Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPM)
[Page E. Approximating to the cumulative normal function and its inverse for use on a pocket calculator. Applied Statistics, vol. 26, pp. 75-76, 1977.]
概
diffusion model和变分界的结合.
对抗鲁棒性上已经有多篇论文用DDPM生成的数据用于训练了, 可见其强大.
主要内容
Diffusion models
reverse process
从\(p(x_T) = \mathcal{N}(x_T; 0, I)\)出发:
\]
注意这个过程我们拟合均值\(\mu_{\theta}\)和协方差矩阵\(\Sigma_{\theta}\).
这部分的过程逐步将噪声'恢复'为图片(信号)\(x_0\).
forward process
\]
其中\(\beta_t\)是可训练的参数或者人为给定的超参数.
这部分为将图片(信号)逐步添加噪声的过程.
变分界
对于参数\(\theta\), 很自然地我们希望通过最小化其负对数似然来优化:
\mathbb{E}_{p_{data}(x_0)} \bigg[-\log p_{\theta}(x_0) \bigg]
&=\mathbb{E}_{p_{data}(x_0)} \bigg[-\log \int p_{\theta}(x_{0:T}) \mathrm{d}x_{0:T} \bigg] \\
&=\mathbb{E}_{p_{data}(x_0)} \bigg[-\log \int q(x_{1:T}|x_0)\frac{p_{\theta}(x_{0:T})}{q(x_{1:T}|x_0)} \mathrm{d}x_{0:T} \bigg] \\
&=\mathbb{E}_{p_{data}(x_0)} \bigg[-\log \mathbb{E}_{q(x_{1:T}|x_0)} \frac{p_{\theta}(x_{0:T})}{q(x_{1:T}|x_0)} \bigg] \\
&\le -\mathbb{E}_{p_{data}(x_0)}\mathbb{E}_{q(x_{1:T}|x_0)} \bigg[\log \frac{p_{\theta}(x_{0:T})}{q(x_{1:T}|x_0)} \bigg] \\
&= -\mathbb{E}_q \bigg[\log \frac{p_{\theta}(x_{0:T})}{q(x_{1:T}|x_0)} \bigg] \\
&= -\mathbb{E}_q \bigg[\log p(x_T) + \sum_{t=1}^T \log \frac{p_{\theta}(x_{t-1}|x_t)}{q(x_t|x_{t-1})} \bigg] \\
&= -\mathbb{E}_q \bigg[\log p(x_T) + \sum_{t=2}^T \log \frac{p_{\theta}(x_{t-1}|x_t)}{q(x_t|x_{t-1})} + \log \frac{p_{\theta}(x_0|x_1)}{q(x_1|x_0)} \bigg] \\
&= -\mathbb{E}_q \bigg[\log p(x_T) + \sum_{t=2}^T \log \frac{p_{\theta}(x_{t-1}|x_t)}{q(x_{t-1}|x_t, x_0)} \cdot \frac{q(x_{t-1}|x_0)}{q(x_t|x_0)} + \log \frac{p_{\theta}(x_0|x_1)}{q(x_1|x_0)} \bigg] \\
&= -\mathbb{E}_q \bigg[\log \frac{p(x_T)}{q(x_T|x_0)} + \sum_{t=2}^T \log \frac{p_{\theta}(x_{t-1}|x_t)}{q(x_{t-1}|x_t, x_0)} + \log p_{\theta}(x_0|x_1) \bigg] \\
\end{array}
\]
注: \(q=q(x_{1:T}|x_0)p_{data}(x_0)\), 下面另\(q(x_0) := p_{data}(x_0)\).
又
\mathbb{E}_q [\log \frac{q(x_T|x_0)}{p(x_T)}]
&= \int q(x_0, x_T) \log \frac{q(x_T|x_0)}{p(x_T)} \mathrm{d}x_0 \mathrm{d}x_T \\
&= \int q(x_0) q(x_T|x_0) \log \frac{q(x_T|x_0)}{p(x_T)} \mathrm{d}x_0 \mathrm{d}x_T \\
&= \int q(x_0) \mathrm{D_{KL}}(q(x_T|x_0) \| p(x_T)) \mathrm{d}x_0 \\
&= \int q(x_{0:T}) \mathrm{D_{KL}}(q(x'_T|x_0) \| p(x'_T)) \mathrm{d}x_{0:T} \\
&= \mathbb{E}_q \bigg[\mathrm{D_{KL}}(q(x'_T|x_0) \| p(x'_T)) \bigg].
