PySide——Python图形化界面入门教程(二)
PySide——Python图形化界面入门教程(二)
——交互Widget和布局容器
——Interactive Widgets and Layout Containers
翻译自:http://pythoncentral.io/pyside-pyqt-tutorial-interactive-widgets-and-layout-containers/
上一个教程中,我们了解了一些QWidget提供的功能,还有一个特殊的子类QLabel。更进一步的,我们完成了一个用来说明简单Python/Qt应用的例子。但是,我们掌握的远远不能满足用户的需求,因为我们只能给他们显示文本,我们的应用只会唱独角戏!我们需要一些方法让用户可以和我们的程序交互,让独角戏变成二人转。Qt提供了丰富的交互式widgets,这里我们将要学习其中的一小部分;我们将使用他们体验如何在图形化(form)上布置widgets。下一个教程,我们将学习如何使用信号和槽来响应用户的交互。
交互式Widgets
Python/Qt有一系列的widgets,可以非常简单的实现与用户交互,并且容易和你的应用逻辑联系。
按钮(Buttons)
一个最简单的交互方式就是让用户点击按钮,Qt中就是QPushButton。QPushButton构造器有三个结构:
QPushButton(parent=None)
QPushButton(text, [parent=None])
QPushButton(icon, text, [parent=None])
parent参数是一个QWidget,text是一个Python string或unicode,icon是一个QIcon。创建一个被some-form拥有的带有文字“Go”的按钮,可以这样:
go_button = QPushButton('Go', some_form)
如果我们想为按钮设置一个键盘快捷键,如Alt-G,我们可以在‘Go’前添加一个‘&G’:
go_button = QPushButton('&Go', some_form)
这还有一些按钮的其他功能,还拿go_button做例子,你可以将其设置为form的默认按键:
go_button.setDefault(True)
还可以设置成平的:
go_button.setFlat(True)
将False传递到方法中会有相反的作用。一个按钮还可以在被点击时弹出一个菜单(menu):传递一个QMenu对象给按钮的setMenu方法。(我们以后再研究菜单)
文本框(Textboxes)
Qt的文本框控件是QLineEdit;它允许用户输入编辑单行的简单文本,其构造器有如下两种:
QLineEdit(parent=None)
QLineEdit(text, [parent=None])
他们的不同就是第二个允许用text参数设置包含的文本。QLineEdit对象有许多的方法,但是我们只关心几个最基本的。你可以使用text()方法取回文本,用setText(text)设置文本,使用setMaxLength(chars)设置最大可输入长度。它可以通过setReadOnly(True)设置为只读的,使用setPlaceholderText(text)设置占位文字(placeholder text,就是那种你输入前提示说明的字)。QLineEdit还有更多的高级属性:可以设置输入过滤器,处理选择和输入历史等等。
组合框(Comboboxes)
QComboBox widget是用来给用户提供多个文本或文本/图标的选择,用户必须选择其一。(多项选择参见QListView和QListWidget)它的构造器如下:
QComboBox(parent)
它的构造如此简单,但是目前还没有任何选项。你可以用多种方式添加选项。如果你的所有选项都是文字的,你可以使用addItems(texts),texts是字符串列表。一个一个的添加选项可以使用addItem,它有两个有效的方式
addItem(icon, text, [userData=None])
addItem(text, [userData=None])
参数icon是QIcon,text是一个unicode对象,userData是任何对象。你可以使用insertItem插入选项:
insertItem(index, icon, text, [userData=None])
insertItem(index, text, [userData=None])
QComboBox是一个灵活的widget,用它还可以做更多的事情。
例子程序:总览
接下来,我们将学习如何把小部件组合成一个表单布局,但在我们可以做到这一点之前,让我们先看一下这个示例应用程序。
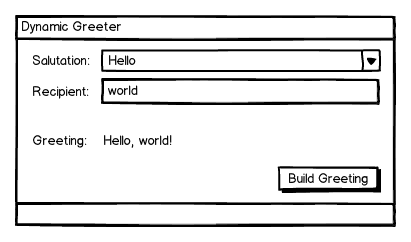
正如你所看到的,这是一个非常简单的应用程序。用户可以选择一个称呼和进入的人的姓名(或其他单位)他们要打招呼,当他们点击“建立问候,问候将在窗体上显示一个标签。
布局管理(Layout Management)
PySide和PyQt有两个可用的方法来管理布局:使用绝对位置,开发者必须明确设置每个widget和位置和大小;使用的布局容器(layout containers),自动安排位置和调整大小。我们将用两种方法构建上面提到的例子程序。
绝对位置
去设置widget的无力位置,你需要使用widget的move(x, y)方法;x和y是水平和垂直距离,这个距离是从外框(form)的左上角到widget的左上角。这是我们使用绝对距离创建的外形:
# Every Qt application must have one and only one QApplication object;
# it receives the command line arguments passed to the script, as they
# can be used to customize the application's appearance and behavior
qt_app = QApplication(sys.argv) class AbsolutePositioningExample(QWidget):
''' An example of PySide absolute positioning; the main window
inherits from QWidget, a convenient widget for an empty window. '''
def __init__(self):
# Initialize the object as a QWidget
QWidget.__init__(self) # We have to set the size of the main window
# ourselves, since we control the entire layout
self.setMinimumSize(400, 185)
self.setWindowTitle('Dynamic Greeter') # Create the controls with this object as their parent and set
# their position individually; each row is a label followed by
# another control # Label for the salutation chooser
self.salutation_lbl = QLabel('Salutation:', self)
