ROS naviagtion analysis: costmap_2d--StaticLayer
博客转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/u013158492/article/details/50493246

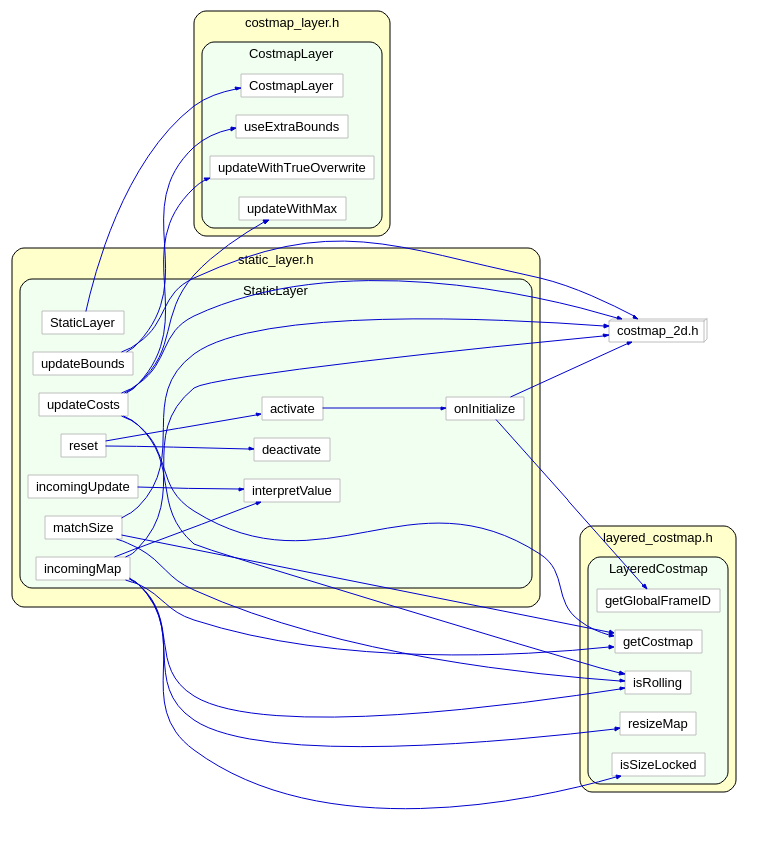
从UML中能够看到,StaticLayer主要是在实现Layer层要求实现的接口。
virtual void onInitialize();
virtual void activate();
virtual void deactivate();
virtual void reset();
virtual void updateBounds(double robot_x, double robot_y, double robot_yaw, double* min_x, double* min_y,double* max_x, double* max_y);
virtual void updateCosts(costmap_2d::Costmap2D& master_grid, int min_i, int min_j, int max_i, int max_j);
virtual void matchSize();
函数virtual void activate()
void StaticLayer::activate()
{
onInitialize();
}
而函数onInitialize() 中,首先初始化了一堆参数,然后调用
map_sub_ = g_nh.subscribe(map_topic, 1, &StaticLayer::incomingMap, this);//一旦收到topic 是“map”的消息,就调用`incomingMap`
while (!map_received_ && g_nh.ok())
{
ros::spinOnce();
r.sleep();
}//如果map_received_一直是false,则阻塞在这里。而更新map_received_的地方在回调函数incomingMap
接下来判断是否接受static map的更新,如果是则开启对topic为map_topic + "_updates" 的更新。最后开启参数动态配置服务。
函数matchSize 中的操作依然是根据master map的尺寸,更新本层的尺寸:
void StaticLayer::matchSize()
{
// If we are using rolling costmap, the static map size is
// unrelated to the size of the layered costmap
if (!layered_costmap_->isRolling())
{
Costmap2D* master = layered_costmap_->getCostmap();
resizeMap(master->getSizeInCellsX(), master->getSizeInCellsY(), master->getResolution(),
master->getOriginX(), master->getOriginY());
}
}
函数interpretValue 则是将参数根据阈值,设定为NO_INFORMATION FREE_SPACE LETHAL_OBSTACLE FREE_SPACE 或者其他值。
unsigned char StaticLayer::interpretValue(unsigned char value)
{
// check if the static value is above the unknown or lethal thresholds
if (track_unknown_space_ && value == unknown_cost_value_)
return NO_INFORMATION;
else if (!track_unknown_space_ && value == unknown_cost_value_)
return FREE_SPACE;
else if (value >= lethal_threshold_)
return LETHAL_OBSTACLE;
else if (trinary_costmap_)
return FREE_SPACE; double scale = (double) value / lethal_threshold_;
return scale * LETHAL_OBSTACLE;
}
以下分析回调函数incomingMap
void StaticLayer::incomingMap(const nav_msgs::OccupancyGridConstPtr& new_map)
{
unsigned int size_x = new_map->info.width, size_y = new_map->info.height; ROS_DEBUG("Received a %d X %d map at %f m/pix", size_x, size_y, new_map->info.resolution); // resize costmap if size, resolution or origin do not match
//这里判断master map的尺寸是否和获取到的static map一致,如果不一致,则应该修改master map
Costmap2D* master = layered_costmap_->getCostmap();
if (!layered_costmap_->isRolling() && (master->getSizeInCellsX() != size_x ||
master->getSizeInCellsY() != size_y ||
master->getResolution() != new_map->info.resolution ||
master->getOriginX() != new_map->info.origin.position.x ||
master->getOriginY() != new_map->info.origin.position.y ||
!layered_costmap_->isSizeLocked()))
{
// Update the size of the layered costmap (and all layers, including this one)
ROS_INFO("Resizing costmap to %d X %d at %f m/pix", size_x, size_y, new_map->info.resolution);
layered_costmap_->resizeMap(size_x, size_y, new_map->info.resolution, new_map->info.origin.position.x, new_map->info.origin.position.y, true);//修改了master map
}
//如果本层的数据和订阅到的map尺寸不一致,则更新本层的尺寸
else if (size_x_ != size_x || size_y_ != size_y ||
resolution_ != new_map->info.resolution ||
origin_x_ != new_map->info.origin.position.x ||
origin_y_ != new_map->info.origin.position.y)
{
// only update the size of the costmap stored locally in this layer
