python 基础之第二天
[root@master script]# vim while_counter.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# coding: utf-8 sum = 0
counter = 0 while counter < 101:
sum += counter
counter += 1
print sum
[root@master script]# cat game.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# coding: utf-8
import random
ch_list = ["剪刀","石头","布"]
prompt = """
(0) 剪刀
(1) 石头
(2) 布
请选择(0/1/2):
"""
win_list = [["石头","剪刀"],["布","石头"],['剪刀',"布"]]
computer = random.choice(ch_list)
ind = int(raw_input(prompt))
player = ch_list[ind] print 'Your_choice:%s,computer_choice:%s' % (player,computer) if [player,computer] in win_list:
print '\033[31;1mplayer win !!!!\033[0m'
elif player == computer:
print '\033[32;1m平局\033[0m' else:
print '\033[33;1mcomputer win!!!\033[0m'
###############range用法################
>>> range(10)
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
>>> range(1,10,2)
[1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
>>> range(2,10,2)
[2, 4, 6, 8]
>>> range(10,1,-1)
[10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2]
##################len用法###############
[fush@xm35 ~ 11:11:47]$ vim alist.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# coding: utf-8 alist = ['bob','jerry','hali','cherry'] for i in range(len(alist)):
print '%s: %s' %(i,alist[i]) [fush@xm35 ~ 11:12:11]$ python alist.py
0: bob
1: jerry
2: hali
3: cherry
###############斐波那契数列##############

#!/usr/bin/python
# coding: utf-8 alist = [0,1] for i in range(8):
sum = alist[-1] + alist[-2]
alist.append(sum)
for n in alist:
print n, [root@master script]# python fbnq.py
0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 ####改进#########
[root@master script]# vim fbnq.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# coding: utf-8 alist = [0,1]
num = int(raw_input('Please a number: '))
for i in range(num):
sum = alist[-1] + alist[-2]
alist.append(sum)
for n in alist:
print n, [root@master script]# python fbnq.py
Please a number: 11
0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 55 89 144
[root@master script]# python fbnq.py
Please a number: 9
0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 55
###############os.system 返回码###############
os.system()操作的结果是一个等价于echo $? 的一个值,成功为0,不成功非0值
[root@master script]# vim system.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# coding:utf-8 import os result = os.system('cat /etc/passwd &> /dev/null')
print result [root@master script]# python system.py
0
ping 主机连通性例子:
[root@master script]# vim ping.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# coding:utf-8 import os for i in range(1,255):
ip = '192.168.244.%s' % i
result = os.system('ping -c2 %s &> /dev/null' % ip)
if result:
print '%s: down' % ip
else:
print '%s: up' % ip 检测:
[root@master script]# python ping.py
192.168.244.1: down
192.168.244.2: up
192.168.244.3: down
192.168.244.4: down
192.168.244.5: down
多线程:
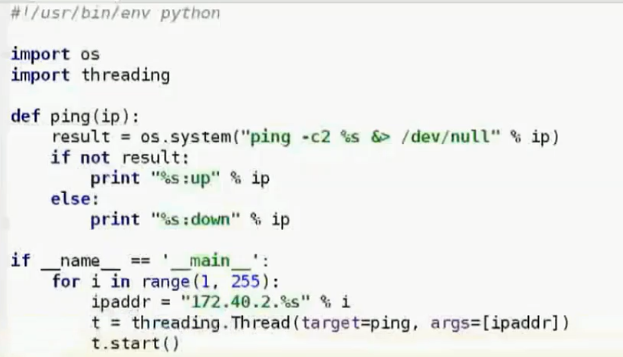
##################解析列表##############
>>> ['hello' for i in range(3)]
['hello', 'hello', 'hello']
>>> [10 for i in range(3)]
[10, 10, 10]
>>> [i for i in range(10)]
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
>>> [i**2 for i in range(10)]
[0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81]
>>> [i**2 for i in range(10) if i%2]
[1, 9, 25, 49, 81]
#############文件对象##############
1.文件读取


例子:
>>> f = open('/etc/hosts')
>>> data = f.read()
>>> print data,
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.244.200 master
192.168.244.201 slave1
192.168.244.202 slave2
>>> f.close()
2.文件写入

>>> f= open('hi.txt','w')
>>> f.write('hello\n')
>>> f.close()
>>> f= open('hi.txt','a')
>>> f.write('fush\n')
>>> f.flush()
注释:‘w’表示以只写方式,不能读取,再次写入内容会覆盖前面的内容,‘a’ 追加内容
>>> f.writelines(['1st line.\n','2th line.\n'])
[root@master script]# cat /root/hi.txt
111
1st line.
2th line.
