Python学习笔记整理总结【MySQL】
一、 数据库介绍
1、什么是数据库?
数据库(Database)是按照数据结构来组织、存储和管理数据的仓库。
每个数据库都有一个或多个不同的API用于创建,访问,管理,搜索和复制所保存的数据。
我们也可以将数据存储在文件中,但是在文件中读写数据速度相对较慢。
所以,现在我们使用关系型数据库管理系统(RDBMS)来存储和管理的大数据量。
所谓的关系型数据库,是建立在关系模型基础上的数据库,借助于集合代数等数学概念和方法来处理数据库中的数据。
RDBMS即关系数据库管理系统(Relational Database Management System)的特点:
①数据以表格的形式出现
②每行为各种记录名称
③每列为记录名称所对应的数据域
④许多的行和列组成一张表单
⑤若干的表单组成database
2、RDBMS 术语
①数据库: 数据库是一些关联表的集合。.
②数据表: 表是数据的矩阵。在一个数据库中的表看起来像一个简单的电子表格。
③列: 一列(数据元素) 包含了相同的数据, 例如邮政编码的数据。
④行:一行(=元组,或记录)是一组相关的数据,例如一条用户订阅的数据。
⑤冗余:存储两倍数据,冗余可以使系统速度更快。(表的规范化程度越高,表与表之间的关系就越多;查询时可能经常需要在多个表之间进行连接查询;而进行连接操作会降低查询速度。例如,学生的信息存储在student表中,院系信息存储在department表中。通过student表中的dept_id字段与department表建立关联关系。如果要查询一个学生所在系的名称,必须从student表中查找学生所在院系的编号(dept_id),然后根据这个编号去department查找系的名称。如果经常需要进行这个操作时,连接查询会浪费很多的时间。因此可以在student表中增加一个冗余字段dept_name,该字段用来存储学生所在院系的名称。这样就不用每次都进行连接操作了。)
⑥主键:主键是唯一的。一个数据表中只能包含一个主键。你可以使用主键来查询数据。
⑦外键:外键用于关联两个表。
⑧复合键:复合键(组合键)将多个列作为一个索引键,一般用于复合索引。
⑨索引:使用索引可快速访问数据库表中的特定信息。索引是对数据库表中一列或多列的值进行排序的一种结构。类似于书籍的目录。
⑩参照完整性: 参照的完整性要求关系中不允许引用不存在的实体。与实体完整性是关系模型必须满足的完整性约束条件,目的是保证数据的一致性。
二、MySQL管理
MySQL的安装、配置、启动、该密码等操作自己动手吧。。。
1、数据类型
MySQL中定义数据字段的类型对你数据库的优化是非常重要的。
MySQL支持多种类型,大致可以分为三类:数值、日期/时间和字符串(字符)类型。
① 数值类型:
MySQL支持所有标准SQL数值数据类型。
*这些类型包括严格数值数据类型(INTEGER、SMALLINT、DECIMAL和NUMERIC),以及近似数值数据类型(FLOAT、REAL和DOUBLE PRECISION)。
*关键字INT是INTEGER的同义词,关键字DEC是DECIMAL的同义词。
*BIT数据类型保存位字段值,并且支持MyISAM、MEMORY、InnoDB和BDB表。
*作为SQL标准的扩展,MySQL也支持整数类型TINYINT、MEDIUMINT和BIGINT
下面的表显示了需要的每个整数类型的存储和范围
② 日期和时间类型:
*表示时间值的日期和时间类型为DATETIME、DATE、TIMESTAMP、TIME和YEAR。
*每个时间类型有一个有效值范围和一个"零"值,当指定不合法的MySQL不能表示的值时使用"零"值。
*TIMESTAMP类型有专有的自动更新特性,将在后面描述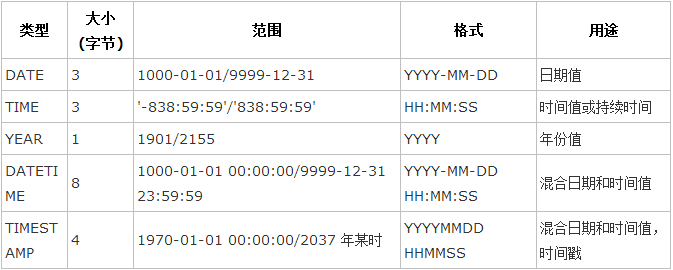
③ 字符串类型:
字符串类型指CHAR、VARCHAR、BINARY、VARBINARY、BLOB、TEXT、ENUM和SET。该节描述了这些类型如何工作以及如何在查询中使用这些类型
*CHAR和VARCHAR类型类似,但它们保存和检索的方式不同。它们的最大长度和是否尾部空格被保留等方面也不同。在存储或检索过程中不进行大小写转换。
*BINARY和VARBINARY类类似于CHAR和VARCHAR,不同的是它们包含二进制字符串而不要非二进制字符串。也就是说,它们包含字节字符串而不是字符字符串。这说明它们没有字符集,并且排序和比较基于列值字节的数值值。
*BLOB是一个二进制大对象,可以容纳可变数量的数据。有4种BLOB类型:TINYBLOB、BLOB、MEDIUMBLOB和LONGBLOB。它们只是可容纳值的最大长度不同。
*有4种TEXT类型:TINYTEXT、TEXT、MEDIUMTEXT和LONGTEXT。这些对应4种BLOB类型,有相同的最大长度和存储需求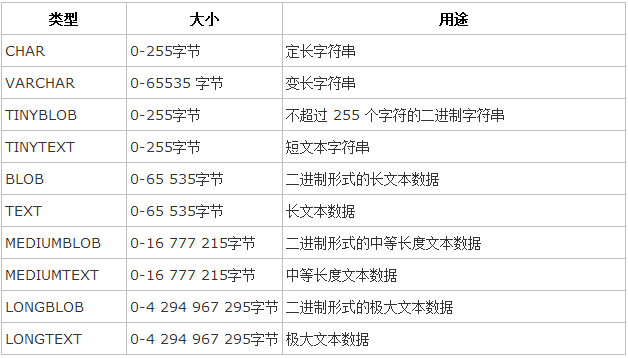
三、MySQL常用命令
以下列出了使用Mysql数据库过程中常用的命令:
USE 数据库名 :选择要操作的Mysql数据库,使用该命令后所有Mysql命令都只针对该数据库。
SHOW DATABASES: 列出 MySQL 数据库管理系统的数据库列表。
SHOW TABLES: 显示指定数据库的所有表,使用该命令前需要使用 use命令来选择要操作的数据库。
SHOW COLUMNS FROM 数据表: 显示数据表的属性,属性类型,主键信息 ,是否为 NULL,默认值等其他信息。
create database testdb charset "utf8"; 创建一个叫testdb的数据库,且让其支持中文
drop database testdb; 删除数据库
SHOW INDEX FROM 数据表:显示数据表的详细索引信息,包括PRIMARY KEY(主键)
<1> 创建数据表:
mysql> create table student(
-> stu_id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
-> name CHAR() NOT NULL,
-> age INT NOT NULL,
-> register_date DATE,
-> PRIMARY KEY ( stu_id )
-> );
Query OK, rows affected (0.41 sec) mysql> desc student;
+---------------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+---------------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| stu_id | int() | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | char() | NO | | NULL | |
| age | int() | NO | | NULL | |