self.salutation_lbl.move(5, 5) # offset the first control 5px
# from top and left
self.salutations = ['Ahoy',
'Good day',
'Hello',
'Heyo',
'Hi',
'Salutations',
'Wassup',
'Yo']
# Create and fill the combo box to choose the salutation
self.salutation = QComboBox(self)
self.salutation.addItems(self.salutations) # Allow 100px for the label and 5px each for borders at the
# far left, between the label and the combobox, and at the far
# right
self.salutation.setMinimumWidth(285)
# Place it five pixels to the right of the end of the label
self.salutation.move(110, 5) # The label for the recipient control
self.recipient_lbl = QLabel('Recipient:', self)
# 5 pixel indent, 25 pixels lower than last pair of widgets
self.recipient_lbl.move(5, 30) # The recipient control is an entry textbox
self.recipient = QLineEdit(self)
# Add some ghost text to indicate what sort of thing to enter
self.recipient.setPlaceholderText('world' or 'Matey')
# Same width as the salutation
self.recipient.setMinimumWidth(285)
# Same indent as salutation but 25 pixels lower
self.recipient.move(110, 30) # The label for the greeting widget
self.greeting_lbl = QLabel('Greeting:', self)
# Same indent as the others, but 45 pixels lower so it has
# physical separation, indicating difference of function
self.greeting_lbl.move(5, 75) # The greeting widget is also a label
self.greeting = QLabel('', self)
# Same indent as the other controls
self.greeting.move(110, 75) # The build button is a push button
self.build_button = QPushButton('&Build Greeting', self) # Place it at the bottom right, narrower than
# the other interactive widgets
self.build_button.setMinimumWidth(145)
self.build_button.move(250, 150) def run(self):
# Show the form
self.show()
# Run the Qt application
qt_app.exec_() # Create an instance of the application window and run it
app = AbsolutePositioningExample()
app.run()
不用说,一个大型的应用程序可能会变得非常麻烦。另外,它也没有大小改变的反应;标签只是坐在指定的位置。不仅如此,想象一下,如果有视觉障碍的用户想把他们的字体设置的大一些;使用固定的位置,您设置的控件将不再适当。
布局容器(Layout Containers)
由于上述种种原因,布局容器比绝对位置更为常用,他们更加灵活,替程序员分担了计算确切位置的任务,并且他们可以调整布局去适应不同平台的GUI设置,如GTK+, KDE, Mac OS X等等。这有5个主要的布局容器,他们都是继承自QLayout:
- QHBoxLayout
- QVBoxLayout
- QGridLayout
- QStackedLayout
- QFormLayout
他们用来满足不同的需求。简而言之,QHBoxLayout和QVBoxLayout将widgets一个挨一个的水平(horizontally)、垂直(vertically)排列;QGridLayout可按照任意大小表格布局;QStackedLayout将他们一个放在一个的上面(就像stack栈一样);QFormLayout是一个特殊的两栏布局,它提供特殊的方法用标签安排内容在第一列,在第二列安排相关的空间。这些布局非常有用,但是你的布局选项不局限于他们,你可以将布局嵌套组合来创建更复杂易用的用户接口。现在,我们来看看水平、垂直布局和QFormLayout。
QVBoxLayout和QHBoxLayout
盒子布局(box layouts)非常的直截了当。使用它作为最上层的布局,创建布局非常简单——它的构造器需要任何参数——并且使用望名知义的方法addWidget来添加widget。接下来你就可以设置它所属的窗口。例如:
win = QWidget() # The three labels
lbl_1 = QLabel("We're")
lbl_2 = QLabel('stacked')
lbl_3 = QLabel('up.') # A vertical box layout
layout = QVBoxLayout() # Add the widgets to the layout
layout.addWidget(lbl_1)
layout.addWidget(lbl_2)
layout.addWidget(lbl_3) # Set layout as the layout for the window
win.setLayout(layout)
QHBoxLayout也可以被同样使用,尽管它不常作为最上层的布局。它常常被作为子布局。为一个布局中添加另一个布局,使用该布局容器的addLayout方法,例如:
layout = QVBoxLayout()
sub_layout = QHBoxLayout() # ... Fill the layouts with widgets ... layout.addLayout(sub_layout)
