【Android - 进阶】之Drawable简介
Drawable是什么?Android给我们的解释是:“A general abstraction for 'something that can be drawn'.”,翻译过来就是:对于可以绘制的东西的一个抽象。也就是说,Drawable是一种可以在Canvas上绘制的东西。在Android开发中,Drawable有两种用法,分别是作为View的背景以及作为ImageView中显示的内容。Android系统中为我们提供了很多种Drawable,这些Drawable大多都是在XML中使用,有些也可以在JAVA代码中写一些辅助代码。我们也可以自定义Drawable。本文主要讲解Android系统为我们提供的Drawable中的13种。
1、ColorDrawable
ColorDrawable 对应的XML顶层标签是 <color> ,代表的是一个纯色的Drawable,通常可以用来做分割线等View的背景。使用方法如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<color xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:color="@android:color/darker_gray" />
2、GradientDrawable
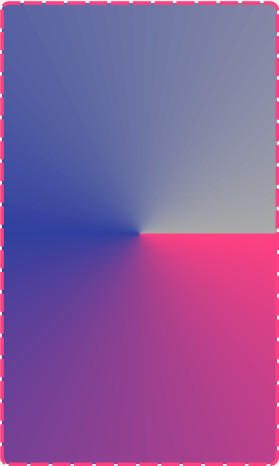
GradientDrawable 对应的XML顶层标签是 <shape> ,是开发中最常用的Drawable之一。通过GradientDrawable,我们可以实现圆角、渐变色、线条等特殊样式。一个使用GradientDrawable的示例代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:shape="rectangle"> <corners android:radius="10.0dip" />
<gradient
android:angle="270"
android:centerColor="@color/colorPrimaryDark"
android:endColor="@android:color/darker_gray"
android:startColor="@color/colorAccent"
android:type="sweep" />
<padding
android:bottom="20.0dip"
android:left="20.0dip"
android:right="20.0dip"
android:top="20.0dip" />
<stroke
android:width="5.0dip"
android:color="@color/colorAccent"
android:dashGap="5.0dip"
android:dashWidth="25.0dip" /> </shape>
通过上面的XML代码,我们可以得到一个圆角的、内边距20dp的、扫描式渐变色的、虚线边框的Drawable。GradientDrawable中常用的属性及子标签的详细介绍如下所示:
android:shape:设置整体的形状,可以是rectangle矩形、oval椭圆、line横线、ring圆环
<corners>:圆角
android:radius:统一设置四个角的圆角程度
android:topLeftRadius:设置左上角的圆角程度
android:topRightRadius:设置右上角的圆角程度
android:bottomLeftRadius:设置左下角的圆角程度
android:bottomRightRadius:设置右下角的圆角程度
<gradient>:渐变色
android:type:渐变色的类型,有linear线性渐变、radial发散渐变、sweep扫描渐变
android:startColor:渐变的起始颜色
android:centerColor:渐变的中心颜色
android:endColor:渐变的结尾颜色
android:angle:线性渐变属性,设置渐变的倾斜角度
android:gradientRadius:发散渐变属性,设置发散渐变的半径
android:centerX:发散渐变属性,设置发散渐变的圆心的X坐标
android:centerY:发散渐变属性,设置发散渐变的圆心的Y坐标
<padding>:内边距
android:left:shape中的内容距离shape左边界的距离
android:right:shape中的内容距离shape右边界的距离
android:top:shape中的内容距离shape上边界的距离
android:bottom:shape中的内容距离shape下边界的距离
<size>:大小
android:width:这个shape的宽度
android:height:这个shape的高度
<solid>:填充色
android:color:形状的填充色
<stroke>:线条
android:width:线条的粗细
android:color:线条的颜色
android:dashWidth:虚线线段的宽度
android:dashGap:虚线线段之间的间隙
上面代码的运行效果如下图所示:
3、StateListDrawable
StateListDrawable 对应的XML顶层标签是 <selector> ,也是开发中最常用的Drawable之一。通过这种Drawable,我们可以让一个View的背景在响应不同状态时显示为不同的样式。一个使用StateListDrawable的示例代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item android:drawable="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:state_pressed="true" />
<item android:drawable="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:state_focused="true" />
<item android:drawable="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:state_selected="true" />
<item android:drawable="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round" />
</selector>
通过上面的代码,我们就为View设置了默认显示的状态和按压、选中、获取焦点等状态下显示的状态。StateListDrawable中几个常用状态解释如下:
android:state_pressed:按下状态
android:state_focused:获取了用户焦点的状态
android:state_selected:被用户选择的状态