| register_date | date | YES | | NULL | |
+---------------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
rows in set (0.01 sec)
注:AUTO_INCREMENT定义列为自增的属性,一般用于主键,数值会自动加1;如果你不想字段为 NULL 可以设置字段的属性为 NOT NULL, 在操作数据库时如果输入该字段的数据为NULL ,就会报错;PRIMARY KEY关键字用于定义列为主键。 您可以使用多列来定义主键,列间以逗号分隔
<2>插入数据表:
mysql> insert into student (name,age,register_date) values ("liwei",,"2017-11-29");
Query OK, row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from student;
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
| stu_id | name | age | register_date |
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
| | liwei | | -- |
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
row in set (0.00 sec)
<3> 查询数据表:
语法:
SELECT column_name,column_name
FROM table_name
[WHERE Clause]
[OFFSET M ][LIMIT N]
#查询语句中你可以使用一个或者多个表,表之间使用逗号(,)分割,并使用WHERE语句来设定查询条件。
#SELECT 命令可以读取一条或者多条记录。
#你可以使用星号(*)来代替其他字段,SELECT语句会返回表的所有字段数据
#你可以使用 WHERE 语句来包含任何条件。
#你可以通过OFFSET指定SELECT语句开始查询的数据偏移量。默认情况下偏移量为0。
#你可以使用 LIMIT 属性来设定返回的记录数。
①一般查询
mysql> select * from student limit offset ;
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
| stu_id | name | age | register_date |
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
| | XinZhiYu | | -- |
| | Alex li | | -- |
| | liwei | | -- |
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
rows in set (0.00 sec)
比如这个SQL ,limit后面跟的是3条数据,offset后面是从第3条开始读取 mysql> select * from student limit ,;
+--------+---------+-----+---------------+
| stu_id | name | age | register_date |
+--------+---------+-----+---------------+
| | Alex li | | -- |
+--------+---------+-----+---------------+
row in set (0.00 sec)
而这个SQL,limit后面是从第3条开始读,读取1条信息
②where子句:
语法:
SELECT field1, field2,...fieldN FROM table_name1, table_name2...
[WHERE condition1 [AND [OR]] condition2.....
以下为操作符列表,可用于 WHERE 子句中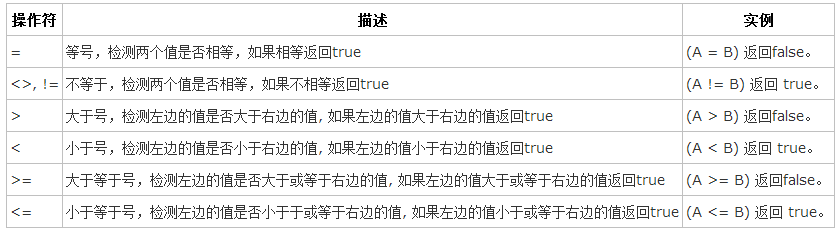
mysql> select * from student where register_date > '2017-11-11'
-> ;
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
| stu_id | name | age | register_date |
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
| | liwei | | -- |
| | GaoCheng | | -- |
| | Alex li | | -- |
| | liwei | | -- |
| | liwei | | -- |
| | liwei | | -- |
| | liwei | | -- |
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from student where stu_id = ;
+--------+----------+-----+---------------+
| stu_id | name | age | register_date |
+--------+----------+-----+---------------+
| | XinZhiYu | | -- |
+--------+----------+-----+---------------+
row in set (0.01 sec)
③模糊查询(like):
mysql> select * from student where register_date like "2017-12-%";
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
| stu_id | name | age | register_date |
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
| | liwei | | -- |
| | GaoCheng | | -- |
| | Alex li | | -- |
| | liwei | | -- |
| | liwei | | -- |
| | liwei | | -- |
| | liwei | | -- |
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
rows in set, warning (0.00 sec)
④查询排序:
SELECT field1, field2,...fieldN table_name1, table_name2...
