框架-spring源码分析(一)
框架-spring源码分析(一)
参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/heavenyes/p/3933642.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/BINGJJFLY/p/9055454.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/leftthen/p/5440107.html
spring容器
一、简介
spring容器是整个spring框架的核心,通常我们说的spring容器就是bean工厂,bean工厂负责创建和初始化bean、装配bean并且管理应用程序中的bean.spring中提供了两个核心接口:BeanFactory和ApplicationContext,ApplicationContext是BeanFactory子接口,它提供了比BeanFactory更完善的功能.
二、ApplicationContext的工作原理
先建立一个新的java项目,搭建好spring的开发环境.然后启动spring的容器,如下面的代码:

public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext cxt = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
}
}

spring容器启动时,会完成两个重要的工作:加载bean的定义信息(BeanDefinition)以及初始化所有单例bean,在初始化bean的过程中注入bean的依赖.bean的定义信息是指:bean的基本属性,例如完整类名,是否单例等等,其实就是<bean id="" class="" scope="">元素的那些属性.在创建bean时需要用到这些属性,所以必须要先加载bean以及它的定义信息.
先说spring容器加载bean的定义信息的实现原理,spring中有两种配置bean的方法:
- 使用配置文件配置bean,需要在<bean>元素中声明bean的信息;spring容器启动时,会读取配置文件并进行解析,这种情况下,只要解析bean元素就可以获取bean的beanName和它的定义信息.
使用注解配置bean,需要在配置文件中配置bean的路径,例如:<context:component-scan base-package="cn.spring"/>,这样容器启动时就会扫描cn.spring包以及子包下面的所有类,如果类上有@Controller 或者 @Service 或者@Repository或者@Component注解,spring就会加载这些类的定义信息;这里就会有几个问题,第一个问题是如何获取base-package的子包以及包下的所有类?spring的做法是将包名转化成文件系统中的路径,然后traverse获取该目录下的所有.class文件,非常巧妙的一个解决方案!接下来的问题是如何从.class文件中获取bean的定义信息呢?有两种方式,第一种就是把通过.class文件的路径获取该类的包名,然后通过类加载器加载该类获取它的定义信息,第二种方式是用asm框架从class文件中直接读取类的定义信息。spring用的是第二种方式,个人觉得spring选择第二种方式是有以下几个原因,其一,可能需要对class文件进行增强处理,也就是在class文件中增加一些新的指令,在生成代理时可能会需要这样做;其二,反射无法获取类完完全全的信息(例如:方法的参数名称),其三,反射的性能问题;
接下来,就是容器初始化单例bean的过程:
spring容器在加载完所有bean的定义信息以后,会有一个refresh()操作,在refresh容器过程中完成两个重要的操作,第一个就是创建所有单例bean,第二个就是装配这些创建bean(注入它们所需要的依赖);
因为前面的操作已经加载了所有bean的定义信息,并且维护了一个<beanName,BeanDefinition>对应关系的Map,遍历Map,就可以取得每个bean的定义信息,从bean的定义信息可以知道bean是否是单例,如果是单例的,下一步就会根据bean的定义信息来决定bean实例的创建策略,如果配置了bean的factory-method,就调用factory-method创建bean实例,如果没有配置factory-method,默认会调用bean的无参构造函数创建bean实例.
创建bean实例之后的工作就是装配bean,现在已经拿到了bean实例,如果bean是在配置文件中配置的,此时就会先把配置文件中配置的属性赋值给bean实例上对应的属性;而后由bean的后处理器(BeanPostProcessor)完成bean实例其他属性(通过注解配置的)的注入.如果bean是通过注解进行配置,这时直接就会由bean的后处理器完成bean的装配.完成bean装配的后处理器的工作原理:遍历bean对象的字段和方法,根据字段和方法上应的注解完成相对应的注入操作.
在装配bean的过程中会出现一个问题:A依赖B,装配A的时候B的实例还没有创建,spring解决这个问题的办法是:先创建B对象,装配好bean,然后把B注入A,继续完成A的装配.
三、容器初始化过程的源码分析
我们从ApplicationContext的构造函数开始,如下代码:

/**
* Create a new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext with the given parent,
* loading the definitions from the given XML files.
* @param configLocations array of resource locations
* @param refresh whether to automatically refresh the context,
* loading all bean definitions and creating all singletons. --->加载所有bean的定义信息,创建所有单例bean
* Alternatively, call refresh manually after further configuring the context.
* @param parent the parent context
* @throws BeansException if context creation failed
* @see #refresh()
*/
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException { super(parent);
// 解析给定的配置文件,完成加载所有bean的定义信息的操作
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
// refresh容器,完成创建单例bean的操作
refresh();
}
}

