Redis 源码简洁剖析 02 - SDS 字符串
C 语言的字符串函数
C 语言 string 函数,在 C 语言中可以使用 char* 字符数组实现字符串,C 语言标准库 string.h 中也定义了多种字符串操作函数。
字符串使用广泛,需要满足:
- 高效的字符串操作,比如追加、拷贝、比较、获取长度
- 能保存任意的二进制数据,比如图片
- 尽可能省内存
为什么 Redis 不直接使用 C 语言的字符串?
- C 语言 char* 以 '\0'标识字符串的结束,则中间含有'\0'的字符串无法被正确表示;也正因为此,没有办法保存图像等二进制数据。
- C 语言 char* 获取字符串长度的时间复杂度是 O(N);追加字符串的时间复杂度也是 O(N),同时可能由于可用空间不足,无法追加。
下面代码展示了 C 语言中 '\0' 结束字符对字符串的影响。下图展示了一个值为 "Redis" 的 C 字符串:

#include "stdio.h"
#include "string.h"
int main(void) {
char *a = "red\0is";
char *b = "redis\0";
printf("%lu\n", strlen(a));
printf("%lu\n", strlen(b));
}
输出结果是 3 和 5。
SDS 定义
SDS(简单动态字符串) 是 simple dynamic string 的简称,Redis 使用 SDS 作为字符串的数据结构。Redis 中所有的键(key)底层都是 SDS 实现的。
比如:
redis> SET msg "hello world"
OK
redis> RPUSH fruits "apple" "banana" "cherry"
(integer) 3
Redis sds 源码主要在 sds.h 和 sds.c 中。其中可以发现 Redis 给 char* 起了别名:
typedef char *sds;
SDS 内部结构
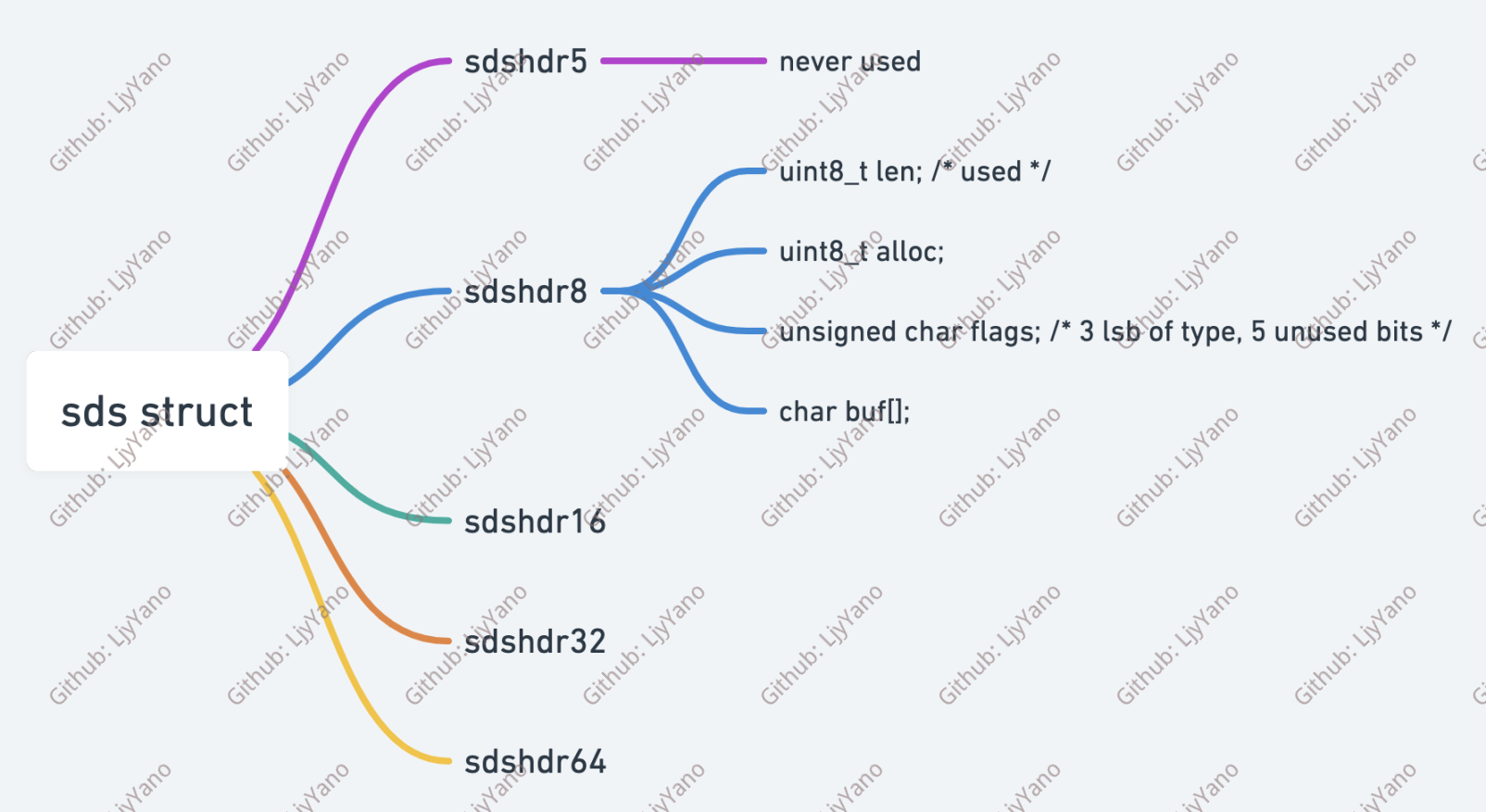
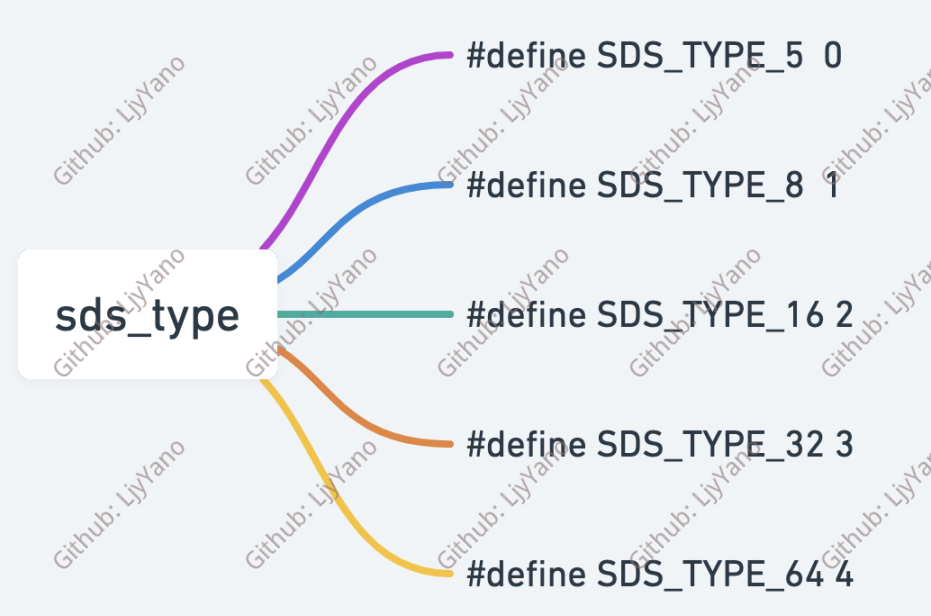
SDS 结构中有一个元数据 flags,表示的是 SDS 类型(最低 3 位)。事实上,SDS 一共设计了 5 种类型,分别是 sdshdr5、sdshdr8、sdshdr16、sdshdr32 和 sdshdr64。这 5 种类型的主要区别就在于,它们数据结构中的字符数组现有长度 len 和分配空间长度 alloc,这两个元数据的数据类型不同。
/* Note: sdshdr5 is never used, we just access the flags byte directly.