\end{array}
\]
又
\mathbb{E}_q [\log \frac{q(x_{t-1}|x_t, x_0)}{p_{\theta}(x_{t-1}|x_t)}]
&=\int q(x_0, x_{t-1}, x_t) \log \frac{q(x_{t-1}|x_t, x_0)}{p_{\theta}(x_{t-1}|x_t)} \mathrm{d}x_0 \mathrm{d}x_{t-1}\mathrm{d}x_t\\
&=\int q(x_0, x_t) \mathrm{D_{KL}}(q(x_{t-1}|x_t, x_0)\| p_{\theta}(x_{t-1}|x_t)) \mathrm{d}x_0 \mathrm{d}x_t\\
&=\mathbb{E}_q\bigg[\mathrm{D_{KL}}(q(x'_{t-1}|x_t, x_0)\| p_{\theta}(x'_{t-1}|x_t)) \bigg].
\end{array}
\]
故最后:
\underbrace{\mathrm{D_{KL}}(q(x'_T|x_0) \| p(x'_T))}_{L_T} +
\sum_{t=2}^T \underbrace{\mathrm{D_{KL}}(q(x'_{t-1}|x_t, x_0)\| p_{\theta}(x'_{t-1}|x_t))}_{L_{t-1}}
\underbrace{-\log p_{\theta}(x_0|x_1)}_{L_0}.
\bigg]
\]
损失求解
因为无论forward, 还是 reverse process都是基于高斯分布的, 我们可以显示求解上面的各项损失:
首先, 对于forward process中的\(x_t\):
x_t
&= \sqrt{1 - \beta_t} x_{t-1} + \sqrt{\beta_t} \epsilon, \: \epsilon \sim \mathcal{N}(0, I) \\
&= \sqrt{1 - \beta_t} (\sqrt{1 - \beta_{t-1}} x_{t-2} + \sqrt{\beta_{t-1}} \epsilon') + \sqrt{\beta} \epsilon \\
&= \sqrt{1 - \beta_t}\sqrt{1 - \beta_{t-1}} x_{t-2} + \sqrt{1 - \beta_t}\sqrt{\beta_{t-1}} \epsilon' + \sqrt{\beta} \epsilon \\
&= \sqrt{1 - \beta_t}\sqrt{1 - \beta_{t-1}} x_{t-2} +
\sqrt{1 - (1 - \beta_t)(1 - \beta_{t-1})} \epsilon \\
&= \cdots \\
&= (\prod_{s=1}^t \sqrt{1 - \beta_s}) x_0 + \sqrt{1 - \prod_{s=1}^t (1 - \beta_s)} \epsilon,
\end{array}
\]
故
\]
对于后验分布\(q(x_{t-1}|x_t, x_0)\), 我们有
q(x_{t-1}|x_t, x_0)
&= \frac{q(x_t|x_{t-1})q(x_{t-1}|x_0)}{q(x_t|x_0)} \\
&\propto q(x_t|x_{t-1})q(x_{t-1}|x_0) \\
&\propto \exp\Bigg\{-\frac{1}{2 (1 - \bar{\alpha}_{t-1})\beta_t} \bigg[(1 - \bar{\alpha}_{t-1}) \|x_t - \sqrt{1 - \beta_t} x_{t-1}\|^2 + \beta_t \|x_{t-1} - \sqrt{\bar{\alpha}_{t-1}}x_0\|^2 \bigg]\Bigg\} \\
&\propto \exp\Bigg\{-\frac{1}{2 (1 - \bar{\alpha}_{t-1})\beta_t} \bigg[(1 - \bar{\alpha}_t)\|x_{t-1}\|^2 - 2(1 - \bar{\alpha}_{t-1}) \sqrt{\alpha_t} x_t^Tx_{t-1} - 2 \sqrt{\bar{\alpha}_{t-1}} \beta_t \bigg]\Bigg\} \\
\end{array}
\]
所以
\]
其中
\]
\]
\(L_{t}\)
\(L_T\)与\(\theta\)无关, 舍去.
作者假设\(\Sigma_{\theta}(x_t, t) = \sigma_t^2 I\)为非训练的参数, 其中
\]
分别为\(x_0 \sim \mathcal{N}(0, I)\)和\(x_0\)为固定值时, 期望下KL散度的最优参数(作者说在实验中二者差不多).