构造方法的注释上写的so nice.接下来,看加载bean的定义信息的过程,setConfigLocations()是在父类中实现的,接收到配置文件以后,容器开始解析配置文件.经过一系列的调用,会调用org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader的doLoadBeanDefinitions(),到这里终于看到Document,下面是该方法的源码:

/**
* Actually load bean definitions from the specified XML file.
* @param inputSource the SAX InputSource to read from
* @param resource the resource descriptor for the XML file
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors
*/
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
int validationMode = getValidationModeForResource(resource);
// 取得Document对象
Document doc = this.documentLoader.loadDocument(
inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler, validationMode, isNamespaceAware());
// 从Document对象中解析bean的定义信息
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
// ...各种异常的处理
}

registerBeanDefinitions()又会经过一系列的检查和处理,然后调用

/**
* Register each bean definition within the given root {@code <beans/>} element.
* @throws IllegalStateException if {@code <beans profile="..."} attribute is present
* and Environment property has not been set
* @see #setEnvironment
*/
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
Assert.state(this.environment != null, "environment property must not be null");
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
if (!this.environment.acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
return;
}
} // any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In
// order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly,
// keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create
// the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes,
// then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference.
// this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one.
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
this.delegate = createHelper(readerContext, root, parent); preProcessXml(root);
// 重点部分,解析bean的定义信息
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
postProcessXml(root); this.delegate = parent;
}
/**
* Parse the elements at the root level in the document:
* "import", "alias", "bean".
* @param root the DOM root element of the document
*/
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate); // 重点:解析bean元素
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele); // 重点:解析其他元素,例如:<context<context:component-scan> or <annotation:config/>
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}

到这里,终于到了关键的地方,如果bean是在配置文件中配置的,由parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate)处理bean元素的解析,如果是注解配置,parseCustomElement(ele)会扫描包下的class文件,并完成解析.我们先看配置文件中bean元素的解析方式。

private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) {
importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) {
processAliasRegistration(ele);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {
// 重点
processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) {
// recurse
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
}
}
/**
* Process the given bean element, parsing the bean definition
* and registering it with the registry.
*/
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
// 获取bean的定义信息,用BeanDefinitionHodler对象封装
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
if (bdHolder != null) {
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
// Register the final decorated instance.---》关键,将bean的定义信息保存到容器
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
// Send registration event.
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}

接下来就是调用org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionReaderUtils的registerBeanDefinition()保存bean定义信息到容器的方法了.

/**
* Register the given bean definition with the given bean factory.
* @param definitionHolder the bean definition including name and aliases
* @param registry the bean factory to register with
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException if registration failed
*/
public static void registerBeanDefinition(
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { // Register bean definition under primary name.---》重点
String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName();
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition()); // Register aliases for bean name, if any.
String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases();
if (aliases != null) {
for (String aliase : aliases) {
registry.registerAlias(beanName, aliase);
}
}
}

ok,来看最终的保存代码:

/** Map of bean definition objects, keyed by bean name */
private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition>();
/** List of bean definition names, in registration order */
private final List<String> beanDefinitionNames = new ArrayList<String>();

保存bean定义信息的方法:

//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Implementation of BeanDefinitionRegistry interface
//--------------------------------------------------------------------- public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null"); if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
}
// 保存bean定义信息,线程同步
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
// 判断当前bean的定义信息是否已经保存
Object oldBeanDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (oldBeanDefinition != null) {
if (!this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Cannot register bean definition [" + beanDefinition + "] for bean '" + beanName +
"': There is already [" + oldBeanDefinition + "] bound.");
}
else {
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"': replacing [" + oldBeanDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
}
else {
// 保存beanName
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
}
// 保存beanName和bean的定义信息到Map
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
}

上面就是spring解析配置文件中的bean定义信息,然后保存beanName和bean定义信息到Map中.这个过程主要就是xml的解析.接下来我们看spring是如何解析注解方式配置的bean.回到parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate)方法,现在重点关注:delegate.parseCustomElement(ele)方法.如果我们在配置文件用<context:component-scan base-package="">方式来指定自动扫描的包,之后就会调用org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser的parse().下面是parse()方法的源代码:

public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
// 解析<context:component-scan元素,获取base-package
String[] basePackages = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(element.getAttribute(BASE_PACKAGE_ATTRIBUTE),
ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS);
// Actually scan for bean definitions and register them.
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = configureScanner(parserContext, element);
//重点: 扫描basePackage下所有的class文件,读取bean的定义信息
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = scanner.doScan(basePackages);
registerComponents(parserContext.getReaderContext(), beanDefinitions, element);
return null;
}

重点关注scanner.doScan(basePackges)方法,该方法完成整个核心操作--->根据包名获取包下所有的class的定义信息.直接看org.springframework.context.annotation.ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner的scan():注意,看源码时一定要多关注注释,例如下面方法上的注释就非常有意义.