ROS_INFO("Resizing static layer to %d X %d at %f m/pix", size_x, size_y, new_map->info.resolution);
resizeMap(size_x, size_y, new_map->info.resolution,new_map->info.origin.position.x, new_map->info.origin.position.y);
} unsigned int index = 0; // initialize the costmap with static data
//这里将订阅拿到的map数据拷贝到了本层static map的数据成员`costmap_`
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < size_y; ++i)
{
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < size_x; ++j)
{
unsigned char value = new_map->data[index];
costmap_[index] = interpretValue(value);
++index;
}
}
map_frame_ = new_map->header.frame_id; // we have a new map, update full size of map
x_ = y_ = 0;
width_ = size_x_;
height_ = size_y_;
map_received_ = true;
has_updated_data_ = true; // shutdown the map subscrber if firt_map_only_ flag is on
if (first_map_only_)
{
map_sub_.shutdown();
}
}
函数 updateBounds 这里设定为整张static map的大小:
void StaticLayer::updateBounds(double robot_x, double robot_y, double robot_yaw, double* min_x, double* min_y,
double* max_x, double* max_y)
{ if( !layered_costmap_->isRolling() ){
if (!map_received_ || !(has_updated_data_ || has_extra_bounds_))
return;
} useExtraBounds(min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y); double wx, wy; mapToWorld(x_, y_, wx, wy);
*min_x = std::min(wx, *min_x);
*min_y = std::min(wy, *min_y); mapToWorld(x_ + width_, y_ + height_, wx, wy);
*max_x = std::max(wx, *max_x);
*max_y = std::max(wy, *max_y); has_updated_data_ = false;
}
函数 updateCosts:
void StaticLayer::updateCosts(costmap_2d::Costmap2D& master_grid, int min_i, int min_j, int max_i, int max_j)
{
if (!map_received_)
return; if (!layered_costmap_->isRolling())
{
// if not rolling, the layered costmap (master_grid) has same coordinates as this layer这里如果不是rolling 选项,则直接将本层数据copy到master map,因为它们尺寸也一样
if (!use_maximum_)
updateWithTrueOverwrite(master_grid, min_i, min_j, max_i, max_j);
else
updateWithMax(master_grid, min_i, min_j, max_i, max_j);
}
else
{
// If rolling window, the master_grid is unlikely to have same coordinates as this layer
unsigned int mx, my;
double wx, wy;
// Might even be in a different frame
//首先获得map坐标系相对于global坐标系的位置,这个时候的map坐标系是随着机器人运动而运动的。
tf::StampedTransform transform;
try
{
tf_->lookupTransform(map_frame_, global_frame_, ros::Time(0), transform);
}
catch (tf::TransformException ex)
{
ROS_ERROR("%s", ex.what());
return;
}
// Copy map data given proper transformations
for (unsigned int i = min_i; i < max_i; ++i)
{
for (unsigned int j = min_j; j < max_j; ++j)
{
// Convert master_grid coordinates (i,j) into global_frame_(wx,wy) coordinates
layered_costmap_->getCostmap()->mapToWorld(i, j, wx, wy);
// Transform from global_frame_ to map_frame_
tf::Point p(wx, wy, 0);
p = transform(p);
// Set master_grid with cell from map
if (worldToMap(p.x(), p.y(), mx, my))
{
if (!use_maximum_)
master_grid.setCost(i, j, getCost(mx, my));
else
master_grid.setCost(i, j, std::max(getCost(mx, my), master_grid.getCost(i, j)));
}
}
}
}
}
重点是这两句:
if (worldToMap(p.x(), p.y(), mx, my))
{
if (!use_maximum_)
master_grid.setCost(i, j, getCost(mx, my));
将static map层的每一点(i,j),都找到对应的master map的(mx,my),这样就可以直接更改master map的对应点了。
OK,静态地图分析到此为止~接下来分析Obstacle 层,这个略微要难点。
ROS naviagtion analysis: costmap_2d--StaticLayer的更多相关文章
- ROS naviagtion analysis: costmap_2d--Costmap2DROS
博客转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/u013158492/article/details/50485418 在上一篇文章中moveBase就有关于costmap_2d的使用: pl ...