###########cp例子###########
[root@master script]# vim cp.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# coding:utf-8 f = open('/etc/passwd')
k = open('/root/passwd','a')
while True:
data = f.read(4096)
if not data:
break
k.write(data) f.close()
k.close() 检测:
[root@master script]# python cp.py
[root@master script]# cat /root/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin
uucp:x:10:14:uucp:/var/spool/uucp:/sbin/nologin
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
games:x:12:100:games:/usr/games:/sbin/nologin
gopher:x:13:30:gopher:/var/gopher:/sbin/nologin
ftp:x:14:50:FTP User:/var/ftp:/sbin/nologin
nobody:x:99:99:Nobody:/:/sbin/nologin
vcsa:x:69:69:virtual console memory owner:/dev:/sbin/nologin
saslauth:x:499:76:Saslauthd user:/var/empty/saslauth:/sbin/nologin
postfix:x:89:89::/var/spool/postfix:/sbin/nologin
sshd:x:74:74:Privilege-separated SSH:/var/empty/sshd:/sbin/nologin
改进版:函数方式 [root@master script]# vim cp.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# coding:utf-8 def cp(sfname,dfname):
f = open(sfname)
k = open(dfname,'w')
while True:
data = f.read(4096)
if not data:
break
k.write(data) f.close()
k.close()
sname = raw_input('source_name: ')
dname = raw_input('destination_name: ')
cp(sname,dname) 检测:
[root@master script]# python cp.py
source_name: /etc/passwd
destination_name: /usr/local/src/passwd
[root@master script]# cat /usr/local/src/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin
uucp:x:10:14:uucp:/var/spool/uucp:/sbin/nologin
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
games:x:12:100:games:/usr/games:/sbin/nologin
gopher:x:13:30:gopher:/var/gopher:/sbin/nologin
ftp:x:14:50:FTP User:/var/ftp:/sbin/nologin
nobody:x:99:99:Nobody:/:/sbin/nologin
vcsa:x:69:69:virtual console memory owner:/dev:/sbin/nologin
saslauth:x:499:76:Saslauthd user:/var/empty/saslauth:/sbin/nologin
postfix:x:89:89::/var/spool/postfix:/sbin/nologin
sshd:x:74:74:Privilege-separated SSH:/var/empty/sshd:/sbin/nologin
增强版:
[root@master script]# vim cp.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# coding:utf-8 import sys
def cp(sfname,dfname):
f = open(sfname)
k = open(dfname,'w')
while True:
data = f.read(4096)
if not data:
break
k.write(data) f.close()
k.close()
cp(sys.argv[1],sys.argv[2]) 检测:
[root@master script]# python cp.py /etc/hosts /home/zhuji
[root@master script]# cat !$
cat /home/zhuji
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.244.200 master
192.168.244.201 slave1
192.168.244.202 slave2
##############函数初识##################
[root@master ~]# vim func01.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# coding:utf-8 def pstar():
print '*' * 20
print '#' * 20 a= pstar()
print a [root@master ~]# python func01.py
********************
####################
None
备注:当函数没有返回值,返回None
形参例子:
1 [root@master ~]# vim func01.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# coding:utf-8 def pstar(num):
return '*' * num n = int(raw_input('number: '))
print pstar(n) [root@master ~]# python func01.py
number: 15
*************** 默认参数例子:
[root@master ~]# vim func01.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# coding:utf-8
def pstar(num=20):
return '*' * num
n = int(raw_input('number: '))
print pstar()
print pstar(n)
[root@master ~]# python func01.py
number: 15
********************
***************
备注:调用函数不带参数时,用默认参数20;有带参数时,不用默认,会覆盖默认的参数
##############函数的位置参数#############
[root@master script]# vim position.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# coding:utf-8 import sys print sys.argv 检测:
[root@master script]# ./position.py
['./position.py']
[root@master script]# ./position.py hello
['./position.py', 'hello']
[root@master script]# ./position.py hello fush
['./position.py', 'hello', 'fush']
备注:sys.argv 是一个list
###############模块相关################
>>> import string
>>> string.upper('abc')
'ABC'
>>> string.__file__
'/usr/lib64/python2.6/string.pyc' ###string模块文件位置 查看模块文件:
[root@master script]# vim /usr/lib64/python2.6/string.py
"""A collection of string operations (most are no longer used). Warning: most of the code you see here isn't normally used nowadays.
Beginning with Python 1.6, many of these functions are implemented as
"""A collection of string operations (most are no longer used).
导入模块:
>>> from random import choice ##只导入random的choice
>>> choice('adfe')
'a'
>>> choice('adfe')
'a'
>>> choice('adfe')
'd'
>>> choice('adfe')
'd'
>>> choice('adfe')
'e'
>>> choice('adfe')
'f'
>>> random.choice('fush') ###前面没有导入random,会报错
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
NameError: name 'random' is not defined
>>> import random as rdm ##把random模块起了个别名rdm
>>> rdm.choice('fush')
's'
>>> rdm.choice('fush')
's'
>>> rdm.choice('fush')
'f'
python 基础之第二天的更多相关文章
- python基础学习——第二天
一.python种类 1.1 Cpython python官方版本,使用c语言实现,运行机制:先编译,py(源码文件)->pyc(字节码文件),最终执行时先将字节码转换成机器码,然后交给cpu执 ...