android:state_checked:被用户选中的状态,适用于CheckBox等控件
android:state_enabled:可用状态
4、BitmapDrawable
BitmapDrawable 对应的XML顶层标签是 <bitmap> ,它的作用是加载一张图片,并对其进行一些性能、平铺模式等的处理。下面是一个使用BitmapDrawable的示例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<bitmap xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:antialias="true"
android:dither="true"
android:filter="true"
android:gravity="fill"
android:src="@mipmap/image02"
android:tileMode="mirror" />
通过上面的代码,我们不仅加载了一张图片资源,还设置了抗锯齿、抖动都性能调优,更设置了图片的平铺模式为镜像重复模式。BitmapDrawable中各种属性的详细解释如下:
src:图片的资源ID
antialias:抗锯齿,让图片变得平滑
dither:抖动,让高质量的图片在低质量的屏幕上能保持较好的显示效果
filter:过滤,当图片尺寸被缩放后,可以保持较好的显示效果
gravity:当图片尺寸小于容器尺寸时,对图片进行定位
tileMode:平铺模式,默认是disabled,还可以有一下值:
clamp:将图片四周的像素扩展到周围区域
repeat:简单的水平竖直方向上的复制效果
mirror:水平竖直方向上的镜像效果
上面代码的执行效果图如下:

5、NinePatchDrawable
NinePatchDrawable 对应的XML顶层标签是 <nine-patch> ,其用法和BitmapDrawable完全一样,只是加载的是一张.9图片。这里不再介绍NinePatchDrawable的具体用法,只介绍一下在Android Studio中如何制作.9图片。具体步骤如下:
Android Studio中制作.9图片的方式:
、选择一张图片,右键点击“Create -Patch File”,即可生成一张.9图片
、生成的.9图片和原始图片在同一个文件夹中,可以根据需要挪动图片位置
、在.9图片的四条边上选取像素,选取的像素是在缩放过程中会变形的像素,其他像素都是不会变形的像素
6、LayerDrawable
LayerDrawable 对应的XML顶层标签是 <layer-list> ,它表示一种层次化的Drawable集合,即它可以将多个Drawable叠加起来使用,达到最终的效果。下面是一个使用LayerDrawable的示例代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layer-list xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item>
<shape>
<solid android:color="@android:color/darker_gray" />
</shape>
</item>
<item android:bottom="10.0dip">
<shape>
<solid android:color="@android:color/white" />
</shape>
</item>
<item
android:bottom="1.0dip"
android:left="1.0dip"
android:right="1.0dip">
<shape>
<solid android:color="@android:color/white" />
</shape>
</item>
</layer-list>
上面代码的运行效果图如下图所示,可以看到是一个类似输入框的效果:

从上面的例子可以看出:<item>标签中可以直接使用 android:drawable 或 android:id 属性指定资源id;也可以在标签内部添加一些其他的Drawable类型,如<shape>等;<item>标签中可以使用 android:top、android:bottom、android:left、android:right属性指定间距。
7、InsetDrawable
InsetDrawable 对应的XML顶层标签是 <inset> 。当一个View希望自己的背景比自己的实际区域小的时候,就可以使用InsetDrawable来实现。例如,我想让我的ImageView中的图片大小距离ImageView边界10dp,我就可以编写如下代码来实现:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<inset xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:drawable="@mipmap/image01"
android:insetBottom="10.0dip"
android:insetLeft="10.0dip"
android:insetRight="10.0dip"
android:insetTop="10.0dip" />
可以看到,InsetDrawable通过设置android:insetTop、android:insetBottom、android:insetLeft、android:insetRight来指定四个边的内凹大小。
当然,这种需求也可以使用LayerDrawable来实现。
8、TransitionDrawable
TransitionDrawable 对应的XML顶层标签是 <transition> ,它可以让一个View的背景从图片A渐变到图片B。这里的渐变的意思是:图片A逐渐消失,同时图片B逐渐显现。我们可以编写如下代码来实现这个效果:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<transition xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item android:drawable="@mipmap/image01" />
<item android:drawable="@mipmap/image02" />
</transition>
一个<transition>标签中只能有两个<item>子标签,也就是说,TransitionDrawable最多只支持两张图片之间进行渐变。但是,只在XML文件中写这些代码是不够的,我们还需要在JAVA代码中设置开始渐变。具体代码如下:
ImageView img = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.drawable_main_iv_img);
TransitionDrawable drawable = (TransitionDrawable) img.getDrawable();
drawable.startTransition(60000);
