HDU4940 Destroy Transportation system(有上下界的最大流)
Let’s represent his enemy’s transportation system as a simple directed graph G with n nodes and m edges. Each node is a city and each directed edge is a directed road. Each edge from node u to node v is associated with two values D and B, D is the cost to destroy/remove such edge, B is the cost to build an undirected edge between u and v.
His enemy can deliver supplies from city u to city v if and only if there is a directed path from u to v. At first they can deliver supplies from any city to any other cities. So the graph is a strongly-connected graph.
He will choose a non-empty proper subset of cities, let’s denote this set as S. Let’s denote the complement set of S as T. He will command his soldiers to destroy all the edges (u, v) that u belongs to set S and v belongs to set T.
To destroy an edge, he must pay the related cost D. The total cost he will pay is X. You can use this formula to calculate X: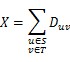
After that, all the edges from S to T are destroyed. In order to deliver huge number of supplies from S to T, his enemy will change all the remained directed edges (u, v) that u belongs to set T and v belongs to set S into undirected edges. (Surely, those edges exist because the original graph is strongly-connected)
To change an edge, they must remove the original directed edge at first, whose cost is D, then they have to build a new undirected edge, whose cost is B. The total cost they will pay is Y. You can use this formula to calculate Y: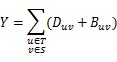
At last, if Y>=X, Tom will achieve his goal. But Tom is so lazy that he is unwilling to take a cup of time to choose a set S to make Y>=X, he hope to choose set S randomly! So he asks you if there is a set S, such that Y<X. If such set exists, he will feel unhappy, because he must choose set S carefully, otherwise he will become very happy.
The first line contains an integer T(T<=200), indicates the number of cases.
For each test case, the first line has two numbers n and m.
Next m lines describe each edge. Each line has four numbers u, v, D, B.
(2=<n<=200, 2=<m<=5000, 1=<u, v<=n, 0=<D, B<=100000)
The meaning of all characters are described above. It is guaranteed that the input graph is strongly-connected.
同上一道题,不过在我不知道这题要用最大流来做的情况下我是不会想到的:
关键是要构造出不等式,而且把不等式对应到可行流。
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=4;
const int inf=;
int Laxt[maxn],Next[maxn],To[maxn],Cap[maxn],cnt;
int dis[maxn],nd[maxn],S,T,num,ans,q[maxn],qnum[maxn],top;
void init()
{
cnt=;ans=num=top=;
memset(Laxt,,sizeof(Laxt));
memset(dis,,sizeof(dis));
memset(nd,,sizeof(nd));
}
int add(int u,int v,int c)
{
Next[++cnt]=Laxt[u];
Laxt[u]=cnt;
To[cnt]=v;
Cap[cnt]=c; Next[++cnt]=Laxt[v];
Laxt[v]=cnt;
To[cnt]=u;
Cap[cnt]=;
}
int sap(int u,int flow)
{
if(u==T||flow==) return flow;
int delta=,tmp;
for(int i=Laxt[u];i;i=Next[i]){
int v=To[i];
if(dis[v]+==dis[u]&&Cap[i]>){
tmp=sap(v,min(Cap[i],flow-delta));
delta+=tmp;
Cap[i]-=tmp;
Cap[i^]+=tmp;
if(flow==delta||dis[]>=T) return delta;
}
}
nd[dis[u]]--;
if(nd[dis[u]]==) dis[]=T;
nd[++dis[u]]++;
return delta;
}
int main()
{
int Case,n,i,j,m,u,v,x,y,k=;
scanf("%d",&Case);
while(Case--){
init();
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
S=;T=n+;
for(i=;i<=m;i++){
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&u,&v,&x,&y);
u++;v++;num+=x;
add(u,v,y);
q[++top]=cnt;
qnum[top]=x;
add(S,v,x);
add(u,T,x);
}
while(dis[S]<T) {
ans+=sap(S,inf);
}
printf("Case #%d: ",++k);
if(num!=ans) printf("unhappy\n");
else printf("happy\n");
}
return ;
}
(希望多遇到几个这样的模型,然后好好理解一下)
HDU4940 Destroy Transportation system(有上下界的最大流)的更多相关文章
- HDU Destroy Transportation system(有上下界的可行流)
前几天正看着网络流,也正研究着一个有上下界的网络流的问题,查看了很多博客,觉得下面这篇概括的还是相当精确的: http://blog.csdn.net/leolin_/article/details/ ...