- ROS naviagtion analysis: move_base
博客转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/u013158492/article/details/50483123 这是navigation的第一篇文章,主要通过分析ROS代码级实现,了解 ...
- ROS naviagtion analysis: costmap_2d--LayeredCostmap
博客转自:https://blog.csdn.net/u013158492/article/details/50490490 在数据成员中,有两个重要的变量:Costmap2D costmap_和 s ...
- ROS naviagtion analysis: costmap_2d--ObstacleLayer
博客转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/u013158492/article/details/50493676 构造函数 ObstacleLayer() { costmap_ = NU ...
- ROS naviagtion analysis: costmap_2d--CostmapLayer
博客转自:https://blog.csdn.net/u013158492/article/details/50493220 这个类是为ObstacleLayer StaticLayer voxelL ...
- ROS naviagtion analysis: costmap_2d--Layer
博客转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/u013158492/article/details/50493113 这个类中有一个LayeredCostmap* layered_costm ...
- ROS naviagtion analysis: costmap_2d--Costmap2D
博客转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/u013158492/article/details/50492506 Costmap2D是存储地图数据的父类.真正的地图数据就存储在数据成员u ...
- ROS 教程之 navigation :在 catkin 环境下创建costmap layer plugin
在做机器人导航的时候,肯定见到过global_costmap和local_costmap.global_costmap是为了全局路径规划服务的,如从这个房间到那个房间该怎么走.local_costma ...
- ROS探索总结(十三)——导航与定位框架
导航与定位是机器人研究中的重要部分. 一般机器人在陌生的环境下需要使用激光传感器(或者深度传感器转换成激光数据),先进行地图建模,然后在根据建立的地图进行导航.定位.在ROS中也有很多 ...
随机推荐
- SSM框架——Spring+SpringMVC+Mybatis的搭建
1.基本概念 1.1.Spring Spring是一个开源框架,Spring是于2003 年兴起的一个轻量级的Java 开发框架,由Rod Johnson 在其著作Expert One-On-One ...
- Windows下安装pillow、opencv库问题,亲测可行
安装pillow 库 python -m pip install pillow 出自:http://blog.csdn.net/Riverhope/article/details/78766969 安 ...
- 使用Volley框架中的ImageLoader来异步的加载图片
Volley框架在请求网络图片方面也做了很多工作,提供了好几种方法.本文介绍使用ImageLoader来进行网络图片的加载.ImageLoader的内部使用ImageRequest来实现,它的构造器可 ...
- 【java反射】Class类型的相关操作演练
[一]获取范型接口的实现类的范型类型 (1)范型接口 package org.springframework.context; import java.util.EventListener; publ ...
- 11.7noip模拟赛
题解:广义斐波那契数列 矩阵乘法 #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #define LL ...
- Oracle 11G RAC:生产环境下架构
转: it168网站 原创 作者:刘炳林 在真实环境搭建一套Oracle RAC就好比是一堂劳动课,劳动前需要准备好劳动工具,对劳动课内容有充分的认识;按照步骤一步一步进行,需要考虑劳动过程中可能遇 ...
- Vue.js:自定义指令
ylbtech-Vue.js:自定义指令 1.返回顶部 1. Vue.js 自定义指令 除了默认设置的核心指令( v-model 和 v-show ), Vue 也允许注册自定义指令. 下面我们注册一 ...
- 第三方引擎应用场景分析--Tokudb,infobright
TokuDBTokuDB的特色:• Fractal Tree而不是B-Tree• 内部结点不仅有指向父子的指针还有Buffer区,数据写入先写buffer区,FIFO结构,写入只需要顺序添加到Buff ...
- Patator-一款很好用的爆破工具
项目地址:https://github.com/lanjelot/patator 打开文件夹 运行一下文件查看帮助 python patator.py --help 这里有很多的爆破选项,就不一一截图 ...
- 自己写着玩的一个天气APP
打开的界面: 向上滑动,进入主界面: 省份界面: 城市界面: 加载天气界面: 显示天气界面: 侧滑,显示地区,然后根据天气来显示一首诗句(晴,多云,雪,雨什么的): 第一次启动App的时候才会加载数据 ...
