Hystrix 源码解读
转载请注明出处:
1.引入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--hystrix官网-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.netflix.hystrix</groupId>
<artifactId>hystrix-core</artifactId>
<version>1.5.18</version>
</dependency> <dependency>
<groupId>com.netflix.hystrix</groupId>
<artifactId>hystrix-javanica</artifactId>
<version>1.5.18</version>
</dependency>
2. 查看自动配置类HystrixCircuitBreakerConfiguration
查看 org.springframework.cloud.spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix 包中的自动配置类,Hystrix 的断路器的自动配置类在 org.springframework.cloud.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCircuitBreakerConfiguration 类中
3.查看 HystrixCircuitBreakerConfiguration 类的实现
@Configuration(
proxyBeanMethods = false
)
public class HystrixCircuitBreakerConfiguration {
public HystrixCircuitBreakerConfiguration() {
} @Bean
public HystrixCommandAspect hystrixCommandAspect() {
return new HystrixCommandAspect();
} }
Hystrix 的熔断开启与实现时通过 上面中的 HystrixCommandAspect 类实现的
4.查看 HystrixCommandAspect 类的实现
该切面类中的实现为:
@Aspect
public class HystrixCommandAspect {
private static final Map<HystrixCommandAspect.HystrixPointcutType, HystrixCommandAspect.MetaHolderFactory> META_HOLDER_FACTORY_MAP; public HystrixCommandAspect() {
} @Pointcut("@annotation(com.netflix.hystrix.contrib.javanica.annotation.HystrixCommand)")
public void hystrixCommandAnnotationPointcut() {
} @Pointcut("@annotation(com.netflix.hystrix.contrib.javanica.annotation.HystrixCollapser)")
public void hystrixCollapserAnnotationPointcut() {
} @Around("hystrixCommandAnnotationPointcut() || hystrixCollapserAnnotationPointcut()")
public Object methodsAnnotatedWithHystrixCommand(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
Method method = AopUtils.getMethodFromTarget(joinPoint);
Validate.notNull(method, "failed to get method from joinPoint: %s", new Object[]{joinPoint});
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(HystrixCommand.class) && method.isAnnotationPresent(HystrixCollapser.class)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("method cannot be annotated with HystrixCommand and HystrixCollapser annotations at the same time");
} else {
HystrixCommandAspect.MetaHolderFactory metaHolderFactory = (HystrixCommandAspect.MetaHolderFactory)META_HOLDER_FACTORY_MAP.get(HystrixCommandAspect.HystrixPointcutType.of(method));
MetaHolder metaHolder = metaHolderFactory.create(joinPoint);
//构建hystrixCommand的实现类
HystrixInvokable invokable = HystrixCommandFactory.getInstance().create(metaHolder);
ExecutionType executionType = metaHolder.isCollapserAnnotationPresent() ? metaHolder.getCollapserExecutionType() : metaHolder.getExecutionType(); try {
Object result;
if (!metaHolder.isObservable()) {
result = CommandExecutor.execute(invokable, executionType, metaHolder);
} else {
result = this.executeObservable(invokable, executionType, metaHolder);
} return result;
} catch (HystrixBadRequestException var9) {
throw var9.getCause();
} catch (HystrixRuntimeException var10) {
throw this.hystrixRuntimeExceptionToThrowable(metaHolder, var10);
}
}
}
}
通过代码看出hystrix 通过封装一个切面,在切面中 拦截 对使用了 @HystrixCommand 与 @HystrixCollapser注解的方法进行增强;
重点看这行代码:
HystrixInvokable invokable = HystrixCommandFactory.getInstance().create(metaHolder);
是如何创建HystrixCommand对象的。
public HystrixInvokable create(MetaHolder metaHolder) {
Object executable;
//判断是不是HystrixCollapser注解
if (metaHolder.isCollapserAnnotationPresent()) {
executable = new CommandCollapser(metaHolder);
} else if (metaHolder.isObservable()) {