- python基础教程-第二章-列表和元组
本章将引入一个新的概念,:数据结构.数据结构是通过某种方式(例如对元素进行编号)组织在 一起的数据元素的集合,这些数据元素可以是数字或者字符,甚至可以是其他数据结构.在python中,最基本的数据结构 ...
- Python基础【第二篇】
一.Python的标准数据类型 Python 3中主要有以下6中数据类型: Number(数字).String(字符串).List(列表).Tuple(元组).Sets(集合).Dictionary( ...
- Python 基础【第二篇】python操作模式
一.交互模式 #python Python 2.6.6 (r266:84292, Jan 22 2014, 09:42:36) [GCC 4.4.7 20120313 (Red Hat 4.4.7-4 ...
- 第二章、元组和列表(python基础教程第二版 )
最基本的数据结构是序列,序列中每个元素被分配一个序号-元素的位置,也称索引.第一个索引为0,最后一个元素索引为-1. python中包含6种内建的序列:元组.列表.字符串.unicode字符串.buf ...
- python基础教程第二版 第一章
1.模块导入python以增强其功能的扩展:三种方式实现 (1). >>> Import math >>> math.floor(32.9) 32.0 #按照 模块 ...
- python基础自学 第二天
注释 分类 单行注释 多行注释 作用 使用自己熟悉的语言,在程序中对某些代码进行标注说明,增强程序可读性 单行注释(行注释) 以 # 开头,#右边所有的东西就被当成说明文字,而不是要执行的程序,只是说 ...
- python基础学习第二天
读文件 r 要以读文件的模式打开一个文件对象,使用Python内置的open()函数,传入文件名和标示符 写文件 w 写文件和读文件是一样的,唯一区别是调用open()函数时,传入标识符’w’或者’w ...
- python基础知识第二篇(字符串)
基本数据类型 数字 整形 int ---int 将字符串 ...
随机推荐
- Android常见的三种内部类
在java里类中再定义类,这种在其他类内部类叫做内部类,在Android开发里最常见有三种内部类分别是(成员内部类.方法内部类.匿名内部类) 一.成员内部类 1 public class Test { ...
- cocos2d-x 事件分发机制 ——触摸事件监听
cocos2d-x 3.0 出来已经好久了,也已经用3.0写了几个小游戏,感觉3.0的事件触发机制太赞了,随这里总结一下.也算是对知识的一种回顾和加深理解. 3.0的事件分发机制中.须要也只须要通过创 ...
- 【翻译自mos文章】当并行事务恢复进程在执行时,禁用并行事务恢复的方法
当并行事务恢复进程在执行时,禁用并行事务恢复的方法 How to Disable Parallel Transaction Recovery When Parallel Txn Recovery is ...
- Spring源代码由浅入深系列三 refresh
Spring中的refresh是一个相当重要的方法. 它完毕IOC的第一个阶段,将xml中的bean转化为beanDefinition.具体说明如上图所看到的. 在上图中,创建obtainFreshB ...
- 指针初始化为NULL的作用
关于空指针NULL.野指针.通用指针,首先说一下什么是指针,只要明白了指针的含义,你就明白null的含义了. 假设 有语句 int a=10;那么编译器就在内存中开辟1个整型单元存放变量a,我们假设这 ...
- 如何去掉Google搜索的跳转 让你的Google搜索不被reset掉
http://www.nowamagic.net/librarys/veda/detail/389 在点击google搜索结果时,google会在结果的URL前做个跳转,且有时这个跳转地址会被墙,这样 ...
- Android摄像头採集的视频数据流怎样通过Socket实时发送到目标服务端
分两块: 1.取得摄像头採集的视频流 2.发送到server端 protected MediaRecorder mMediaRecorder; private LocalServerSocket mL ...
- AMD单桥主板上电时序的详细解释
3个待机条件: 1.桥需要得到待机电压:3.3V,1.5V/1.2V2.25M起振注:NV的RTC电路,一般不会导致时序故障,都可以出CPURST#3.PWRGD-SB(即INTEL芯片组的RSMRS ...
- java中使用opencv
Java + opencv学习:在Eclipse下配置基于Java的OpenCV开发环境 2016-04-08 17:43 6491人阅读 评论(0) 收藏 举报 分类: OpenCV学习(10) ...
- 2016年最值得新手程序猿阅读的书:《增长project师指南》
这本书的来源于根据我在<Repractise简单介绍篇:Web开发的七天里>中所说的 Web 开发的七个步骤而展开的电子书.当然它也是一个 APP.它一本关于怎样成为增长project师的 ...