ORDER BY field1, [field2...] [ASC [DESC]]
使用 ASC 或 DESC 关键字来设置查询结果是按升序或降序排列。 默认情况下,它是按升序排列 mysql> select * from student order by age desc;
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
| stu_id | name | age | register_date |
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
| | wupeiqi | | -- |
| | Alex li | | -- |
| | liwei | | -- |
| | XinZhiYu | | -- |
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
rows in set (0.00 sec)
⑤分组统计:
#语法
SELECT column_name, function(column_name)
FROM table_name
WHERE column_name operator value
GROUP BY column_name; mysql> select * from student;
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
| stu_id | name | age | register_date |
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
| | liwei | | -- |
| | XinZhiYu | | -- |
| | Alex li | | -- |
| | wupeiqi | | -- |
| | liwei | | -- |
| | liwei | | -- |
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
rows in set (0.00 sec) 接下来我们使用 GROUP BY 语句 将数据表按名字进行分组,并统计每个人有多少条记录:
mysql> select name,count(*) from student group by name;
+------------+----------+
| name | count(*) |
+------------+----------+
| Alex li | |
| liwei | |
| wupeiqi | |
| XinZhiYu | |
+------------+----------+
rows in set (0.00 sec) 按名字进行分组,并统计按组划分显示所有年龄的汇总
mysql> select name,sum(age) from student group by name with rollup;
+------------+----------+
| name | sum(age) |
+------------+----------+
| Alex li | |
| liwei | |
| wupeiqi | |
| XinZhiYu | |
| NULL | |
+------------+----------+
rows in set (0.00 sec) 其中记录 NULL 表示所有人的年龄和
我们可以使用 coalesce 来设置一个可以取代 NUll 的名称,coalesce 语法:
mysql> select coalesce(name,"Total"),sum(age) from student group by name with rollup;
+------------------------+----------+
| coalesce(name,"Total") | sum(age) |
+------------------------+----------+
| Alex li | |
| liwei | |
| wupeiqi | |
| XinZhiYu | |
| Total | |
+------------------------+----------+
rows in set (0.00 sec)
<4>修改数据表
#语法
UPDATE table_name SET field1=new-value1, field2=new-value2
[WHERE Clause] mysql> update student set name = "wupeiqi",age = where stu_id =;
Query OK, row affected (0.06 sec)
Rows matched: Changed: Warnings: mysql>
mysql> select * from student;
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
| stu_id | name | age | register_date |
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
| | liwei | | -- |
| | GaoCheng | | -- |
| | XinZhiYu | | -- |
| | Alex li | | -- |
| | liwei | | -- |
| | wupeiqi | | -- |
| | liwei | | -- |
| | liwei | | -- |
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
rows in set (0.00 sec)
<5> 删除数据表:
mysql> delete from student where age = ;
Query OK, rows affected (0.01 sec) mysql> select * from student;
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
| stu_id | name | age | register_date |
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
| | liwei | | -- |
| | XinZhiYu | | -- |
| | Alex li | | -- |
| | wupeiqi | | -- |
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
rows in set (0.00 sec)
<6>操作表字段(alter):
我们需要修改数据表名或者修改数据表字段时,就需要使用到MySQL ALTER命令
①插入表字段:
mysql> alter table student add sex enum("F","M") not null ;
Query OK, rows affected (0.08 sec)
Records: Duplicates: Warnings:
mysql> select * from student;
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+-----+
| stu_id | name | age | register_date | sex |
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+-----+
| | liwei | | -- | F |
| | XinZhiYu | | -- | F |
| | Alex li | | -- | F |
| | wupeiqi | | -- | F |
| | liwei | | -- | F |
| | liwei | | -- | F |
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+-----+
rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> desc student;
+---------------+---------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+---------------+---------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| stu_id | int() | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | char() | NO | | NULL | |
| age | int() | NO | | NULL | |
| register_date | date | YES | | NULL | |
| sex | enum('F','M') | NO | | NULL | |
+---------------+---------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
rows in set (0.00 sec)
②修改表字段:
#change修改字段名 类型 mysql> alter table student change sex gender char() not null default "X";
Query OK, rows affected (0.08 sec)
Records: Duplicates: Warnings: mysql> select * from student;
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+--------+
| stu_id | name | age | register_date | gender |
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+--------+
| | liwei | | -- | F |
| | XinZhiYu | | -- | F |
| | Alex li | | -- | F |
| | wupeiqi | | -- | F |
| | liwei | | -- | F |
| | liwei | | -- | F |