故
\]
又
\]
所以
\mathbb{E}_q [L_{t-1} - C]
&= \mathbb{E}_{x_0, \epsilon} \bigg\{
\frac{1}{2 \sigma_t^2} \| \mu_{\theta}(x_t, t) - \tilde{u}_t\big( x_t, (\frac{1}{\sqrt{\bar{\alpha}_t}}x_t - \frac{\sqrt{1 - \bar{\alpha}_t} }{\sqrt{\bar{\alpha}_t}} \epsilon) \big)\|^2 \bigg\} \\
&= \mathbb{E}_{x_0, \epsilon} \bigg\{
\frac{1}{2 \sigma^2_t} \| \mu_{\theta}(x_t, t) -
\frac{1}{\sqrt{\alpha_t}} \big( x_t - \frac{\beta_t}{\sqrt{1 - \bar{\alpha}_t}} \epsilon \big) \bigg\} \\
\end{array}
\]
注: 上式子中\(x_t\)由\(x_0, \epsilon\)决定, 实际上\(x_t = x_t(x_0, \epsilon)\), 故期望实际上是对\(x_t\)求期望.
既然如此, 我们不妨直接参数化\(\mu_{\theta}\)为
\frac{1}{\sqrt{\alpha_t}} \big( x_t - \frac{\beta_t}{\sqrt{1 - \bar{\alpha}_t}} \epsilon_{\theta}(x_t, t) \big),
\]
即直接建模残差\(\epsilon\).
此时损失可简化为:
\frac{\beta_t^2}{2\sigma_t^2 \alpha_t (1 - \bar{\alpha}_t)} \|\epsilon_{\theta}(\sqrt{\bar{\alpha}_t}x_0 + \sqrt{1 - \bar{\alpha}_t}\epsilon, t) - \epsilon\|^2
\bigg\}
\]
这个实际上时denoising score matching.
类似地, 从\(p_{\theta}(x_{t-1}|x_t)\)采样则为:
\frac{1}{\sqrt{\alpha_t}} \big( x_t - \frac{\beta_t}{\sqrt{1 - \bar{\alpha}_t}} \epsilon_{\theta}(x_t, t) \big) + \sigma_t z, \: z \sim \mathcal{N}(0, I),
\]
这是Langevin dynamic的形式(步长和权重有点变化)
注: 这部分见here.
\(L_0\)
最后我们要处理\(L_0\), 这里作者假设\(x_0|x_1\)满足一个离散分布, 首先图片取值于\(\{0, 1, 2, \cdots, 255\}\), 并标准化至\([-1, 1]\). 假设
\delta_+(x) =
\left \{
\begin{array}{ll}
+\infty & \text{if } x = 1, \\
x + \frac{1}{255} & \text{if } x < 1.
\end{array}
\right .
\delta_- (x)
\left \{
\begin{array}{ll}
-\infty & \text{if } x = -1, \\
x - \frac{1}{255} & \text{if } x > -1.
\end{array}
\right .
\]
实际上就是将普通的正态分布划分为:
\]
各取值落在其中之一.
在实际代码编写中, 会遇到高斯函数密度函数估计的问题(直接求是做不到的), 作者选择用下列的估计方式:
\]
这样梯度也就能够回传了.
注: 该估计属于Page.
最后的算法
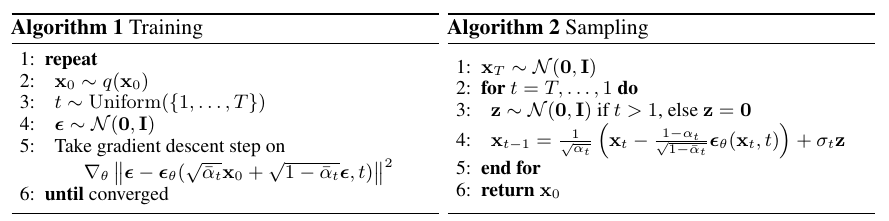
注: \(t=1\)对应\(L_0\), \(t=2,\cdots, T\)对应\(L_{1}, \cdots, L_{T-1}\).
注: 对于\(L_t\)作者省略了开始的系数, 这反而是一种加权.
作者在实际中是采样损失用以训练的.