/**
* Perform a scan within the specified base packages,
* returning the registered bean definitions.
* <p>This method does <i>not</i> register an annotation config processor
* but rather leaves this up to the caller.
* @param basePackages the packages to check for annotated classes
* @return set of beans registered if any for tooling registration purposes (never {@code null})
*/
protected Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified");
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet<BeanDefinitionHolder>();
for (String basePackage : basePackages) { // 遍历每一个basepackages
// 1.获取basePackage下bean的定义信息
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) {
//2.根据扫描的信息,解析bean的一些定义信息
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(candidate);
candidate.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(candidate, this.registry);
if (candidate instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
postProcessBeanDefinition((AbstractBeanDefinition) candidate, beanName);
}
if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidate);
}
if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) {
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName);
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder);
// 3.将bean的定义信息添加到容器中
registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
}
}
return beanDefinitions;
}

第1个步骤我们核心关注点,它完成从文件系统中读取class文件的操作,第3个步骤在之前已经说了,就是保存bean的定义信息到容器的DefaultListableBeanFactory的beanDefinitionMap 中.重点关注第1个步骤,看findCandidateComponents()的源代码:

/**
* Scan the class path for candidate components.
* @param basePackage the package to check for annotated classes
* @return a corresponding Set of autodetected bean definitions
*/
public Set<BeanDefinition> findCandidateComponents(String basePackage) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<BeanDefinition>();
try {
String packageSearchPath = ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX +
resolveBasePackage(basePackage) + "/" + this.resourcePattern;
// 1.获取包下的class文件路径,例如E:\Program Files (x86)\MyEclipse10\workplace2\spr\bin\cn\jack\domain\User.class,
// 每一个class文件的路径封装成Resource对象.
Resource[] resources = this.resourcePatternResolver.getResources(packageSearchPath);
boolean traceEnabled = logger.isTraceEnabled();
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
for (Resource resource : resources) {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Scanning " + resource);
}
if (resource.isReadable()) {
try {
// 2.使用asm框架读取class文件,获取类的定义信息
MetadataReader metadataReader = this.metadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(resource);
if (isCandidateComponent(metadataReader)) {
ScannedGenericBeanDefinition sbd = new ScannedGenericBeanDefinition(metadataReader);
sbd.setResource(resource);
sbd.setSource(resource);
if (isCandidateComponent(sbd)) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Identified candidate component class: " + resource);
}
candidates.add(sbd);
}
else {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Ignored because not a concrete top-level class: " + resource);
}
}
}
else {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Ignored because not matching any filter: " + resource);
}
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to read candidate component class: " + resource, ex);
}
}
else {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Ignored because not readable: " + resource);
}
}
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("I/O failure during classpath scanning", ex);
}
//3.返回benadefinition集合
return candidates;
}

第1个步骤主要是解析文件路径,然后遍历文件夹获取每个class文件的地址;第2个步骤用asm框架来读取class文件获取类的信息封装成BeanDefinition对象.
第2个步骤最后调用的是org.springframework.core.type.classreading.SimpleMetadataReader的构造函数,下面是该类的部分源代码:

final class SimpleMetadataReader implements MetadataReader {
private final Resource resource;
private final ClassMetadata classMetadata;
private final AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata;
SimpleMetadataReader(Resource resource, ClassLoader classLoader) throws IOException {
InputStream is = resource.getInputStream();
ClassReader classReader = null;
try {
// asm框架读取class文件
classReader = new ClassReader(is);
} finally {
is.close();
}
// 采用访问者模式来获取class类信息
AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor visitor = new AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor(classLoader);
classReader.accept(visitor, true);
this.annotationMetadata = visitor;
// (since AnnotationMetadataReader extends ClassMetadataReadingVisitor)
this.classMetadata = visitor;
this.resource = resource;
}

ClassReader是asm框架中核心类,具体用法可以参考asm的官网.
上面说的过程就是spring容器加载bean定义信息的过程.过程很长,但实现原理却并不复杂.
2. 初始化单例bean的过程
上面分析了spring容器加载bean定义信息的过程,接下来分析bean的初始化以及创建bean的过程.回到ApplicationContext中的构造函数,入口为refresh().refresh方法在父类中实现的。下面是AbstractApplicationContext类refresh()方法的源代码:

public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // 线程同步
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);// 容器的后处理器
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);//调用容器的后处理器
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);//注册bean的后处理器
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);// 重点,注释写的so nice,初始化所有单例bean
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
}
}

