ViewStub 的使用
一、内容概述
举例说明ViewStub标签的使用
二、ViewStub类的文档说明及应用场举例
文档描述:
A ViewStub is an invisible, zero-sized View that can be used to lazily inflate layout resources at runtime. When a ViewStub is made visible, or when inflate() is invoked, the layout resource is inflated. The ViewStub then replaces itself in its parent with the inflated View or Views. Therefore, the ViewStub exists in the view hierarchy until setVisibility(int) or inflate() is invoked. The inflated View is added to the ViewStub's parent with the ViewStub's layout parameters. Similarly, you can define/override the inflate View's id by using the ViewStub's inflatedId property. For instance:
<ViewStub android:id="@+id/stub"
android:inflatedId="@+id/subTree"
android:layout="@layout/mySubTree"
android:layout_width="120dip"
android:layout_height="40dip" />
The ViewStub thus defined can be found using the id "stub." After inflation of the layout resource "mySubTree," the ViewStub is removed from its parent. The View created by inflating the layout resource "mySubTree" can be found using the id "subTree," specified by the inflatedId property. The inflated View is finally assigned a width of 120dip and a height of 40dip. The preferred way to perform the inflation of the layout resource is the following:
ViewStub stub = (ViewStub) findViewById(R.id.stub);
View inflated = stub.inflate();
When inflate() is invoked, the ViewStub is replaced by the inflated View and the inflated View is returned. This lets applications get a reference to the inflated View without executing an extra findViewById().
上面的问题大致意思是:
ViewStub 是一种不可见且不占屏幕大小的View,它可以用于运行时延迟加载一个布局文件,当它的visibility被设置为View.visiable或者它的inflate方法被调用时
它所引用的布局文件就会被加载,接着ViewStub会用它加载的那个布局文件的View来替代自己。
在上面的例子中,我们可以用id为stub来findViewById,而当我们调用ViewStub.inflate()或者ViewStub.setVisiable(View.VISIABLE)时,那么它的将变成一个由mySubTree布局文件指定的View,而我们可以使用id为subTree去索引这个View。
应用举例:
如下是应用的布局框架,中间的那个FrameLayout正式我们当前Activity的布局,而上面就有一个ViewStub,具体它是系统用来干嘛呢,可以进一步查找。
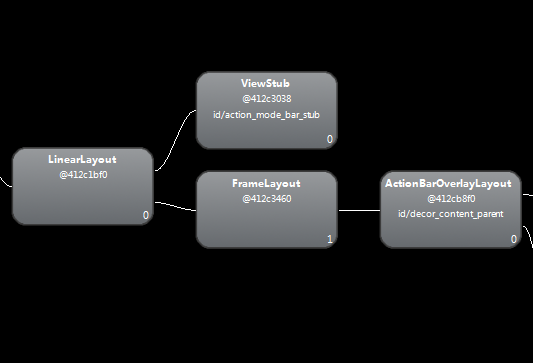
三、我的demo
1. 定义一个用ViewStub延迟加载的布局文件,这里简单定义如下(headbar.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" > <Button
android:id="@+id/back"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:text="back" >
</Button> <Button
android:id="@+id/go"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:text="go" >
</Button> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/go"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/back"
android:text="as you see" >
</TextView> </RelativeLayout>
2.mainActivity的布局文件(activity_main.xml)
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.example.stubview.MainActivity" > <ViewStub
android:id="@+id/hiddenHead"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inflatedId="@+id/headbar"
android:layout="@layout/headbar" >
</ViewStub> <Button
android:id="@+id/show"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:text="加载View" /> </RelativeLayout>
3.mainActivity中的使用ViewStub 代码
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
findViewById(R.id.show).setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
ViewStub stubView = (ViewStub) findViewById(R.id.hiddenHead);
View view = stubView.inflate();
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),
"hiddenHead View 的id为" + view.getId(),
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
});
}
附代码参考https://github.com/LuLei2013/StubView.git
ViewStub 的使用的更多相关文章
- ViewStub的使用
ViewStub是一个不可见的.大小为0的控件,运行时ViewStub可以滞后加载.当ViewStub置为可见或者调用inflate()的时候,布局就会加载出来.用加载进来的布局取代ViewStub在 ...
- ViewStub源码分析
ViewStub是一种特殊的View,Android官方给出的解释是:一种不可见的(GONE).size是0的占位view,多用于运行时 延迟加载的,也就是说真正需要某个view的时候.在实际项目中, ...
