九. Python基础(9)--命名空间, 作用域
九. Python基础(9)--命名空间, 作用域
1 ● !a 与 not a
|
注意, C/C++可以用if !a表示if a == 0, 但是Python中只能用if not a来表示同样的意义. |
|
>>> a = [] >>> if a: ... print("Hello") ... >>> if not a: ... print("Hello") ... Hello |
2 ● 函数对字典的修改
|
如果一个函数需要对一个字典做修改, 不要新建一个临时的字典, 避免字典体积过大导致内存崩溃. |
3 ●三元运算:
|
结果 = if条件成立的结果 if条件 else if条件不成立的结果 在C++中的写法: 结果 = if条件?if条件成立的结果:if条件不成立的结果 a = 10 b = 5 if a > b: c = a else: c=b
# 等价于: c = a if a > b else b 即C++中的: c = if a > b ? a:b |
4 ● 命名空间(Namespace) & 作用域(scope)
|
Namespaces refer to sections(程序段) within which a particular name is unique and unrelated to the same name in other namespaces. 命名空间是一个程序段, 在这个程序段内, 每一个名称是唯一的, 并且和其它命名空间中的命名空间无关. A namespace ia s a space that holds a bunch of names, and its a mapping from names to objects. Most namespaces are currently implemented as Python dictionaries 命名空间是一个包含一堆名称的空间, 它是从名称到对象的映射. 大部分命名空间是通过python字典实现的.
(图片引自: http://cryptroix.com/2016/10/23/namespaces-scope-resolution-legb-rule/) |
|
A scope refers to a region of a program from where a namespace can be directly accessed, i.e., without a namespace prefix, e.g. a dot. 如果一个变量/命名空间可以在一个程序段(LEGB)内可以直接使用, 也就是说, 不需要不通过前缀(例如点)来使用, 那么这个程序段就是这个变量/命名空间的作用域. A scope defines the visibility of a name within a block. If a local variable is defined in a block, its scope includes that block. 一个作用域定义了一个语句块内的 |
|
※ Names refer to objects. ※※ A block is a piece of Python program text that is executed as a unit. The following are blocks: a module, a function body, and a class definition. Python lacks declarations and allows name binding operations to occur anywhere within a code block. |
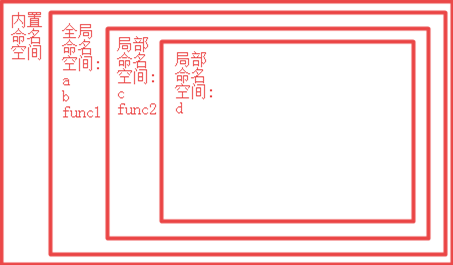
5 ● 命名空间的分类
6 ● 命名空间的加载顺序
|
①启动python ②内置加载命名空间 ③加载全局命名空间中--从上到下顺序加载 ④加载局部命名空间中--调用一个函数的时候, 从上到下去加载 ※ |
7 ● 作用域的分类
|
Variables defined within a function have local scope, and those at the highest level in a module have global scope.(定义在函数内的变量具有局部作用域, 在一个模块中最高级别的变量有全局作用域.) 具体来说, 包括: ① 全局作用域(global scope):在所有函数之外的作用域称为全局作用域. 这个作用域里面的命名在整个文件的任意位置都能被引用、全局有效. 内置命名空间和全局命名空间里面的命名在全局作用域里可以使用, 被global关键字修饰的命名也在全局作用域内.
