快速遍历OpenCV Mat图像数据的多种方法和性能分析 | opencv mat for loop
本文首发于个人博客https://kezunlin.me/post/61d55ab4/,欢迎阅读!
opencv mat for loop
Series
- Part 1: compile opencv on ubuntu 16.04
- Part 2: compile opencv with CUDA support on windows 10
- Part 3: opencv mat for loop
- Part 4: speed up opencv image processing with openmp
Guide
Mat
- for gray image, use type
<uchar> - for RGB color image,use type
<Vec3b>
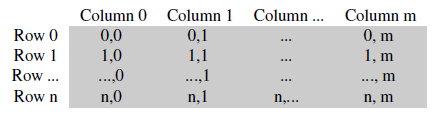
gray format storage
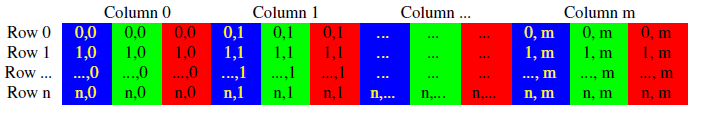
color format storage: BGR
we can use method
isContinuous()to judge whether the memory buffer is continuous or not.
color space reduction
uchar color_space_reduction(uchar pixel){/*0-9 ===>010-19===>1020-29===>20...240-249===>24250-255===>25map from 256*256*256===>26*26*26*/int divideWith = 10;uchar new_pixel = (pixel / divideWith)*divideWith;return new_pixel;}
color table
void get_color_table(){// cache color value in table[256]int divideWith = 10;uchar table[256];for (int i = 0; i < 256; ++i)table[i] = divideWith* (i / divideWith);}
C++
ptr []
// C ptr []: faster but not safeMat& ScanImageAndReduce_Cptr(Mat& I, const uchar* const table){// accept only char type matricesCV_Assert(I.depth() != sizeof(uchar));int channels = I.channels();int nRows = I.rows;int nCols = I.cols* channels;if (I.isContinuous()){nCols *= nRows;nRows = 1;}int i, j;uchar* p;for (i = 0; i < nRows; ++i){p = I.ptr<uchar>(i);for (j = 0; j < nCols; ++j){p[j] = table[p[j]];}}return I;}
ptr ++
// C ptr ++: faster but not safeMat& ScanImageAndReduce_Cptr2(Mat& I, const uchar* const table){// accept only char type matricesCV_Assert(I.depth() != sizeof(uchar));int channels = I.channels();int nRows = I.rows;int nCols = I.cols* channels;if (I.isContinuous()){nCols *= nRows;nRows = 1;}uchar* start = I.ptr<uchar>(0); // same as I.ptr<uchar>(0,0)uchar* end = start + nRows * nCols;for (uchar* p=start; p < end; ++p){*p = table[*p];}return I;}
at(i,j)
// at<uchar>(i,j): random access, slowMat& ScanImageAndReduce_atRandomAccess(Mat& I, const uchar* const table){// accept only char type matricesCV_Assert(I.depth() != sizeof(uchar));const int channels = I.channels();switch (channels){case 1:{for (int i = 0; i < I.rows; ++i)for (int j = 0; j < I.cols; ++j)I.at<uchar>(i, j) = table[I.at<uchar>(i, j)];break;}case 3:{Mat_<Vec3b> _I = I;for (int i = 0; i < I.rows; ++i)for (int j = 0; j < I.cols; ++j){_I(i, j)[0] = table[_I(i, j)[0]];_I(i, j)[1] = table[_I(i, j)[1]];_I(i, j)[2] = table[_I(i, j)[2]];}I = _I;break;}}return I;}
Iterator
// MatIterator_<uchar>: safe but slowMat& ScanImageAndReduce_Iterator(Mat& I, const uchar* const table){// accept only char type matricesCV_Assert(I.depth() != sizeof(uchar));const int channels = I.channels();switch (channels){case 1:{MatIterator_<uchar> it, end;for (it = I.begin<uchar>(), end = I.end<uchar>(); it != end; ++it)*it = table[*it];break;}case 3:{MatIterator_<Vec3b> it, end;for (it = I.begin<Vec3b>(), end = I.end<Vec3b>(); it != end; ++it){(*it)[0] = table[(*it)[0]];(*it)[1] = table[(*it)[1]];(*it)[2] = table[(*it)[2]];}}}return I;}
opencv LUT
// LUTMat& ScanImageAndReduce_LUT(Mat& I, const uchar* const table){Mat lookUpTable(1, 256, CV_8U);uchar* p = lookUpTable.data;for (int i = 0; i < 256; ++i)p[i] = table[i];cv::LUT(I, lookUpTable, I);return I;}
forEach
forEachmethod of theMatclass that utilizes all the cores on your machine to apply any function at every pixel.