* However is here to document the layout of type 5 SDS strings. */
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr5 {
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, and 5 msb of string length */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr8 {
uint8_t len; /* used */
uint8_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr16 {
uint16_t len; /* used */
uint16_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr32 {
uint32_t len; /* used */
uint32_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr64 {
uint64_t len; /* used */
uint64_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
static inline size_t sdslen(const sds s) {
unsigned char flags = s[-1];
switch(flags&SDS_TYPE_MASK) {
case SDS_TYPE_5:
return SDS_TYPE_5_LEN(flags);
case SDS_TYPE_8:
return SDS_HDR(8,s)->len;
case SDS_TYPE_16:
return SDS_HDR(16,s)->len;
case SDS_TYPE_32:
return SDS_HDR(32,s)->len;
case SDS_TYPE_64:
return SDS_HDR(64,s)->len;
}
return 0;
}
获取剩余容量:sdsavail 函数,总容量 alloc - 已使用长度 len,时间复杂度是 O(1)。
static inline size_t sdsavail(const sds s) {
unsigned char flags = s[-1];
switch(flags&SDS_TYPE_MASK) {
case SDS_TYPE_5: {
return 0;
}
case SDS_TYPE_8: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(8,s);
return sh->alloc - sh->len;
}
case SDS_TYPE_16: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(16,s);
return sh->alloc - sh->len;
}
case SDS_TYPE_32: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(32,s);
return sh->alloc - sh->len;
}
case SDS_TYPE_64: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(64,s);
return sh->alloc - sh->len;
}
}
return 0;
}
SDS 的主要操作 API
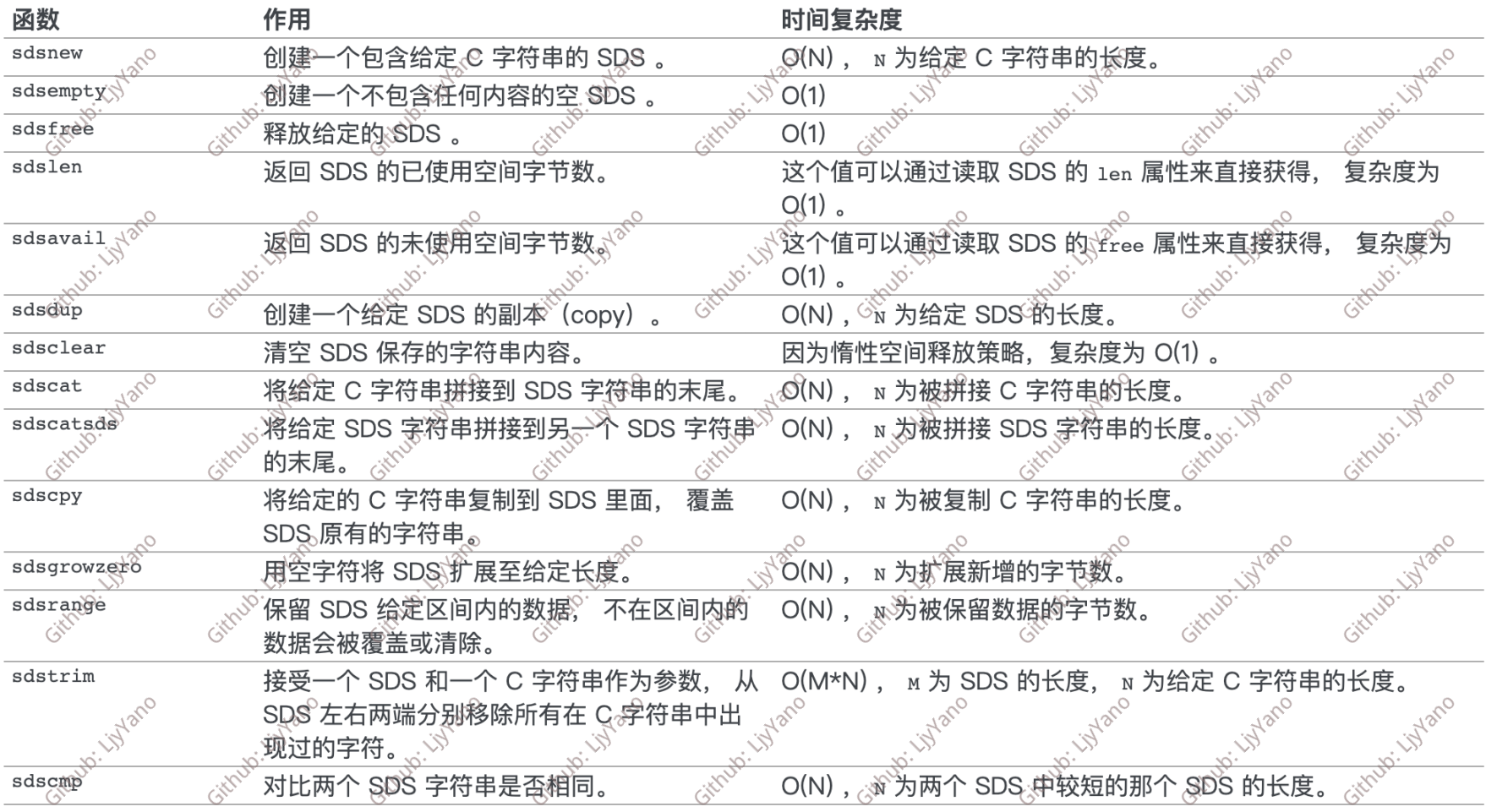
基础方法有:
sds sdsnewlen(const void *init, size_t initlen);
sds sdstrynewlen(const void *init, size_t initlen);
sds sdsnew(const char *init);
sds sdsempty(void);
sds sdsdup(const sds s);
void sdsfree(sds s);
sds sdsgrowzero(sds s, size_t len);