- include、merge 、ViewStub
在布局优化中,Androi的官方提到了这三种布局<include />.<merge />.<ViewStub />,并介绍了这三种布局各有的优势,下面也是简单说一 ...
- Android实战技巧:ViewStub的应用
在开发应用程序的时候,经常会遇到这样的情况,会在运行时动态根据条件来决定显示哪个View或某个布局.那么最通常的想法就是把可能用到的View都写在上面,先把它们的可见性都设为View.GONE,然后在 ...
- ViewStub的简单用法和说明
最近无意间知道了ViewStub,所以特地的去了解了一下 都知道ViewStub是一个不可见的,大小为0的View,实际上跟include差不多,但是ViewStub要更加节约资源.被称为是" ...
- Android引导指示层的制作 (ViewStub + SharePreference)
引导指示界面是个什么鬼东西?一张图即明了:
- 【转】Android布局优化之ViewStub
ViewStub是Android布局优化中一个很不错的标签/控件,直接继承自View.虽然Android开发人员基本上都听说过,但是真正用的可能不多. ViewStub可以理解成一个非常轻量级的Vie ...
- Android性能优化之一:ViewStub
ViewStub是Android布局优化中一个很不错的标签/控件,直接继承自View.虽然Android开发人员基本上都听说过,但是真正用的可能不多. ViewStub可以理解成一个非常轻量级的Vie ...
- Android优化——UI优化(三)使用ViewStub延迟加载
使用ViewStub延迟加载 1.ViewStub延迟加载 ViewStub是一个不可见的,大小为0的View,最佳用途就是实现View的延迟加载,在需要的时候再加载View,可Java中常见的性能优 ...
- ViewStub的简单解析和使用场景
ViewStub是Android布局优化中一个很不错的标签/控件,直接继承自View.虽然Android开发人员基本上都听说过,但是真正用的可能不多. ViewStub可以理解成一个非常轻量级的Vie ...
随机推荐
- Hive知识
HIVEQL CREATE DATABASE financials(创建数据库) SHOW DATABASES(显示数据库) SHOW TABLES IN 数据库(列出数据库的所有表) SHOW DA ...
- SDL安装小结
SDL是一个基于C的简易实现,安装过程中也多亏了,各位大神的助攻,这里简单mark一下遇到的问题,以备查找: 关于VS的版本:目前文档里确定支持的VS为2008到2013,我的VS是2013,2015 ...
- 洛谷——P1586 四方定理
P1586 四方定理 题目描述 四方定理是众所周知的:任意一个正整数nn,可以分解为不超过四个整数的平方和.例如:25=1^{2}+2^{2}+2^{2}+4^{2}25=12+22+22+42,当然 ...
- 洛谷——P1226 取余运算||快速幂
P1226 取余运算||快速幂 题目描述 输入b,p,k的值,求b^p mod k的值.其中b,p,k*k为长整型数. 输入输出格式 输入格式: 三个整数b,p,k. 输出格式: 输出“b^p mod ...
- QTWebKit之QWebView学习
QWebView是一个simple web 浏览器 一般打开页面的方法为: app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv) web = QWebView() web.load(Q ...
- Oracle 后台进程
一.基本后台进程 1.数据库写入进程(DBWn): 数据库写入程序讲数据库告诉缓存区中的修改块写入数据文件.对于多数系统来说,一个数据库写入程序(DBW0)就已经足够,但是对于 ...
- [CF98E]Help Shrek and Donkey
题意:A和B两个卡牌大师玩游戏,A有$n$张牌,B有$m$张牌,桌上有$1$张牌,这$n+m+1$张牌互不相同且A和B都知道这些牌里有什么牌(但他们互相不知道对方有什么牌,两个人也都不知道桌上的那张牌 ...
- 【mybatis】mybatis方法访问报错:org.apache.ibatis.builder.IncompleteElementException: Could not find result map com.pisen.cloud.luna.ms.goods.base.domain.GoodsConfigQuery
在调用mapper.xml中的方法的时候,报错: org.apache.ibatis.builder.IncompleteElementException: Could not find result ...
- python中list/tuple/dict/set的区别
序列是Python中最基本的数据结构.序列中的每个元素都分配一个数字 - 它的位置,或索引,第一个索引是0,第二个索引是1,依此类推.Python有6个序列的内置类型,但最常见的是列表list和元组t ...
- 【转载】【Todo】Nodejs的优缺点
Nodejs的优缺点,这里面讲的比较详细.有时间可以多看看别人的分析. https://www.zhihu.com/question/19653241 Node.js 的架构与 Django, Rai ...
