可以在notebook中画图。
- matplotlib:(标准库),使用%matplotlib inline激活.
- -%matplotlib notebook:该命令也能提供交互但由于在服务器端做渲染所以比较慢。
- -mpld3:使用d3给matplotlib代码做渲染。虽然不完整,但很漂亮。
- -bokeh:做交互图像的很好选择。
- -plot.ly:能产生很漂亮的图形但是收费。
5 Jupyter的魔法命令
上面提到的%matplotlib inline只是Jupyter魔法命令的一个例子。
- In [53]:
- # This will list all magic commands
- %lsmagic
- Out[53]:
- Available line magics:
- %alias %alias_magic %autocall %automagic %autosave %bookmark %cat %cd %clear %colors %config %connect_info %cp %debug %dhist %dirs %doctest_mode %ed %edit %env %gui %hist %history %killbgscripts %ldir %less %lf %lk %ll %load %load_ext %loadpy %logoff %logon %logstart %logstate %logstop %ls %lsmagic %lx %macro %magic %man %matplotlib %mkdir %more %mv %notebook %page %pastebin %pdb %pdef %pdoc %pfile %pinfo %pinfo2 %popd %pprint %precision %profile %prun %psearch %psource %pushd %pwd %pycat %pylab %qtconsole %quickref %recall %rehashx %reload_ext %rep %rerun %reset %reset_selective %rm %rmdir %run %save %sc %set_env %store %sx %system %tb %time %timeit %unalias %unload_ext %who %who_ls %whos %xdel %xmode
- Available cell magics:
- %%! %%HTML %%SVG %%bash %%capture %%debug %%file %%html %%javascript %%js %%latex %%perl %%prun %%pypy %%python %%python2 %%python3 %%ruby %%script %%sh %%svg %%sx %%system %%time %%timeit %%writefile
作者推荐查看文档the documentation for all Jupyter magic commands ,在该文档中总能找到你想查的。作者比较喜欢的语法糖如下所示:
6 Jupyter语法糖: -%env:设置环境变量
可以在不启动Jupyter server进程的情况下管理notebook的环境变量。一些包如theano用环境变量来控制行为。此时,%env就很方便。
- In [55]:
- # Running %env without any arguments
- # lists all environment variables
- # The line below sets the environment
- # variable OMP_NUM_THREADS
- %env OMP_NUM_THREADS=4
- env: OMP_NUM_THREADS=4
7 Jupyter语法糖:-%run:执行Python代码
%run可以运行.py文件。鲜为人知的是,该语法糖也可以执行其他的Jupyter notebooks。这非常有用。
注意:用%run和import 一个包不是一回事。
- In [56]:
- # this will execute and show the output from
- # all code cells of the specified notebook
- %run ./two-histograms.ipynb
8 Jupyter语法糖:-%:load:从外部脚本插入代码
- In [ ]:
- # Before Running
- %load ./hello_world.py
- In [61]:
- # After Running
- # %load ./hello_world.py
- if __name__ == "__main__":
- print("Hello World!")
- Hello World!
9 Jupyter语法糖: -%store:在不同的notebooks之间传递变量
%store命令可以在两个不同的notebooks之间传递变量。
- In [62]:
- data = 'this is the string I want to pass to different notebook'
- %store data
- del data # This has deleted the variable
- Stored 'data' (str)
- Now, in a new notebook…
- In [1]:
- %store -r data
- print(data)
- this is the string I want to pass to different notebook
10 Jupyter语法糖 -%who:列出所有的全局变量
%who命令在没有参数的情况下能列出目前存在的所有全局变量。如果使用一个参数例如str,则只会列出对应类型的变量。
- In [1]:
- one = "for the money"
- two = "for the show"
- three = "to get ready now go cat go"
- %who str
- one three two
11 Jupyter语法糖——Timing
对timing很有用的有两个语法糖:%%time和%timeit。当一些代码很慢且有想知道哪些地方慢时这两个语法糖很有用。
%%time展示单元格中代码单次运行信息。
- In [4]:
- %%time
- import time
- for _ in range(1000):
- time.sleep(0.01)# sleep for 0.01 seconds
- CPU times: user 21.5 ms, sys: 14.8 ms, total: 36.3 ms
- Wall time: 11.6 s
%%timeit使用Python的timeit包。该命令默认运行代码100,000次,求最快三次的均值。
- In [3]:
- import numpy
- %timeit numpy.random.normal(size=100)
- The slowest run took 7.29 times longer than the fastest. This could mean that an intermediate result is being cached.