后处理器是一种特殊bean,用于完成一些自身操作.
容器后处理器:对容器本身进行处理,在容器实例化其他任何Bean之前读取配置文件的元数据并可能修改这些数据.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer就是一个容器后处理器,用于完成beans.xml中引入其他配置文件中内容操作.
Bean后处理器:即当Spring容器创建完Bean实例之后对bean进行一些处理,例如:完成bean的装配等操作。
回到refresh()方法,重点关注:finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);这个方法会调用DefaultListableBeanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons方法.

public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) { // 线程同步
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<String>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {// 遍历beanNames
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {//单例非延迟实例的bean
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) { // 工厂bean.FactoryBean接口的子类
final FactoryBean factory = (FactoryBean) getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Boolean>() {
public Boolean run() {
return ((SmartFactoryBean) factory).isEagerInit();
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {//普通bean
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
else {
getBean(beanName); // 从容器中获取bean,如果没有创建,并完成装配
}
}
}
}
}

getBean(beanName)方法会调用doGetBean方法.这是个很关键的地方,切记注释很重要

/**
* Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean.
* @param name the name of the bean to retrieve
* @param requiredType the required type of the bean to retrieve
* @param args arguments to use if creating a prototype using explicit arguments to a
* static factory method. It is invalid to use a non-null args value in any other case.
* @param typeCheckOnly whether the instance is obtained for a type check,
* not for actual use
* @return an instance of the bean
* @throws BeansException if the bean could not be created
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected <T> T doGetBean(
final String name, final Class<T> requiredType, final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)
throws BeansException { final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean; // Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) { //bean已创建,调用方法返回该bean
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
logger.debug("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName +
"' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference");
}
else {
logger.debug("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
//如果是工厂bean,则返回beanFactory.getObject(),普通bean直接返回sharedInstance
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
} else { //bean未创建
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
} // Check if bean definition exists in this factory.
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
// 检查父容器是否已经创建该bean,有则从父容器获取bean返回
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// Not found -> check parent.
String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name);
if (args != null) {
// Delegation to parent with explicit args.
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);
}
else {
// No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);
}
} if (!typeCheckOnly) {
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
} final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args); // Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dependsOnBean : dependsOn) {
getBean(dependsOnBean);
registerDependentBean(dependsOnBean, beanName);
}
} // Create bean instance.---》创建单例bean
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, new ObjectFactory() {
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);// ---> 创建bean的方法
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
});
// 返回创建的单例bean
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
} else if (mbd.isPrototype()) { // 创建原型bean,scope="prototype"
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
} else {
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, new ObjectFactory() {
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; " +
"consider defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton",
ex);
}
}
} // Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance.
if (requiredType != null && bean != null && !requiredType.isAssignableFrom(bean.getClass())) {
try {
return getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);
}
catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type [" +
ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "]", ex);
}
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
}
// 返回bean
return (T) bean;
}

createBean(beanName, mbd, args)方法会调用doCreateBean()完成bean的创建工作,源代码如下:

/**
* Actually create the specified bean. Pre-creation processing has already happened
* at this point, e.g. checking <code>postProcessBeforeInstantiation</code> callbacks.
* <p>Differentiates between default bean instantiation, use of a
* factory method, and autowiring a constructor.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean
* @param args arguments to use if creating a prototype using explicit arguments to a
* static factory method. This parameter must be <code>null</code> except in this case.
* @return a new instance of the bean
* @throws BeanCreationException if the bean could not be created
* @see #instantiateBean
* @see #instantiateUsingFactoryMethod
* @see #autowireConstructor
*/
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args) {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
// 1.创建bean的包装类,装饰设计模式
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
final Object bean = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance() : null);
Class beanType = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass() : null); // Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
} // Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, new ObjectFactory() {
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
return getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean);
}
});
} // Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
//2.装配bean
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
if (exposedObject != null) {
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
} if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<String>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
} // Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
//3.返回
return exposedObject;
}

首先看第1个步骤,这个步骤中会创建bean实例和bean的包装类,这里使用了装饰设计模式.创建bean的实例过程比较简单,如果配置bean时指定了bean的创建方法 factory-method,就用factory-method创建bean实例,默认会使用无参构造函数创建bean实例.这部分重点关注装配bean的过程.