sds sdscatlen(sds s, const void *t, size_t len);
sds sdscat(sds s, const char *t);
sds sdscatsds(sds s, const sds t);
sds sdscpylen(sds s, const char *t, size_t len);
sds sdscpy(sds s, const char *t);
sds sdscatvprintf(sds s, const char *fmt, va_list ap);
#ifdef __GNUC__
sds sdscatprintf(sds s, const char *fmt, ...)
__attribute__((format(printf, 2, 3)));
#else
sds sdscatprintf(sds s, const char *fmt, ...);
#endif
sds sdscatfmt(sds s, char const *fmt, ...);
sds sdstrim(sds s, const char *cset);
void sdssubstr(sds s, size_t start, size_t len);
void sdsrange(sds s, ssize_t start, ssize_t end);
void sdsupdatelen(sds s);
void sdsclear(sds s);
int sdscmp(const sds s1, const sds s2);
sds *sdssplitlen(const char *s, ssize_t len, const char *sep, int seplen, int *count);
void sdsfreesplitres(sds *tokens, int count);
void sdstolower(sds s);
void sdstoupper(sds s);
sds sdsfromlonglong(long long value);
sds sdscatrepr(sds s, const char *p, size_t len);
sds *sdssplitargs(const char *line, int *argc);
sds sdsmapchars(sds s, const char *from, const char *to, size_t setlen);
sds sdsjoin(char **argv, int argc, char *sep);
sds sdsjoinsds(sds *argv, int argc, const char *sep, size_t seplen);
/* Callback for sdstemplate. The function gets called by sdstemplate
* every time a variable needs to be expanded. The variable name is
* provided as variable, and the callback is expected to return a
* substitution value. Returning a NULL indicates an error.
*/
typedef sds (*sdstemplate_callback_t)(const sds variable, void *arg);
sds sdstemplate(const char *template, sdstemplate_callback_t cb_func, void *cb_arg);
/* Low level functions exposed to the user API */
sds sdsMakeRoomFor(sds s, size_t addlen);
void sdsIncrLen(sds s, ssize_t incr);
sds sdsRemoveFreeSpace(sds s);
size_t sdsAllocSize(sds s);
void *sdsAllocPtr(sds s);
/* Export the allocator used by SDS to the program using SDS.