- 100000 loops, best of 3: 5.5 µs per loop
12 Jupyter语法糖—%%writefile和%pycat:导出单元格内容/展示外部脚本内容
使用语法糖%%writefile保存单元格内容到外部文件。%pycat正好相反,该命令高亮展示外部文件内容。
- %%writefile pythoncode.py
- import numpy
- def append_if_not_exists(arr, x):
- if x not in arr:
- arr.append(x)
- def some_useless_slow_function():
- arr = list()
- for i in range(10000):
- x = numpy.random.randint(0, 10000)
- append_if_not_exists(arr, x)
- Writing pythoncode.py
- In [8]:
- %pycat pythoncode.py
- import numpy
- def append_if_not_exists(arr, x):
- if x not in arr:
- arr.append(x)
- def some_useless_slow_function():
- arr = list()
- for i in range(10000):
- x = numpy.random.randint(0, 10000)
- append_if_not_exists(arr, x)
13 语法糖—%prun:展示程序中每个函数耗费的时间
使用%run statement_name将以有序表展示代码中每个内部函数被调用次数,每次调用花费的时间及运行耗费的总时间。
- %prun some_useless_slow_function()
- 26324 function calls in 0.556 seconds
- Ordered by: internal time
- ncalls tottime percall cumtime percall filename:lineno(function)
- 10000 0.527 0.000 0.528 0.000 <ipython-input-46-b52343f1a2d5>:2(append_if_not_exists)
- 10000 0.022 0.000 0.022 0.000 {method 'randint' of 'mtrand.RandomState' objects}
- 1 0.006 0.006 0.556 0.556 <ipython-input-46-b52343f1a2d5>:6(some_useless_slow_function)
- 6320 0.001 0.000 0.001 0.000 {method 'append' of 'list' objects}
- 1 0.000 0.000 0.556 0.556 <string>:1(<module>)
- 1 0.000 0.000 0.556 0.556 {built-in method exec}
- 1 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 {method 'disable' of '_lsprof.Profiler' objects}
14 Jupyter语法糖—%pdb
Jupyter有自己的调试接口The Python Debugger (pdb). 。调试能进入函数内部并判断函数内部发生事项。
在这里看pdb可使用的命令列表:pdb
- In [ ]:
- %pdb
- def pick_and_take():
- picked = numpy.random.randint(0, 1000)
- raise NotImplementedError()
- pick_and_take()
- Automatic pdb calling has been turned ON
- ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
- NotImplementedError Traceback (most recent call last)
- <ipython-input-24-0f6b26649b2e> in <module>()
- 5 raise NotImplementedError()
- 6
- ----> 7 pick_and_take()
- <ipython-input-24-0f6b26649b2e> in pick_and_take()
- 3 def pick_and_take():
- 4 picked = numpy.random.randint(0, 1000)
- ----> 5 raise NotImplementedError()
- 6
- 7 pick_and_take()
- NotImplementedError:
- > <ipython-input-24-0f6b26649b2e>(5)pick_and_take()
- 3 def pick_and_take():
- 4 picked = numpy.random.randint(0, 1000)
- ----> 5 raise NotImplementedError()
- 6
- 7 pick_and_take()
15 压缩最后一行函数的输出
有时抑制最后一行代码的函数输出很有必要且方便:只需要在代码末尾价格分号。例如画图。
- In [4]:
- %matplotlib inline
- from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
- import numpy
- x = numpy.linspace(0, 1, 1000)**1.5
- In [5]:
- # Here you get the output of the function
- plt.hist(x)
- Out[5]:
- (array([ 216., 126., 106., 95., 87., 81., 77., 73., 71., 68.]),
- array([ 0. , 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1. ]),
- <a list of 10 Patch objects>)
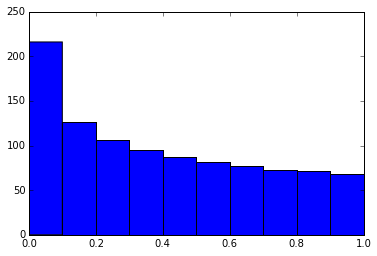
- In [6]:
- # By adding a semicolon at the end, the output is suppressed.
