laravel框架的中间件middleware的详解
本篇文章给大家带来的内容是关于laravel框架的中间件middleware的详解,有一定的参考价值,有需要的朋友可以参考一下,希望对你有所帮助。
laravel中间件是个非常方便的东西,能将一些逻辑实现解耦,并且在laravel中,
中间件的编写也是非常的方便。谁用谁知道。
1.装饰器模式
laravel中的中间件使用的就是装饰器模式,什么是[装饰器模式][1],先去了解一下吧,这里大概说一下,就是这个模式主要的就是用于解决 当一个类需要动态扩展功能的时候,使用继承的方式会让子类膨胀,并且这个扩展的功能是个公用功能的情况下,不利于功能的复用以及代码的解耦。
在laravel,使用对于使用这种模式的功能,称为请求处理管道,也就是pipeline
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 |
|
输出:

这个就是一个简单的基于装饰器模式的管道。他的本质其实就是基于闭包和递归。
通过分析这个程序,对于最终生成的$a变量,它的值大概是这样的 MiddleStepOne.handle(MiddleStepTwo.handle(first)),当执行的时候因为在handle中有个next()函数的存在,所以这是一个递归的调用。对于laravel的中间件,他的实现原理也是和这个一样的。

链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1v5gm7n0L7TGyejCmQrMh2g 提取码:x2p5
免费分享,但是X度限制严重,如若链接失效点击链接或搜索加群 群号518475424。
2.laravel中的中间件和请求处理管道
在laravel中,我们我们可以通过设置中间件来在请求执行之前做一些预先的处理。
从请求入口 public/index.php开始
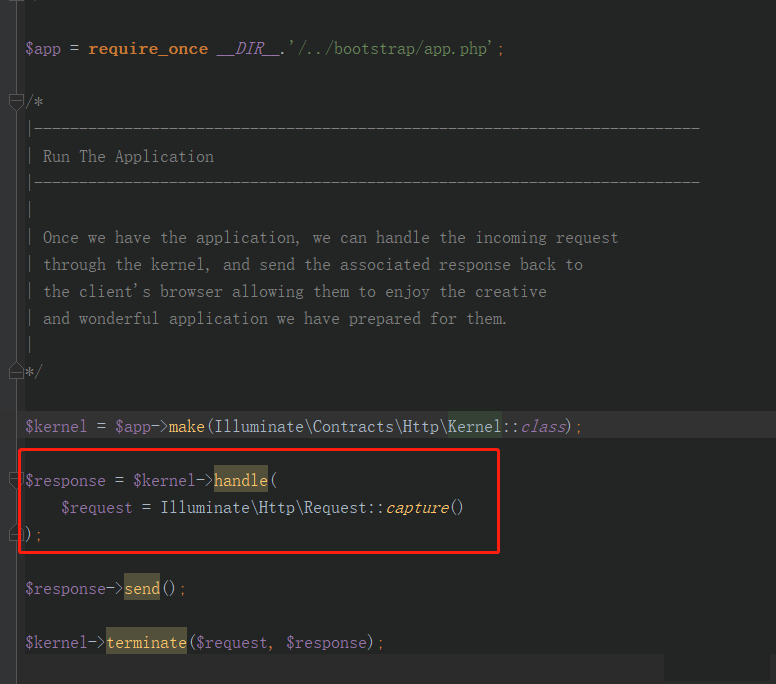
重要的是这段代码:即 处理请求,返回请求的响应
|
1 2 3 |
|
接着我们进入kernel中看他的具体实现 IlluminateFoundationHttpKernel.php中
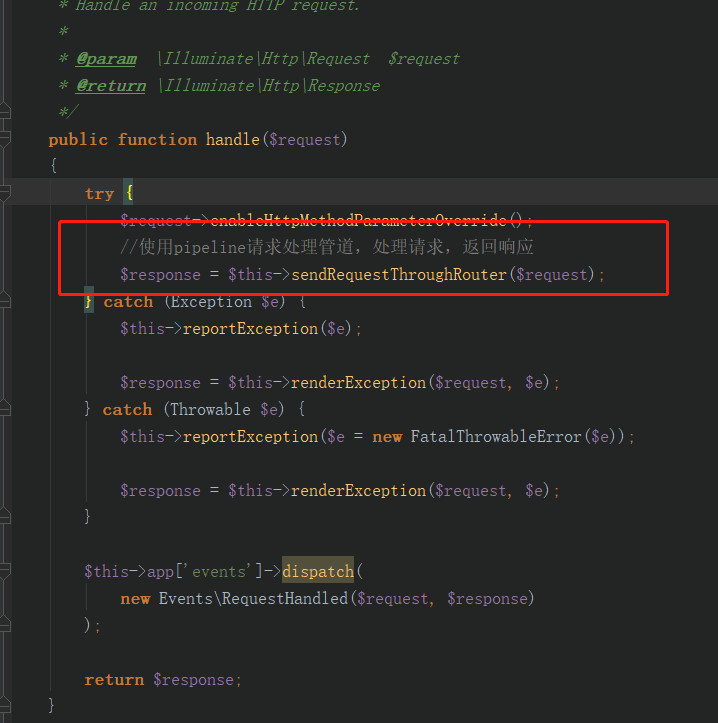
