Matlab周期图法使用FFT实现
参考文章:http://www.cnblogs.com/adgk07/p/9314892.html
首先根据他这个代码和我之前手上已经拥有的那个代码,编写了一个适合自己的代码。
首先模仿他的代码,测试成功。
思路:
短时傅里叶变换,其实还是傅里叶变换,只不过把一段长信号按信号长度(nsc)、重叠点数(nov)重新采样。
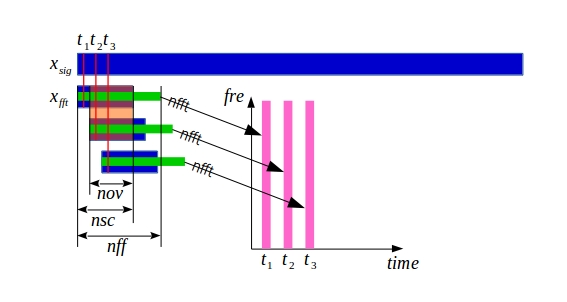
% 结合之前两个版本的stft,实现自己的周期图法,力求通俗易懂,代码分明。
% 该代码写的时候是按照输入信号为实数的思路写的,在每个片段fft时进行前一半行的转置存储。后续代码思路已修改。
clear; clc; close all
% %---------------------Chirp 信号生成(start)---------------------
fa = [ ]; % 扫描频率上下限
fs = ; % 采样频率
% 分辨率相关设定参数
te = ; % [s] 扫频时间长度
fre = ; % [s] 频率分辨率
tre = 0.002; % [Hz] 时间分辨率
t = :/fs:te; % [s] 时间序列
sc = chirp(t,fa(),te,fa()); % 信号生成 %待传参(实参)
signal = sc;
nsc = floor(fs/fre);
nff = ^nextpow2(nsc);%每个窗口进行fft的长度
nov = floor(nsc*0.9);
% %---------------------Chirp 信号生成(end)---------------------
%% 使用fft实现周期图法
% Input
% signal - Signal vector 输入信号(行向量)
% nsc - Number SeCtion 每个小分段的信号长度
% nov - Number OverLap 重叠点数
% fs - Frequency of Sample 采样率
% Output
% S - A matrix that each colum is a FFT for time of nsc
% 如果nfft为偶数,则S的行数为(nfft/+),如果nfft为奇数,则行数为(nfft+)/
% 每一列是一个小窗口的FFT结果,因为matlab的FFT结果是对称的,只需要一半
% W - A vector labeling frequency % T - A vector labeling time
% Signal Preprocessing
h = hamming(nsc, 'periodic'); % Hamming weight function 海明窗加权,窗口大小为nsc
L = length(signal); % Length of Signal 信号长度
nstep = nsc-nov; % Number of STep per colum 每个窗口的步进
ncol = fix( (L-nsc)/nstep ) + ; % Number of CoLum 信号被分成了多少个片段
nfft = ^nextpow2(nsc); % Number of Fast Fourier Transformation 每个窗口FFT长度
nrow = nfft/+;
%Symmetric results of FFT
STFT_X = zeros(nrow,ncol); %STFT_X is a matrix,初始化最终结果
index=;%当前片段第一个信号位置在原始信号中的索引
for i=:ncol
%提取当前片段信号值,并用海明窗进行加权(均为长度为nsc的行向量)
temp_S=signal(index:index+nsc-).*h';
%对长度为nsc的片段进行nfft点FFT变换
temp_X=fft(temp_S,nfft);
%从长度为nfft点(行向量)的fft变换中取一半(转换为列向量),存储到矩阵的列向量
STFT_X(:,i)=temp_X(:nrow)';
%将索引后移
index=index + nstep;
end % Turn into DFT in dB
STFT1 = abs(STFT_X/nfft);
STFT1(:end-,:) = *STFT1(:end-,:); % Add the value of the other half
STFT3 = *log10(STFT1); % Turn sound pressure into dB level
% Axis Generating
fax =(:(nfft/)) * fs/nfft; % Frequency axis setting
tax = (nsc/ : nstep : nstep*(ncol-)+nsc/)/fs; % Time axis generating
[ffax,ttax] = meshgrid(tax,fax); % Generating grid of figure % Output
W = ffax;
T = ttax;
S = STFT3; %% 画频谱图
subplot(,,) % 绘制自编函数结果
my_pcolor(W,T,S)
caxis([-130.86,-13.667]);
title('自编函数');
xlabel('时间 second');
