Codeforces Round #460 (Div. 2)
Now imagine you'd like to buy m kilos of apples. You've asked n supermarkets and got the prices. Find the minimum cost for those apples.
You can assume that there are enough apples in all supermarkets.
The first line contains two positive integers n and m (1 ≤ n ≤ 5 000, 1 ≤ m ≤ 100), denoting that there are n supermarkets and you want to buy m kilos of apples.
The following n lines describe the information of the supermarkets. Each line contains two positive integers a, b (1 ≤ a, b ≤ 100), denoting that in this supermarket, you are supposed to pay a yuan for b kilos of apples.
The only line, denoting the minimum cost for m kilos of apples. Please make sure that the absolute or relative error between your answer and the correct answer won't exceed 10 - 6.
Formally, let your answer be x, and the jury's answer be y. Your answer is considered correct if 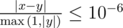 .
.
3 5
1 2
3 4
1 3
1.66666667
2 1
99 100
98 99
0.98989899
In the first sample, you are supposed to buy 5 kilos of apples in supermarket 3. The cost is 5 / 3 yuan.
In the second sample, you are supposed to buy 1 kilo of apples in supermarket 2. The cost is 98 / 99 yuan.
找最便宜的超市买东西即可。
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main()
{ int n;
double m;
scanf("%d%lf",&n,&m); double minx = 0x3f3f3f3f;
for(int i = ; i < n; i++) {
double a,b;
scanf("%lf%lf",&a,&b);
minx = min(minx,a/b);
} printf("%lf\n",m*minx); return ;
}
We consider a positive integer perfect, if and only if the sum of its digits is exactly 10. Given a positive integer k, your task is to find the k-th smallest perfect positive integer.
A single line with a positive integer k (1 ≤ k ≤ 10 000).
A single number, denoting the k-th smallest perfect integer.
1
19
2
28
The first perfect integer is 19 and the second one is 28.
暴力打表
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool calc(int x) {
int sum = ;
while(x) {
sum+=(x%);
x/=;
}
return sum==;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> ans;
for(int i = ; i < ; i++) {
if(calc(i))
ans.push_back(i);
}
//printf("%d\n",ans.size());
int k;
scanf("%d",&k);
printf("%d\n",ans[k-]);
return ;
}
Suppose that you are in a campus and have to go for classes day by day. As you may see, when you hurry to a classroom, you surprisingly find that many seats there are already occupied. Today you and your friends went for class, and found out that some of the seats were occupied.
The classroom contains n rows of seats and there are m seats in each row. Then the classroom can be represented as an n × m matrix. The character '.' represents an empty seat, while '*' means that the seat is occupied. You need to find k consecutive empty seats in the same row or column and arrange those seats for you and your friends. Your task is to find the number of ways to arrange the seats. Two ways are considered different if sets of places that students occupy differs.
The first line contains three positive integers n, m, k (1 ≤ n, m, k ≤ 2 000), where n, m represent the sizes of the classroom and k is the number of consecutive seats you need to find.
Each of the next n lines contains m characters '.' or '*'. They form a matrix representing the classroom, '.' denotes an empty seat, and '*' denotes an occupied seat.
A single number, denoting the number of ways to find k empty seats in the same row or column.
2 3 2
**.
...
3
1 2 2
..
1
3 3 4
.*.
*.*
.*.
0
In the first sample, there are three ways to arrange those seats. You can take the following seats for your arrangement.
- (1, 3), (2, 3)
- (2, 2), (2, 3)
- (2, 1), (2, 2)
k连坐
做的时候把我做傻了,一步三坑。以至于我算重复了。
1 ,行数只有一行
2 ,k = 1
搞得我换了两种写法。第二种好看一点。
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int maxn = ;
char maps[maxn][maxn]; int main()
{
//freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
int n,m,K;
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&K);
int ans = ;
for(int i = ; i < n; i++) scanf("%s",maps[i]);
if(K == ) {
for(int i = ; i < n; i++) {
for(int j = ; j < m; j++) {
if(maps[i][j]=='.')
ans++;
}
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
return ;
} for(int i = ; i < n; i++) {
for(int j = ; j < m; j++)
{
if(maps[i][j]=='.') {
int cnt = ;
int k;
for(k = j; k < m; k++) {
if(maps[i][k]=='.')