/**
* Create a new instance for the specified bean, using an appropriate instantiation strategy:
* factory method, constructor autowiring, or simple instantiation.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @param args arguments to use if creating a prototype using explicit arguments to a
* static factory method. It is invalid to use a non-null args value in any other case.
* @return BeanWrapper for the new instance
* @see #instantiateUsingFactoryMethod
* @see #autowireConstructor
* @see #instantiateBean
*/
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] args) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
Class beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName); if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName());
} if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {// 使用工厂方法创建bean,<bean factory-method="">
return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args);
} // Shortcut when re-creating the same bean...
boolean resolved = false;
boolean autowireNecessary = false;
if (args == null) {
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {
if (mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod != null) {
resolved = true;
autowireNecessary = mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved;
}
}
}
if (resolved) {
if (autowireNecessary) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null, null);
}
else {
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
} // Need to determine the constructor...
Constructor[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName);
if (ctors != null ||
mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR ||
mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args);
}
// 用默认的构造函数创建bean,反射获取构造函数,constructor.newInstance()创建bean.
// No special handling: simply use no-arg constructor.
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}

现在来看装配bean的过程,这个过程完成注入bean的依赖对象,如果bean是在配置文件配置的,则把从xml中解析出来的属性注入给bean实例,如果是用注解配置的依赖(@Resource 或者@AutoWired),则会解析bean的字段或者方法上的注解,根据这些注解找到对应的依赖,如果依赖对象已经创建,就直接注入依赖,否则,先创建依赖对象,在完成注入操作.

/**
* Populate the bean instance in the given BeanWrapper with the property values
* from the bean definition.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @param bw BeanWrapper with bean instance
*/
protected void populateBean(String beanName, AbstractBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw) {
PropertyValues pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues(); if (bw == null) {
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
} // Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true; if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
continueWithPropertyPopulation = false;
break;
}
}
}
} if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) {
return;
}
// 根据beanName或者type完成自动装配
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME ||
mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs); // Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
} // Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
} pvs = newPvs;
} boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != RootBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
// 调用bean后处理器
if (hasInstAwareBpps || needsDepCheck) {
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw);
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
// 重点:获取bean要装配的属性和属性值
pvs = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvs == null) {
return;
}
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
}
// 给bean的属性赋值
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}

InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor是BeanPostProcessor的子接口,能在bean初始化前后对bean进行处理.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor有以下几个子类:
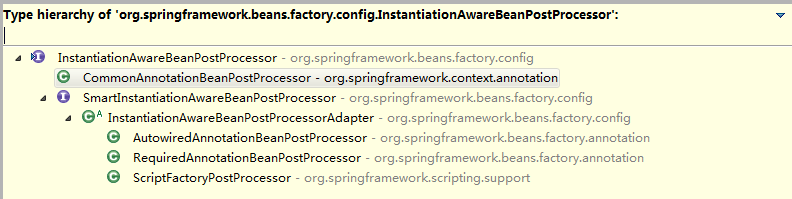
@Resource注解注入依赖的工作就是由CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor完成的.下面是该类postProcessPropertyValues()的源码:

public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(
PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
//1.根据bean的字节码,遍历所有的字段和方法,获取需要注入的字段或者方法
InjectionMetadata metadata = findResourceMetadata(bean.getClass());
try {
//2.从容器中查找依赖对象,并赋值给相应的字段,完成bean的装配
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of resource dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}