* Sometimes the program SDS is linked to, may use a different set of
* allocators, but may want to allocate or free things that SDS will
* respectively free or allocate. */
void *sds_malloc(size_t size);
void *sds_realloc(void *ptr, size_t size);
void sds_free(void *ptr);
字符串初始化
整体和 Java 的 StringBuilder 很像了 O_o
/* Create a new sds string starting from a null terminated C string. */
sds sdsnew(const char *init) {
size_t initlen = (init == NULL) ? 0 : strlen(init);
return sdsnewlen(init, initlen);
}
首先是判断输入的 init 字符串的长度,接着调用 sdsnewlen 分配内存空间并赋值。
sds sdsnewlen(const void *init, size_t initlen) {
return _sdsnewlen(init, initlen, 0);
}
核心函数_sdsnewlen 如下,主要就是先确保空间是否足够、分配空间,然后再调用 memcpy 将 *init 复制到对应的内存空间。
/* Create a new sds string with the content specified by the 'init' pointer
* and 'initlen'.
* If NULL is used for 'init' the string is initialized with zero bytes.
* If SDS_NOINIT is used, the buffer is left uninitialized;
*
* The string is always null-termined (all the sds strings are, always) so
* even if you create an sds string with:
*
* mystring = sdsnewlen("abc",3);
*
* You can print the string with printf() as there is an implicit \0 at the
* end of the string. However the string is binary safe and can contain
* \0 characters in the middle, as the length is stored in the sds header. */
sds _sdsnewlen(const void *init, size_t initlen, int trymalloc) {
void *sh;
sds s;
char type = sdsReqType(initlen);
/* Empty strings are usually created in order to append. Use type 8
* since type 5 is not good at this. */
if (type == SDS_TYPE_5 && initlen == 0) type = SDS_TYPE_8;
int hdrlen = sdsHdrSize(type);
unsigned char *fp; /* flags pointer. */
size_t usable;
assert(initlen + hdrlen + 1 > initlen); /* Catch size_t overflow */
sh = trymalloc?
s_trymalloc_usable(hdrlen+initlen+1, &usable) :
s_malloc_usable(hdrlen+initlen+1, &usable);
if (sh == NULL) return NULL;
if (init==SDS_NOINIT)
init = NULL;
else if (!init)
memset(sh, 0, hdrlen+initlen+1);
s = (char*)sh+hdrlen;
fp = ((unsigned char*)s)-1;
usable = usable-hdrlen-1;
if (usable > sdsTypeMaxSize(type))
usable = sdsTypeMaxSize(type);
switch(type) {
case SDS_TYPE_5: {
*fp = type | (initlen << SDS_TYPE_BITS);
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_8: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(8,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = usable;
*fp = type;
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_16: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(16,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = usable;
*fp = type;
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_32: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(32,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = usable;
*fp = type;
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_64: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(64,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = usable;
*fp = type;
break;
}
}
if (initlen && init)
memcpy(s, init, initlen);
s[initlen] = '\0';
return s;
}
Redis 源码简洁剖析系列
Java 编程思想-最全思维导图-GitHub 下载链接,需要的小伙伴可以自取~
原创不易,希望大家转载时请先联系我,并标注原文链接。
Redis 源码简洁剖析 02 - SDS 字符串的更多相关文章
- Redis 源码简洁剖析 07 - main 函数启动
前言 问题 阶段 1:基本初始化 阶段 2:检查哨兵模式,执行 RDB 或 AOF 检测 阶段 3:运行参数解析 阶段 4:初始化 server 资源管理 初始化数据库 创建事件驱动框架 阶段 5:执 ...
- Redis 源码简洁剖析 06 - quicklist 和 listpack
quicklist 为什么要设计 quicklist 特点 数据结构 quicklistCreate quicklistDelIndex quicklistDelEntry quicklistInse ...
- Redis 源码简洁剖析 16 - 客户端
整体概述 客户端属性 套接字描述符 标志 输入缓冲区 命名及命令参数 命令的实现函数 输出缓冲区 客户端的创建与关闭 创建普通客户端 关闭普通客户端 参考链接 Redis 源码简洁剖析系列 整体概述 ...
- Redis 源码简洁剖析 04 - Sorted Set 有序集合
Sorted Set 是什么 Sorted Set 命令及实现方法 Sorted Set 数据结构 跳表(skiplist) 跳表节点的结构定义 跳表的定义 跳表节点查询 层数设置 跳表插入节点 zs ...