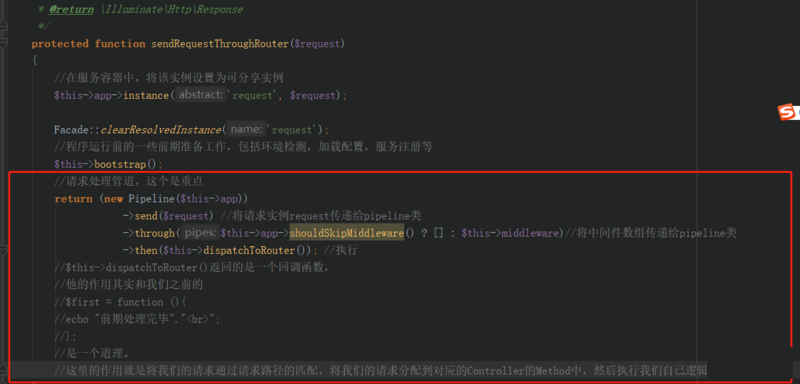
关于dispatchToRouter()函数请大家自己去看,这里就不多说了。
接下来就是激动人心的PipeLine类了,
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 |
|
总的来说pipeLine类的实现和我之前写的修饰器是差不多,这里主要麻烦的地方就在于就在于
protected function carry()函数内部,对于当pip是闭包,字符串,还有对象的处理。
之前觉得laravel的中间件是个很神秘的东西,但是看了之后才觉得也就那样,很精巧,在实际开发中这种模式也是很有帮助的,例如我们目前用的一个gateway项目,因为没有使用任何框架,所以将判断条件剥离,写入到中间件中, 这样实现了一定程度上的模块化编程。
laravel框架的中间件middleware的详解的更多相关文章
- Laravel框架中的make方法详解
为什么网上已经有这么多的介绍Laravel的执行流程了,Laravel的容器详解了,Laravel的特性了,Laravel的启动过程了之类的文章,我还要来再分享呢? 因为,每个人的思维方式和方向是不一 ...
- [转帖]ASP.NET Core 中间件(Middleware)详解
ASP.NET Core 中间件(Middleware)详解 本文为官方文档译文,官方文档现已非机器翻译 https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/aspnet/core/ ...
- Django框架 之 ORM查询操作详解
Django框架 之 ORM查询操作详解 浏览目录 一般操作 ForeignKey操作 ManyToManyField 聚合查询 分组查询 F查询和Q查询 事务 Django终端打印SQL语句 在Py ...
- ORM框架对比以及Mybatis配置文件详解
ORM框架对比以及Mybatis配置文件详解 0.数据库操作框架的历程 (1) JDBC JDBC(Java Data Base Connection,java数据库连接)是一种用于执行SQL语句 ...