第1个步骤主要就是根据字节码获取所有字段和方法,然后遍历查找有@Resource注解的字段或方法以及依赖bean的beanName,第2个步骤从容器中依赖对象的beanName(@Resource的name属性值),如果容器中没有该依赖对象就创建,有的话就直接获取,并赋值给bean的属性.这样,就通过bean的后处理器完成了bean的装配过程.
到这里,容器的启动过程就完成了,此时就可以对外提供服务了.上面就是本人对spring容器部分源码学习的一些总结.日后,了解更多会不定时更新上来!
Spring bean是如何加载的
Spring bean是如何加载的
加载bean的主要逻辑
在AbstractBeanFactory中doGetBean对加载bean的不同情况进行拆分处理,并做了部分准备工作
具体如下
- 获取原始bean name
- 根据alia获取原始bean name
- 去除FactoryBean时的& [如果是需要获取FactoryBean自省,配置时需要在bean name前添加&]
- 尝试从缓存中获取实例
- 如果获取到实例,还要委托getObjectForBeanInstance解决FactoryBean的场景,就是调用getObject
- 判断原型场景的循环依赖问题,如果是原型同时bean又正在创建,说明是循环依赖,那直接抛异常,spring不尝试解决原型的循环依赖
- 如果在本容器中没有定义该bean,需要去父容器查找
- 如果有参数,结合参数初始化
- 如果没有参数,需要结合类型初始化,这边的调用是这个分支(当然这边一样没有类型)
- 如果不是类型检查,这边需要标记bean正在实例化
- bean实例化的准备工作
- 合并父bean的定义,并转化GenericBeanDefinition为RootBeanDefinition
- 校验BeanDefinition,如果是抽象类或者非原型带参数抛异常[这边注释说的是只有原型才可以配置构造方法的参数]
- 解决bean的依赖
- 注册依赖的bean
- 递归调用getBean实例化依赖bean
- 创建单例的实例
- 为解决循环依赖问题,这边使用ObjectFactory在实例化前先暴露bean
- 老规矩,需要委托getObejctForBeanInstance解决FactoryBean的问题
- 创建原型实例
- 创建前的准备工作,使用prototypesCurrentlyInCreation标记bean正在实例化
- 委托createBean实例化bean
- 创建后的善后工作,从prototypesCurrentlyInCreation中删除标记
- 老规矩,委托getObjectForBeanInstance解决工厂方法的问题
- 创建其他scope的实例,这边的逻辑结合了单例跟原型的处理逻辑,即使用解决循环依赖的ObjectFactory也使用prototypeCreation的标记
- 获取作用域scope,并校验是否已配置
- 使用ObjectFactory提早暴露实例
- 标记bean正在创建并委托createBean实例化
- 又是委托getObjectForBeanInstance解决工厂方法问题
- 最后需要对创建的实例进行类型校验,如果不一致,这边还需要委托TypeConverter进行类型装换
AbstractBeanFactory
@Override
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
return doGetBean(name, null, null, false);
}
protected <T> T doGetBean(
final String name, final Class<T> requiredType, final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)
throws BeansException {
// 获取原始的bean name,去除&,解决alias问题
final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean;
// 尝试从缓存中获取bean
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
// ...
}
else {
logger.debug("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
// 如果从缓存中或得bean,还需要判断是否是FactoryBean,并调用getObejct
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
}
else {
// 如果是原型scope,这边又是正在创建,说明有循环依赖,而原型的循环依赖Spring是不解决的
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
// 如果当前容器没有配置bean,那么去父容器查找
// Check if bean definition exists in this factory.
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// Not found -> check parent.
String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name);
if (args != null) {
// Delegation to parent with explicit args.
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);
}
else {
// No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);
}
}
// 如果不是类型检查,这边需要标记类正在创建
if (!typeCheckOnly) {
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
}
try {
// 实例化类之前,先去容器中获取配置的bean信息,这边需要将之前的GenericBeanDefinition转化为RootBeanDefinition
// 同时如果父bean的话,需要合并到子bean
final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
// Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dependsOnBean : dependsOn) {
if (isDependent(beanName, dependsOnBean)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dependsOnBean + "'");
}
// 解决依赖
registerDependentBean(dependsOnBean, beanName);
getBean(dependsOnBean);
}
}
// 创建单例的实例
// Create bean instance
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// 单例情况下,为解决循环依赖,在实例化之前,先新建一个ObjectFactory实例
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() {
@Override
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
// 创建原型实例
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
// 创建其他scope的实例
else {
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
// 还是先创建ObejctFactory,只是这边没有处理
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() {
@Override
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; " +
"consider defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton",
ex);
}
}
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
// 这边需要对实例进行类型校验,如果与requiredType不一致,需要委托TypeConverter尝试类型转换
// Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance.
if (requiredType != null && bean != null && !requiredType.isAssignableFrom(bean.getClass())) {
try {
return getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);
}
catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type [" +
ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "]", ex);
}
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
}
return (T) bean;
}bean实例的缓存分析
上面提到在加载bean的时候,doGetBean首先尝试的是从缓存读取,这边我们来细细分析下缓存具体是如何处理的.
这边逻辑是定义在DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry中,它是AbstractBeanFactory的父类,主要职责是共享实例的注册.
这边虽然定义的是singleton,但是实际使用的时候,处理prototype,其他scope均使用了这边进行缓存.
这边主要是需要理解singletonObjects,singletonFactories,earlySingletonObjects,registeredSingletons这4个变量.
singletonObjects 缓存bean name ->实例
Cache of singleton objects: bean name --> bean instance
这边缓存的是实例
singletonFactories 缓存bean name -->ObjectFactory
Cache of singleton factories: bean name --> ObjectFactory
这边缓存的是为解决循环依赖而准备的ObjectFactory
earlySingletonObjects 缓存提早暴露的实例 bean name -->bean instance
Cache of early singleton objects: bean name --> bean instance
这边缓存的也是实例,只是这边的是为解决循环依赖而提早暴露出来的实例,其实是ObjectFactory
registeredSingletons 已经注册的单例bean name
Set of registered singletons, containing the bean names in registration order
上面三个变量,任意一个添加了,这边都会添加bean name,标记已经注册
4个变量的关系如下:
- singletonObjects与singletonFactories,earlySingletonObjects,是互斥的.就是一个bean如果在其中任意一个变量中就,不会存在在另一变量中.这三个变量用于记录一个bean的不同状态.
- 如果bean已经添加到singletonObjects中,那么singltonFactories和earlySinletonObjects都不会考虑
- singltonFactories中的bean 通过 ObjectFactory的getObject实例化后,添加到earlySingletonObjects
我们从下面几个方法,可以清楚看懂上面4个变量的使用:
DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
/**
* 添加实例化的bean
* Add the given singleton object to the singleton cache of this factory.
* <p>To be called for eager registration of singletons.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param singletonObject the singleton object
*/
protected void addSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
this.singletonObjects.put(beanName, (singletonObject != null ? singletonObject : NULL_OBJECT));
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}
/**
* 为解决单例的循环依赖,这边注册ObjectFactory
* Add the given singleton factory for building the specified singleton
* if necessary.
* <p>To be called for eager registration of singletons, e.g. to be able to
* resolve circular references.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param singletonFactory the factory for the singleton object
*/
protected void addSingletonFactory(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(singletonFactory, "Singleton factory must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
if (!this.singletonObjects.containsKey(beanName)) {
this.singletonFactories.put(beanName, singletonFactory);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}
}
/**
* 清除实例
* Remove the bean with the given name from the singleton cache of this factory,
* to be able to clean up eager registration of a singleton if creation failed.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @see #getSingletonMutex()
*/
protected void removeSingleton(String beanName) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
this.singletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.remove(beanName);
}
}
/**
* 获取实例时,调用ObejctFactory的getObject 获取实例
* Return the (raw) singleton object registered under the given name.
* <p>Checks already instantiated singletons and also allows for an early
* reference to a currently created singleton (resolving a circular reference).
* @param beanName the name of the bean to look for
* @param allowEarlyReference whether early references should be created or not
* @return the registered singleton object, or {@code null} if none found
*/
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
return (singletonObject != NULL_OBJECT ? singletonObject : null);
}BeanPostProcessor Bean实例的初始化前后的自定义修改
BeanPostProcessor接口的行为方法