ylabel('频率 Hz'); subplot(,,) % 绘制 Matlab 函数结果
s = spectrogram(signal,hamming(nsc),nov,nff,fs,'yaxis');
% Turn into DFT in dB
s1 = abs(s/nff);
s2 = s1(:nff/+,:); % Symmetric results of FFT
s2(:end-,:) = *s2(:end-,:); % Add the value of the other half
s3 = *log10(s2); % Turn sound pressure into dB level
my_pcolor(W,T,s3 )
caxis([-130.86,-13.667]);
title('Matlab 自带函数');
xlabel('时间 second');
ylabel('频率 Hz');
subplot(,,) % 两者误差
my_pcolor(W,T,*log10(abs(.^(s3/)-.^(S/))))
caxis([-,-13.667]);
title('error');
ylabel('频率 Hz');
xlabel('时间 second');
suptitle('Spectrogram 实现与比较');
内部调用了my_pcolor.m
function [ ] = my_pcolor( f , t , s )
%MY_PCOLOR 绘图函数
% Input
% f - 频率轴矩阵
% t - 时间轴矩阵
% s - 幅度轴矩阵
gca = pcolor(f,t,s); % 绘制伪彩色图
set(gca, 'LineStyle','none'); % 取消网格,避免一片黑
handl = colorbar; % 彩图坐标尺
set(handl, 'FontName', 'Times New Roman', 'FontSize', )
ylabel(handl, 'Magnitude, dB') % 坐标尺名称
end
function [ ] = my_pcolor( f , t , s )
%MY_PCOLOR 绘图函数
% Input
% f - 频率轴矩阵
% t - 时间轴矩阵
% s - 幅度轴矩阵
gca = pcolor(f,t,s); % 绘制伪彩色图
set(gca, 'LineStyle','none'); % 取消网格,避免一片黑
handl = colorbar; % 彩图坐标尺
set(handl, 'FontName', 'Times New Roman', 'FontSize', )
ylabel(handl, 'Magnitude, dB') % 坐标尺名称
end
接下来在主体不变的情况下,修改输入信号和函数返回结果,使其和自己之前的代码效果相同。
其实只要搞清楚了理论,实现上很简单。
一、首先分析Matlab周期图法API。
[spec_X,spec_f,spec_t]=spectrogram(signal,hamming(nsc, 'periodic'),nov,nff,Fs);
如果函数没有返回结果的调用,MATLAB直接帮我们绘图了。
1)当输入信号为复数时的代码:
clear
clc
close all
Fs = ; % Sampling frequency
T = /Fs; % Sampling period
L = ; % Length of signal
t = (:L-)*T; % Time vector
S = *sin(**pi*t)+*cos(**pi*t)*j; nsc=;%海明窗的长度,即每个窗口的长度
nov=;%重叠率
nff= max(,^nextpow2(nsc));%N点采样长度
%% matlab自带函数
figure()
spectrogram(S,hamming(nsc, 'periodic'),nov,nff,Fs);
title('spectrogram函数画图')
[spec_X,spec_f,spec_t]=spectrogram(S,hamming(nsc, 'periodic'),nov,nff,Fs);
变量:

其中:
spec_X矩阵行数为nff,列数是根据信号signal的长度和每个片段nsc分割决定的,共计col列。
spec_f 为nff*1的列向量。
spec_t为 1*ncol的行向量。
此时自己实现的Matlab代码为:
% 结合之前两个版本的stft,实现自己的周期图法,力求通俗易懂,代码分明。
clear; clc; close all
%% 信号输入基本参数
Fs = ; % Sampling frequency
T = /Fs; % Sampling period
L = ; % Length of signal
t = (:L-)*T; % Time vector
S = *sin(**pi*t)+*cos(**pi*t)*j; %传参
signal = S;
nsc = ; %每个窗口的长度,也即海明窗的长度
nff = max(,^nextpow2(nsc));%每个窗口进行fft的长度
nov = ; %重叠率
fs = Fs; %采样率 %% 使用fft实现周期图法
%后续可封装为函数:
% function [ S , W , T ] = mf_spectrogram...