// Parallel execution with function object.struct ForEachOperator{uchar m_table[256];ForEachOperator(const uchar* const table){for (size_t i = 0; i < 256; i++){m_table[i] = table[i];}}void operator ()(uchar& p, const int * position) const{// Perform a simple operationp = m_table[p];}};// forEach use multiple processors, very fastMat& ScanImageAndReduce_forEach(Mat& I, const uchar* const table){I.forEach<uchar>(ForEachOperator(table));return I;}
forEach with lambda
// forEach lambda use multiple processors, very fast (lambda slower than ForEachOperator)Mat& ScanImageAndReduce_forEach_with_lambda(Mat& I, const uchar* const table){I.forEach<uchar>([=](uchar &p, const int * position) -> void{p = table[p];});return I;}
time cost
no foreach
[1 Cptr ] times=5000, total_cost=988 ms, avg_cost=0.1976 ms[1 Cptr2 ] times=5000, total_cost=1704 ms, avg_cost=0.3408 ms[2 atRandom] times=5000, total_cost=9611 ms, avg_cost=1.9222 ms[3 Iterator] times=5000, total_cost=20195 ms, avg_cost=4.039 ms[4 LUT ] times=5000, total_cost=899 ms, avg_cost=0.1798 ms[1 Cptr ] times=10000, total_cost=2425 ms, avg_cost=0.2425 ms[1 Cptr2 ] times=10000, total_cost=3391 ms, avg_cost=0.3391 ms[2 atRandom] times=10000, total_cost=20024 ms, avg_cost=2.0024 ms[3 Iterator] times=10000, total_cost=39980 ms, avg_cost=3.998 ms[4 LUT ] times=10000, total_cost=103 ms, avg_cost=0.0103 ms
foreach
[5 forEach ] times=200000, total_cost=199 ms, avg_cost=0.000995 ms[5 forEach lambda] times=200000, total_cost=521 ms, avg_cost=0.002605 ms[5 forEach ] times=20000, total_cost=17 ms, avg_cost=0.00085 ms[5 forEach lambda] times=20000, total_cost=23 ms, avg_cost=0.00115 ms
results
Loop Type | Time Cost (us)
:----: |
ptr [] | 242
ptr ++ | 339
at | 2002
iterator | 3998
LUT | 10
forEach | 0.85
forEach lambda | 1.15
forEach is 10x times faster than LUT, 240~340x times faster than ptr [] and ptr ++, and 2000~4000x times faster than at and iterator.
code
Python
pure python
# import the necessary packagesimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport cv2print(cv2.__version__)%matplotlib inline
3.4.2
# load the original image, convert it to grayscale, and display# it inlineimage = cv2.imread("cat.jpg")image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)print(image.shape)#plt.imshow(image, cmap="gray")
(360, 480)
%load_ext cython
The cython extension is already loaded. To reload it, use:%reload_ext cython
%%cython -adef threshold_python(T, image):# grab the image dimensionsh = image.shape[0]w = image.shape[1]# loop over the image, pixel by pixelfor y in range(0, h):for x in range(0, w):# threshold the pixelimage[y, x] = 255 if image[y, x] >= T else 0# return the thresholded imagereturn image
%timeit threshold_python(5, image)
263 ms ± 20.2 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1 loop each)
cython
%%cython -aimport cython@cython.boundscheck(False)cpdef unsigned char[:, :] threshold_cython(int T, unsigned char [:, :] image):# set the variable extension typescdef int x, y, w, h# grab the image dimensionsh = image.shape[0]w = image.shape[1]# loop over the imagefor y in range(0, h):for x in range(0, w):# threshold the pixelimage[y, x] = 255 if image[y, x] >= T else 0# return the thresholded imagereturn image
numba
%timeit threshold_cython(5, image)
150 µs ± 7.14 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
from numba import njit@njitdef threshold_njit(T, image):# grab the image dimensionsh = image.shape[0]w = image.shape[1]# loop over the image, pixel by pixelfor y in range(0, h):for x in range(0, w):# threshold the pixelimage[y, x] = 255 if image[y, x] >= T else 0# return the thresholded imagereturn image
%timeit threshold_njit(5, image)
43.5 µs ± 142 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
numpy
def threshold_numpy(T, image):image[image > T] = 255return image
%timeit threshold_numpy(5, image)
111 µs ± 334 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
conclusions
image = cv2.imread("cat.jpg")image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)print(image.shape)%timeit threshold_python(5, image)%timeit threshold_cython(5, image)%timeit threshold_njit(5, image)%timeit threshold_numpy(5, image)
(360, 480)251 ms ± 6.5 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1 loop each)143 µs ± 1.19 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)43.8 µs ± 284 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)113 µs ± 957 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
image = cv2.imread("big.jpg")image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)print(image.shape)%timeit threshold_python(5, image)%timeit threshold_cython(5, image)%timeit threshold_njit(5, image)%timeit threshold_numpy(5, image)
(2880, 5120)21.8 s ± 460 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1 loop each)12.3 ms ± 231 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)3.91 ms ± 66.1 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)10.3 ms ± 179 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)
60,480
- python: 251 ms
- cython: 143 us
- numba: 43 us
- numpy: 113 us
2880, 5120
- python: 21 s
- cython: 12 ms
- numba: 4 ms
- numpy: 10 ms
Reference
- Part1: OpenCV访问Mat图像中每个像素的值 4种对比
- Part2: OpenCV访问Mat图像中每个像素的值 13种对比
- parallel-pixel-access-in-opencv-using-foreach
- fast-optimized-for-pixel-loops-with-opencv-and-python
- python performance tips
History
- 20180823: created.