public interface BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>before</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one; if
* {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
*/
Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>after</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>In case of a FactoryBean, this callback will be invoked for both the FactoryBean
* instance and the objects created by the FactoryBean (as of Spring 2.0). The
* post-processor can decide whether to apply to either the FactoryBean or created
* objects or both through corresponding {@code bean instanceof FactoryBean} checks.
* <p>This callback will also be invoked after a short-circuiting triggered by a
* {@link InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation} method,
* in contrast to all other BeanPostProcessor callbacks.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one; if
* {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean
*/
Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
}

自定义的BeanPostProcessor

package com.wjz.spring; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor; import com.wjz.core.CustomInitializable; public class CustomBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof CustomInitializable) {
System.out.println("before init......");
((CustomInitializable) bean).init();
}
return bean;
} public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("after init......");
return bean;
} }

自定义的修改

package com.wjz.core;
public abstract interface CustomInitializable {
abstract void init();
}


package com.wjz.core;
public class Realm implements CustomInitializable {
public void init() {
System.out.println("init......");
}
}

关于Shiro框架对于BeanPostProcessor的使用
LifecycleBeanPostProcessor
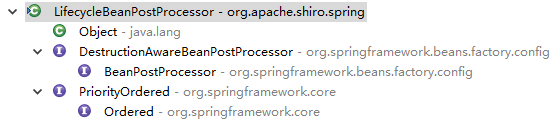

public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object object, String name) throws BeansException {
if (object instanceof Initializable) {
try {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Initializing bean [" + name + "]...");
}
((Initializable) object).init();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new FatalBeanException("Error initializing bean [" + name + "]", e);
}
}
return object;
}
/**
* Does nothing - merely returns the object argument immediately.
*/
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object object, String name) throws BeansException {
// Does nothing after initialization
return object;
}