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+--------+
rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> desc student;
+---------------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+---------------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| stu_id | int() | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | char() | NO | | NULL | |
| age | int() | NO | | NULL | |
| register_date | date | YES | | NULL | |
| gender | char() | NO | | X | |
+---------------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
rows in set (0.00 sec)
③删除表字段:
mysql> alter table student drop sex;
ERROR (): Can't DROP 'sex'; check that column/key exists
mysql> alter table student drop gender;
Query OK, rows affected (0.04 sec)
Records: Duplicates: Warnings: mysql> select * from student;
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
| stu_id | name | age | register_date |
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
| | liwei | | -- |
| | XinZhiYu | | -- |
| | Alex li | | -- |
| | wupeiqi | | -- |
| | liwei | | -- |
| | liwei | | -- |
+--------+------------+-----+---------------+
rows in set (0.00 sec)
<7>外键
一个特殊的索引,用于关联2个表,只能是指定内容
#先创建两张表
mysql> create table class(
-> id int not null primary key,
-> name char());
Query OK, rows affected (0.02 sec) CREATE TABLE `student2` (
`id` int() NOT NULL,
`name` char() NOT NULL,
`class_id` int() NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `fk_class_key` (`class_id`),
CONSTRAINT `fk_class_key` FOREIGN KEY (`class_id`) REFERENCES `class` (`id`)
) mysql> desc class;
+-------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int() | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| name | char() | YES | | NULL | |
+-------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+
rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> desc student2
-> ;
+----------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+----------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int() | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| name | char() | NO | | NULL | |
| class_id | int() | NO | MUL | NULL | |
+----------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+
rows in set (0.00 sec) #操作
此时如果class 表中不存在id ,student表也插入不了,这就叫外键约束
mysql> insert into student2(id,name,class_id) values(,'alex', );
ERROR (): Cannot add or update a child row: a foreign key constraint fails (`testdb`.`student2`,
CONSTRAINT `fk_class_key` FOREIGN KEY (`class_id`) REFERENCES `class` (`id`)) mysql> insert into class(id,name) values(,"linux");
Query OK, row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> insert into student2(id,name,class_id) values(,'alex', );
Query OK, row affected (0.00 sec) #如果有student表中跟这个class表有关联的数据,你是不能删除class表中与其关联的纪录的
mysql> delete from class where id =;
ERROR (): Cannot delete or update a parent row: a foreign key constraint fails (`testdb`.`student2`,
CONSTRAINT `fk_class_key` FOREIGN KEY (`class_id`) REFERENCES `class` (`id`))
<8>NULL 值处理
我们已经知道MySQL使用 SQL SELECT 命令及 WHERE 子句来读取数据表中的数据,但是当提供的查询条件字段为 NULL 时,该命令可能就无法正常工作。
为了处理这种情况,MySQL提供了三大运算符:
①IS NULL: 当列的值是NULL,此运算符返回true。
②IS NOT NULL: 当列的值不为NULL, 运算符返回true。
③<=>: 比较操作符(不同于=运算符),当比较的的两个值为NULL时返回true。
关于 NULL 的条件比较运算是比较特殊的。你不能使用 = NULL 或 != NULL 在列中查找 NULL 值 。
在MySQL中,NULL值与任何其它值的比较(即使是NULL)永远返回false,即 NULL = NULL 返回false 。
MySQL中处理NULL使用IS NULL和IS NOT NULL运算符。
<9>连接(left join, right join, inner join ,full join)
我们已经学会了如果在一张表中读取数据,这是相对简单的,但是在真正的应用中经常需要从多个数据表中读取数据。
本章节我们将向大家介绍如何使用 MySQL 的 JOIN 在两个或多个表中查询数据。
你可以在SELECT, UPDATE 和 DELETE 语句中使用 Mysql 的 JOIN 来联合多表查询。
JOIN 按照功能大致分为如下三类:
①INNER JOIN(内连接,或等值连接):获取两个表中字段匹配关系的记录。
②LEFT JOIN(左连接):获取左表所有记录,即使右表没有对应匹配的记录。
③RIGHT JOIN(右连接): 与 LEFT JOIN 相反,用于获取右表所有记录,即使左表没有对应匹配的记录。
④Full join(全连接):存在匹配,匹配显示;同时,将各个表中不匹配的数据与空数据行匹配进行显示。可以看成是左外连接与右外连接的并集。
#给出两张表作为以下操作的的初始数据
A B
- - ①INNER JOIN(内连接,或等值连接)
select * from a INNER JOIN b on a.a = b.b;
select a.*,b.* from a,b where a.a = b.b; a | b
--+--
|
| #其实就是只显示2个表的交集。
②LEFT JOIN(左连接)
select * from a LEFT JOIN b on a.a = b.b; a | b
--+-----
| null
| null
|
| ③RIGHT JOIN(右连接)
select * from a RIGHT JOIN b on a.a = b.b; a | b
-----+----
|
|
null |
null | ④Full join(全连接)
select * from a FULL JOIN b on a.a = b.b; a | b
-----+-----
| null
| null
|
|
null |
null | #mysql 并不直接支持full join,but 总是难不到我们
select * from a left join b on a.a = b.b UNION select * from a right join b on a.a = b.b;
+------+------+
| a | b |
+------+------+
| | |
| | |
| | NULL |
| | NULL |
| NULL | |
| NULL | |
+------+------+
rows in set (0.00 sec)
<10>事务
MySQL事务主要用于处理操作量大,复杂度高的数据。比如说,在人员管理系统中,你删除一个人员,你即需要删除人员的基本资料,也要删除和该人员相关的信息,如信箱,文章等等,这样,这些数据库操作语句就构成一个事务!