- Redis 源码简洁剖析 13 - RDB 文件
RDB 是什么 RDB 文件格式 Header Body DB Selector AUX Fields Key-Value Footer 编码算法说明 Length 编码 String 编码 Scor ...
- Redis 源码简洁剖析 15 - AOF
AOF 是什么 AOF 持久化的实现 命令追加 AOF 文件的写入和同步 AOF 文件的载入和数据还原 AOF 重写 为什么需要重写 什么是重写 如何重写 AOF 后台重写 为什么需要后台重写 带来的 ...
- Redis 源码简洁剖析 03 - Dict Hash 基础
Redis Hash 源码 Redis Hash 数据结构 Redis rehash 原理 为什么要 rehash? Redis dict 数据结构 Redis rehash 过程 什么时候触发 re ...
- Redis 源码简洁剖析 05 - ziplist 压缩列表
ziplist 是什么 Redis 哪些数据结构使用了 ziplist? ziplist 特点 优点 缺点 ziplist 数据结构 ziplist 节点 pre_entry_length encod ...
- Redis 源码简洁剖析 09 - Reactor 模型
Reactor 模型 事件驱动框架 Redis 如何实现 Reactor 模型 事件的数据结构:aeFileEvent 主循环:aeMain 函数 事件捕获与分发:aeProcessEvents 函数 ...
随机推荐
- 这几种Java异常处理方法,你会吗?
摘要:我们在软件开发的过程中,任何语言的开发过程中都离不开异常处理. 本文分享自华为云社区<Java异常处理学习总结>,作者: zekelove . 我们在软件开发的过程中,任何语言的开发 ...
- CF468C Hack it! 超详细解答
CF468C Hack it! 超详细解答 构造+数学推导 原文极简体验 CF468C Hack it! 题目简化: 令\(f(x)\)表示\(x\)在十进制下各位数字之和 给定一整数\(a\)构造\ ...
- fastjson反序列化-JdbcRowSetImpl利用链
fastjson反序列化-JdbcRowSetImpl利用链 JdbcRowSetImpl利用链 fastjson反序列化JdbcRowSetImpl - Afant1 - 博客园 (cnblogs. ...
- 【UE4 C++】UObject 创建、销毁、内存管理
UObject 的创建 NewObject 模板类 本例使用 UE 4.26,只剩下 NewObject 用来创建 UObject,提供两个带不同可选参数构造函数的模板类 Outer 表示这个对象的外 ...
- zlib开发笔记(四):zlib库介绍、编译windows vs2015x64版本和工程模板
前言 Qt使用一些压缩解压功能,介绍过libzip库编译,本篇说明zlib库.需要用到zlib的msvc2015x64版本,编译一下. 版本编译引导 zlib在windows上的mingw32 ...
- AIApe问答机器人Scrum Meeting 4.25
Scrum Meeting 2 日期:2021年4月25日 会议主要内容概述:前后端针对WebAPI进行协调与统一工作,商量接下来两日计划:敲定部分设计细节. 一.进度情况 组员 负责 两日内已完成的 ...
- Beta阶段第四次会议
Beta阶段第四次会议 时间:2020.5.20 完成工作 姓名 工作 难度 完成度 ltx 1.对小程序进行修改2.提出相关api修改要求 轻 85% xyq 1.设计所需api文档2.编写相关技术 ...
- 并发编程从零开始(九)-ConcurrentSkipListMap&Set
并发编程从零开始(九)-ConcurrentSkipListMap&Set CAS知识点补充: 我们都知道在使用 CAS 也就是使用 compareAndSet(current,next)方法 ...
- SprinMvc快速入门
1.spring mvc Spring MVC是Spring Framework的一部分,是基于Java实现MVC的轻量级Web框架. 查看官方文档:https://docs.spring.io/sp ...
- cf 11D A Simple Task(状压DP)
题意: N个点构成的无向图,M条边描述这个无向图. 问这个无向图中共有多少个环. (1 ≤ n ≤ 19, 0 ≤ m) 思路: 例子: 4 6 1 2 1 3 1 4 2 3 2 4 3 4 答案: ...