executable = new GenericObservableCommand(HystrixCommandBuilderFactory.getInstance().create(metaHolder));
} else {
//会执行这个。
executable = new GenericCommand(HystrixCommandBuilderFactory.getInstance().create(metaHolder));
}
return (HystrixInvokable)executable;
}
分析的是HystrixCommand注解,所以走else里的分析。整体构造过程是 GenericCommand -> AbstractHystrixCommand -> HystrixCommand -> AbstractCommand, 构建GenericCommand的过程,我们主要还是看AbstractCommand的构造方法。
abstract class AbstractCommand<R> implements HystrixInvokableInfo<R>, HystrixObservable<R> {
//构造方法
protected AbstractCommand(HystrixCommandGroupKey group, HystrixCommandKey key,
HystrixThreadPoolKey threadPoolKey, HystrixCircuitBreaker circuitBreaker,
HystrixThreadPool threadPool,
HystrixCommandProperties.Setter commandPropertiesDefaults,
HystrixThreadPoolProperties.Setter threadPoolPropertiesDefaults,
HystrixCommandMetrics metrics,
TryableSemaphore fallbackSemaphore,
TryableSemaphore executionSemaphore,
HystrixPropertiesStrategy propertiesStrategy,
HystrixCommandExecutionHook executionHook) {
this.commandGroup = initGroupKey(group);
this.commandKey = initCommandKey(key, getClass());
this.properties = initCommandProperties(this.commandKey, propertiesStrategy, commandPropertiesDefaults);
this.threadPoolKey = initThreadPoolKey(threadPoolKey,
this.commandGroup,
this.properties.executionIsolationThreadPoolKeyOverride().get());
this.metrics = initMetrics(metrics, this.commandGroup, this.threadPoolKey, this.commandKey, this.properties);
//初始化熔断器
this.circuitBreaker = initCircuitBreaker(this.properties.circuitBreakerEnabled().get(),
circuitBreaker, this.commandGroup,
this.commandKey, this.properties, this.metrics);
//初始化线程池
this.threadPool = initThreadPool(threadPool, this.threadPoolKey, threadPoolPropertiesDefaults);
//Strategies from plugins
this.eventNotifier = HystrixPlugins.getInstance().getEventNotifier();
this.concurrencyStrategy = HystrixPlugins.getInstance().getConcurrencyStrategy();
HystrixMetricsPublisherFactory.createOrRetrievePublisherForCommand(this.commandKey, this.commandGroup,
this.metrics, this.circuitBreaker,
this.properties);
this.executionHook = initExecutionHook(executionHook);
this.requestCache = HystrixRequestCache.getInstance(this.commandKey, this.concurrencyStrategy);
this.currentRequestLog = initRequestLog(this.properties.requestLogEnabled().get(), this.concurrencyStrategy);
/* fallback semaphore override if applicable */
this.fallbackSemaphoreOverride = fallbackSemaphore;
/* execution semaphore override if applicable */
this.executionSemaphoreOverride = executionSemaphore;
}
}
5.查看 切面方法实现细节
hystrix 执行的流程图:
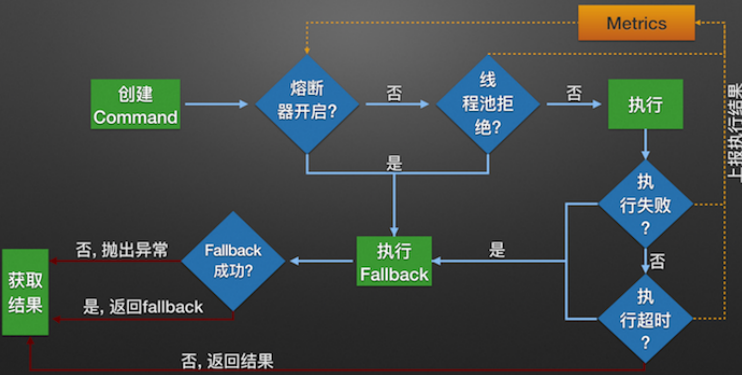
构造一个 HystrixCommand或HystrixObservableCommand对象,用于封装请求,并在构造方法配置请求被执行需要的参数;
执行命令,Hystrix提供了4种执行命令的方法
判断是否使用缓存响应请求,若启用了缓存,且缓存可用,直接使用缓存响应请求。Hystrix支持请求缓存,但需要用户自定义启动;
判断熔断器是否打开,如果打开,执行第8步;
判断线程池/队列/信号量是否已满,已满则执行第8步;
执行HystrixObservableCommand.construct()或HystrixCommand.run(),如果执行失败或者超时,执行第8步;否则,跳到第9步;
统计熔断器监控指标;
走Fallback备用逻辑
返回请求响应
6.核心实现
HystrixCommandAspect.methodsAnnotatedWithHystrixCommand 中的execute方法,execute 方法为 hystrix 实现的核心:
public static Object execute(HystrixInvokable invokable, ExecutionType executionType, MetaHolder metaHolder) throws RuntimeException {
Validate.notNull(invokable);
Validate.notNull(metaHolder);
switch(executionType) {
case SYNCHRONOUS:
return castToExecutable(invokable, executionType).execute();
case ASYNCHRONOUS:
HystrixExecutable executable = castToExecutable(invokable, executionType);
if (metaHolder.hasFallbackMethodCommand() && ExecutionType.ASYNCHRONOUS == metaHolder.getFallbackExecutionType()) {