在MySQL中只有使用了Innodb数据库引擎的数据库或表才支持事务
事务处理可以用来维护数据库的完整性,保证成批的SQL语句要么全部执行,要么全部不执行
事务用来管理insert,update,delete语句
一般来说,事务是必须满足4个条件(ACID):
1、原子性(Atomicity):一组事务,要么成功;要么撤回。
2、稳定性(Consistency): 有非法数据(外键约束之类),事务撤回。
3、隔离性(Isolation):事务独立运行。一个事务处理后的结果,影响了其他事务,那么其他事务会撤回。事务的100%隔离,需要牺牲速度。
4、可靠性(Durability):软、硬件崩溃后,InnoDB数据表驱动会利用日志文件重构修改。可靠性和高速度不可兼得, innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit选项 决定什么时候吧事务保存到日志里。
在Mysql控制台使用事务来操作:
mysql> begin; #开始一个事务
mysql> insert into a (a) values(555);
mysql>rollback; 回滚 , 这样数据是不会写入的 #如果上面的数据没问题,就输入commit提交命令就行;
<11>索引
①普通索引
1.创建索引:
这是最基本的索引,它没有任何限制
CREATE INDEX indexName ON mytable(username(length));
#如果是CHAR,VARCHAR类型,length可以小于字段实际长度;如果是BLOB和TEXT类型,必须指定 length 2.修改表结构:
ALTER mytable ADD INDEX [indexName] ON (username(length)) 3.创建表的时候直接指定:
CREATE TABLE mytable(
ID INT NOT NULL,
username VARCHAR(16) NOT NULL,
INDEX [indexName] (username(length))
); 4.删除索引的语法:
DROP INDEX [indexName] ON mytable;
②唯一索引
它与前面的普通索引类似,不同的就是:索引列的值必须唯一,但允许有空值。如果是组合索引,则列值的组合必须唯一。
1.创建索引:
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX indexName ON mytable(username(length)) 2.修改表结构
ALTER mytable ADD UNIQUE [indexName] ON (username(length)) 3.创建表的时候直接指定
CREATE TABLE mytable(
ID INT NOT NULL,
username VARCHAR(16) NOT NULL,
UNIQUE [indexName] (username(length))
); .使用ALTER 命令添加和删除索引:
有四种方式来添加数据表的索引:
ALTER TABLE tbl_name ADD PRIMARY KEY (column_list): 该语句添加一个主键,这意味着索引值必须是唯一的,且不能为NULL。
ALTER TABLE tbl_name ADD UNIQUE index_name (column_list): 这条语句创建索引的值必须是唯一的(除了NULL外,NULL可能会出现多次)。
ALTER TABLE tbl_name ADD INDEX index_name (column_list): 添加普通索引,索引值可出现多次。
ALTER TABLE tbl_name ADD FULLTEXT index_name (column_list):该语句指定了索引为 FULLTEXT ,用于全文索引。 以下实例为在表中添加索引。
mysql> ALTER TABLE testalter_tbl ADD INDEX (c);
你还可以在 ALTER 命令中使用 DROP 子句来删除索引。尝试以下实例删除索引:
mysql> ALTER TABLE testalter_tbl DROP INDEX (c); 5.使用 ALTER 命令添加和删除主键
主键只能作用于一个列上,添加主键索引时,你需要确保该主键默认不为空(NOT NULL)。实例如下:
mysql> ALTER TABLE testalter_tbl MODIFY i INT NOT NULL;
mysql> ALTER TABLE testalter_tbl ADD PRIMARY KEY (i); 你也可以使用 ALTER 命令删除主键:
mysql> ALTER TABLE testalter_tbl DROP PRIMARY KEY;
删除指定时只需指定PRIMARY KEY,但在删除索引时,你必须知道索引名。 6.显示索引信息:
mysql> SHOW INDEX FROM table_name\G
MySQL练习题
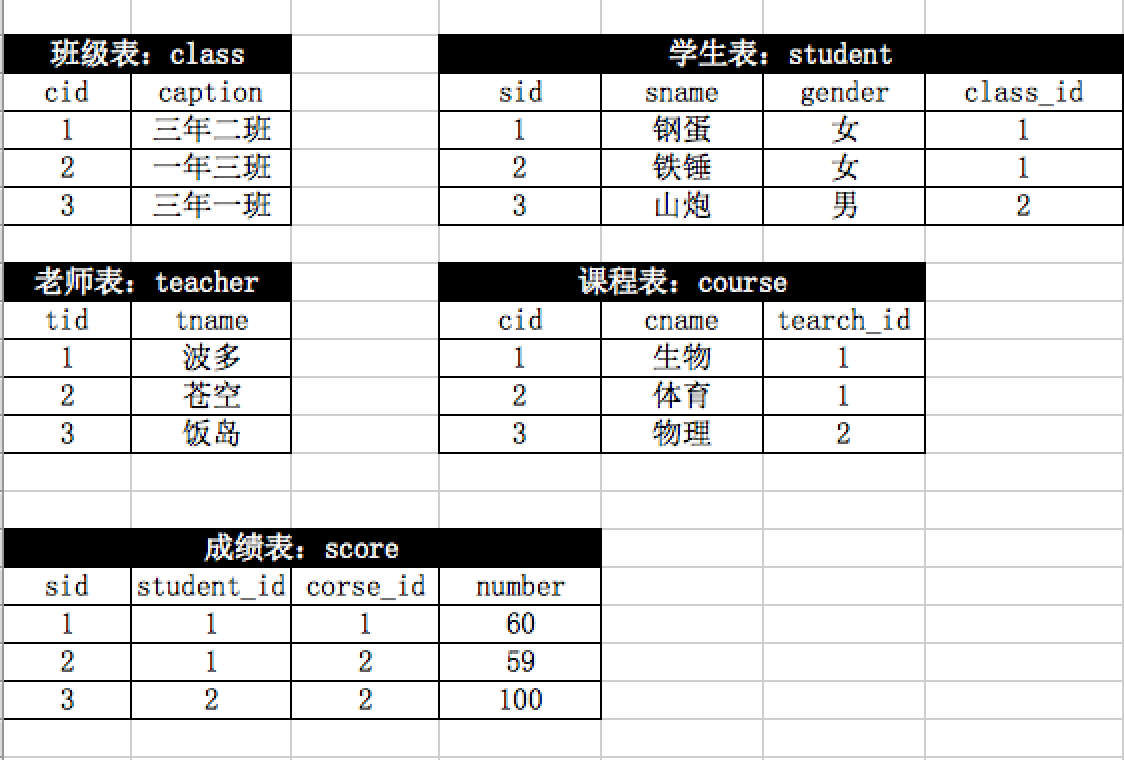
select * from score where num>60;
1.查询成绩大于60分的学生
select teacher_id,count(cname) from score group by teacher_id;
2.查询每个老师任教的课程
select * from course
left join teacher on course.teacher_id=teacher_id;
3.查询每门课程对应的老师中文名字
select gender,count(sid) from student group by gender;
4.查询男生、女生的个数
#思路:根据学生分组,使用avg获取平均值,通过having对avg进行筛选
select student_id,avg(num) from score group by student_id having avg(num) > 60;
5.查询平均成绩大于60分的同学的学号和平均成绩
select B.student_id,student.sname,b.cc from (select student_id,avg(num) as cc from score group by student_id having avg(num) > 60) as B
left join student on B.student_id = student.sid;
6.查询平均成绩大于60分的同学的姓名和平均成绩
select score.student_id,student.sname,count(score.student_id),sum(score.num)
from score left join student on score.student_id = student.sid group by score.student_id;
7.查询所有同学的学号、姓名、选课数、总成绩
select count(tid) from teacher where tname like '李%';
#//select count(1) from (select tid from teacher where tname like '李%') as B
8.查询姓“李”的老师的个数
#思路:先查到“李平老师”教的所有课ID、获取选过“李平老师”课的所有学生ID、学生表中筛选
select student.sid,student.sname from student where sid not in (
select DISTINCT student_id from score where score.course_id in (
select course.cid from course left join teacher on course.teacher_id = teacher.tid where tname = '李平老师'
) group by student_id
);
9.查询没学过“李平老师”课的同学的学号、姓名
#思路:1、获取所有有生物课程的人(学号,成绩) - 临时表
# 2、获取所有有物理课程的人(学号,成绩) - 临时表
# 3、根据【学号】连接两个临时表:学号 - 物理成绩 - 生物成绩
# 4、然后再进行筛选
select A.student_id,A.num,B.num from