细节
注意到, 作者的\(\epsilon_{\theta}(\cdot, t)\)是有显示强调\(t\), 作者在实验中是通过attention中的位置编码实现的, 假设位置编码为\(P\):
- $ t = \text{Linear}(\text{ACT}(\text{Linear}(t * P)))$, 即通过两层的MLP来转换得到time_steps;
- 作者用的是U-Net结构, 在每个residual 模块中:
\]
| 参数 | 值 |
|---|---|
| \(T\) | 1000 |
| \(\beta_t\) | \([0.0001, 0.02]\), 线性增长\(1,2,\cdots, T\). |
| backbone | U-Net |
注: 作者在实现中还用到了EMA等技巧.
代码
lucidrains-denoising-diffusion-pytorch
Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPM)的更多相关文章
- (转) RNN models for image generation
RNN models for image generation MARCH 3, 2017 Today we’re looking at the remaining papers from the ...
- {ICIP2014}{收录论文列表}
This article come from HEREARS-L1: Learning Tuesday 10:30–12:30; Oral Session; Room: Leonard de Vinc ...
- CVPR 2015 papers
CVPR2015 Papers震撼来袭! CVPR 2015的文章可以下载了,如果链接无法下载,可以在Google上通过搜索paper名字下载(友情提示:可以使用filetype:pdf命令). Go ...
- ICLR 2014 International Conference on Learning Representations深度学习论文papers
ICLR 2014 International Conference on Learning Representations Apr 14 - 16, 2014, Banff, Canada Work ...
- cvpr2015papers
@http://www-cs-faculty.stanford.edu/people/karpathy/cvpr2015papers/ CVPR 2015 papers (in nicer forma ...
- Official Program for CVPR 2015
From: http://www.pamitc.org/cvpr15/program.php Official Program for CVPR 2015 Monday, June 8 8:30am ...
- Machine and Deep Learning with Python
Machine and Deep Learning with Python Education Tutorials and courses Supervised learning superstiti ...
- Notes(一)
Numerous experimental measurements in spatially complex systems have revealed anomalous diffusion in ...
- 斯坦福CS课程列表
http://exploredegrees.stanford.edu/coursedescriptions/cs/ CS 101. Introduction to Computing Principl ...
随机推荐
- ICCV2021 | TOOD:任务对齐的单阶段目标检测
前言 单阶段目标检测通常通过优化目标分类和定位两个子任务来实现,使用具有两个平行分支的头部,这可能会导致两个任务之间的预测出现一定程度的空间错位.本文提出了一种任务对齐的一阶段目标检测(TOOD) ...
- JDBC01 获取数据库连接
概述 Java Database Connectivity(JDBC)直接访问数据库,通用的SQL数据库存取和操作的公共接口,定义访问数据库的标准java类库(java.sql,javax.sql) ...
- LeetCode替换空格
LeetCode 替换空格 题目描述 请实现一个函数,把字符串 s 中的每个空格替换成"%20". 实例 1: 输入:s = "We are happy." 输 ...
- a这个词根
a是个词根,有三种意思:1. 以某种状态或方式,如: ablaze, afire, aflame, alight, aloud, alive, afloat等2. at, in, on, to sth ...
- acute, adapt
acute In Euclidean [欧几里得] geometry, an angle is the figure [图形] formed by two rays, called the sides ...
- 容器的分类与各种测试(三)——deque
deque是双端队列,其表象看起来是可以双端扩充,但实际上是通过内存映射管理来营造可以双端扩充的假象,如图所示 比如,用户将最左端的buff用光时,map会自动向左扩充,继续申请并映射一个新的buff ...
- MediaPlayer详解
[1]MediaPlayer 详细使用细则 [2]MediaPlayer使用详解_为新手准备 [3]MediaPlayer 概览
- 集合类——Collection、List、Set接口
集合类 Java类集 我们知道数组最大的缺陷就是:长度固定.从jdk1.2开始为了解决数组长度固定的问题,就提供了动态对象数组实现框架--Java类集框架.Java集合类框架其实就是Java针对于数据 ...
- 【Matlab】find函数用法
find(A):返回向量中非零元素的位置 注意返回的是位置的脚标 //类似python,还是很好用的 如果是二维矩阵,是先横行后列的 b=find(a),a是一个矩阵,查询非零元素的位置 如果X是一个 ...
- 【HarmonyOS】【xml】初学XML布局作业
首先要明确,有两种布局方式 线性布局:DirectionalLayout 依赖布局:DependentLayout 好,接下来看一看下面的例子 页面案例1 代码如下: <?xml version ...