9、AnimationDrawable
AnimationDrawable 对应的XML顶层标签是 <animation-list> ,表示的是一个帧动画Drawable。下面是一个使用AnimationDrawable的示例代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<animation-list xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:oneshot="false"
android:visible="true"> <item
android:drawable="@mipmap/image01"
android:duration="1000" />
<item
android:drawable="@mipmap/image02"
android:duration="1000" />
<item
android:drawable="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:duration="1000" />
<item
android:drawable="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:duration="1000" /> </animation-list>
在上面的代码中,我们使用 android:oneshot 属性设置帧动画是否只进行一次,如果为false,则可以永久进行。我们可以设置<item>子标签,设置每一帧显示的图片和显示时长。最后,我们还需要在JAVA代码中调用AnimationDrawable的 start() 方法,开始播放帧动画。代码如下:
AnimationDrawable drawable = (AnimationDrawable) img.getDrawable();
drawable.start();
10、LevelListDrawable
LevelListDrawable 对应的XML顶层标签是 <level-list> ,它表示一个Drawable集合,集合中的每个Drawable都有一个等级(Level)的概念,LevelListDrawable可以根据不同等级选择显示集合中的不同Drawable。下面是一个使用LevelListDrawable的示例代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<level-list xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item
android:drawable="@mipmap/image01"
android:maxLevel="5" />
<item
android:drawable="@mipmap/image02"
android:maxLevel="50" />
<item
android:drawable="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:maxLevel="500" />
<item
android:drawable="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:maxLevel="5000" />
</level-list>
我们在LevelListDrawable的集合中放了四个Drawable,分别使用 android:maxLevel 设置Drawable的Level,然后在JAVA代码中,当我们点击图片的时候,就会随机选择一张图片。JAVA代码如下:
int[] levels = {5, 50, 500, 5000};
ImageView img = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.drawable_main_iv_img);
img.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
int index = (int) (Math.random() * 4);
img.setImageLevel(levels[index]);
}
});
通过调用ImageView的 setImageLevel() 方法来设置图片的Level。除了这种方法之外,我们还可以直接调用Drawable对象的 setLevel() 方法设置Level。这样,我们就可以在每次点击图片的时候随机生成一个下标,从数组中取出对应的Level设置给LevelListDrawable。
还需要注意一点,这里的Level最好介于 0 和 10000 之间。
11、RotateDrawable
RotateDrawable 对应的XML顶层标签是 <rotate> ,用来制作一个可以旋转的Drawable。下面是使用RotateDrawable的一个示例代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<rotate xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:drawable="@mipmap/image02"
android:fromDegrees="0"
android:pivotX="50%"
android:pivotY="50%"
android:toDegrees="360"
android:visible="true" />
RotateDrawable中各个属性的详细解释如下:
android:drawable:Drawable中显示的图片
android:fromDegrees:旋转开始时的角度
android:toDegrees:旋转结束时的角度
android:pivotX:选中中心点X坐标在宽度上的百分比
android:pivotY:选中中心点Y坐标在高度上的百分比
使用RotateDrawable时,我们也需要在JAVA代码中设置Drawable的Level(0<=Level<=10000,默认为0),来控制旋转的百分比。例如,在上面的代码中,我设置了这个Drawable从0°旋转到360°,那么当这个Drawable旋转角度为0°时,其Level是0,当旋转到360°时,Level是10000。因此,如果我在JAVA代码中设置Level为1000,那么这个Drawable就会旋转10%,即36°。
现在我想在JAVA代码中控制这个Drawable翻转,即旋转180°,JAVA代码如下:
ImageView img = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.drawable_main_iv_img);
RotateDrawable drawable = (RotateDrawable) img.getDrawable();
drawable.setLevel(5000);
11、ScaleDrawable