(select student_id,num as sw from score left join course on score.course_id = course.cid where course.cname = '生物') as A
inner join //为空的时候不显示
(select student_id,num as wl from score left join course on score.course_id = course.cid where course.cname = '物理') as B
on A.student_id = B.student_id where A.num > B.num;
10.查询“生物”课程比“物理”课程成绩高的所有学生的学号、生物成绩、物理成绩
#思路:1、先查到选择001或者选择002课程的所有同学
# 2、根据学生进行分组,如果学生数量等于2表示,两门均已选择
select score.student_id,student.sname from score
left join student on score.student_id = student.sid
where course_id = 1 or course_id = 2 group by student_id HAVING count(course_id) > 1;
11.查询学过“001”并且也学过编号“002”课程的同学的学号、姓名
select student_id from score where course_id in (
select cid from course left join teacher on course.teacher_id = teacher.tid where teacher.tname = "李平"
) group by student_id having count(course_id) = (select count(cid) from course left join teacher on course.teacher_id = teacher.tid where teacher.tname = "李平");
12.查询学过“李平”老师所教的所有课的同学的学号、姓名
select sid,sname from student where sid in (
select distinct student_id from score where num < 60
);
13.查询有课程成绩小于60分的同学的学号、姓名
#思路:1、在分数表中根据学生进行分组,获取每一个学生选课数量
# 2、如果数量 == 总课程数量,表示已经选择了所有课程
select student_id,sname
from score left join student on score.student_id = student.sid
group by student_id HAVING count(1) < (select count(1) from course);
14.查询没有学全所有课的同学的学号、姓名
#思路:获取 001 同学选择的所有课程
# 获取课程在其中的所有人以及所有课程
# 根据学生筛选,获取所有学生信息
# 再与学生表连接,获取姓名
select student_id,sname, count(course_id)
from score left join student on score.student_id = student.sid
where student_id != 1 and course_id in (select course_id from score where student_id = 1) group by student_id
15.查询至少有一门课与学号为“001”的同学所学相同的同学的学号和姓名
#思路:先找到和001的学过的所有人
# 然后个数 = 001所有学科 ==》 其他人可能选择的更多
select student_id,sname, count(course_id)
from score left join student on score.student_id = student.sid
where student_id != 1 and course_id in (select course_id from score where student_id = 1) group by student_id having count(course_id) = (select count(course_id) from score where student_id = 1)
16.查询至少学过学号为“001”同学所有课的其他同学学号和姓名
#思路:1、个数相同
# 2、002学过的也学过
select student_id,sname from score left join student on score.student_id = student.sid where student_id in (
select student_id from score where student_id != 1 group by student_id HAVING count(course_id) = (select count(1) from score where student_id = 1)
) and course_id in (select course_id from score where student_id = 1) group by student_id HAVING count(course_id) = (select count(1) from score where student_id = 1)
17.查询和“001”号的同学学习的课程完全相同的其他同学学号和姓名
delete from score where course_id in (
select cid from course left join teacher on course.teacher_id = teacher.tid where teacher.name = '李平'
)
18.删除学习“李平”老师课的score表记录
#思路:1、由于insert 支持 :inset into tb1(xx,xx) select x1,x2 from tb2;
# 2、获取所有没上过002课的所有人,获取002的平均成绩
insert into score(student_id, course_id, num) select student_id,2,(select avg(num) from score where course_id = 2)
from student where sid where course_id != 2
19.向score表中插入一些记录,这些记录要求符合以下条件:①没有上过编号“002”课程的同学学号;②插入“002”号课程的平均成绩
select B.student_id,
(select num from score left join course on score.course_id = course.cid where course.cname = "语文" and score.student_id=B.student_id) as 语文,
(select num from score left join course on score.course_id = course.cid where course.cname = "数学" and score.student_id=B.student_id) as 数学,
(select num from score left join course on score.course_id = course.cid where course.cname = "英语" and score.student_id=B.student_id) as 英语,
count(B.course_id),
avg(B.num)
from score as B
group by student_id desc
20.按平均成绩从低到高显示所有学生的“语文”、“数学”、“英语”三门的课程成绩,按如下形式显示: 学生ID,语文,数学,英语,有效课程数,有效平均分
select course_id, max(num) as max_num, min(num) as min_num from score group by course_id