return new FutureDecorator(executable.queue());
}
return executable.queue();
case OBSERVABLE:
HystrixObservable observable = castToObservable(invokable);
return ObservableExecutionMode.EAGER == metaHolder.getObservableExecutionMode() ? observable.observe() : observable.toObservable();
default:
throw new RuntimeException("unsupported execution type: " + executionType);
}
}
判断是否为同步,还是异步,还是观察着模式,异步方式是通过 Future 封装,用Future 对象的get方法,阻塞等待返回结果,以达到同步效果。
在这里只查看同步的方式: 调用链路是:HystrixCommand.execute() -> queue() -> toObservable()
1.是否使用缓存
如果开启缓存,请求首先会返回缓存中的结果。
2.是否开启熔断
当运行hystrix命令时,会判断是否熔断,如果已经熔断,hystrix将不会执行命令,而是直接执行fallback。等熔断关闭了,在执行命令。
熔断器关闭或打开的判断,
private Observable<R> applyHystrixSemantics(AbstractCommand<R> _cmd) {
this.executionHook.onStart(_cmd);
//判读是不是熔断了。
if (this.circuitBreaker.allowRequest()) {
/**
*如果使用的是信号量返回TryableSemaphoreActual,不是返回
*TryableSemaphoreNoOp,TryableSemaphoreNoOp.tryAcquire()永远都是返回true
*/
final TryableSemaphore executionSemaphore = getExecutionSemaphore();
。。。
//信号量的控制
if (executionSemaphore.tryAccaquire()) {
try {
this.executionResult = this.executionResult.setInvocationStartTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
//如果都成功的话会执行executeCommandAndObserve
return this.executeCommandAndObserve(_cmd)
.doOnError(markExceptionThrown)
.doOnTerminate(singleSemaphoreRelease)
.doOnUnsubscribe(singleSemaphoreRelease);
} catch (RuntimeException var7) {
return Observable.error(var7);
}
} else {
return this.handleSemaphoreRejectionViaFallback();
}
} else {//执行熔断后的逻辑
return this.handleShortCircuitViaFallback();
}
}
熔断器降级分析
接着分析 this.circuitBreaker.allowRequest()
static class HystrixCircuitBreakerImpl implements HystrixCircuitBreaker {
private final HystrixCommandProperties properties;
private final HystrixCommandMetrics metrics;
//熔断器是否开启
/* track whether this circuit is open/closed at any given point in time (default to false==closed) */
private AtomicBoolean circuitOpen = new AtomicBoolean(false);
/* when the circuit was marked open or was last allowed to try a 'singleTest' */
private AtomicLong circuitOpenedOrLastTestedTime = new AtomicLong();
protected HystrixCircuitBreakerImpl(HystrixCommandKey key, HystrixCommandGroupKey commandGroup, HystrixCommandProperties properties, HystrixCommandMetrics metrics) {
this.properties = properties;
this.metrics = metrics;
}
//当半开半闭状态下,如果这次请求成功而了,则把熔断器设为false,且让统计指标reset
public void markSuccess() {
if (circuitOpen.get()) {
if (circuitOpen.compareAndSet(true, false)) {
//win the thread race to reset metrics
//Unsubscribe from the current stream to reset the health counts stream. This only affects the health counts view,
//and all other metric consumers are unaffected by the reset
metrics.resetStream();
}
}
}
@Override
public boolean allowRequest() {
//判断是否强制打开熔断器
if (properties.circuitBreakerForceOpen().get()) {
return false;
}
//是否强制关闭熔断器
if (properties.circuitBreakerForceClosed().get()) {
isOpen();
return true;
}
return !isOpen() || allowSingleTest();
}
public boolean allowSingleTest() {
long timeCircuitOpenedOrWasLastTested = circuitOpenedOrLastTestedTime.get();
// 1) if the circuit is open
// 2) and it's been longer than 'sleepWindow' since we opened the circuit
//熔断器是开启的,且当前时间比开启熔断器的时间加上sleepWindow时间还要长
if (circuitOpen.get() && System.currentTimeMillis() > timeCircuitOpenedOrWasLastTested + properties.circuitBreakerSleepWindowInMilliseconds().get()) {
// We push the 'circuitOpenedTime' ahead by 'sleepWindow' since we have allowed one request to try.