ScaleDrawable 对应的XML顶层标签是 <scale> ,用来控制Drawable的缩放。下面是一个使用ScaleDrawable的示例代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<scale xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:drawable="@mipmap/image01"
android:scaleGravity="center"
android:scaleHeight="70%"
android:scaleWidth="70%" />
ScaleDrawable中各个属性的详细解释如下:
android:drawable:Drawable中显示的图片
android:scaleWidth:Drawable缩放的宽度的百分比
android:scaleHeight:Drawable缩放的高度的百分比
android:scaleGravity:Drawable缩放后显示的位置,有以下值:
top:将图片放在容器顶部,不改变其大小
bottom:将图片放在容器底部,不改变其大小
left:将图片放在容器左部,不改变其大小(默认值)
right:将图片放在容器右部,不改变其大小
center:将图片放其容器的中心,不改变其大小
center_horizontal:将图片放在容器水平中间,不改变其大小
center_vertical:将图片放在容器垂直中间,不改变其大小
fill:将图片填充容器的宽和高
fill_horizontal:将图片水平填充容器的宽,图片的高不变
fill_vertical:将图片垂直填充容器的高,图片的宽不变
ScaleDrawable也需要在JAVA代码中设置Level(0<=Level<=10000,默认为0),这里的Level一定不能为0,且Level会与scaleWidth、scaleHeight属性一起控制Drawable的缩放。缩放后Drawable显示的实际大小的计算方法如下:
w -= (int) (w * (10000 - level) * mState.mScaleWidth / 10000);
h -= (int) (h * (10000 - level) * mState.mScaleHeight / 10000);
因此,我们在实际使用中,Level一般设置为1即可。JAVA代码如下:
ImageView img = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.drawable_main_iv_img);
ScaleDrawable drawable = (ScaleDrawable) img.getDrawable();
drawable.setLevel(1);
12、ClipDrawable
ClipDrawable 对应的XML顶层标签是 <clip> ,它可以用来裁剪一张图片。下面是一个使用ClipDrawable的示例代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<clip xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:clipOrientation="horizontal"
android:drawable="@mipmap/image02"
android:gravity="center" />
ClipDrawable中各个属性的详细解释如下:
android:drawable:Drawable中显示的图片
android:clipOrientation:Drawable的裁剪方向
android:gravity:Drawable裁剪后的显示方式(Drawable的裁剪方式),可以有以下值:
top:将图片放在容器顶部,其大小不变;如果为垂直裁剪,则从底部开始裁剪
bottom:将图片放在容器底部,其大小不变;如果为垂直裁剪,则从顶部开始裁剪
left:将图片放在容器左侧,其大小不变;如果为水平裁剪,则从右侧开始裁剪
right:将图片放在容器右侧,其大小不变;如果为水平裁剪,则从左侧开始裁剪
center:将图片放在容器中央,其大小不变;如果为水平裁剪,则从左右两侧同时开始裁剪;如果为垂直裁剪,则从上下两侧同时开始裁剪
center_horizontal:将图片在水平方向居中显示,其大小不变;如果为水平裁剪,则从左右两侧同时裁剪
center_vertical:将图片在垂直方向居中显示,其大小不变;如果为垂直裁剪,则从上下两侧同时裁剪
fill:将图片填充容器,仅当Level为0时才会裁剪,此处裁剪为全部裁剪掉
fill_horizontal:将图片水平方向填充容器,垂直方向不变,仅当Level为0时才会裁剪,此处裁剪为全部裁剪掉
fill_vertical:将图片垂直方向填充容器,水平方向不变,仅当Level为0时才会裁剪,此处裁剪为全部裁剪掉
ClipDrawable也需要在JAVA代码中设置Level(0<=Level<=10000,默认为0),这里的Level决定的是裁剪的百分比。当Level为0时,表示全部裁剪,当Level为10000时,表示不裁剪。裁掉的区域所占原图的百分比的计算公式为: (10000 - Level) / 10000 。
使用ClipDrawable,需要注意以下两点:
(1)当clipOrientation和gravity两个属性发生冲突的时候,以clipOrientation属性为准,且gravity属性值自动变为center;
(2)如果gravity属性设置成左右/上下同时裁剪,那么左右/上下分别裁剪总裁剪区域的一半。如:我的Level设置为2000,且gravity属性值为center_vertical,那么上下两侧各被裁剪10%。
Drawable的其他用法
1、获取Drawable的两种方式
(1)当Drawable作为View的背景时:Drawable drawable = view.getBackground();
(2)当Drawable作为ImageView的资源时:Drawable drawable = view.getDrawable();
2、获取Drawable宽高的两种方式(以宽为例)
(1)int width = drawable.getBounds().width();
(2)int width = drawable.getIntrinsicWidth();
【Android - 进阶】之Drawable简介的更多相关文章
- 我的Android进阶之旅------>经典的大牛博客推荐(排名不分先后)!!
本文来自:http://blog.csdn.net/ouyang_peng/article/details/11358405 今天看到一篇文章,收藏了很多大牛的博客,在这里分享一下 谦虚的天下 柳志超 ...
- Android中的Drawable和动画
Android中Drawable是一种可以在Canvas上进行绘制抽象的概念,种类很多,常见的颜色和图片都可以是一个Drawable.Drawable有很多种,它们表示一种图像的概念,但是它们又不全是 ...