21.查询各科成绩最高和最低的分:以如下形式显示:课程ID,最高分,最低分
#思路:case when .. then
select course_id, avg(num) as avgnum,sum(case when score.num > 60 then 1 else 0 END)/sum(1) as percent from score group by course_id order by avgnum asc,percent desc;
22.按各科平均成绩从低到高和及格率的百分数从高到低顺序
select score.course_id,course.cname,avg(if(isnull(score.num),0,score.num)),teacher.tname from score
left join score on score.course_id = course.cid
left join teacher on teacher.tid = course.teacher_id
group by score.course_id
23.课程平均分从高到低显示(现实任课老师)
select score.sid,score.course_id,score.num,B.first_num,B.second_num from score left join
(
select
sid,
(select num from score as s2 where s2.course_id = s1.course_id order by num desc limit 0,1) as first_num,
(select num from score as s2 where s2.course_id = s1.course_id order by num desc limit 2,1) as second_num
from
score as s1
) as B
on score.sid =B.sid
where score.num <= B.first_num and score.num >= B.second_num
24.查询各科成绩前两名的记录
select course.cname,count(1) from score
left join course on score.course_id = course.cid
group by course_id
25.查询各个课程及相应的选修人数
select course_id, count(1) from score group by course_id having count(1) > 5
26.查询热门课程(选修的学生数>5)
select student.sid, student.sname, count(1) from score
left join student on score.student_id = student.sid
group by course_id having count(1) = 1
27.查询出只选修了一门课程的全部学生的学号和姓名
select gender,count(1) from student group by gender
28.查询男生、女生的人数
select sname from student where sname like '张%'
29.查询姓“张”的学生名单
select sname,count(1) as count from student group by sname;
30.查询同名同姓学生名单,并统计同名人数
select course_id,avg(if(isnull(num), 0 ,num)) as avg from score group by course_id order by avg asc,course_id desc
31.查询每门课程的平均成绩,结果按平均成绩升序排列,平均成绩相同时,按课程号降序排列
select student_id,sname, avg(if(isnull(num), 0 ,num)) from score left join student on score.student_id = student.sid group by student_id
32.查询平均成绩大于85的所有学生的学号、姓名和平均成绩
select student.sname,score.num from score
left join course on score.course_id = course.cid
left join student on score.student_id = student.sid
where score.num < 60 and course.cname = '数学'
33.查询课程名称为“数学”,且分数低于60的学生姓名和分数
select * from score where score.student_id = 3 and score.num > 80
34.查询课程编号为003且课程成绩在80分以上的学生的学号和姓名
select count(distinct student_id) from score
35.求选了课程的学生人数
select sname,num from score
left join student on score.student_id = student.sid
where score.course_id in (select course.cid from course left join teacher on course.teacher_id = teacher.tid where tname='杨艳') order by num desc limit 1
36.查询选修“杨艳”老师所授课程的学生中,成绩最高的学生姓名及其成绩
select DISTINCT s1.course_id,s2.course_id,s1.num,s2.num from score as s1, score as s2 where s1.num = s2.num and s1.course_id != s2.course_id
37.查询不同课程但成绩相同的学生的学号、课程号、学生成绩
select student_id from score group by student_id having count(student_id) > 1
38.检索至少选修两门课程的学生学号
select course_id,count(1) from score group by course_id having count(1) = (select count(1) from student)
39.查询学生都选修的课程、以及课程号和课程名
select sid,student.sname from student where sid not in (select student_id from score where course_id in
(select cid from course left join teacher on course.teacher_id = teacher.tid where tname = '李平')
) group by sid
40.查询没学过“李平”老师讲授的任一门课程的学生姓名
select student_id,count(1) from score where num < 60 group by student_id having count(1) > 2
41.查询两门以上不及格课程的同学的学号及其平均成绩
select student_id from score where num< 60 and course_id = 4 order by num desc;
42.检索“004”课程分数小于60,按分数降序排列的同学学号
delete from score where course_id = 1 and student_id = 2
43.删除“002”同学的“001”课程的成绩
Python学习笔记整理总结【MySQL】的更多相关文章
- python学习笔记整理——字典
python学习笔记整理 数据结构--字典 无序的 {键:值} 对集合 用于查询的方法 len(d) Return the number of items in the dictionary d. 返 ...