- 第十九节:Scrapy爬虫框架之Middleware文件详解
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # 在这里定义蜘蛛中间件的模型# Define here the models for your spider middleware## See doc ...
- Django 框架篇(四) : 视图(view)详解 以及 路由系统(url)
|--Django的View(视图) |-- CBV和FBV: |-- 给视图增加装饰器: |-- request对象: |-- response对象: |-- Django的路由系统(url): | ...
- Hadoop框架:NameNode工作机制详解
本文源码:GitHub·点这里 || GitEE·点这里 一.存储机制 1.基础描述 NameNode运行时元数据需要存放在内存中,同时在磁盘中备份元数据的fsImage,当元数据有更新或者添加元数据 ...
- Hadoop框架:DataNode工作机制详解
本文源码:GitHub·点这里 || GitEE·点这里 一.工作机制 1.基础描述 DataNode上数据块以文件形式存储在磁盘上,包括两个文件,一个是数据本身,一个是数据块元数据包括长度.校验.时 ...
- Django框架之中间件MiddleWare
Django中的中间件是一个轻量级.底层的插件系统,可以介入Django的请求和响应处理过程,修改Django的输入或输出.中间件的设计为开发者提供了一种无侵入式的开发方式,增强了Django框架的健 ...
随机推荐
- .NET Core 使用NPOI读取Excel返回泛型List集合
我是一名 ASP.NET 程序员,专注于 B/S 项目开发.累计文章阅读量超过一千万,我的博客主页地址:https://www.itsvse.com/blog_xzz.html 网上有很多关于npoi ...
- .net webapi跨域问题
2019年11月8日,近期做项目开始实行前后端分离的方式开发,前端使用vue的框架,打包发布后,调用后端接口出现跨域的问题,网上搜索出来的都是以下的配置方式: 但是,在我的项目中,按这种方式配置没有效 ...
- Java学习——泛型
Java学习——泛型 摘要:本文主要介绍了什么是泛型,为什么要用泛型,以及如何使用泛型. 部分内容来自以下博客: https://www.cnblogs.com/lwbqqyumidi/p/38376 ...
- 6 、 图论—NP 搜索
6.1 最大团 //最大团 //返回最大团大小和一个方案,传入图的大小 n 和邻接阵 mat //mat[i][j]为布尔量 #define MAXN 60 void clique(int n, in ...
- Angular i18n(国际化方案)
一.引言 i18n(其来源是英文单词 internationalization的首末字符i和n,18为中间的字符数)是“国际化”的简称.在资讯领域,国际化(i18n)指让产品(出版物,软件,硬件等)无 ...
- E203译码模块(3)
下面的代码译码出指令的立即数,不同的指令有不同的立即数编码形式. //I类型指令的imm,[31:20],符号位扩展成32位. wire [31:0] rv32_i_imm = { {20{rv32_ ...
- 绕过基于签名的XSS筛选器:修改HTML
绕过基于签名的XSS筛选器:修改HTML 在很多情况下,您可能会发现基于签名的过滤器只需切换到一个不太熟悉的执行脚本的方法即可.如果失败了,您需要查看混淆攻击的方法. 本文提供了HTML语法可以被混淆 ...
- EM算法-完整推导
前篇已经对EM过程,举了扔硬币和高斯分布等案例来直观认识了, 目标是参数估计, 分为 E-step 和 M-step, 不断循环, 直到收敛则求出了近似的估计参数, 不多说了, 本篇不说栗子, 直接来 ...
- linux 本地套接字通信
本地套接字通信 利用本地套接字,也可以进程间通信. 本地套接字和有名管道一样都利用伪文件 管道的文件类型是p 本地套接字的文件类型是s. 当调用bind函数后,就会生成本地套接字对应的伪装文件 srw ...
- Linux---进程控制类命令
1.查看系统中的进程命令 (1)ps (2)top 2.控制系统中的进程命令 (1)kill (2)killall (3)nice (4)renice 3.进程后台运行命令 (1)& 4.进程 ...