- plt.hist(x);
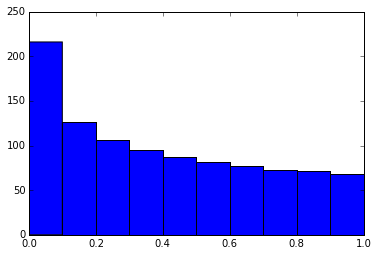
16 执行shell命令
在notebook中执行shell命令很简单。可通过在notebook中执行shell命令检查当前文件夹中包含哪些数据集。
- In [7]:
- !ls *.csv
- nba_2016.csv titanic.csv
- pixar_movies.csv whitehouse_employees.csv
- Or to check and manage packages.
- In [8]:
- !pip install numpy
- !pip list | grep pandas
- Requirement already satisfied (use --upgrade to upgrade): numpy in /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.4/lib/python3.4/site-packages
- pandas (0.18.1)
17 使用LaTeX写公式
当在Markdown单元格中写LaTeX时,会使用MathJax展示成公式。
This:
$$ P(A \mid B) = \frac{P(B \mid A) \, P(A)}{P(B)} $$
显示形式如下:
P(A∣B)=P(B∣A)P(A)P(B)P(A∣B)=P(B∣A)P(A)P(B)
Markdown是notebooks重要的一部分,记得要用它。
18 在notebook中运行使用不同kernel的代码
如果愿意,可以把使用不同kernels的代码放在一个notebook中。
只需要在每个单元格的开头使用Jupyter语法糖加上相应kernel的名称。
- %%bash
- %%HTML
- %%python2
- %%python3
- %%ruby
- %%perl
- In []:
- %%bash
- for i in {..}
- do
- echo "i is $i"
- done
- i is
- i is
- i is
- i is
- i is
19 为Jupyter安装其他的kernels
能运行不同的语言是Jupyter很好的一个特性。下面为如何运行R kernel的例子。
- 简安装:使用Anaconda安装R kernel
如果用Anaconda启动环境,运行R很简单。只需要在终端运行下面的代码:
- conda install –c r r-essentials
- 非简安装:手动安装R kernel
如果你不用Anaconda,安装过程稍微复杂。你如果没安装R,首先需要安装R。
安装后,启动R界面并运行下面的代码:
- install.packages(c('repr', 'IRdisplay', 'crayon', 'pbdZMQ', 'devtools'))
- devtools::install_github('IRkernel/IRkernel')
- IRkernel::installspec() # to register the kernel in the current R installation
20 在同一个notebook中运行R和Python
最好的解决方案是安装rpy2:可以通过pip install rpy2安装。
安装后就可以同时使用两种语言,并可以在两种语言之间传递变量。
- In [1]:
- %load_ext rpy2.ipython
- In [2]:
- %R require(ggplot2)
- Out[2]:
- array([1], dtype=int32)
- In [3]:
- import pandas as pd
- df = pd.DataFrame({
- 'Letter': ['a', 'a', 'a', 'b', 'b', 'b', 'c', 'c', 'c'],
- 'X': [4, 3, 5, 2, 1, 7, 7, 5, 9],
- 'Y': [0, 4, 3, 6, 7, 10, 11, 9, 13],
- 'Z': [1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3]
- })
- In [4]:
- %%R -i df
- ggplot(data = df) + geom_point(aes(x = X, y= Y, color = Letter, size = Z))
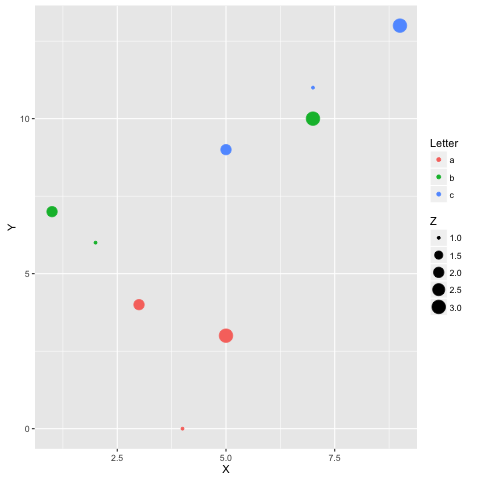
21 使用其他语言写函数
有时候numpy的速度比较慢,需要写效率更高的代码。原则上,可以在动态包中编译代码和写Python wrappers.
如果这些枯燥的部门有人帮你做是不是很好?
可以在cpython中写fortran代码并直接在Python代码中使用。
首先需要安装:
- !pip install cython fortran-magic
- In [ ]:
- %load_ext Cython
- In [ ]:
- %%cython
- def myltiply_by_2(float x):
- return 2.0 * x
- In [ ]:
- myltiply_by_2(23.)
- Personally I prefer to use fortran, which I found very convenient for writing number-crunching functions. More details of usage can be found here.