% ( signal , nsc , nov , fs )
% Input
% signal - Signal vector 输入信号(行向量)
% nsc - Number SeCtion 每个小分段的信号长度
% nov - Number OverLap 重叠点数
% fs - Frequency of Sample 采样率
% Output
% S - A matrix that each colum is a FFT for time of nsc
% 如果nfft为偶数,则S的行数为(nfft/+),如果nfft为奇数,则行数为(nfft+)/
% 每一列是一个小窗口的FFT结果,因为matlab的FFT结果是对称的,只需要一半
% W - A vector labeling frequency 频率轴
% T - A vector labeling time 时间轴
% Signal Preprocessing
h = hamming(nsc, 'periodic'); % Hamming weight function 海明窗加权,窗口大小为nsc
L = length(signal); % Length of Signal 信号长度
nstep = nsc-nov; % Number of STep per colum 每个窗口的步进
ncol = fix( (L-nsc)/nstep ) + ; % Number of CoLum 信号被分成了多少个片段
nfft = max(,^nextpow2(nsc)); % Number of Fast Fourier Transformation 每个窗口FFT长度
nrow = nfft/+;
%
%
STFT1 = zeros(nfft,ncol); %STFT1 is a matrix 初始化最终结果
index = ;%当前片段第一个信号位置在原始信号中的索引
for i=:ncol
%提取当前片段信号值,并用海明窗进行加权(均为长度为nsc的行向量)
temp_S=signal(index:index+nsc-).*h';
%对长度为nsc的片段进行nfft点FFT变换
temp_X=fft(temp_S,nfft);
%将长度为nfft点(行向量)的fft变换转换为列向量,存储到矩阵的列向量
STFT1(:,i)=temp_X';
%将索引后移
index=index + nstep;
end %如果是为了和标准周期图法进行误差比较,则后续计算(abs,*,log(+1e-))不需要做,只需
%plot(abs(spec_X)-abs(STFT1))比较即可 STFT2 = abs(STFT1/nfft);
%nfft是偶数,说明首尾是奈奎斯特点,只需对2:end-1的数据乘以2
STFT2(:end-,:) = *STFT2(:end-,:); % Add the value of the other half
%STFT3 = *log10(STFT1); % Turn sound pressure into dB level
STFT3 = *log10(STFT2 + 1e-); % convert amplitude spectrum to dB (min = - dB) % Axis Generating
fax =(:(nfft-)) * fs./nfft; % Frequency axis setting
tax = (nsc/ : nstep : nstep*(ncol-)+nsc/)/fs; % Time axis generating % Output
W = fax;
T = tax;
S = STFT3; %% matlab自带函数
figure();
spectrogram(signal,hamming(nsc, 'periodic'),nov,nff,Fs);
title('spectrogram函数画图')
[spec_X,spec_f,spec_t]=spectrogram(signal,hamming(nsc, 'periodic'),nov,nff,Fs);
%减法,看看差距
figure()
plot(abs(spec_X)-abs(STFT1)) %% 画频谱图
figure
%利用了SIFT3
surf(W, T, S')
shading interp
axis tight
box on
view(, )
set(gca, 'FontName', 'Times New Roman', 'FontSize', )
xlabel('Frequency, Hz')
ylabel('Time, s')
title('Amplitude spectrogram of the signal')
handl = colorbar;
set(handl, 'FontName', 'Times New Roman', 'FontSize', )
ylabel(handl, 'Magnitude, dB') %跳频图
figure();
surf(T,W,S)
shading interp
axis tight
box on
view(, )
set(gca, 'FontName', 'Times New Roman', 'FontSize', )
ylabel('Frequency, Hz')
xlabel('Time, s')
title('Amplitude spectrogram of the signal')