// If it succeeds the circuit will be closed, otherwise another singleTest will be allowed at the end of the 'sleepWindow'.
//设置当前时间到timeCircuitOpenedOrWasLastTested,
//如果半开半闭的状态下,如果这次请求成功了则会调用markSuccess,让熔断器状态设为false,
//如果不成功,就不需要了。
//案例:半开半合状态下,熔断开启时间为00:00:00,sleepWindow为10s,如果00:00:15秒的时候调用,如果调用失败,
//在00:00:15至00:00:25秒这个区间都是熔断的,
if (circuitOpenedOrLastTestedTime.compareAndSet(timeCircuitOpenedOrWasLastTested, System.currentTimeMillis())) {
// if this returns true that means we set the time so we'll return true to allow the singleTest
// if it returned false it means another thread raced us and allowed the singleTest before we did
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean isOpen() {
//判断是否熔断了,circuitOpen是熔断的状态 ,true为熔断,false为不熔断
if (circuitOpen.get()) {
return true;
}
//获取统计到的指标信息
HealthCounts health = metrics.getHealthCounts();
// 一个时间窗口(默认10s钟)总请求次数是否大于circuitBreakerRequestVolumeThreshold 默认为20s
if (health.getTotalRequests() < properties.circuitBreakerRequestVolumeThreshold().get()) {
return false;
}
// 错误率(总错误次数/总请求次数)小于circuitBreakerErrorThresholdPercentage(默认50%)
if (health.getErrorPercentage() < properties.circuitBreakerErrorThresholdPercentage().get()) {
return false;
} else {
// 反之,熔断状态将从CLOSED变为OPEN,且circuitOpened==>当前时间戳
if (circuitOpen.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
//并且把当前时间设置到circuitOpenedOrLastTestedTime,可待后面的时间的对比
circuitOpenedOrLastTestedTime.set(System.currentTimeMillis());
return true;
} else {
return true;
}
}
}
}
判断是否强制开启熔断器和强制关闭熔断器
先判断熔断是否开启,然后判断是否需要熔断,如果需要熔断则个性熔断状态并重置熔断时间为当前时间。熔断的条件是: 1)时间窗口内(默认10s钟)总请求次数大于20次 2)时间窗口内(默认10s钟)失败率大于50%
熔断的情况下就执行allowSingleTest,让开启熔断的都能往下执行。可以执行的条件是: 1)circuitOpen.get() 为true,确保是普通的熔断,而不是强制熔断 2)当前时间比开启熔断器的时间加上sleepWindow时间还要长
在半开半必的状态下请求成功了,再调用markSuccess()方法,从而将熔断器关闭并重新统计各项指标
其余的实现细节可以参考这篇文章:https://github.com/doocs/advanced-java/tree/main/docs/high-availability
https://www.iocoder.cn/Hystrix/command-execute-mode/
Hystrix 源码解读的更多相关文章
- SDWebImage源码解读之SDWebImageDownloaderOperation
第七篇 前言 本篇文章主要讲解下载操作的相关知识,SDWebImageDownloaderOperation的主要任务是把一张图片从服务器下载到内存中.下载数据并不难,如何对下载这一系列的任务进行设计 ...
- SDWebImage源码解读 之 NSData+ImageContentType
第一篇 前言 从今天开始,我将开启一段源码解读的旅途了.在这里先暂时不透露具体解读的源码到底是哪些?因为也可能随着解读的进行会更改计划.但能够肯定的是,这一系列之中肯定会有Swift版本的代码. 说说 ...
- SDWebImage源码解读 之 UIImage+GIF
第二篇 前言 本篇是和GIF相关的一个UIImage的分类.主要提供了三个方法: + (UIImage *)sd_animatedGIFNamed:(NSString *)name ----- 根据名 ...
- SDWebImage源码解读 之 SDWebImageCompat
第三篇 前言 本篇主要解读SDWebImage的配置文件.正如compat的定义,该配置文件主要是兼容Apple的其他设备.也许我们真实的开发平台只有一个,但考虑各个平台的兼容性,对于框架有着很重要的 ...