Copyright
- Post author: kezunlin
- Post link: https://kezunlin.me/post/61d55ab4/
- Copyright Notice: All articles in this blog are licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 unless stating additionally.
快速遍历OpenCV Mat图像数据的多种方法和性能分析 | opencv mat for loop的更多相关文章
- 用 Python 排序数据的多种方法
用 Python 排序数据的多种方法 目录 [Python HOWTOs系列]排序 Python 列表有内置就地排序的方法 list.sort(),此外还有一个内置的 sorted() 函数将一个可迭 ...
- Python的list循环遍历中,删除数据的正确方法
在遍历list,删除符合条件的数据时,总是报异常,代码如下: num_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] print(num_list) for i in range(len(num_lis ...
- Delphi导出数据的多种方法
//Dxdbgrid,则直接用SaveToexcel即可//使用 ExcelWithOdbc 控件function TDataModule1.GetDataToFile(DsData: TObject ...
- php遍历目录与文件夹的多种方法详解
遍历目录或遍历目录下指定类型的文件,这是每一个童鞋在写程序的时候难免会用到的.PHP本身也提供了很多灰常有用的函数,正确地使用它们,不会有错滴.下面就我个人学习过程中的一些总结,希望对想学PHP的童鞋 ...
- 遍历Map和List的几种方法和性能比较
public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, Stri ...
- android+opencv+opencl: cv::dft()的opencl版本的性能分析
在小米mix 2s + 高通骁龙 845 + Adreno 630 上测试了opencl版本的cv::dft(). 测试数据 先看表格里面的描述: 名称 函数名 最大时间(ms) 平均时间(ms) 说 ...
- OpenCV图像数据字节对齐
目录 1. IplImage的data字段,是char*类型,是4字节对齐. 2. 手动创建的Mat通常是没有字节对齐的 3. 从IplImage转过来的Mat,是字节对齐的 4. 总结 图像数据是否 ...
- opencv-4-成像系统与Mat图像颜色空间
opencv-4-成像系统与Mat图像颜色空间 opencvc++qtmat 目标 知道 opencv 处理图像数据的格式 介绍 mat 基础内容 知道 BGR 颜色 显示 颜色转换 BGR 到 灰度 ...
- Python使用plotly绘制数据图表的方法
转载:http://www.jb51.net/article/118936.htm 本篇文章主要介绍了Python使用plotly绘制数据图表的方法,实例分析了plotly绘制的技巧. 导语:使用 p ...
随机推荐
- springMVC初学简单例子
新建web项目,保留web.xml. 配置web.xml文件(/WEB-INF/下): <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8&qu ...
- odoo联调
odoo联调(剑飞花 373500710) 1.准备工作 1.1.参考文章“odoo8.0+PyCharm4.5开发环境配置”配置好odoo开发环境 1.2.下载Chrome浏览器,安装. 1.3.下 ...
- 玩转u8g2 OLED库,一篇就够
授人以鱼不如授人以渔,目的不是为了教会你具体项目开发,而是学会学习的能力.希望大家分享给你周边需要的朋友或者同学,说不定大神成长之路有博哥的奠基石... QQ技术互动交流群:ESP8266&3 ...
- 解决Zend OPcache huge_code_pages: mmap(HUGETLB) failed: Cannot allocate memory报错
前几日看到鸟哥介绍的 <让你的PHP7更快之Hugepage>, 于是想试试手给服务器加上,参照格式安装好扩展,调整好配置文件,然后重启php-fpm,结果启动一直报Zend OPcach ...
- vue-class-component使用Mixins
vue-class-component提供了mixinshelper函数,以类样式的方式使用mixins.通过使用mixins帮助程序,TypeScript可以推断mixin类型并在组件类型上继承它们 ...
- day05整理
目录 一.上节课回顾 (一)数据类型 (1)数字类型 (2)字符串类型str (3)列表类型list (4)字典类型dict (二)jieba模块 (三)wordcloud模块 二.文本处理 (一)什 ...
- 用最复杂的方式学会数组(Python实现动态数组)
Python序列类型 在本博客中,我们将学习探讨Python的各种"序列"类,内置的三大常用数据结构--列表类(list).元组类(tuple)和字符串类(str). 不知道你发现 ...
- MyBatis与Spring的整合实例详解
从之前的代码中可以看出直接使用 MyBatis 框架的 SqlSession 访问数据库并不简便.MyBatis 框架的重点是 SQL 映射文件,为方便后续学习,本节讲解 MyBatis 与 Spri ...
- Shiro笔记---身份验证
1.shiro有哪些主要功能 2.搭建shiro环境(*) idea2018.2.maven3.5.4.jdk1.8 项目结构: pom.xml: <dependencies> < ...
- ABP WebApi的请求类型
Api对应的请求类型分为以下四种方法: 1.POST 2.PUT 3.DELETE 4.GET 一般abp的请求类型都是根据接口命名来定义的,Create——POST,Delete——DELETE,U ...