cnt++;
else break;
}
if(cnt>=K) {
ans = ans + cnt-K+;
}
j = k;
}
}
} if(n!=) {
for(int j = ; j < m; j++) {
for(int i = ; i < n; i++)
{
if(maps[i][j]=='.') {
int cnt = ;
int k;
for(k = i; k < n; k++) {
if(maps[k][j]=='.')
cnt++;
else break;
}
if(cnt>=K)
ans=ans + cnt - K +;
i = k;
}
}
}
} printf("%d\n",ans);
return ;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int maxn = ;
char maps[maxn][maxn]; int main()
{
//freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
int n,m,K;
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&K); for(int i = ; i < n; i++) scanf("%s",maps[i]); if(K == ) {
int ans = ;
for(int i = ; i < n; i++) {
for(int j = ; j < m; j++) {
if(maps[i][j]=='.')
ans++;
}
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
return ;
} int ans = ;
int cnt = ;
int i,j;
for(i = ; i < n; i++)
{
cnt = ;
for(j = ; j < m; j++)
{
if(maps[i][j]=='*'||maps[i][j+]=='\0')
{
if(maps[i][j]=='.') cnt++;
ans += cnt>=K ? cnt - K + :;
cnt = ;
continue;
}
cnt ++;
}
}
if(n!=)
{
for(i = ; i < m; i++)
{
cnt = ;
for(j = ; j < n; j++)
{
if(maps[j][i]=='*'||maps[j+][i]=='\0')
{
if(maps[j][i]=='.') cnt++;
ans += cnt>=K ? cnt - K + :;
cnt = ;
continue;
}
cnt++;
}
}
} printf("%d\n",ans);
return ;
}
You are given a graph with n nodes and m directed edges. One lowercase letter is assigned to each node. We define a path's value as the number of the most frequently occurring letter. For example, if letters on a path are "abaca", then the value of that path is 3. Your task is find a path whose value is the largest.
The first line contains two positive integers n, m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 300 000), denoting that the graph has n nodes and m directed edges.
The second line contains a string s with only lowercase English letters. The i-th character is the letter assigned to the i-th node.
Then m lines follow. Each line contains two integers x, y (1 ≤ x, y ≤ n), describing a directed edge from x to y. Note that x can be equal to y and there can be multiple edges between x and y. Also the graph can be not connected.
Output a single line with a single integer denoting the largest value. If the value can be arbitrarily large, output -1 instead.
5 4
abaca
1 2
1 3
3 4
4 5
3
6 6
xzyabc
1 2
3 1
2 3
5 4
4 3
6 4
-1
10 14
xzyzyzyzqx
1 2
2 4
3 5
4 5
2 6
6 8
6 5
2 10
3 9
10 9
4 6
1 10
2 8
3 7
4
In the first sample, the path with largest value is 1 → 3 → 4 → 5. The value is 3 because the letter 'a' appears 3 times.
题意:
给定 n 个点,m条边,每个点上都有字母,求一条路径上,最多字母的那条路径,那个字母有多少。
我开始的思路是,先拓扑判断是否有环,然后回溯法,d[u] : u 结点出发的最优解,那么 d[u] 和 d[v] 之间转移。
v 结点有多解,那么要根据 u 来选择其中一个,也就是说,对于每一个u的最优解,都得是一个vector类型的pair 数据。
这样是比较麻烦的。
看官方题解的做法:
他的状态定义就不一样了,f[i][j] :当前顶点是 i 时,字母 j 是顶点的路径上的最优值。

大神的代码就是厉害了,判环和求解写在一起。
直接深搜下去,注意边界。
然后如果有环,用特殊值标记。学习了!
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int MAXN = ;
int f[MAXN][],n,m;
vector<int> G[MAXN];
char s[MAXN]; int dfs(int u,int c) {
if(f[u][c]==-) {
puts("-1");
exit();
}
if(f[u][c]!=-)
return f[u][c];
f[u][c] = -;
int res = ;
for(int i = ; i <(int)G[u].size(); i++) {
int v = G[u][i];
res = max(res,dfs(v,c));
} res += s[u]-'a'==c;
f[u][c] = res;
return res;
} int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
scanf("%s",s+); for(int i = ; i<= m; i++) {
int u,v;
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
G[u].push_back(v);
} memset(f,-,sizeof(f));
int ans = ;
for(int i = ; i<= n; i++)
for(int j = ; j <; j++)
ans = max(ans,dfs(i,j));
printf("%d\n",ans); return ;
}
Codeforces Round #460 (Div. 2)的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #460 (Div. 2) ABCDE题解
原文链接http://www.cnblogs.com/zhouzhendong/p/8397685.html 2018-02-01 $A$ 题意概括 你要买$m$斤水果,现在有$n$个超市让你选择. ...
