Spring深入浅出(二)IOC的单例 ,继承,依赖,JDBC,工厂模式以及自动装载
IOC的单例模式--Bean
Spring中的bean是根据scope来决定的。
scope有4种类型:
1.singleton:单例模型,表示通过Spring容器获取的该对象是唯一的。常用并且默认。
2.prototype:多例模型,表示通过Spring容器获取的对象都是不同的(类似于Java基础中new出来的对象地址是唯一的)。
3.reqeust:请求,表示在一次http请求内有效。
4.session:会话,表示在一个用户会话内有效。
1.创建一个对象
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
2.在spring的l配置文件中将User的实例化。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="user" class="com.test.entity.User">
<property name="id" value="1"></property>
<property name="name" value="User1"></property>
</bean> </beans>
3.测试类中通过Spring容器获取两个User实例化对象,并且通过==方法判断是否为同一个对象。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
User u1 = (User) applicationContext.getBean("user");
User u2 = (User) applicationContext.getBean("user");
System.out.println(u1 == u2);
}
}
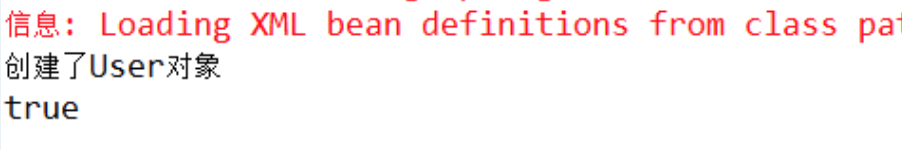
总结:看到结果打印true,表示user1和user2是同一个对象,所以scope默认值为singleton(单例模式),也就是用spring创建的对象是单例的。
改成多例模式的代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="user" class="com.test.entity.User" scope="prototype">
<property name="id" value="2"></property>
<property name="name" value="User2"></property>
</bean> </beans>
Spring的继承
Spring的继承,与Java的继承不一样,子bean和父bean的方法一样,子bean可以继承父bean中的属性。
如果子bean继承父bean,同时子bean给属性赋值,那么会覆盖掉父bean的值。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="user" class="com.test.entity.User">
<property name="id" value="1"></property>
<property name="name" value="张三1"></property>
</bean> <bean id="user2" class="com.test.entity.User" parent="user">
<!-- 覆盖掉user的name属性值 -->
<property name="name" value="张三2"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
Spring的依赖
与继承类似,依赖也是bean和bean之间的一种关联方式,配置依赖关系后,被依赖的bean一定先创建,再创建依赖的bean。
使用的关键字是depends-on="被依赖的bean的id"
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- user依赖于car -->
<bean id="user" class="com.test.entity.User" depends-on="car">
<property name="id" value="1"></property>
<property name="name" value="张三"></property>
</bean> <bean id="car" class="com.test.entity.Car">
<property name="id" value="1"></property>
<property name="brand" value="宝马"></property>
</bean> </beans>
上述代码执行顺序是:car-->user。先创建car,再创建user
Spring读取外部资源。
在开发中,类似于数据库等文件的配置会保存在一个properties文件中,便于维护,因此使用Spring需要来读取数据源对象。
1.先创建一个peoperties文件在路径下,具体位置根据项目需求来放置。
##key==value的形式
driverName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shop
user = root
pwd = root
2.spring的配置文件中配置数据源,这里用到的是C3P0数据源。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> <!-- 导入外部的资源文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder> <!-- 创建数据源 ,通过${}读取资源文件中的数据,${}中填写key,name中的值根据连接池的不同名字可能不同,尽量反编译代码去找一下对应的属性名-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="user" value="${user}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${pwd}"></property>
<property name="driverClass" value="${driverName}"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${url}"></property>
</bean> </beans>
3.测试
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
DataSource ds = (DataSource) applicationContext.getBean("dataSource");
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = ds.getConnection();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(conn);
}
}
IOC通过工厂方法创建对象
Spring中的IOC是典型的工厂模式,那么如何使用工厂模式来创建bean?