- 我的Android进阶之旅------> Android在TextView中显示图片方法
面试题:请说出Android SDK支持哪些方式显示富文本信息(不同颜色.大小.并包括图像的文本信息).并简要说明实现方法. 答案:Android SDK支持例如以下显示富文本信息的方式. 1.使用T ...
- Android进阶(十八)AndroidAPP开发问题汇总(二)
Android进阶(十八)AndroidAPP开发问题汇总(二) 端口被占用解决措施: Android使用SimpleAdapter更新ListView里面的Drawable元素: http://ww ...
- 我的Android进阶之旅------>Android利用温度传感器实现带动画效果的电子温度计
要想实现带动画效果的电子温度计,需要以下几个知识点: 1.温度传感器相关知识. 2.ScaleAnimation动画相关知识,来进行水印刻度的缩放效果. 3.android:layout_weight ...
- 我的Android进阶之旅------>Android实现用Android手机控制PC端的关机和重启的功能(三)Android客户端功能实现
我的Android进阶之旅------>Android实现用Android手机控制PC端的关机和重启的功能(一)PC服务器端(地址:http://blog.csdn.net/ouyang_pen ...
- 我的Android进阶之旅------> Android在TextView中显示图片方法
面试题:请说出Android SDK支持哪些方式显示富文本信息(不同颜色.大小.并包含图像的文本信息),并简要说明实现方法. 答案:Android SDK支持如下显示富文本信息的方式. 1.使用Tex ...
- 我的Android进阶之旅------>Android疯狂连连看游戏的实现之加载界面图片和实现游戏Activity(四)
正如在<我的Android进阶之旅------>Android疯狂连连看游戏的实现之状态数据模型(三)>一文中看到的,在AbstractBoard的代码中,当程序需要创建N个Piec ...
- 我的Android进阶之旅------>Android疯狂连连看游戏的实现之开发游戏界面(二)
连连看的游戏界面十分简单,大致可以分为两个区域: 游戏主界面区 控制按钮和数据显示区 1.开发界面布局 本程序使用一个RelativeLayout作为整体的界面布局元素,界面布局上面是一个自定义组件, ...
随机推荐
- 适用于Windows桌面应用程序的.NET Core 3
介绍 9月,微软发布了新版.NET Core,用于构建Windows桌面应用程序,包括WPF和Windows Forms.从那时起开发人员可以将传统的nfx桌面应用程序(和控件库)迁移到.NET Co ...
- Spring Cloud gateway 三 自定义过滤器GatewayFilter
之前zuul 网关介绍.他有过滤器周期是四种,也是四种类型的过滤器.而gateway 只有俩种过滤器:"pre" 和 "post". PRE: 这种过滤器在请求 ...
- 利用python的requests和BeautifulSoup库爬取小说网站内容
1. 什么是Requests? Requests是用Python语言编写的,基于urllib3来改写的,采用Apache2 Licensed 来源协议的HTTP库. 它比urllib更加方便,可以节约 ...
- 基于 Jenkins Pipeline 自动化部署
最近在公司推行Docker Swarm集群的过程中,需要用到Jenkins来做自动化部署,Jenkins实现自动化部署有很多种方案,可以直接在jenkins页面写Job,把一些操作和脚本都通过页面设置 ...
- windows使用docker运行mysql等工具(一)windows安装docker
由于我本地的mysql版本比较低,最近想着要升级一下mysql版本,鉴于docker容器的火热,就想着在本地装个docker环境,然后下载最新版的mysql镜像,完成mysql8.0的安装.电脑是wi ...
- UiPath之DataTable转换为List和Array
今天给大家分享一下,如何将DataTable转为List和Array,为此小U也花了不少时间研究,最后发现没有那么复杂. 先来说说List和Array的区别: List:就像一个链条,存储数据的空间可 ...
- 2019年10月13日 计算机英语习题 wangqingchao
Match the explanations in Column B with words and expressions in Columna. (搭配每组中意义相同的词或短语) Types of ...
- php ffmpeg视频和序列帧转化
php ffmpeg视频和序列帧转化 <pre>$cmd=shell_exec("ffmpeg -i ".__DIR__ . "/shipin1.mp4 -r ...
- one of neural network
map source:https://github.com/microsoft/ai-edu Fundamental Principle inputs: characteristic value th ...
- mysql双主互为主从配置
在使用双主互为主从的模式前提是互为主从的两个数据库,表的主键必须是自增的. 环境不多说了 ,多台mysql单实例或单台多实例都可以.多实例的配置请参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/ ...