- In [ ]:
- %load_ext fortranmagic
- In [ ]:
- %%fortran
- subroutine compute_fortran(x, y, z)
- real, intent(in) :: x(:), y(:)
- real, intent(out) :: z(size(x, 1))
- z = sin(x + y)
- end subroutine compute_fortran
- In [ ]:
- compute_fortran([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6])
22. Multicursor support
Jupyter支持多种cursors,类似Sublime text.按下Alt键拖动鼠标。

23 Jupyter-contrib extensions
Jupyter-contrib extensions是一个家族,该家族使Jupyter功能更强大,例如jupyter shell-checker 和code-formatter。
下面的命令会安装extensions,
The following commands will install the extensions, as well as a menu based configurator that will help you browse and enable the extensions from the main Jupyter notebook screen.
!pip install https://github.com/ipython-contrib/jupyter_contrib_nbextensions/tarball/master
!pip install jupyter_nbextensions_configurator
!jupyter contrib nbextension install --user
!jupyter nbextensions_configurator enable --user
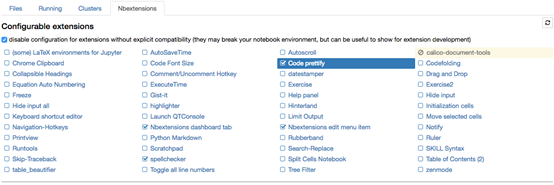
24 根据Jupyter notebook创建演示用文档
使用Damian Avila的RISE能根据现存的notebook创建PowerPoint形式的演示文档。
可以使用conda安装RISE:
- conda install -c damianavila82 rise
或者使用pip:
pip install RISE
通过下面的代码安装entension并使其生效:
jupyter-nbextension install rise --py --sys-prefix
jupyter-nbextension enable rise --py --sys-prefix
25 Jupyter输出系统
notebook以HTML的形式展示,单元格中的内容也可以输出成HTML。因此几乎可以输出任何内容:video/audio/images
下面的例子浏览文件夹中的所有图像,并展示前5个的粗略图。
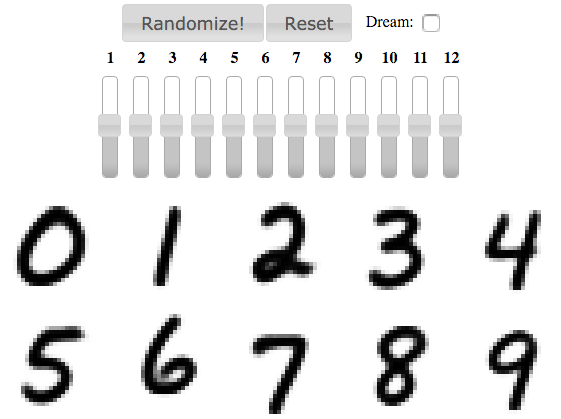
通过bash命令也可以创建同样的List,因为语法糖和bash命令偶读返回Python变量。
- In []:
- names = !ls ../images/ml_demonstrations/*.png
- names[:5]
- Out[10]:
- ['../images/ml_demonstrations/colah_embeddings.png',
- '../images/ml_demonstrations/convnetjs.png',
- '../images/ml_demonstrations/decision_tree.png',
- '../images/ml_demonstrations/decision_tree_in_course.png',
- '../images/ml_demonstrations/dream_mnist.png']
26 大数据分析
查询和处理大数据有很多解决方案:
- ipyparallel (以前叫IPython cluster) 是在Python中使用map-reduce的很好选择。在rep中我们用该选项并行训练了很多机器学习模型。
- pyspark
- spark-sql 语法糖:%%sql
27 共享notebooks
共享notebook最简单的方法是使用notebook文件(.ipynb)。对于不使用Jupyter的人,有下面一些可行办法:
- 使用File>Download as >HTML菜单选项把notebook转换成HTML文件。
- 通过gists或github分享notebook File。例子。
- 如果把notebook上传到notebook,你可以使用mybinder服务允许别人在半个小时内通过Jupyter访问你的内容。
- 使用jupyterhub启动你的系统。在准备课程且没时间考虑学生的机器性能时使用该功能很方便。
将notebook保存到比如dropbox中,然后将连接放到nbviewer. nbviewer将会渲染你存储在任何地方的notebook.
使用File>Download as >PDF菜单将notebook保存为一个PDF。如果你打算这么做,强烈推荐你阅读Julius Schulz非常棒的一篇文章Making publication ready Python notebooks.