- hdu4940 Destroy Transportation system(2014多校联合第七场)
题意很容易转化到这样的问题:在一个强连通的有向图D中是否存在这样的集合划分S + T = D,从S到T集合的边权大于从T到S集合的边权. 即D(i, j) > B(j, i) + D(j, i ...
- hdu 4940 Destroy Transportation system (无源汇上下界可行流)
Destroy Transportation system Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 ...
- hdu 4940 Destroy Transportation system(水过)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4940 Destroy Transportation system Time Limit: 2000/1 ...
- ZOJ 2314 带上下界的可行流
对于无源汇问题,方法有两种. 1 从边的角度来处理. 新建超级源汇, 对于每一条有下界的边,x->y, 建立有向边 超级源->y ,容量为x->y下界,建立有向边 x-> 超级 ...
- 【UVALive - 5131】Chips Challenge(上下界循环费用流)
Description A prominent microprocessor company has enlisted your help to lay out some interchangeabl ...
- SGU 176.Flow construction (有上下界的最大流)
时间限制:0.5s 空间限制:4M 题意: 有一个由管道组成的网络,有n个节点(n不大于100),1号节点可以制造原料,最后汇集到n号节点.原料通过管道运输.其中有一些节点有管道连接,这些管道都有着最 ...
- zoj3229 Shoot the Bullet(有源汇有上下界的最大流)
题意: 一个屌丝给m个女神拍照,计划拍照n天,每一天屌丝给给定的C个女神拍照,每天拍照数不能超过D张,而且给每个女神i拍照有数量限制[Li,Ri],对于每个女神n天的拍照总和不能少于Gi,如果有解求屌 ...
- zoj 3229 有源汇有上下界的最大流模板题
/*坑啊,pe的程序在zoj上原来是wa. 题目大意:一个屌丝给m个女神拍照.计划拍照n天,每一天屌丝最多个C个女神拍照,每天拍照数不能超过D张,并且给每一个女神i拍照有数量限制[Li,Ri], 对于 ...
随机推荐
- iOS UIFont 的学习与使用
通常,我们使用字体 都是系统默认的字体. 有时候 从阅读体验,美观度 设计师都会考虑用一些 更高大尚的字体. 系统字体库 给英文 各种style的发挥空间很大,但是 中文则不然. 但是苹果 给使用中文 ...
- Spring session共享(使用redis)
SpringBoot+Redis实现HttpSession共享 前提:需要使用redis做session存储 一.效果演练(这里使用SpringBoot工程,Spring同理) 1.一个工程使用两个端 ...
- Struts2笔记03——架构(转)
原始内容:https://www.tutorialspoint.com/struts_2/basic_mvc_architecture.htm 架构(很重要!尤其是图!) 从一个比较高的层次来看,St ...
- JSP笔记03——环境搭建(转)
不完全翻译,结合谷歌,一定主观性,还可能有误,原始内容地址:https://www.tutorialspoint.com/jsp/jsp_environment_setup.htm [注释]这篇貌似有 ...
- Ubuntu登陆不进去(已解决)【转】
本文转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/u010925447/article/details/72236387 Ubuntu一直在登陆界面循环:登陆密码是正确的,但是登陆后自动退回登陆 ...
- dreamweaver8快捷键
替换Ctrl+H 处理表格 选择表格(光标在表格中) Ctrl+A 移 动到下一单元格Tab 移 动到上一单元格Shift+Tab 插入行(在当前行之前)Ctrl+M 在表格末插入一行 在最后一个单元 ...
- linux基础(6)-shell编程
shell脚本 shell脚本程序:以文件形式存放批量的linux命令集合,该文件能够被shell释放执行.通常由一段linux命令.shell命令.控制语句以及注释语句构成. shell脚本特点: ...
- HDU 3966 & POJ 3237 & HYSBZ 2243 & HRBUST 2064 树链剖分
树链剖分是一个很固定的套路 一般用来解决树上两点之间的路径更改与查询 思想是将一棵树分成不想交的几条链 并且由于dfs的顺序性 给每条链上的点或边标的号必定是连着的 那么每两个点之间的路径都可以拆成几 ...
- Log4j2的日志配置文件,log4j2.xml文件的配置(实现控制台输出,各级别分别文件输出,自动压缩等)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W ...
- nova instance启动中的同步与异步
instance create:nova/api/servers.create -- self.compute_api.create -- self.compute_task_api.build_in ...