handl = colorbar;
set(handl, 'FontName', 'Times New Roman', 'FontSize', )
ylabel(handl, 'Magnitude, dB')
重点关注8行、59行、66行、69行、82行
其实此时只要牢牢记住结果集中行数为nfft就行了。
2)当输入信号为实数时的代码:
clear
clc
close all
Fs = 1000; % Sampling frequency
T = 1/Fs; % Sampling period
L = 1000; % Length of signal
t = (0:L-1)*T; % Time vector
S = 20*sin(150*2*pi*t)+40*cos(250*2*pi*t);
nsc=100;%海明窗的长度,即每个窗口的长度
nov=0;%重叠率
nff= max(256,2^nextpow2(nsc));%N点采样长度
%% matlab自带函数
figure(1)
spectrogram(S,hamming(nsc, 'periodic'),nov,nff,Fs);
title('spectrogram函数画图')
[spec_X,spec_f,spec_t]=spectrogram(S,hamming(nsc, 'periodic'),nov,nff,Fs);
其中:
spec_X矩阵行数为nff/2+1,列数是根据信号signal的长度和每个片段nsc分割决定的,共计col列。
spec_f 为nff/2+1*1的列向量。
spec_t为 1*ncol的行向量。
主要是因为输入信号为实数时,fft变换的结果有一半是对称的,不必考虑。
自己实现的Matlab代码为:
% 结合之前两个版本的stft,实现自己的周期图法,力求通俗易懂,代码分明。
clear; clc; close all
%% 信号输入基本参数
Fs = ; % Sampling frequency
T = /Fs; % Sampling period
L = ; % Length of signal
t = (:L-)*T; % Time vector
S = *sin(**pi*t)+*cos(**pi*t); %传参
signal = S;
nsc = ; %每个窗口的长度,也即海明窗的长度
nff = max(,^nextpow2(nsc));%每个窗口进行fft的长度
nov = ; %重叠率
fs = Fs; %采样率 %% 使用fft实现周期图法
%后续可封装为函数:
% function [ S , W , T ] = mf_spectrogram...
% ( signal , nsc , nov , fs )
% Input
% signal - Signal vector 输入信号(行向量)
% nsc - Number SeCtion 每个小分段的信号长度
% nov - Number OverLap 重叠点数
% fs - Frequency of Sample 采样率
% Output
% S - A matrix that each colum is a FFT for time of nsc
% 如果nfft为偶数,则S的行数为(nfft/+),如果nfft为奇数,则行数为(nfft+)/
% 每一列是一个小窗口的FFT结果,因为matlab的FFT结果是对称的,只需要一半
% W - A vector labeling frequency 频率轴
% T - A vector labeling time 时间轴
% Signal Preprocessing
h = hamming(nsc, 'periodic'); % Hamming weight function 海明窗加权,窗口大小为nsc
L = length(signal); % Length of Signal 信号长度
nstep = nsc-nov; % Number of STep per colum 每个窗口的步进
ncol = fix( (L-nsc)/nstep ) + ; % Number of CoLum 信号被分成了多少个片段
nfft = max(,^nextpow2(nsc)); % Number of Fast Fourier Transformation 每个窗口FFT长度
nrow = nfft/+;
%
%
STFT1 = zeros(nfft,ncol); %STFT1 is a matrix 初始化最终结果
index = ;%当前片段第一个信号位置在原始信号中的索引
for i=:ncol
%提取当前片段信号值,并用海明窗进行加权(均为长度为nsc的行向量)
temp_S=signal(index:index+nsc-).*h';
%对长度为nsc的片段进行nfft点FFT变换
temp_X=fft(temp_S,nfft);
%将长度为nfft点(行向量)的fft变换转换为列向量,存储到矩阵的列向量
STFT1(:,i)=temp_X';
%将索引后移
index=index + nstep;
end % -----当输入信号为实数时,对其的操作(也就是说只考虑信号的前一半)
% 由于实数FFT的对称性,提取STFT1的nrow行
STFT_X = STFT1(:nrow,:); % Symmetric results of FFT %如果是为了和标准周期图法进行误差比较,则后续计算(abs,*,log(+1e-))不需要做,只需