② 局部作用域(local scope):函数之内的作用域称为局部作用域. 这个作用域里面的命名只在局部范围内有效. 局部命名空间里面的命名在局部作用域里可以使用 |
|
※ |
|
内置命名空间和全局命名空间的作用域: 整个文件→globals() 局部命名空间的作用域: 所在的函数→locals() |
|
※ |
|
※ |
|
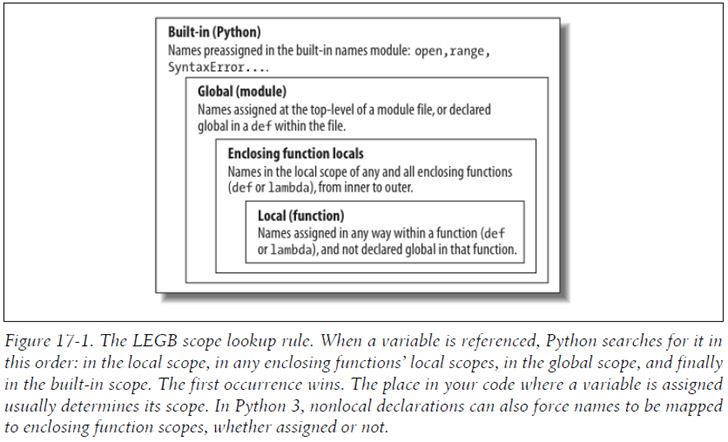
① L, Local(局部作用域), scope of function 可以被使用的名称包括: Names assigned in any way within a function (def or lambda)), and not declared global in that function.
E, Enclosing-function locals(封闭函数作用域), scope of enclosing function 可以被使用的名称包括: Names in the local scope of any and all statically enclosing functions (def or lambda), from inner to outer. Also, names stated by the keyword "nonlocal" in a def within the file.
G, Global (全局作用域), scope of module 可以被使用的名称包括: Names assigned at the top-level of a module file, or names stated by the keyword "global" in a def within the file.
B, Built-in (内置作用域), scope of Python/outermost scope 可以被使用的名称包括: Names preassigned in the built-in names module : open,range,SyntaxError,... |
※ Python变量的分类
|
1.局部变量 If a name is bound in a block, it is a local variable of that block, unless declared as nonlocal or global. 2.全局变量 If a name is bound at the module level, it is a global variable. (The variables of the module code block are local and global.) 3.自由变量 If a variable is used in a code block but not defined there, it is a free variable.(就是闭包函数体内使用的外部的变量) |
|
Actually "global variables are a subset of free variables". The CPython implementation detail is if CPython marks a variable as "free", it means the marked variable is pure "free" but not "global" (in turn it means if a variable is free and global, is_free in CPython will return false). |
|
|
|
|
※ 命名空间的产生和生命周期
|
1、内置命名空间在 Python 解释器启动时创建,会一直保留,不被删除。 2、模块的全局命名空间在模块定义被读入时创建,通常模块命名空间也会一直保存到解释器退出。 3、当函数被调用时创建一个局部命名空间,当函数返回结果 |
|
Not every namespace, which may be used in a script or program is accessible (or alive) at any moment during the execution of the script. Namespaces have different lifetimes, because they are often created at different points in time. ① There is one namespace which is present from beginning to end: The namespace containing the built-in names is created when the Python interpreter starts up, and is never deleted. ② The global namespace of a module is generated when the module is read in. Module namespaces normally last until the script ends, i.e. the interpreter quits. ③ When a function is called, a local namespace is created for this function. This namespace is deleted either if the function ends, i.e. returns, or if the function raises an exception, which is not dealt with within the function. |
※ 作用域的产生
|