IOC通过工厂模式创建bean有两种方式:
1.静态工厂方法
2.实例工厂方法
静态工厂实例化
1.先创建一个实体类
2.创建静态工厂类,静态工厂方法。
3.编写Spring的配置文件
4.编写测试类
//步骤1:创建一个实体类
public class Car {
private int num;
private String brand;
public int getNum() {
return num;
}
public void setNum(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public Car(int num, String brand) {
super();
this.num = num;
this.brand = brand;
}
public Car() {
super();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car [num=" + num + ", brand=" + brand + "]";
}
}
//步骤2:创建一个静态类
public class StaticCarFactory {
private static Map<Integer,Car> cars;
//静态代码块
static{
cars = new HashMap<Integer,Car>();
cars.put(1, new Car(1,"奥迪"));
cars.put(2, new Car(2,"宝马"));
}
//静态方法
public static Car getCar(int num){
return cars.get(id);
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 配置静态工厂创建car对象 -->
<!-- factory-method:指向静态方法 getCar() -->
<bean id="car1" class="com.test.entity.StaticCarFactory" factory-method="getCar">
<!-- value为要生成的哪个对象的key -->
<constructor-arg value="1"></constructor-arg>
</bean> </beans>
//步骤4:测试类
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Car car = (Car) applicationContext.getBean("car1");
System.out.println(car);
}
}
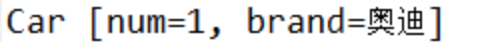
实例工厂方法
1.创建实例工厂类,工厂方法 。
2.spring的配置文件中配置bean。
3.在测试类中直接获取car2对象。
//步骤1:创建实例工厂类
public class InstanceCarFactory {
private Map<Integer,Car> cars;
public InstanceCarFactory() {
cars = new HashMap<Integer,Car>();
cars.put(1, new Car(1,"奥迪"));
cars.put(2, new Car(2,"宝马"));
}
public Car getCar(int num){
return cars.get(num);
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 配置实例工厂对象 -->
<bean id="carFactory" class="com.test.entity.InstanceCarFactory"></bean> <!-- 通过实例工厂对象创建car对象 factory-bean:放置实例化的工厂对象bean的id,然后再设置factory-method:调用方法 -->
<bean id="car2" factory-bean="carFactory" factory-method="getCar">
<constructor-arg value="1"></constructor-arg>
</bean> </beans>
测试类与静态工程的方式一样,并且结果也是生成key为1的car对象。
总结
两种方式的区别:
(1)使用静态工厂方法的方式创建car对象,不需要实例化工厂对象,因为静态工厂的静态方法,不需要创建对象即可调用。所以spring的配置文件只需要配置一个Car的bean,而不需要配置工厂bean。
(2)使用实例工厂方法创建car对象,必须先实例化工厂对象,因为调用的是非静态方法,必须通过对象调用,不能直接通过类来调用,所以spring的配置文件中需要先配置工厂bean,再配置Car bean。
IOC的自动装载
Spring框架提供了一种更加简便的方式:自动装载,不需要手动配置property,IOC容器会根据bean的配置自动选择bean完成依赖注入(DI)。
自动装载有两种方式:
byName:通过属性名自动装载。
byType:通过属性对应的数据类型自动装载。
//先创建一个实体类,并且生成setter/getter方法和toString方法
public class Person {
private int id;
private String name;
private Car car;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Car getCar() {
return car;
}
public void setCar(Car car) {
this.car = car;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", car=" + car + "]";
} }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--
创建person对象时,没有在property中配置car属性
所以IOC容器会自动进行装载
autowire="byName"表示通过匹配属性名的方式去装载对应的bean
Person实体类中有car属性,所以就将的bean注入到person中。
-->
<bean id="p1" class="com.test.entity.Person" autowire="byName">
<property name="id" value="1"></property>
<property name="name" value="ZhangSan"></property>
</bean> <bean id="car1" class="com.test.entity.StaticCarFactory" factory-method="getCar">
<constructor-arg value="1"></constructor-arg>
</bean> <!-- byType即通过属性的数据类型来配置。
关键字:autowire="byType"
-->
<bean id="p2" class="com.test.entity.Person" autowire="byType">
<property name="id" value="1"></property>
<property name="name" value="张三"></property>
</bean> <bean id="car2" class="com.test.entity.StaticCarFactory" factory-method="getCar">
<constructor-arg value="1"></constructor-arg>
</bean> </beans>
注意:
(1)使用了byType进行自动装载,如果spring的配置文件中配置了两个Car的bean,但是IOC容器不知道应该将哪一个bean装载到person对象中,因此可能会报错。所以在使用byType进行自动装载时,spring的配置文件中只能配置一个Car的bean才能使用byType。
(2)通过property标签手动进行属性的注入优先级更高,若自动注入和手动配置两种方式同时存在,则以property的配置为主。
所以在日常的代码编写过程中,尽量避免的使用byType去自动装配。
Spring深入浅出(二)IOC的单例 ,继承,依赖,JDBC,工厂模式以及自动装载的更多相关文章
- spring的controller默认是单例还是多例
转: spring的controller默认是单例还是多例 先看看spring的bean作用域有几种,分别有啥不同. spring bean作用域有以下5个: singleton:单例模式,当spri ...
- spring如何解决单例循环依赖问题?