%plot(abs(spec_X)-abs(STFT_X))比较即可 STFT2 = abs(STFT_X/nfft);
%nfft是偶数,说明首尾是奈奎斯特点,只需对2:end-1的数据乘以2
STFT2(:end-,:) = *STFT2(:end-,:); % Add the value of the other half
%STFT3 = *log10(STFT1); % Turn sound pressure into dB level
STFT3 = *log10(STFT2 + 1e-); % convert amplitude spectrum to dB (min = - dB) % Axis Generating
fax =(:(nrow-)) * fs./nfft; % Frequency axis setting
tax = (nsc/ : nstep : nstep*(ncol-)+nsc/)/fs; % Time axis generating % Output
W = fax;
T = tax;
S = STFT3; %% matlab自带函数
figure();
spectrogram(signal,hamming(nsc, 'periodic'),nov,nff,Fs);
title('spectrogram函数画图')
[spec_X,spec_f,spec_t]=spectrogram(signal,hamming(nsc, 'periodic'),nov,nff,Fs);
%减法,看看差距
figure()
plot(abs(spec_X)-abs(STFT_X)) %% 画频谱图
figure
%利用了SIFT3
surf(W, T, S')
shading interp
axis tight
box on
view(, )
set(gca, 'FontName', 'Times New Roman', 'FontSize', )
xlabel('Frequency, Hz')
ylabel('Time, s')
title('Amplitude spectrogram of the signal')
handl = colorbar;
set(handl, 'FontName', 'Times New Roman', 'FontSize', )
ylabel(handl, 'Magnitude, dB') %跳频图
figure();
surf(T,W,S)
shading interp
axis tight
box on
view(, )
set(gca, 'FontName', 'Times New Roman', 'FontSize', )
ylabel('Frequency, Hz')
xlabel('Time, s')
title('Amplitude spectrogram of the signal')
handl = colorbar;
set(handl, 'FontName', 'Times New Roman', 'FontSize', )
ylabel(handl, 'Magnitude, dB')
主要记到行数为nrow=nfft/2+1行。
重点关注代码8行,57行,62行,85行。
二、分析思路
1)自己在使用fft实现时,通过一个for循环,对每个nsc长度的片段进行加窗、nfft点的fft变换。
2)
1. 当输入信号为实数时,由于fft的对称性,从结果SIFT1仅取fft结果行数的一半放到结果矩阵SIFT_X中去。
2. 当输入信号为复数时,该矩阵的行数仍然为nff行,因此结果集即为SIFT1。
3. 此时每一列即是一个小片段的fft变换的结果,该列结果是复数。 可以和Matlab API得到的结果进行差值比较,发现结果完全一样。
这3处分析的不同,也正是两个自己实现代码的修改处,可参考上述代码。
3)后续由于考虑到绘图、幅值、频谱的影响,因此又在复数矩阵的结果上进行了一些运算,因此在后续封装为函数时根据需要进行改进。
Matlab周期图法使用FFT实现的更多相关文章
- 基2时抽8点FFT的matlab实现流程及FFT的内部机理
前言 本来想用verilog描述FFT算法,虽然是8点的FFT算法,但写出来的资源用量及时延也不比调用FFT IP的好, 还是老实调IP吧,了解内部机理即可,无需重复发明轮子. 参考 https:// ...
- 【Matlab】快速傅里叶变换/ FFT/ fftshift/ fftshift(fft(fftshift(s)))
[自我理解] fft:可以指定点数的快速傅里叶变换 fftshift:将零频点移到频谱的中间 用法: Y=fftshift(X) Y=fftshift(X,dim) 描述:fftshift移动零频点到 ...
- MatLab实现FFT与功率谱
FFT和功率谱估计 用Fourier变换求取信号的功率谱---周期图法 clf; Fs=1000; N=256;Nfft=256;%数据的长度和FFT所用的数据长度 n=0:N-1;t=n/Fs;%采 ...
- FFT原理及C++与MATLAB混合编程详细介绍
一:FFT原理 1.1 DFT计算 在一个周期内的离散傅里叶级数(DFS)变换定义为离散傅里叶变换(DFT). \[\begin{cases} X(k) = \sum_{n=0}^{N-1}x(n)W ...