public abstract interface org.apache.shiro.util.Initializable {
public abstract void init() throws org.apache.shiro.ShiroException;
}
AuthenticatingRealm
public final void init() {
//trigger obtaining the authorization cache if possible 如果可能,触发获得授权缓存
getAvailableAuthenticationCache();
onInit();
}
框架-spring源码分析(一)的更多相关文章
- spring源码分析之spring-core总结篇
1.spring-core概览 spring-core是spring框架的基石,它为spring框架提供了基础的支持. spring-core从源码上看,分为6个package,分别是asm,cgli ...
- 【Spring源码分析】非懒加载的单例Bean初始化过程(上篇)
代码入口 上文[Spring源码分析]Bean加载流程概览,比较详细地分析了Spring上下文加载的代码入口,并且在AbstractApplicationContext的refresh方法中,点出了f ...
- 【spring源码分析】IOC容器初始化(二)
前言:在[spring源码分析]IOC容器初始化(一)文末中已经提出loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory)的重要性,本文将以此为切入点继续分析. ...
- spring源码分析系列 (8) FactoryBean工厂类机制
更多文章点击--spring源码分析系列 1.FactoryBean设计目的以及使用 2.FactoryBean工厂类机制运行机制分析 1.FactoryBean设计目的以及使用 FactoryBea ...
- spring源码分析系列 (3) spring拓展接口InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
更多文章点击--spring源码分析系列 主要分析内容: 一.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor简述与demo示例 二.InstantiationAwareBean ...
- Spring源码分析:非懒加载的单例Bean初始化过程(上)
上文[Spring源码分析]Bean加载流程概览,比较详细地分析了Spring上下文加载的代码入口,并且在AbstractApplicationContext的refresh方法中,点出了finish ...
- 框架-springmvc源码分析(二)
框架-springmvc源码分析(二) 参考: http://www.cnblogs.com/leftthen/p/5207787.html http://www.cnblogs.com/leftth ...
- 框架-springmvc源码分析(一)
框架-springmvc源码分析(一) 参考: http://www.cnblogs.com/heavenyes/p/3905844.html#a1 https://www.cnblogs.com/B ...
- Spring源码分析专题 —— IOC容器启动过程(上篇)
声明 1.建议先阅读<Spring源码分析专题 -- 阅读指引> 2.强烈建议阅读过程中要参照调用过程图,每篇都有其对应的调用过程图 3.写文不易,转载请标明出处 前言 关于 IOC 容器 ...
随机推荐
- \r\n和\n的区别
写Java代码的时候习惯用\r\n换行,这样可移植性比较好但是,在UVa - 160中就出现了错误,来看看是为什么吧. http://bbs.csdn.net/topics/220033879
- java EE ME SE有什么关系
1. Java SE(Java Platform,Standard Edition).Java SE 以前称为 J2SE.它允许开发和部署在桌面.服务器.嵌入式环境和实时环境中使用的 Java 应用程 ...
- Egret Wing4.0.3 合并资源图片问题
一 发布项目时,选择合并图片资源 选择合图大小 发布后,图片合并.随机了图片名字. 二 随机名的问题 当资源不变更的情况下,多次发布,每次发布后资源的图片随机名是不变的. 现在改变preload组 ...
- ios 图片拉伸不变形的方法
如果一个椭圆图片,原图大小为30*30,而我们让它显示100*30,那么这个图片就会被拉伸,而且效果很难看.用下边的方法可以创建一个局部不被拉伸的图片. UIImage * buttonBg = [[ ...
- linux grep命令(linux在文件中搜索内容)
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/end/archive/2012/02/21/2360965.html linux grep命令 1.作用Linux系统中grep命令是一种强大的 ...
- mysql5.6主从
1.环境 操作系统:centos6.5(主服务器IP:192.168.100.170,从服务器IP:192.168.100.171)软件版本:mysql5.6.24 2.开始安装: a.主库上设置从库 ...
- Oracle等待事件之等待事件详解
一. 等待事件的相关知识:1.1 等待事件主要可以分为两类:即空闲(IDLE)等待事件和非空闲(NON-IDLE)等待事件.1). 空闲等待事件指ORACLE正等待某种工作,在诊断和优化数据库的时候, ...
- Java-idea-FindBugs字节码级别潜在bug查看
一.概述 静态分析工具承诺无需开发人员费劲就能找出代码中已有的缺陷. FindBugs 不注重样式或者格式,它试图只寻找真正的缺陷或者潜在的性能问题. FindBugs 是一个静态分析工具,它检查类或 ...
- Django Rest Framework(3)-----APIView与Viewsets
REST framework提供了一个APIView类,它是Django的View类的子类. REST framework主要的几种view以及他们之间的关系: mixins 到目前为止,我们使用的创 ...
- (转) SpringBoot非官方教程 | 第二十四篇: springboot整合docker
这篇文篇介绍,怎么为 springboot程序构建一个Docker镜像.docker 是一个开源的应用容器引擎,基于 Go 语言 并遵从Apache2.0协议开源.Docker 可以让开发者打包他们的 ...