更多文章点击--spring源码分析系列 1.spring循环依赖场景2.循环依赖解决方式: 三级缓存 1.spring循环引用场景 循环依赖的产生可能有很多种情况,例如: A的构造方法中依赖了B的实 ...
- 【开发者笔记】揣摩Spring-ioc初探,ioc是不是单例?
前言: 控制反转(Inversion of Control,英文缩写为IoC)把创建对象的权利交给框架,是框架的重要特征,并非面向对象编程的专用术语.它包括依赖注入(Dependency Inject ...
- java-静态-单例-继承
概要图 一.静态 1.1 静态方法 创建对象就是为了产生实例,并进行数据的封装. 而调用功能时,确没有用到这些对象中封装的数据. 该对象的创建有意义吗?虽然可以编译并运行,但是在堆内存中空间较为浪费. ...
- 【Java面试宝典】说说你对 Spring 的理解,非单例注入的原理?它的生命周期?循环注入的原理, aop 的实现原理,说说 aop 中的几个术语,它们是怎么相互工作的?
AOP与IOC的概念(即spring的核心) IOC:Spring是开源框架,使用框架可以使我们减少工作量,提高工作效率并且它是分层结构,即相对应的层处理对应的业务逻辑,减少代码的耦合度.而sprin ...
- Struts2 本是非单例的,与Spring集成就默认为单例
1.Struts2本身action类是多例,此设计的原因在于本身action担任了数据载体,如果做成单例,则会便多用户数据受到影响: 2.当Struts2 与 spring整合时,Struts2的Ac ...
- spring中如何向一个单例bean中注入非单例bean
看到这个题目相信很多小伙伴都是懵懵的,平时我们的做法大都是下面的操作 @Component public class People{ @Autowired private Man man; } 这里如 ...
- filter和spring 的interceptor都是单例的,都不是线程安全的
Filter 是在 Servlet 容器启动时就初始化的,因此可以认为是以单例对象存在的,如果一个请求线程对其中的成员变量修改的话,会影响到其他的请求线程,因此认为是多线程不安全的.
- 漫谈设计模式(二):单例(Singleton)模式
1.前言 实际业务中,大多业务类只需要一个对象就能完成所有工作,另外再创建其他对象就显得浪费内存空间了,例如web开发中的servlet,这时便要用到单例模式,就如其名一样,此模式使某个类只能生成唯一 ...
随机推荐
- oracle 下操作blob字段是否会产生大量redo
操作blob字段是否会产生大量redo,答案是不会.以下来做一个实验,測试数据库版本号是11.2.0.1.0: --创建一张表做測试之用 create table test_blob ( id n ...
- Linux内核编译測试
内核编译: Step 1:配置内核编译选项. make menuconfig Optional Step :排除编译结果文件(.o)等之间的依赖性. make mrproper Optional St ...
- CoreData 从入门到精通(四)并发操作
通常情况下,CoreData 的增删改查操作都在主线程上执行,那么对数据库的操作就会影响到 UI 操作,这在操作的数据量比较小的时候,执行的速度很快,我们也不会察觉到对 UI 的影响,但是当数据量特别 ...
- Pandas与Matplotlib
Pandas与Matplotlib基础 pandas是Python中开源的,高性能的用于数据分析的库.其中包含了很多可用的数据结构及功能,各种结构支持相互转换,并且支持读取.保存数据.结合matplo ...
- 制作可以SSH的Docker容器
以 Ubuntu 16.04为例: Docker里的root密码是随机的, 用passwd来设置新的密码 安装完SSH_SERVER后, 默认是不能用root登录的. vi /etc/ssh/sshd ...
- Java7里try-with-resources分析--转
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/hengyunabc/article/details/18459463 这个所谓的try-with-resources,是个语法糖.实际上就是自动调 ...
- Linux mount挂载umount卸载
mount/umount挂载/卸载 对于Linux用户来讲,不论有几个分区,分别分给哪一个目录使用,它总归就是一个根目录.一个独立且唯一的文件结构 Linux中每个分区都是用来组成整个文件系统的一部分 ...
- Win7 利用批处理文件结束进程
@echo offtitle 结束进程正在进行... ::结束进程TeamViewer.exewmic process where name="TeamViewer.exe" ca ...
- python 3.x 学习笔记12 (反射 and 异常)
1.反射通过字符串映射或修改程序运行时的状态.属性.方法 getattr(obj,name_str): 根据字符串name_str去获取obj对象里的对应的方法的内存地址 hasttr(obj,na ...
- <%=%>、<%%>、<%@%>、<%#%>的区别
1.<%= %> 里面放变量名,获取后台的变量值,直接输入变量到页面上,里面放的变量名,未经过encode eg: 后台: seession["ab"]=ab; 前台: ...