原文地址:27 Jupyter Notebook tips, tricks and shortcuts
27个Jupyter Notebook使用技巧及快捷键(翻译版)的更多相关文章
- Jupyter notebook操作技巧
学习笔记:Jupyter notebook操作技巧 一.jupyter notebook简介.用途.优势和缺点 二. 单元Cell: 三.操作技巧 - 给Jupyter换主题 - 笔记本扩展(nbex ...
- [Jupyter Notebook] 01 这么多快捷键,我可顶不住!先记个八成吧
0. 一些说明 为了入门 Python3 安装了 Anaconda,它集成了 Jupyter Notebook 1. 调出快捷键表 打开 Jupyter Notebook,新建一个 Python3(我 ...
- jupyter notebook使用技巧
shift + tab 键可以查看对应源代码(注意:需要先将代码运行才能查看) Jupyter Notebook 的快捷键 Jupyter Notebook 有两种键盘输入模式:1.命令模式,键盘输入 ...
- jupyter notebook 小技巧
Converting notebooks to other formats¶ !pip install https://github.com/ipython-contrib/jupyter_contr ...
- 27 个Jupyter Notebook的小提示与技巧
不多说,直接上干货! 见 http://liuchengxu.org/pelican-blog/jupyter-notebook-tips.html
- Jupyter notebook 中常用的快捷键
1.注释和缩进 注释一行或多行: Ctrl + / 多行同时缩进:Tab 或者 Ctrl + ] 多行取消缩进: Shift + Tab 或者 ctrl + [ 2.编辑和运行 Enter : 转入编 ...
- Jupyter Notebook快捷键总结
1. Jupyter Notebook有两种mode Enter:进入edit模式 Esc:进入command模式 2. Command命令快捷键: A:在上方增加一个cell B:在下方增加一个ce ...
- anaconda及jupyter notebook的了解及使用方法(1)
今日内容 anaconda软件使用 jupyter notebook基本使用及快捷键 numpy anaconda软件使用 1.进入anaconda主页点击jupyter启动即可 呼起一个jupyte ...
- 27个Jupyter快捷键、技巧(原英文版)
本文是转发自:https://www.dataquest.io/blog/jupyter-notebook-tips-tricks-shortcuts/ 的一篇文章,先记录在此,等有空时我会翻译成中文 ...
随机推荐
- Delphi 动态创建组件,单个创建、单个销毁
效果图如下: 实现部分代码如下: var rec: Integer = 0; //记录增行按钮点击次数 implementation {$R *.dfm} //动态释放单个组件内存,即销毁组件 pro ...
- cocos2d-x 实现粒子飞行特效
效果图 说明 实现效果: 按下鼠标并且移动, 所到之处产生光圈 光圈会以窗口中心为终点, 并且会偏移自身角度对准终点, 然后持续飞行, 直到终点. 附件 下载源码, 请猛击这里!
- Q我音乐
- Tweet button with a callback – How to?
原文: http://jaspreetchahal.org/tweet-button-with-a-callback-how-to/ 两种方式:1. 原生的button <a href=&quo ...
- gearmand的安装
1.安装gperf libuuid-devel yum install -y gperf libuuid-devel 2.安装 libevent yum install libevent libeve ...
- 初涉JavaScript模式 (6) : 原型模式 【二】
原型与in操作符 有两种方式使用in操作符:单独使用和在for-in循环中使用. 在单独使用时,in操作符会遍历实例公开(可枚举)的属性,如果找到该指定属性则返回true,无论该指定属性是存在与实例中 ...
- JS indexOf() lastIndexOf()与substring()截取字符串的区别
1. String.IndexOf 方法 (value[,startIndex]) value:要查找的 Unicode 字符. 必选项startIndex:搜索起始位置. 可选项 不写从开头查找 ...
- 【行为型】Memento模式
备忘录模式顾名思义就是一种能有备忘作用的设计模式,其目的是在对象外部保存其在某一时刻的状态信息,并且在任何需要的时候,都可以通过备忘录中保存的状态数据恢复对象在当时情形下的状态. 备忘录模式旨在对象的 ...
- [Python笔记]第五篇:递归
本篇主要内容:递归以及冒泡排序 参考文章:(http://www.cnblogs.com/balian/archive/2011/02/11/1951054.html) 递归的概念 递归的概念很简单, ...
- POJ - 3903 Stock Exchange(LIS最长上升子序列问题)
E - LIS Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:65536KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u Descripti ...