① def/lambda会创建新的作用域,生成器表达式都有引入新的作用域, ② class的定义没有引入作用域,只是创建一个隔离的命名空间。 ③ 在Python2中, 列表推导式(list comprehension)没有引入新的作用域, 在Python3中, 列表推导式引入了新的作用域. ④ 而对于Python 2和Python 3,生成器表达式都有引入新的作用域。 |
8 ● global & nonlocal
|
# 被global声明的变量会引用到当前模块的全局命名空间的变量(module-level namespace),如果该变量没有定义,也会在全局空间中添加这个变量。 # (Python3新语法)nonlocal变量声明在内部(inner)函数里, 它会从内向外引用找到的第一个外部函数的变量. |
|
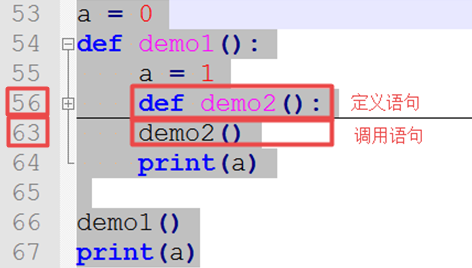
# 仔细揣摩下面程序的执行步骤: a = 0
def demo1(): a = 1
def demo2(): def demo3(): global a a = '小神仙' print('demo3 : ', a) # demo3 : 小神仙
demo3() print('demo2 : ', a) # demo2 : 1
demo2() print(a)
demo1() print(a) ''' demo3 : 小神仙 demo2 : 1 1 小神仙 ''' |
|
a = 0
def f1(): a = 1 def f2(): nonlocal a a = 2 f2() print('a in f1 : ',a)
f1() # a in f1 : 2
print(a) # 0 ''' a in f1 : 2 0 ''' |
|
※
|
9 ● 作用域链 (scope chain, nested scopes)
|
Python的作用域链指的是Python 的作用域解析顺序, 当Python需要使用(解析)一个变量的时候, Python会由内到外搜索需要使用的变量--先去自己所在函数产生的作用域去找,如果自己没有, 就到上一层作用域去找,直到找到为止, 找不到就会报错. |
10 ● 命名空间与变量的使用
|
① 在局部命令空间可以使用(access)全局命名空间中的命名,但是全局命名空间中不可以使用(access)局部命名空间中的名字 ② 对于局部命名空间来说, 局部命名空间如果有某个命名, 就使用自己的这个命名,如果没有, 再用全局的相同的命名(全局命名空间没有的话就报错) |
|
※ |
11 ● 函数的类型
|
type(func1()) # 类型是function |
12 ●函数的本质—变量
|
① 存储一个函数内存地址 ② 可以被赋值, 可以作为列表等容器的元素 ③ 可以作为函数的参数/返回值 ※ |
13 ● 闭包
|
闭包的概念: 如果一个内部函数 引用(reference)了 外部函数的 变量, 那么这个内部函数就叫做闭包(closure)函数 we have a closure in Python when a nested function references a value in its A "closure" is an expression (typically a function) that can have free variables together with an environment that binds those variables (that "closes" the expression). 闭包的目的: 把内部函数作为一个变量返回给调用者
函数内在包含子函数,并最终return子函数 而闭包函数的最大价值在于:我们可以在函数的外部(即子函数),直接读取该函数的局部变量。 |
|
常见的使用场景: 在函数外部调用函数内部的函数, 例如下面的在get_url()函数外调用函数内部的inner函数 |
|
from urllib.request import urlopen #模块 def get_url(): url = 'http://www.cnblogs.com/Eva-J/articles/7156261.html' def inner(): ret = urlopen(url).read() # 内部函数inner()引用了外部函数的url变量 return ret return inner #返回函数名 # print(inner.__closure__) # 返回一个元组(<cell at 0x00000000025265B8: str object at 0x0000000000459CC8>,) # 所有的函数对象都有一个__closure__属性,如果它是一个闭包函数,那么它包含一个cell objects元组。 # 如果inner.__closure__返回None, 说明inner不是闭包函数
get_web = get_url() # 将函数名赋值给get_web(), get_web就相当于一个函数了, 可以加()调用 res = get_web() # print(res) |
|
※ from urllib.request import urlopen def get_url(): url = 'http://www.cnblogs.com' def inner(): ret = urlopen(url).read() return ret return inner() # 直接调用
print(get_url()) |
九. Python基础(9)--命名空间, 作用域的更多相关文章
- 十九. Python基础(19)--异常
十九. Python基础(19)--异常 1 ● 捕获异常 if VS异常处理: if是预防异常出现, 异常处理是处理异常出现 异常处理一般格式: try: <............. ...
- 十一. Python基础(11)—补充: 作用域 & 装饰器
十一. Python基础(11)-补充: 作用域 & 装饰器 1 ● Python的作用域补遗 在C/C++等语言中, if语句等控制结构(control structure)会产生新的作用域 ...
