POJ 3321 Apple Tree 【树状数组+建树】
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=3321
Apple Tree
Time Limit: 2000MS |
Memory Limit: 65536K |
|
Total Submissions: 34812 |
Accepted: 10469 |
Description
There is an apple tree outside of kaka's house. Every autumn, a lot of apples will grow in the tree. Kaka likes apple very much, so he has been carefully nurturing the big apple tree.
The tree has N forks which are connected by branches. Kaka numbers the forks by 1 to N and the root is always numbered by 1. Apples will grow on the forks and two apple won't grow on the same fork. kaka wants to know how many apples are there in a sub-tree, for his study of the produce ability of the apple tree.
The trouble is that a new apple may grow on an empty fork some time and kaka may pick an apple from the tree for his dessert. Can you help kaka?

Input
The first line contains an integer N (N ≤ 100,000) , which is the number of the forks in the tree.
The following N - 1 lines each contain two integers u and v, which means fork u and fork v are connected by a branch.
The next line contains an integer M (M ≤ 100,000).
The following M lines each contain a message which is either
"C x" which means the existence of the apple on fork x has been changed. i.e. if there is an apple on the fork, then Kaka pick it; otherwise a new apple has grown on the empty fork.
or
"Q x" which means an inquiry for the number of apples in the sub-tree above the fork x, including the apple (if exists) on the fork x
Note the tree is full of apples at the beginning
Output
Sample Input
3
1 2
1 3
3
Q 1
C 2
Q 1
Sample Output
3
2
Source
题意概括:
给一个 N 阶无向图,要求把这个无向图转换为一颗以 1 为根的树后进行两种操作:
C x :x结点上如果有苹果就摘掉,如果没有苹果就长出一个新的来
Q x: 查询 x 结点与它的所有后代分支一共有几个苹果
解题思路:
因为原本苹果之间的关系我们不好处理,所以就给他们这些结点重新编号。
并且为了方便子树的苹果数求和(即区间查询)我们在给结点增加一个左值一个右值表示当前结点管辖的范围。
如何建树?
根据题目一开始给的边与边的关系我们可以通过 dfs 进行建树。
L[ x ] (X的左值): X结点的新编号就是该结点的左值,表示它管辖范围的下限
R[ x ] (X的右值):而子树的编号最大值为该结点的右值,表示它管辖范围的上限。
至于dfs顺序,如下
举个栗子:
N = 6;
1 - 2
1 - 6
2 - 5
2 - 3
6 - 4
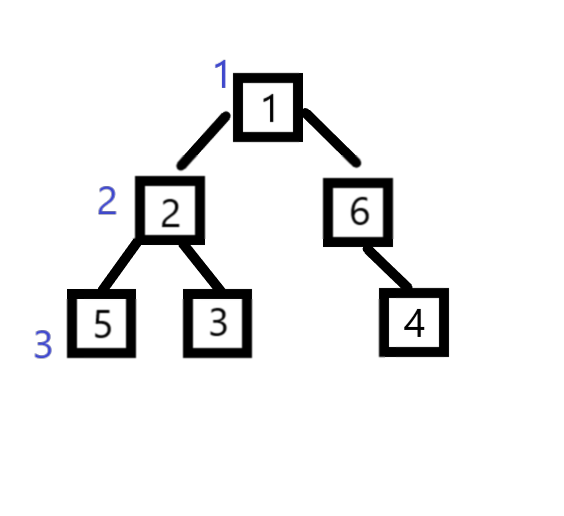
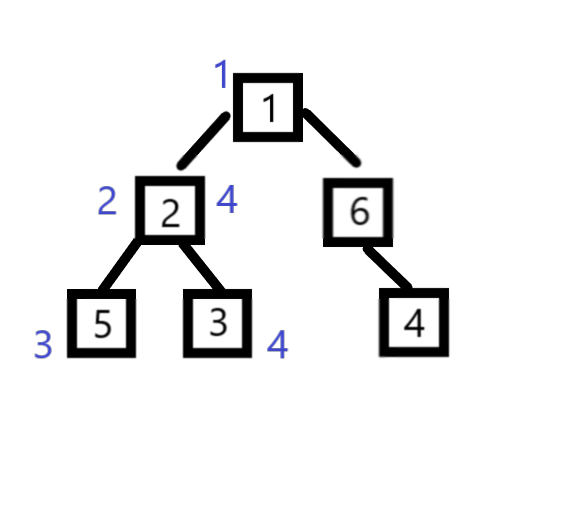

到这里感觉有一点点线段树的味道了。。。
但这里要用树状数组对这些区间进行维护和查询。
例如:我要 Q 2;
由上面建好的新树我们可以知道 结点2这颗子树包含了结点2、结点5、结点3,而结点2所管辖的区间【2,4】刚好把它们包括进去了。
如果我们要求 这可子树的苹果数量,其实就是用树状数组求区间【2,4】的苹果总数
也就是右值的前缀和减去左值的前缀和(但不包括左值,因为结点本身也要算进去)即:ans = sum( R[ 2 ] ) - sum( L[ 2 ] - 1);
而C操作其实就是树状数组的单点更新而已。
注意事项:
一开始用 stl 的 vector 存无向图,虽然过了但效率不咋地。想想好久没用静态邻接表了,换了一下,快了好多。
AC code:
///建树+树状数组(stl)8080k 1047ms
/*