- Codeforces Round #460 (Div. 2) E. Congruence Equation (CRT+数论)
题目链接: http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/919/E 题意: 让你求满足 \(na^n\equiv b \pmod p\) 的 \(n\) 的个数. ...
- Codeforces Round #460 (Div. 2) 前三题
Problem A:题目传送门 题目大意:给你N家店,每家店有不同的价格卖苹果,ai元bi斤,那么这家的苹果就是ai/bi元一斤,你要买M斤,问最少花多少元. 题解:贪心,找最小的ai/bi. #in ...
- Codeforces Round #460 (Div. 2): D. Substring(DAG+DP+判环)
D. Substring time limit per test 3 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input ...
- Codeforces Round #460 (Div. 2).E 费马小定理+中国剩余定理
E. Congruence Equation time limit per test 3 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input stand ...
- Codeforces Round #460 (Div. 2)-D. Substring
D. Substring time limit per test3 seconds memory limit per test256 megabytes Problem Description You ...
- Codeforces Round #460 (Div. 2)-C. Seat Arrangements
C. Seat Arrangements time limit per test1 second memory limit per test256 megabytes Problem Descript ...
- Codeforces Round #460 (Div. 2)-B. Perfect Number
B. Perfect Number time limit per test2 seconds memory limit per test256 megabytes Problem Descriptio ...
- Codeforces Round #460 (Div. 2)-A. Supermarket
A. Supermarket time limit per test2 seconds memory limit per test256 megabytes Problem Description W ...
随机推荐
- kindeditor<=4.1.5文件上传漏洞
最近发现很多网页篡改与暗链都是利用kindeditor编辑器,于是搜了一下kindeditor的漏洞,发现低于4.1.5版本的存在文件上传的漏洞,可以上传txt,html后缀的文档,许多恶意的文档貌似 ...
- Oracle ASM 常用命令
01, 查看磁盘路径 select name,path,group_number from v$asm_disk_stat; 02, 查看磁盘组信息 select state,name,type,to ...
- C#DataTable与Model互转
/// <summary> /// 实体转换辅助类 /// </summary> public class ModelConvertHelper<T> where ...
- 阿里云服务器对外开放tomcat端口访问
今天第一次在阿里云服务器ecs上安装完成tomcat,然后启动tomcat之后.在本地输入ip:端口,发现不能访问. 出现这个的原因可能是你购买的服务器是 专有网络 类型的 如果是专有网络类型的服务器 ...
- HDU 1800——Flying to the Mars——————【字符串哈希】
Flying to the Mars Time Limit: 5000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Other ...
- [转]Asp.Net大型项目实践(11)-基于MVC Action粒度的权限管理【续】【源码在这里】(在线demo,全部源码)
本文转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/legendxian/archive/2010/01/25/1655551.html 接上篇Asp.Net大型项目实践(10)-基于MVC Ac ...
- 分支结构if……else
语法: if(条件) 语句或语句块1 end else begin 语句或者语句块2 end 特点: . else并不一定是必须的. . 如否条件为真,将执行语句和语句块1,条件为假时执行语句或语句块 ...
- Android4.4 在Framework新增内部资源编译不过的问题
如果在Frameworks新增内部资源,并在Java代码中使用类似形式来引用资源:com.android.internal.R.layout.xxx,需要在frameworks/base/core/r ...
- Bootstrap导航栏navbar源码分析
1.本文目地:分析bootstrap导航栏及其响应式的实现方式,提升自身css水平 先贴一个bootstrap的导航栏模板 http://v3.bootcss.com/examples/navbar- ...
- [原创]vs2012创建的ado.net模型无法实例化的问题
最近从vs2010升级到vs2012,建立数据模型,发现生成的东西跟以前不一样了,而且也无法实例化使用.百度尝试了n种关键词,终于被我找到解决的方法.在这里记录一下. 1.打开设计器,也就是双击这个 ...