- python学习笔记整理——集合 set
python学习整理笔记--集合 set 集合的用途:成员测试和消除重复的条目,进行集合运算 注意:花括号或set()函数可以用于创建集合. 注意:若要创建一个空的集合你必须使用set(),不能用{} ...
- python学习笔记整理——元组tuple
Python 文档学习笔记2 数据结构--元组和序列 元组 元组在输出时总是有括号的 元组输入时可能没有括号 元组是不可变的 通过分拆(参阅本节后面的内容)或索引访问(如果是namedtuples,甚 ...
- python学习笔记整理——列表
Python 文档学习笔记 数据结构--列表 列表的方法 添加 list.append(x) 添加元素 添加一个元素到列表的末尾:相当于a[len(a):] = [x] list.extend(L) ...
- python 学习笔记整理
首先自我批评一下,说好的一天写一篇博客,结果不到两天,就没有坚持了,发现自己做什么事情都没有毅力啊!不能持之以恒.但是,这次一定要从写博客开始来改掉自己的一个坏习惯. 可是写博客又该写点什么呢? 反正 ...
- Python学习笔记整理总结【Django】【MVC/MTV/路由分配系统(URL)/视图函数 (views)/表单交互】
一.Web框架概述 Web框架本质上其实就是一个socket服务端,用户的浏览器其实就是一个socket客户端. #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 ...
- Python学习笔记9-Python 链接MySql数据库
Python 链接MySql数据库,方法很简单: 首先需要先 安装一个MySql链接插件:MySQL-python-1.2.3.win-amd64-py2.7.exe 下载地址:http://dev. ...
- Python学习笔记整理总结【语言基础篇】
一.变量赋值及命名规则① 声明一个变量及赋值 #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- # _author_soloLi name1="sol ...
- Python学习笔记整理总结【RabbitMQ队列】
RabbitMQ是消息队列.之前学过的队列queue:线程queue(threading queue),只是多个线程之间进行数据交互.进程queue(processing queue),只是父进程与子 ...
随机推荐
- Egret白鹭开发微信小游戏分享功能
今天给大家分享一下微信分享转发功能,话不多说,直接干 方法一: 1.在egret中打开Platfrom.ts文件,添加代码如下(当然,你也可以直接复制粘贴) /** * 平台数据接口. * 由于每款游 ...
- Leetcode之回溯法专题-216. 组合总和 III(Combination Sum III)
Leetcode之回溯法专题-216. 组合总和 III(Combination Sum III) 同类题目: Leetcode之回溯法专题-39. 组合总数(Combination Sum) Lee ...
- 一块钱哪里去了?--java浮点型背后的故事
有这样一道智力题:三人住旅馆,老板娘说30元她们付钱后进去了,老板娘想起今天是特价25元,就叫伙计拿5元还给三位顾客,可伙计藏了2元,给了她们3元,这样她们每人得1元,就是说每人付了9元,那3*9=2 ...
- Oracle - Sequences
创建计数器 --最小值1,最大值999999999999999999999999999,从1开始,每次自增1,缓存20 --SQL语句: -- Create sequence create seque ...
- 第8章 浏览器对象模型BOM 8.1 window对象
ECMAScript是javascript的核心,但如果要在web中使用javascript,那么BOM(浏览器对象模型)则无疑是真正的核心.BOM提供了很多对象,用于访问浏览器的功能,在浏览器之间共 ...
- 牛客第五场多校 J plan 思维
链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/143/J来源:牛客网 There are n students going to travel. And hotel ...
- dp递推 hdu1978
How many ways Time Limit: 3000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Tot ...
- Git的合并
merge: A---B---C topic / D---E---F---G master A---B---C topic / \ D---E---F---G---H master (在当前的bran ...
- shell中日期循环的方式
第一种 # 这里的例子以周为循环 !/bin/bash begin_date="20160907" end_date="20170226" while [ &q ...
- 【Offer】[26] 【树的子结构】
题目描述 思路分析 测试用例 Java代码 代码链接 题目描述 输入两棵二叉树A和B,判断B是不是A的子结构.图中右边的树是左边的子结构  思路分析 先对树A进行遍历,找到与树B的根结点值相同的节点 ...