盒子布局有另一个更重要并且常用的方法:addStretch。一个常见的布局有很多的控件,他们之间具有灵活的空间。为了完成这个目的,在盒子的开始添加widgets,然后添加一个设置大于0的空闲空间,layout.addStretch(1),然后再添加剩下的widgets。
QFormLayout
QFormLayout非常像QVBoxLayout,但是它可以不用创建子布局就轻松的将每一行分成两列。这通过使用外观布局的addRow方法,它有很多重载(overloaded?)。单参数的版本:
addRow(QWidget)
addRow(QLayout)
添加widget或布局在整个QFormLayout的最后。双参数版本:
unicode, QLayout
unicode, QWidget
QWidget, QWidget
QWidget, QLayout
作为一个“标签”在第一列中初始化元素,第二个是第二列。unicode参数作为QLabel的文本,QWidget可以是任意的widget。
盒子布局的例子(Box Layout Example)
现在我们已经了解了如何创建交互式widget和用灵活的布局管理他们,现在我们重新创建例子应用。我们窗口的主布局是QVBoxLayout,它有两个子布局,一个QformLayout包含所有的标签控件,和一个QHBoxLayout来管理右下角的按钮位置。我们将使用addStretch来分离QFormLayout,并且把按钮挤到QHBoxLayout的右边。你会注意到,许多代码同绝对位置版本是一样的;比如,创建单独控件的时候。
qt_app = QApplication(sys.argv) class LayoutExample(QWidget):
''' An example of PySide/PyQt absolute positioning; the main window
inherits from QWidget, a convenient widget for an empty window. ''' def __init__(self):
# Initialize the object as a QWidget and
# set its title and minimum width
QWidget.__init__(self)
self.setWindowTitle('Dynamic Greeter')
self.setMinimumWidth(400) # Create the QVBoxLayout that lays out the whole form
self.layout = QVBoxLayout() # Create the form layout that manages the labeled controls
self.form_layout = QFormLayout() # The salutations that we want to make available
self.salutations = ['Ahoy',
'Good day',
'Hello',
'Heyo',
'Hi',
'Salutations',
'Wassup',
'Yo'] # Create and fill the combo box to choose the salutation
self.salutation = QComboBox(self)
self.salutation.addItems(self.salutations) # Add it to the form layout with a label
self.form_layout.addRow('&Salutation:', self.salutation) # Create the entry control to specify a recipient
# and set its placeholder text
self.recipient = QLineEdit(self)
self.recipient.setPlaceholderText("e.g. 'world' or 'Matey'") # Add it to the form layout with a label
self.form_layout.addRow('&Recipient:', self.recipient) # Create and add the label to show the greeting text
self.greeting = QLabel('', self)
self.form_layout.addRow('Greeting:', self.greeting) # Add the form layout to the main VBox layout
self.layout.addLayout(self.form_layout) # Add stretch to separate the form layout from the button
self.layout.addStretch(1) # Create a horizontal box layout to hold the button
self.button_box = QHBoxLayout() # Add stretch to push the button to the far right
self.button_box.addStretch(1) # Create the build button with its caption
self.build_button = QPushButton('&Build Greeting', self) # Add it to the button box
self.button_box.addWidget(self.build_button) # Add the button box to the bottom of the main VBox layout
self.layout.addLayout(self.button_box) # Set the VBox layout as the window's main layout
self.setLayout(self.layout) def run(self):
# Show the form
self.show()
# Run the qt application
qt_app.exec_() # Create an instance of the application window and run it
app = LayoutExample()
app.run()
注意到这些对程序员来说是多么的容易。当代码不太短的时候——不是每个便捷都会使代码量减少,创建和嵌套布局有一定的代码开销的时候——精神上的负担就小多了。开发人员只需完成一个组合的布局,产生所需的效果,并创建他们;控件的创建和修改是隔离的,很少再要去考虑其影响到布局和其他控件。下一部分,我们将以这个例子创建的界面,让它实际上做些事。
By Ascii0x03
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/ascii0x03/p/5496699.html
PySide——Python图形化界面入门教程(二)的更多相关文章
- PySide——Python图形化界面入门教程(四)
PySide——Python图形化界面入门教程(四) ——创建自己的信号槽 ——Creating Your Own Signals and Slots 翻译自:http://pythoncentral ...