- python基础11_函数作用域_global_递归
看到了一个16进制转换的小知识点,就验证了一下运行结果. #!/usr/bin/env python # coding:utf-8 # 看到了16进制转换的问题.顺便验证一下. a = 255 b = ...
- python函数对象-命名空间-作用域-02
函数对象 函数是第一对象: # 函数名指向的值可以被当做参数传递 函数对象的特性(*****灵活运用,后面讲装饰器会用到) 函数名可以像变量一样被传递 # 变量可以被传递 name = 'jason' ...
- Python基础之变量作用域
一.分类: 二.变量名的查找规则: 三.局部变量: 四.全局变量: 五.global语句: 六.nonlocal语句: 七.基础代码: # 全局变量:当前.py文件内部都可访问 g01 = 100 d ...
- python基础之命名空间
前言 命名空间通俗的理解就是对象或变量的作用范围,在python中分为局部命令空间.模块命名空间和build-in全局命名空间. 局部命名空间 局部命名空间即在一个函数或一个类中起作用的变量或引用的字 ...
- Python基础知识笔记-作用域
Python 中,程序的变量并不是在哪个位置都可以访问的,访问权限决定于这个变量是在哪里赋值的. 变量的作用域决定了在哪一部分程序可以访问哪个特定的变量名称.Python的作用域一共有4种,分别是: ...
- Python基础-作用域和命名空间(Scope and Namespace)
在Python中,对象是独立的,不同作用域中的不同名字都可以被绑定在同一个对象上,当然对这个对象的修改会影响所有的引用.赋值操作就是名字和对象的绑定或重绑定.这和C++中的引用是一样的. 1,基础概念 ...
- python基础(7)-函数&命名空间&作用域&闭包
函数 动态参数 *args def sum(*args): ''' 任何参数都会被args以元组的方式接收 ''' print(type(args)) # result:<class 'tupl ...
随机推荐
- centos php5.4 升级 php7
接上篇,edusoho需要php5.5以上版本,于是需要升级本地php php是通过yum默认安装的.以下安装参考 link https://blog.csdn.net/u012569217/arti ...
- [Database]各数据库连接配置:Oracle:thin 数据库连接/MySQL 连接配置
MySQL: String Driver="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; //驱动程序 String URL="jdb ...
- Server SQL Modes
The MySQL server can operate in different SQL modes, and can apply these modes differently for diffe ...
- 雷林鹏分享:C# 判断
C# 判断 判断结构要求程序员指定一个或多个要评估或测试的条件,以及条件为真时要执行的语句(必需的)和条件为假时要执行的语句(可选的). 下面是大多数编程语言中典型的判断结构的一般形式: 判断语句 C ...
- DNA sequence open reading frames (ORFs) | DNA序列的开放阅读框ORF预测
常见的ORF预测工具 Open Reading Frame Finder- NCBI ORF Finder - SMS OrfPredictor - YSU 基本概念 开放阅读框(英语:Open r ...
- LeetCode--020--括号匹配
题目描述: 给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串,判断字符串是否有效. 有效字符串需满足: 左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合. 左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合. 注意空 ...
- 树分治TLE原因
1.树分治有logn层,如果各层都进行一次memset相当于大小没变,可能TLE: 2.根节点全局变量会变,需要用局部变量记录,还有子树大小. 3.找根的时候的size是当前size,而不是输入数据中 ...
- Okhttp 插入缓存拦截器 解析
我们在做网络请求的时候,如果网络请求过于频繁而且请求的数据变动不大,或者基本没有变动,这个时候如果没有缓存功能,我们想一下 会浪费掉多少资源,一次请求刷新一次,去请求一次,不但会消耗用户的流量,而且还 ...
- 小程序模板中data传值有无...
A:<template is="gemSelectColor" data="{{optionData}}" />B:<template is= ...
- [Fiddler] ReadResponse() failed: The server did not return a complete response for this request. Server returned 0 bytes.
待解决 [Fiddler] ReadResponse() failed: The server did not return a complete response for this request. ...