- SDWebImage源码解读_之SDWebImageDecoder
第四篇 前言 首先,我们要弄明白一个问题? 为什么要对UIImage进行解码呢?难道不能直接使用吗? 其实不解码也是可以使用的,假如说我们通过imageNamed:来加载image,系统默认会在主线程 ...
- SDWebImage源码解读之SDWebImageCache(上)
第五篇 前言 本篇主要讲解图片缓存类的知识,虽然只涉及了图片方面的缓存的设计,但思想同样适用于别的方面的设计.在架构上来说,缓存算是存储设计的一部分.我们把各种不同的存储内容按照功能进行切割后,图片缓 ...
- SDWebImage源码解读之SDWebImageCache(下)
第六篇 前言 我们在SDWebImageCache(上)中了解了这个缓存类大概的功能是什么?那么接下来就要看看这些功能是如何实现的? 再次强调,不管是图片的缓存还是其他各种不同形式的缓存,在原理上都极 ...
- AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读 总结(干货)(下)
承接上一篇AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读 总结(干货)(上) 21.网络服务类型NSURLRequestNetworkServiceType 示例代码: typedef NS_ENUM(N ...
- AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读 总结(干货)(上)
养成记笔记的习惯,对于一个软件工程师来说,我觉得很重要.记得在知乎上看到过一个问题,说是人类最大的缺点是什么?我个人觉得记忆算是一个缺点.它就像时间一样,会自己消散. 前言 终于写完了 AFNetwo ...
- AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读(十一)之 UIButton/UIProgressView/UIWebView + AFNetworking
AFNetworking的源码解读马上就结束了,这一篇应该算是倒数第二篇,下一篇会是对AFNetworking中的技术点进行总结. 前言 上一篇我们总结了 UIActivityIndicatorVie ...
随机推荐
- Linux配置成代理服务器
简介: 代理服务器(Proxy Server)是一种位于计算机网络中的中间服务器,它充当了客户端和目标服务器之间的中介,用于转发客户端请求并获取目标服务器的响应.代理服务器的主要功能包括以下几点: 什 ...
- 5分钟攻略Spring-Retry框架实现经典重试场景
前言 今天分享干货,控制了篇幅,5分钟内就能看完学会. 主题是Spring-Retry框架的应用,做了一个很清晰的案例,代码可下载自测. 框架介绍 Spring-Retry框架是Spring自带的功能 ...
- 聊聊流式数据湖Paimon(五)
从Demo入手,了解Paimon/Flink项目搭建的全过程.记录下采坑之旅. 创建Flink项目 在IDEA中创建Flink项目,由于没有Flink的archetype,因此需要手动创建一下. 参考 ...
- Vue学习笔记-指令
- PersistenceException、ReflectionException、IllegalArgumentException、wrapException持久性异常 反射异常 非法参数异常 包装异常
PersistenceException.ReflectionException.IllegalArgumentException.wrapException wrapException 持久性异常 ...
- ElasticSearch之cat datafeeds API
命令样例如下: curl -X GET "https://localhost:9200/_cat/ml/datafeeds?v=true&pretty" --cacert ...
- DVWA Cross Site Scripting (XSS) 跨站脚本攻击
文章目录 DVWA_XSS(Stored) 存储性XSS 1.Low 2.Medium 3.High 4.Impossible XSS平台 DVWA_XSS(Stored) 存储性XSS 一句话概括: ...
- 2024-01-13:用go语言,现在有一个打怪类型的游戏,这个游戏是这样的,你有n个技能, 每一个技能会有一个伤害, 同时若怪物小于等于一定的血量,则该技能可能造成双倍伤害, 每一个技能最多只能释放
2024-01-13:用go语言,现在有一个打怪类型的游戏,这个游戏是这样的,你有n个技能, 每一个技能会有一个伤害, 同时若怪物小于等于一定的血量,则该技能可能造成双倍伤害, 每一个技能最多只能释放 ...
- LeetCode 图篇
743. 网络延迟时间 有 N 个网络节点,标记为 1 到 N. 给定一个列表 times,表示信号经过有向边的传递时间. times[i] = (u, v, w),其中 u 是源节点,v 是目标节点 ...
- html2pdf
nodejs 生成pdf比较靠谱,使用chrome核心渲染: puppeteer / phantom 爬虫都好用 good