- PySide——Python图形化界面入门教程(六)
PySide——Python图形化界面入门教程(六) ——QListView和QStandardItemModel 翻译自:http://pythoncentral.io/pyside-pyqt-tu ...
- PySide——Python图形化界面入门教程(五)
PySide——Python图形化界面入门教程(五) ——QListWidget 翻译自:http://pythoncentral.io/pyside-pyqt-tutorial-the-qlistw ...
- PySide——Python图形化界面入门教程(三)
PySide——Python图形化界面入门教程(三) ——使用内建新号和槽 ——Using Built-In Signals and Slots 上一个教程中,我们学习了如何创建和建立交互widget ...
- PySide——Python图形化界面入门教程(一)
PySide——Python图形化界面入门教程(一) ——基本部件和HelloWorld 翻译自:http://pythoncentral.io/intro-to-pysidepyqt-basic-w ...
- PySide——Python图形化界面
PySide——Python图形化界面 PySide——Python图形化界面入门教程(四) PySide——Python图形化界面入门教程(四) ——创建自己的信号槽 ——Creating Your ...
- python+pycharm+PyQt5 图形化界面安装教程
python图形化界面安装教程 配置环境变量 主目录 pip所在目录,及script目录 更新pip(可选) python -m pip install --upgrade pip ps:更新出错一般 ...
- Oracle数据库及图形化界面安装教程详解
百度云盘oracle数据库及图形化界面安装包 链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1DHfui-D2n1R6_ND3wDziQw 密码: f934 首先在电脑D盘(或者其他不是C盘 ...
- 如何使用python图形化界面wxPython
GUI库主要有三类:tkinter,wxPython和PyQt5,下面主要是针对wxPython的使用说明. 下面的操作均在win10 + pycharm上进行 wxPython的安装: pip in ...
随机推荐
- Redis的增删改查、持久化你会了吗
原文:Redis的增删改查.持久化你会了吗 Redis是用C语言实现的,一般来说C语言实现的程序"距离"操作系统更近,执行速度相对会更快. Redis使用了单线程架构,预防了多线程 ...
- python启动应用程序和终止应用程序
python启动应用程序和终止应用程序 1. 目的 每天上班,工作需要,电脑上需要每天开机启动一些软件,下班时候,需要关掉一些软件.一个一个打开和关闭貌似是很繁琐的,于是乎,这个脚本产生了. 2. 环 ...
- jsp与servlet(转)
一.基本概念 1.1 Servlet Servlet是一种服务器端的Java应用程序,具有独立于平台和协议的特性,可以生成动态的Web页面.它担当客户请求(Web浏览器或其他HTTP客户程序)与服务器 ...
- 检索01-c#中基本数据类型和引用类型的区别
1.基本定义 基本数据类型包括:整型.浮点型.字符型.结构体.布尔型.日期时间.枚举类型等 引用类型包括:字符串.类.数组.接口等 堆定义:是一种特殊的树形数据结构,每个结点都有一个值,一般由程序员分 ...
- 利用spingmvc及servlet实现对url的地址去除后缀,更改后缀为html
效果图 1.在web.xml中加上如下配置.其实就是利用servlet的目录过滤,这样所有带有news的地址都会被拦截 <!-- restfull风格约定,去除前台超链接访问的后缀 --> ...
- [Codevs 1107][NOIP 1107]等效表达
主题连接:http://codevs.cn/problem/1107/ 一道非常奇妙的题目. 对于算术表达式一类的问题,能够採用编译原理里的后缀表达式的方式来做.详细做法是分别维护两个栈,一个栈里保存 ...
- 【BZOJ 1034】[ZJOI2008]泡泡堂BNB
[题目链接]:http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=1034 [题意] [题解] 如果己方最小的大于对方最小的(严格大于) 或己方最大的大于对 ...
- 【27.66%】【codeforces 592D】Super M
time limit per test2 seconds memory limit per test256 megabytes inputstandard input outputstandard o ...
- 【cordova】cordova安装步骤(windows)
原文:[cordova]cordova安装步骤(windows) 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载. https://blog.csdn.net/snow_finland/artic ...
- hexo的url路径修改以及发布与修改时间
hexo默认url是年/月/日,这样其实不利于SEO.hexo生成新文章命令,hexo new [layout] <title>,这个title最好是英文的,因为我们要把这个title放在 ...