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
typedef vector<int>ve; const int MAXN = 1e5+10;
int t[MAXN], l[MAXN], r[MAXN];
bool vis[MAXN];
int N, M, cnt; vector<ve>node(MAXN); int lowbit(int x)
{
return x&(-x);
}
void add(int x, int value)
{
for(int i = x; i <= N; i+=lowbit(i))
t[i]+=value;
}
int sum(int x)
{
int res = 0;
for(int i = x; i > 0; i-=lowbit(i))
res+=t[i];
return res;
}
void dfs(int k)
{
l[k] = cnt;
for(int i = 0; i < node[k].size(); i++)
{
cnt++;
dfs(node[k][i]);
}
r[k] = cnt;
return;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &N);
int a, b;
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
vis[i] = 1;
add(i, 1);
}
for(int i = 1; i < N; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
node[a].push_back(b);
}
cnt = 1;
dfs(1);
scanf("%d", &M);
while(M--)
{
char com[3];
int px;
scanf("%s", &com);
if(com[0] == 'C')
{
scanf("%d", &px);
if(vis[px]) add(l[px], -1);
else add(l[px], 1);
vis[px] = !vis[px];
}
else
{
scanf("%d", &px);
int ans = sum(r[px]) - sum(l[px]-1);
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
}
return 0;
}
*/ ///建树+树状数组(静态连接表) 4940k 454ms
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std; const int MAXN = 1e5+;
const int MAXM = 1e5+; struct node
{
int to, next;
}edge[MAXM<<]; int head[MAXN];
bool vis[MAXN];
int t[MAXN], l[MAXN], r[MAXN];
int N, M, cnt, key; int lowbit(int x)
{
return x&(-x);
}
void add(int x, int value)
{
for(int i = x; i <= N; i+=lowbit(i))
t[i]+=value;
}
int sum(int x)
{
int res = ;
for(int i = x; i > ; i-=lowbit(i))
res+=t[i];
return res;
} void dfs(int k)
{
l[k] = key;
for(int i = head[k]; i != -; i = edge[i].next)
{
if(l[edge[i].to]) continue;
key++;
dfs(edge[i].to);
}
r[k] = key;
} void init()
{
memset(head, -, sizeof(head));
cnt = ;
} void add_e(int u, int v)
{
edge[cnt].to = v;
edge[cnt].next = head[u];
head[u] = cnt++;
} int main()
{
scanf("%d", &N);
init();
int a, b;
for(int i = ; i <= N; i++)
{
vis[i] = ; //每个节点一开始都有苹果
add(i, ); //初始化树状数组
}
for(int i = ; i < N; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b); ///建无向图
add_e(a, b);
add_e(b, a);
}
key = ; dfs(); //建树
scanf("%d", &M);
int px;
char com[];
while(M--)
{
scanf("%s", &com);
if(com[] == 'C')
{
scanf("%d", &px);
if(vis[px]) add(l[px], -);
else add(l[px], );
vis[px] = !vis[px];
}
else
{
scanf("%d", &px);
printf("%d\n", sum(r[px])-sum(l[px]-));
}
}
return ;
}
POJ 3321 Apple Tree 【树状数组+建树】的更多相关文章
- POJ 3321 Apple Tree(树状数组)
Apple Tree Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Lim ...