- C#实现FFT(递归法)
C#实现FFT(递归法) 1. C#实现复数类 我们在进行信号分析的时候,难免会使用到复数.但是遗憾的是,C#没有自带的复数类,以下提供了一种复数类的构建方法. 复数相比于实数,可以理解为一个二维数, ...
- MATLAB处理信号得到频谱、相谱、功率谱
(此帖引至网络资源,仅供参考学习)第一:频谱 一.调用方法 X=FFT(x):X=FFT(x,N):x=IFFT(X);x=IFFT(X,N) 用MATLAB进行谱分析时注意: (1)函数FFT返回值 ...
- 经典功率谱估计及Matlab仿真
原文出自:http://www.cnblogs.com/jacklu/p/5140913.html 功率谱估计在分析平稳各态遍历随机信号频率成分领域被广泛使用,并且已被成功应用到雷达信号处理.故障诊断 ...
- matlab 功率谱分析
matlab 功率谱分析 1.直接法:直接法又称周期图法,它是把随机序列x(n)的N个观测数据视为一能量有限的序列,直接计算x(n)的离散傅立叶变换,得X(k),然后再取其幅值的平方,并除以N,作为序 ...
- (转) 经典功率谱估计及Matlab仿真
原文出自:http://www.cnblogs.com/jacklu/p/5140913.html 功率谱估计在分析平稳各态遍历随机信号频率成分领域被广泛使用,并且已被成功应用到雷达信号处理.故障诊断 ...
随机推荐
- Linux 读书笔记 三 (第二章)
一.学习目标 1. 理解二进制在计算机中的重要地位 2. 掌握布尔运算在C语言中的应用 3. 理解有符号整数.无符号整数.浮点数的表示 4. 理解补码的重要性 5. 能避免C语言中溢出,数据类型转 ...
- 剑指offer:矩形覆盖
题目描述: 我们可以用2*1的小矩形横着或者竖着去覆盖更大的矩形.请问用n个2*1的小矩形无重叠地覆盖一个2*n的大矩形,总共有多少种方法? 解题思路: 和跳台阶那道题差不多.分别以矩形的两条边长做拓 ...
- 【CS231N】4、神经网络
一.疑问 二.常用激活函数 1. Sigmoid sigmoid将输入实数值"挤压"到0到1范围内.更具体地说,很大的负数变成0,很大的正数变成1.它对于神经元的激活频率有良好 ...
- java属性编辑器,即PropertyEditor
出处:http://www.iteye.com/topic/1123628
- 如何解决abd.exe已停止工作
打开电脑,右键点击属性会出现如下界面: 点击左边高级系统设置:将会出现如下界面: 点击环境变量,点编辑. 把环境变量中的 ANDROID_ADB_SERVER_PORT 改成1122以后还遇到这个问 ...
- iOS开发短信验证码封装 方便好用
---恢复内容开始--- 1.RootViewControler// Copyright © 2016年 Chason. All rights reserved.// #import "V ...
- grunt入门讲解5:创建插件,安装Grunt以及常见问题
创建插件 创建插件主要有以下几个步骤: (1)通过 npm install -g grunt-init 命令安装 grunt-init .(2)通过 git clone git://github.co ...
- 高性能页面加载技术--BigPipe设计原理及Java简单实现
1.技术背景 动态web网站的历史可以追溯到万维网初期,相比于静态网站,动态网站提供了强大的可交互功能.经过几十年的发展,动态网站在互动性和页面显示效果上有了很大的提升,但是对于网站动态网站的整体页面 ...
- delphi(假三层之数据访问层)(第一天)
本论文主要是通过三天来讲解三层的结构,今天是第一天,先讲解一下delphi下的Models层,我主要封装了两个查询得到数据集的函数,主要是通过在表示层上创建的数数据集控件传递进来,通过业务逻辑对语句的 ...
- ZJOI2018外省选手酱油记Day1
Day0 上午考试...又爆零了 下午讲完题后放假 然后就滚回去收拾行李准备去\(ZJ\) Day1 衢州?我怎么从来没听过这个地方..肯定是我见识少 下午 上高铁出发,\(3个小时\),看了一下电影 ...