- POJ 3321 Apple Tree (树状数组+dfs序)
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=3321 给你n个点,n-1条边,1为根节点.给你m条操作,C操作是将x点变反(1变0,0变1),Q操作是询问x节点以及它子树的值之和.初 ...
- POJ 3321 Apple Tree 树状数组+DFS
题意:一棵苹果树有n个结点,编号从1到n,根结点永远是1.该树有n-1条树枝,每条树枝连接两个结点.已知苹果只会结在树的结点处,而且每个结点最多只能结1个苹果.初始时每个结点处都有1个苹果.树的主人接 ...
- POJ 3321 Apple Tree 树状数组 第一题
第一次做树状数组,这个东西还是蛮神奇的,通过一个简单的C数组就可以表示出整个序列的值,并且可以用logN的复杂度进行改值与求和. 这道题目我根本不知道怎么和树状数组扯上的关系,刚开始我想直接按图来遍历 ...
- 3321 Apple Tree 树状数组
LIANJIE:http://poj.org/problem?id=3321 给你一个多叉树,每个叉和叶子节点有一颗苹果.然后给你两个操作,一个是给你C清除某节点上的苹果或者添加(此节点上有苹果则清除 ...
- POJ 3321:Apple Tree 树状数组
Apple Tree Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 22131 Accepted: 6715 Descr ...
- POJ--3321 Apple Tree(树状数组+dfs(序列))
Apple Tree Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 22613 Accepted: 6875 Descripti ...
- E - Apple Tree(树状数组+DFS序)
There is an apple tree outside of kaka's house. Every autumn, a lot of apples will grow in the tree. ...
- POJ3321 Apple Tree(树状数组)
先做一次dfs求得每个节点为根的子树在树状数组中编号的起始值和结束值,再树状数组做区间查询 与单点更新. #include<cstdio> #include<iostream> ...
- POJ 2486 Apple Tree [树状DP]
题目:一棵树,每个结点上都有一些苹果,且相邻两个结点间的距离为1.一个人从根节点(编号为1)开始走,一共可以走k步,问最多可以吃多少苹果. 思路:这里给出数组的定义: dp[0][x][j] 为从结点 ...
随机推荐
- setContentView和inflate区别
一般用LayoutInflater做一件事:inflate inflate这个方法总共有四种形式(见下面),目的都是把xml表述的layout转化为View对象.其中有一个比较常用,View infl ...
- [转]sudo: sorry, you must have a tty to run sudo问题
使用不同账户,执行执行脚本时候sudo经常会碰到 sudo: sorry, you must have a tty to run sudo这个情况,其实修改一下sudo的配置就好了vi /etc/su ...
- ksframework的xlua版本
https://github.com/zhaoqingqing/KSFramework_xlua
- Bitmap图片查看器
在Android 应用中使用assets目录下存放的资源文件,assets目录下存放的资源代表应用无法直接访问的原生资源,应用程序通过AssetManager以二 进制流的形式来读取资源.此应用是查看 ...
- linux服务器上创建svn版本库
1. 创建存放各个svn版本库的目录svnrepos(自己定义路径) -bash: cd /usr/local/apache/htdocs/ -bash: mkdir svnrepos 2. 假设我要 ...
- mysql 字符串转换呈毫秒值
SELECT CEIL((UNIX_TIMESTAMP('2011-05-31 23:59:59') - UNIX_TIMESTAMP('2011-05-31 00:59:59'))/1000/60/ ...
- html5格式样式
<b> 加粗 <b style="font-size: 100px;">大字体</b>
- c语言进制转化
#include <stdio.h> // 进制转化 int main(void) { ; ; int i3 = 0x32C; printf( printf( printf("十 ...
- 修改mysql编码方式
第一种: 通过mysql命令行修改: 1)首先查看数据库字符编码,命令为: show variables like’collation_%’; show variables like’char ...
- PrintDocument打印、预览、打印机设置和打印属性的方法(较完整) .
private void Form1_Load(object sender, System.EventArgs e) { //获取或设置一个值,该值指示是否发送到文件或端口 printDocument ...
